The History of Art
GA 292
15 November 1916, Dornach
IV. Mid-European and Southern Art
Sluter, Multscher, Riemenschneider, Stoss and Baldung.
Continuing our studies on the great works of Art, we will show some further slides today, supplementing those that were shown last week. Today I propose in the main to supplement what I endeavoured to explain last week, of the connections and contrasts between the Mid-European, or Northern, and the Southern Art. I tried to show how the specifically artistic quality is always influenced by the character of the South or of the North, while, on the other hand, there were continual interpenetrations of the Southern and Mid-European impulses, layer upon layer, as it were, so that it is by no means easy now to see how these things really worked together. Spiritual scientific investigations will in course of time have to bring more and more light into these matters.
Today I wish to draw attention to the contrasts from certain other points of view. You will remember what I emphasised last time. From underlying impulses of the Mid-European spiritual life, there arose what we may call the art of expression—expression of Will and Intelligence—the power to express the ever-mobile life of the soul. The soul in movement—that is the goal of the Mid-European impulse; while the Southern (which was, however, influenced at a very early stage by the Mid-European) looks more to all that enters our perceptions from the Divine-spiritual in the Cosmos, which finds expression in the power of composition, and in features which transcend the human.
It is a characteristic abuse of our time to consider Art—even the plastic Arts—far too much from the mere point of view of the narrative and subject matter, while appreciating far too little the specifically artistic qualities. At the same time there is another equally pernicious error. Art is very frequently severed nowadays from the general life of culture and civilisation, and treated as though it were something that lives a life apart. This, too, is wrong. For we need only have a feeling for the specifically artistic qualities, for all that works in form and colouring, in composition and the like—we need only wean ourselves of the tendency to explain everything symbolically, or in other artificial ways; we need but feel—before such pictures as Dürer's ‘St. Jerome,’ or ‘Melancholia,’ for example,—how infinitely deeper is the mysterious ebb and flow of the masses of light themselves, than any artificial symbolism we may choose to read into these pictures. Then we shall recognise that the specifically artistic qualities that come to expression in the great works of Art, are also living in the whole general life of civilisation. Out of the common feeling of his time the artist works into the spheres of form and color and expression. The time itself works through the soul of the artist. The whole culture of the age finds expression in the characteristic works of Art.
We saw last time how the Mid-European, or Northern element, works its way upwards more or less independently, while at the same time it grows together with all that is brought to it through the Church—through Christianity from the side of Rome. Until the 12th and 13th centuries we witness the development of a unique artistic life in Middle Europe, uniting the more Roman or Latin elements with a strongly individual characterisation of all that is life and movement in the human soul. We cannot understand what took place until the 12th and 13th centuries if we merely consider what we know of the spread of Christianity in the succeeding time. For the whole spread of Christianity was a very different thing in those earlier centuries from what it afterwards became. It was only in later times that the rigidly dogmatic qualities which so repel us, came into prominence, though, needless to say, there were all manner of excesses even before the twelfth century. And while in Middle Europe the systemmatising, formal tendency of Rome was always felt like a foreign body, still the Christian impulses found their way most wonderfully into the soul-life of the people—especially into the more subconscious, feeling elements of the soul.
This entry of Christianity into the soul found expression especially in the sphere of Art, where there was a wrestling for plastic power of expression.
Here we may point to a truth which can be characterised in two very simple statements which are, none the less, very far-reaching. We may ask this question: To what does Art appeal among the Southern peoples? To what did it appeal already in antiquity? And elsewhere in the South, in the period of its decline and in its resurrection from the early to the late Renaissance? To what does Art appeal in the more southern regions? It appeals to the fancy and imagination. This statement is of infinite importance. The appeal is to the life of the fancy and the imagination, which is present in the souls of the southern people with a slight, suggestion of a sanguine temperament in these respects. Thus in the southern regions we see the Christian ideas entering, above all, into the imaginative life, and borne by fancy into the realm of Art.
Needless to say, such a statement must not be pressed too far. I would say, the statement itself should be artistically understood.
Only so, my dear friends, could it come about that in the time of the Renaissance artistic fancy rose to such great heights of creation, while the moral life, as we showed in a recent lecture, fell to the state revealed in the attacks of Francis of Assisi, and later of Savonarola. The situation stands before us when we contrast the fiery attacks of Savonarola which were all in vain, with the infinitely rich life of Christian vision and imagination in the plastic works of Donatello, Michelangelo, Raphael, Leonardo and many others.
Art in the North speaks differently and appeals to a different element of soul, namely, to mind and feeling. Once more, these things must not be pressed; nevertheless, in such a statement guiding lines are given for the understanding of whole epochs of History. However we may believe that Christianity contains a peculiar, morally religious impulse of the soul, this impulse did not find its way into the element of fancy and imagination in the Southern culture which reached such giddy heights in the Renaissance. But in the North, the centuries until the 12th—nay, the beginning of the 13th—reveal in Art the progressive appeal of Christianity, and especially the tragic elements of Christianity, to human heart and feeling. The Art of the Italian Renaissance strives to make the countenance of Christianity itself as fair as possible—that, after all, is the essential element in the Renaissance Art: But the centuries to which I now refer, in Middle Europe, are all devoted to the striving to realise the Story of the Passion—with all its tragedy and drama, until the tragic story becomes their very own in heart and soul.
Down to the Carolingian period in Middle Europe, Mid-European paganism continually breaks through into the life of feeling. But in the centuries from that time onward until the 12th and 13th there arises out of the very soul of Middle Europe an inherently Christian Feeling for all human life. And the strange thing is that from the 13th century onward a certain decline can be observed. Yet, as I explained last time, even now when another element once more overwhelms it, there is still the constant striving for the Mid-European soul to assimilate into its deepest inner life all things that come to it, so that, after all, there is a continuity of work and progress in the best souls, from the 11th century on into the 15th and 16th.
The gradual entry of Christianity into the life of the people is also recognisable, or, rather, would be recognisable, if the dramatic representations which did, indeed, grow more and more significant toward the 13th century, had been preserved. All that we now bring to light again—the Christmas and Easter Plays, and Plays of the Three Wise Men—are of a later date, and are but a faint reflection of those earlier ones which tended to a more universal presentation of the Christian world-conception. The Play concerning Anti-Christ, of the 12th century, which has been found at Tegernsee in Bavaria, and a later Play on the Ten Virgins, these, too, are but echoes of Plays that were presented everywhere, dramatising the Biblical stories and the sacred legends. Out of this life with the Christian world-conception as a whole, there arose the works of Art which we shall see again today and which we say last time. There followed what I might call a slow and silent working towards the deepening of the soul's life and its artistic power of expression. It finds expression wonderfully in Dürer's representations of the Passion, and notably in the head of Christ Himself as conceived by Dürer and others. It will be a satisfaction to me if we can show these pictures, too, on some future occasion; we do not possess them at present.
If we study the progress of artistic penetration in pictures of the countenance of Christ till Dürer's time, and in other things as well, we find there was really attained in Mid-Europe at that time an astonishing degree of maturity. It lies inherent in the subtle difference between the Mid-European and Northern, and the Southern life, which developed, as it were, the last phases of the Fourth Post-Atlantean epoch—(albeit the Fifth epoch already shone into the Renaissance);—the South in its deepest tendencies of feeling was still expressing the last phases of the Fourth; while in Mid-Europe and the North the Fifth Post-Atlantean epoch was preparing. What afterwards became the expression of the individual, and of all that is mobile in the human soul—the soul in movement and emotion—all this was working its way up from unconscious depths.
Here we see the whole life of the two regions in their essential difference. We need only bear in mind how much in the Southern Art is due to the fact that there still existed a living atavistic perception of what plays from spiritual regions into the realms of sense. For this was, indeed, preserved in what are known to us of the Byzantine forms of Art—in all the suggestive forms and figures that have come down to us. Take, for instance, what works upon us with such suggestive power in the Art of the Mosaics, and in all that is connected with the name of Cimabue. Here it is more the Christ Figure that works upon us. In Middle Europe it is, rather, the life of Jesus that is presented to us, for the artistic forms are created directly out of the inner life of the soul.
Superhuman as is the Byzantine type of Christ, inwardly human is the Christ type which was afterwards worked out by Dürer.
The Fourth Post-Atlantean epoch, including the latest flower (in the Italian Renaissance) has essentially the quality of looking upward to the superhuman and typical; the superhuman and generic nature of the soul, setting aside the individually human. The Southern peoples brought to their Art, in a far higher degree, the ancient, the generic nature of the soul in its superhuman and divine quality.
In the Northern Art, on the other hand, we see the strong decided striving of the individual, as it works its way upwards out of every single human soul. The more these things are understood, the more this will be confirmed.
The southern life still contains mankind as a whole. Think how intensely an Athenian was an Athenian, or a Spartan a Spartan, so that Aristotle rightly called man a “Zoon politicos”—a political animal. The “political animal” was developed to its greatest height in Rome, where, we might say, man lived more in the streets than in his own house; and with his soul-life, also, he lived more in the life that surrounded him than in the house of his own soul. Such, truly, was the Southern imagination as it worked in the world of space. From the very outset men live together, live together as a whole, and the life of Art itself arises out of this principle. This is a feature common to all the Southern Art. They decorate the churches and the public squares; everywhere we see how they reckon with the fact that the people run gladly together, crowd gladly into the churches, or in the public squares, drawn thither by their very temperament and expecting what will there be set before them. To possess themselves fully, they need this life in the outer world, this living with the group-soul nature—with all that is most eminently political—in the right sense of the word.
All this is different in Middle Europe. In Middle Europe man lives within himself; seeks his experiences in his own house and home, even the house of his soul. And if he is to dedicate himself to the group-nature, his heart must first be conquered for it, he must in some way be summoned to it. Many of the underlying impulses of Gothic architecture will be found to lie in this direction. The buildings erected by Gothic architecture stand there not because the people are already running together of their own accord, but, on the contrary, because they must first call the people, bring them together, as it were, through mysterious and suggestive influences. This is expressed in the very forms of the Gothic. The individuals must first be called to the group-life. And the same thing lies inherent in the whole treatment of light and darkness which I described to you the other day. In the elemental surging and interweaving of the light into the darkness, man finds an element into which he can enter to free himself from his own separate existence; albeit he can carry his individual existence, his individuality with him into this very element, because it is so akin to the nature of the soul.
In all these things we find the distinguishing feature of the Northern as against the Southern Art. Hence the striving—the successful striving—of the Northern Art to express inwardness of life and soul. We need only call to mind the portraits, the Madonnas, for instance, of Van Eyck. These Madonnas—their facial expression altogether determined by a turning inward of the life of the human soul—this speaking from an inwardness of soul in the countenance and gesture—all this, Raphael would never have painted. Raphael raises what he paints beyond the human; Van Eyck lifts it into the still more deeply human, so as to seize the human emotions with his paintings, the human hearts of those who see them. Once more it is a question of grasping the human soul.
The priesthood until the 12th and 13th centuries were well aware of these possibilities of the human soul in Europe. They reckoned with these things. They worked with the heart and mind of the people. And without a doubt, much that arose out of this wrestling for artistic powers of expression, came about through the co-operation of the religious orders with that inner life and character of the people which we have here described. We must by all means understand how these more Northerly qualities of artistic creation are connected with the protesting folk-soul of the North, rising up in opposition against the Roman element.
Luther went to Rome. But he saw nothing of the sublime heights of artistic creation; he saw only the moral degradation there. And this implies very much. No doubt he met one or another of the great painters of Rome on the Square of St. Peter's, but what concern had they for him, these men who created out of al altogether different mood of soul, something to which he had no inner relationship. And yet, Luther's very radical one-sidedness was in another way the product of the same Mid-European characteristics which, if I may say so, wrestled most sublimely in the realm of plastic, pictorial expression, and attained an artistic height that stands, in a certain way, so magnificently and independently side by side with the Art of the Italian Renaissance. (We need make no comparisons, for they are always trivial.)
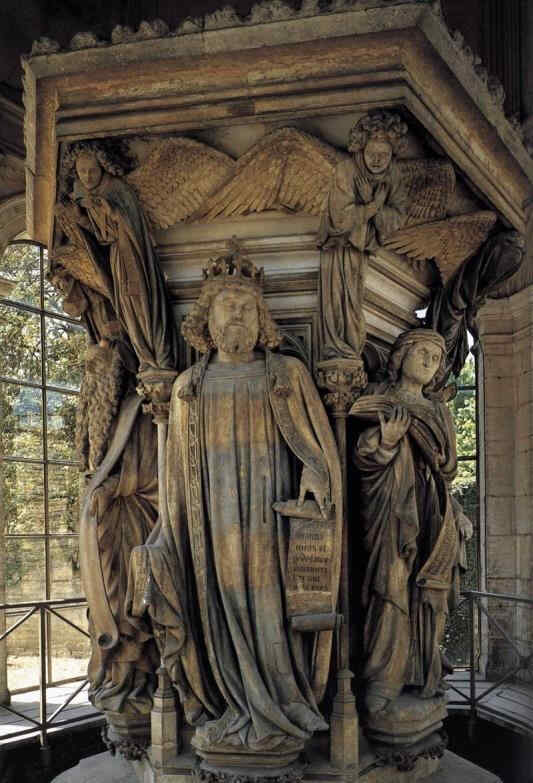
We will therefore now show a few more pictures, supplementing those we showed last week. First we will show some wood-sculptures from the very beginning of the 13th century. They are at Halberstadt.
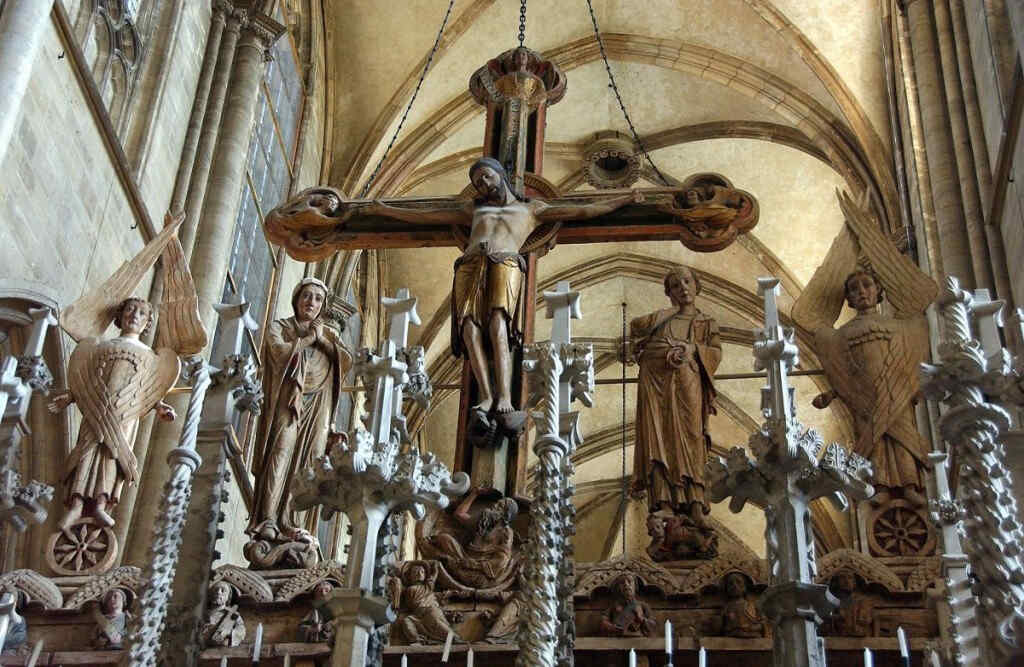
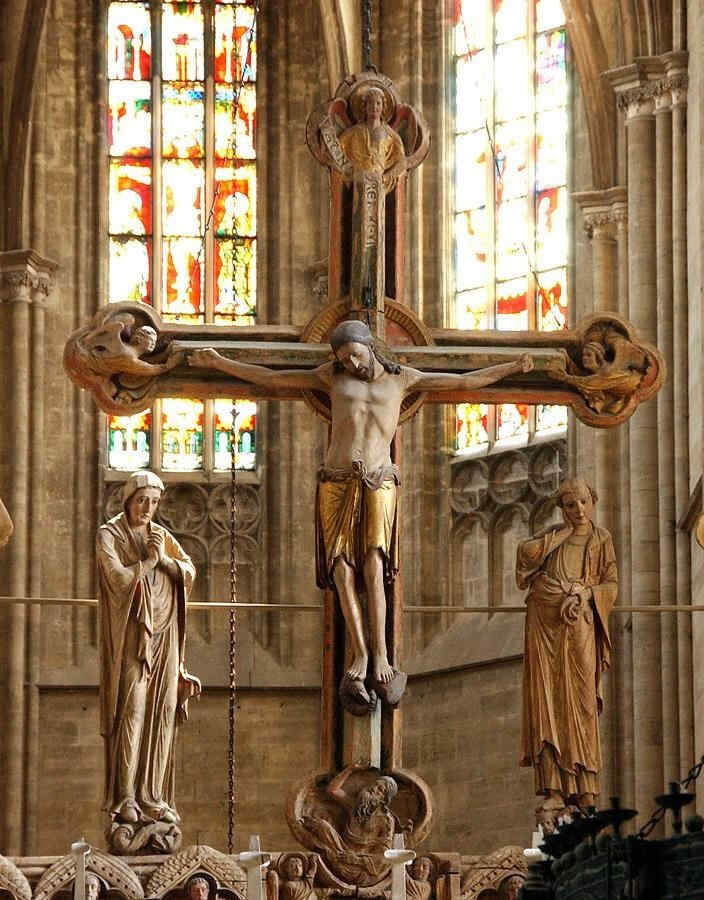
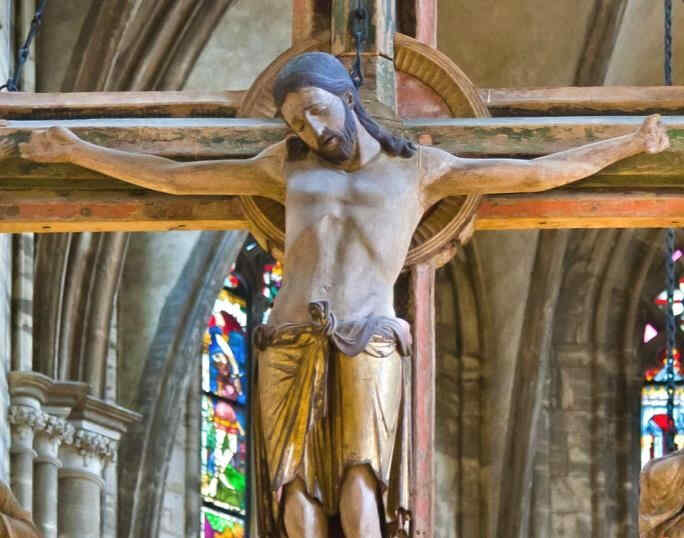




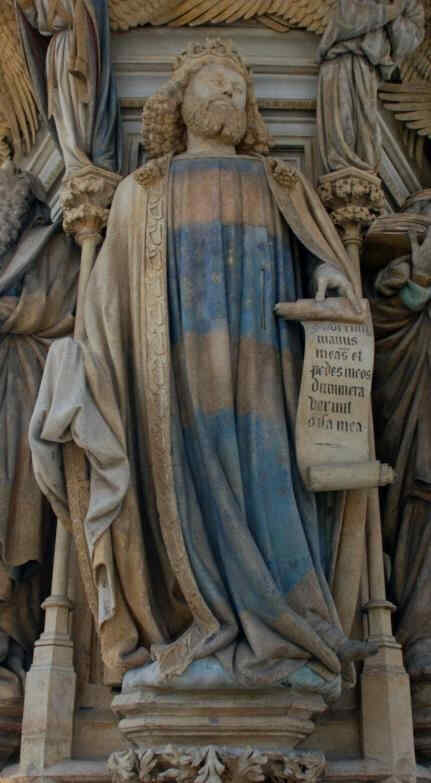
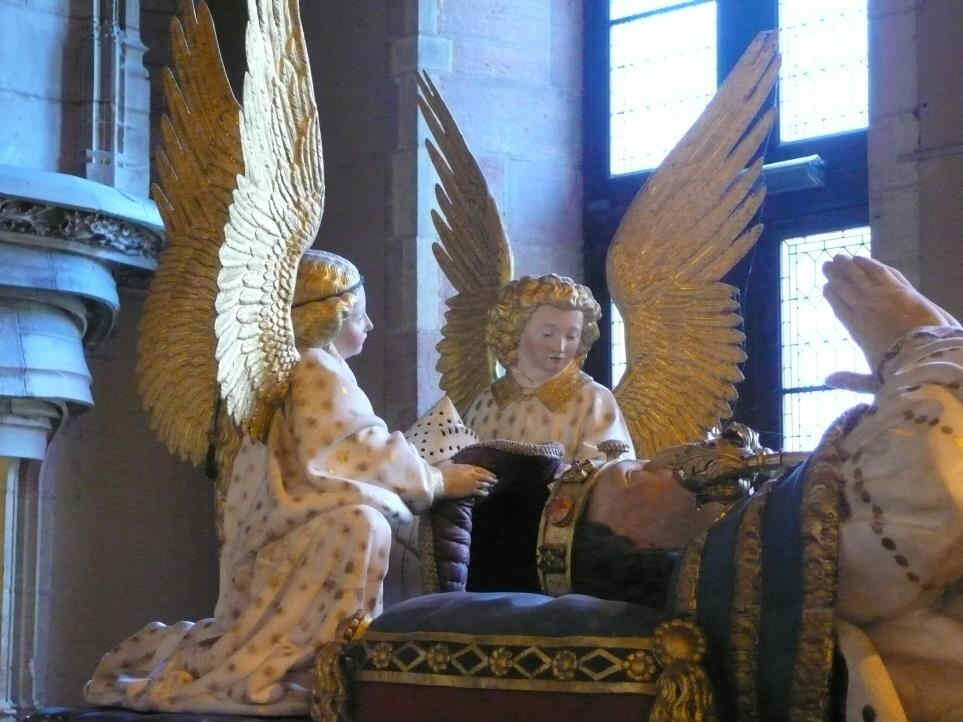
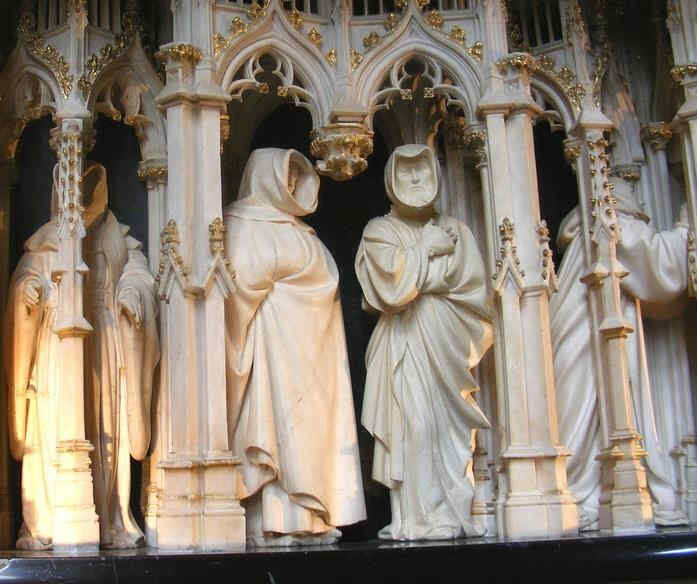
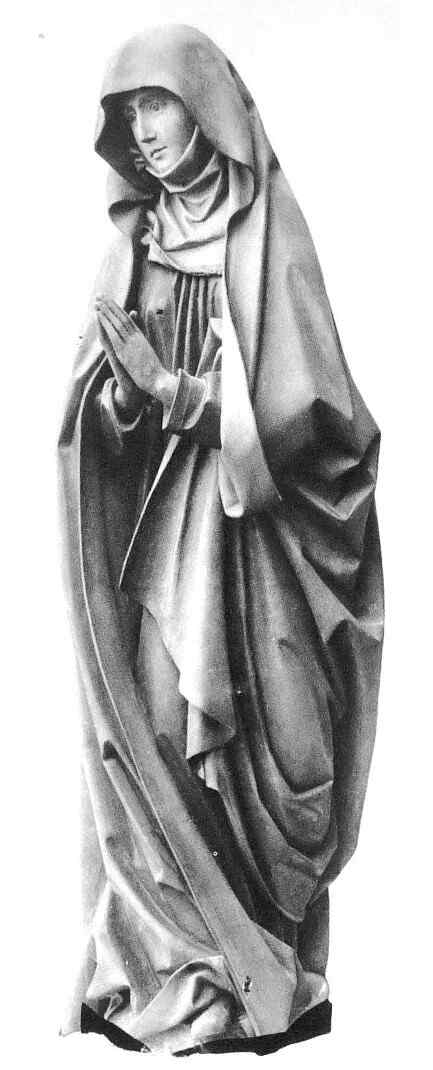
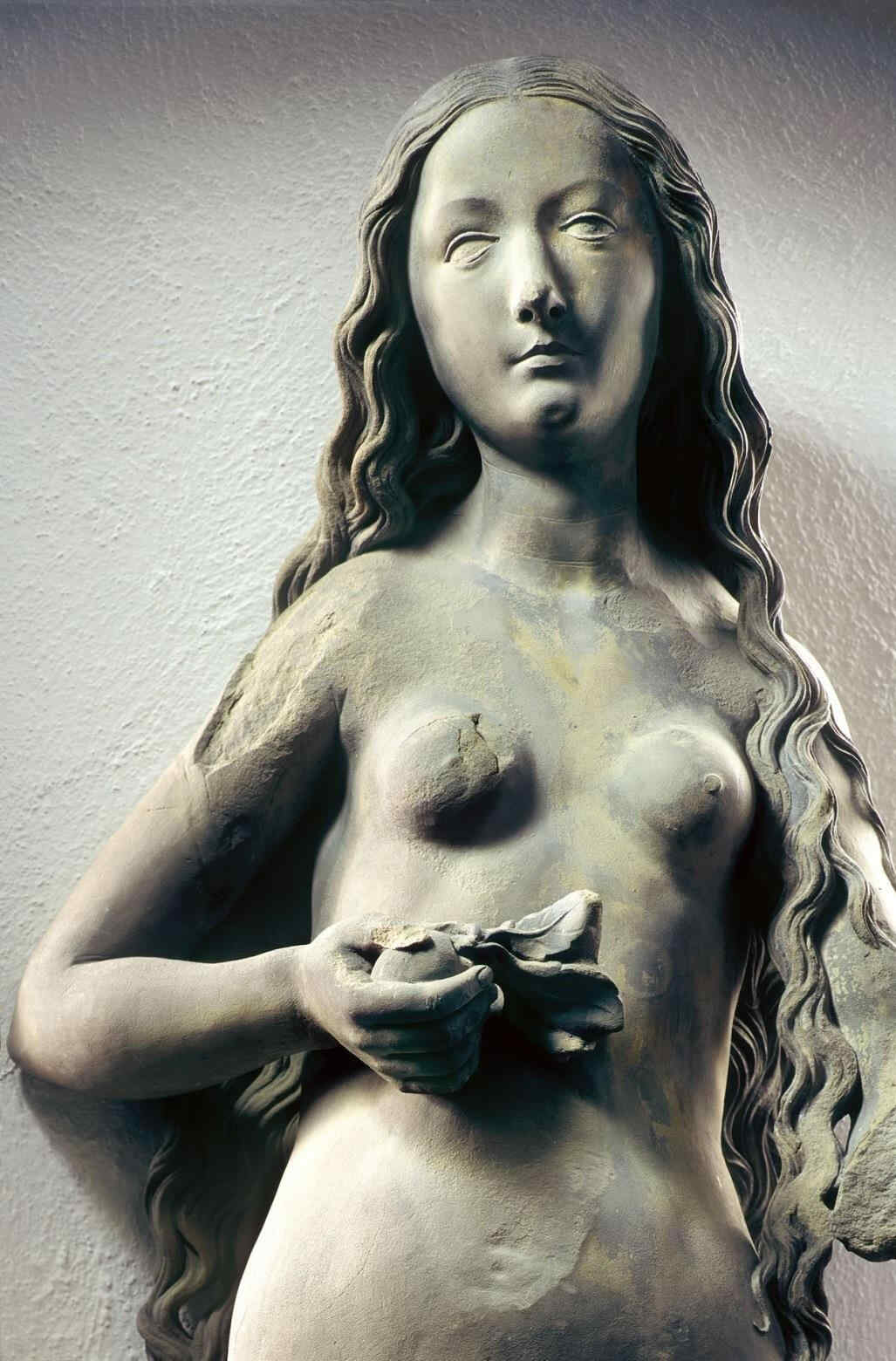
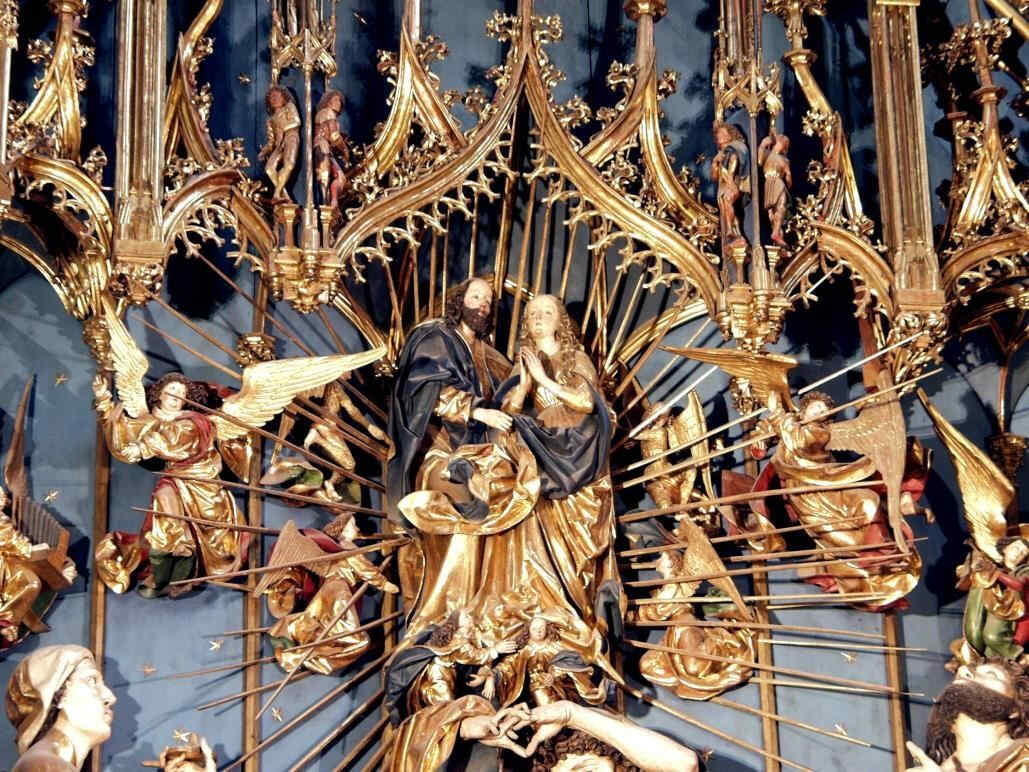
Look at this Crucifixion Group. I will only say one thing to characterise what is most important. In this group you can see how deeply the story of the Passion had found its way into their lives by that time. There is Mary, there is St. John, and in the center the Christ, looking down towards her. If you could see the face you would see an infinite deepening of soul in the expression, an overwhelming depth. In Mary, if you have a feeling for these things, you will recognise at once the flowing together of the more Roman, priestly conception with the Mid-European depth and tenderness of feeling. Here it is recognisable in a most wonderful way. We shall presently show the face of Mary in detail.
This group reveals how they contrived, out of the specifically Mid-European creative impulse of the soul, to mould the Christianity which had conquered the Mid-European country. We will now show the detail.
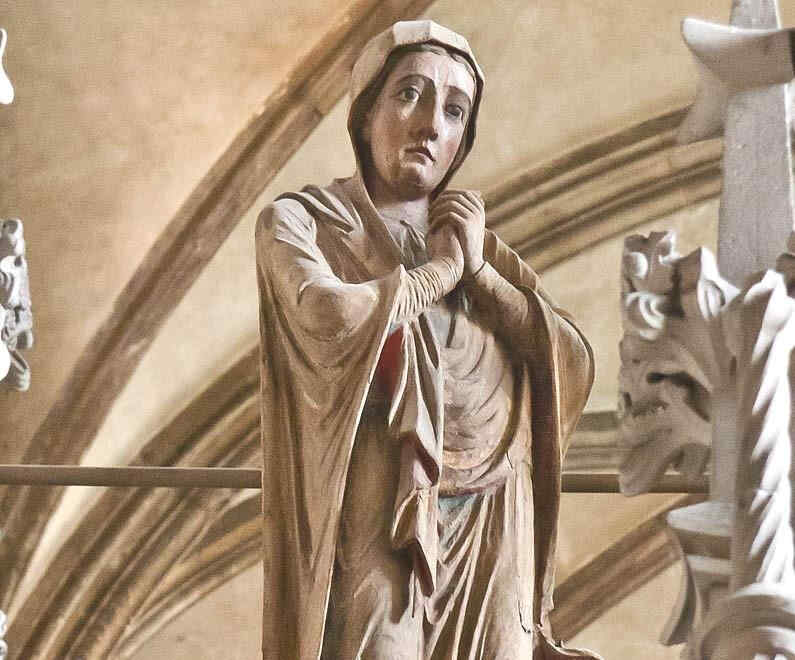

Wonderfully characteristic is the expression of the face. The expression in the Southern Art is such that the eyes look far out into the world; in the Northern Art the soul, as it were, presses forward into the look of the eyes from within. Here the two are altogether interwoven—united with one another. A tenderness of soul in the expressions hovers gently, wonderfully, over a more Latin, Roman rounding and perfection of the features.
These things must not be pressed. But I beg of you to observe in all the following pictures how very differently the clothing and drapery is treated in the Mid-European Art and in the Southern. Undoubtedly, such things must not be pressed too far; yet it is true to say that in all the Southern Art the drapery rather surrounds and veils the human form, follows the lines of the form closely, continuing, as it were, the bodily forms. In the Mid-European Art the treatment of the drapery is different. It proceeds from the emotion and movement of the soul. According to the gesture of the hand and the whole attitude of the figure, the quick, mobile life of soul is continued into the raiment. The latter adheres less closely to the body. It does not seek, as in the Southern Art, to veil or to express the forms of the body. It is, rather, like a continuation of the living experience of the soul. You will see this more and more distinctly as we go on into the following centuries.
We have now come to the famous:
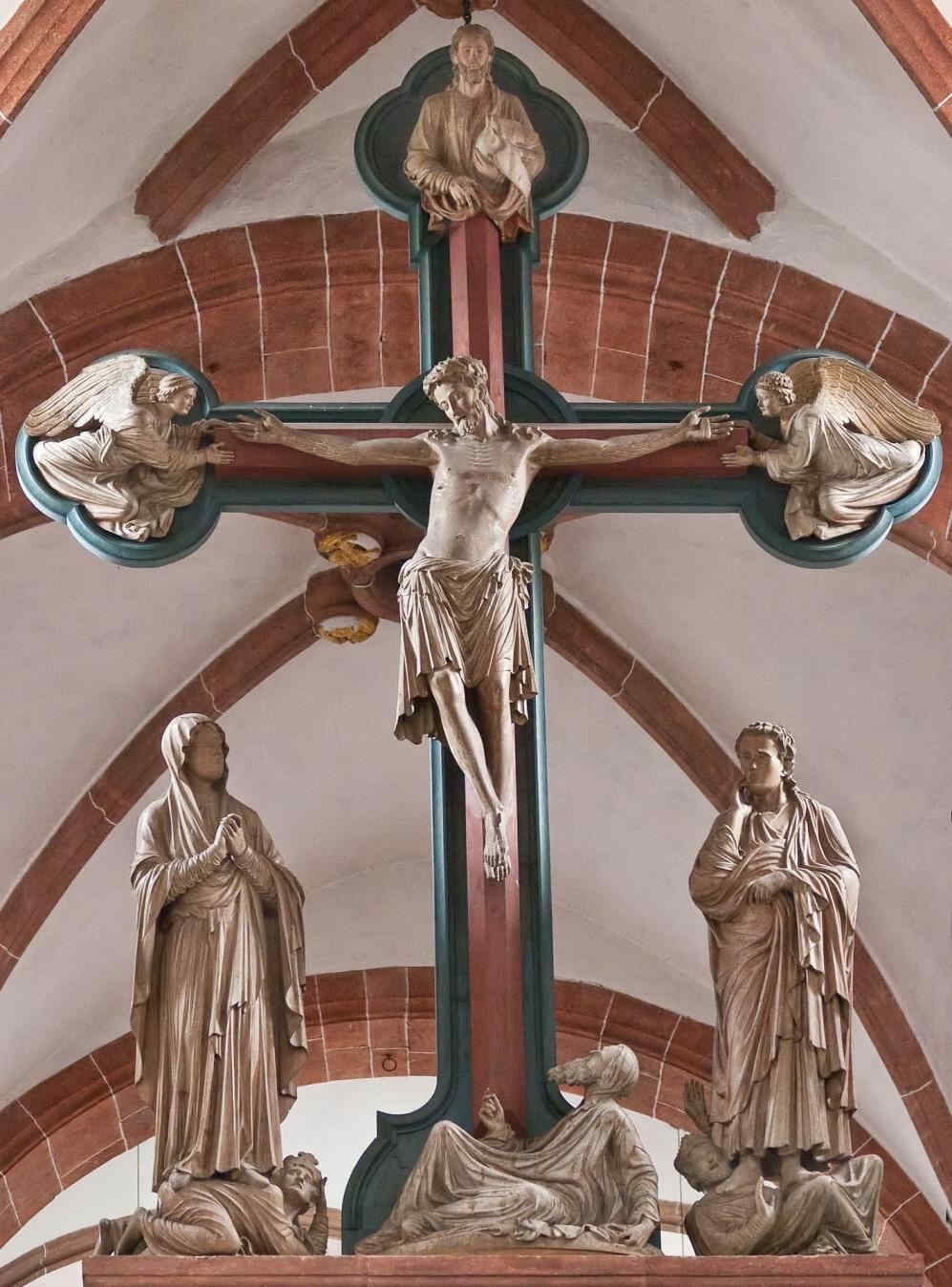

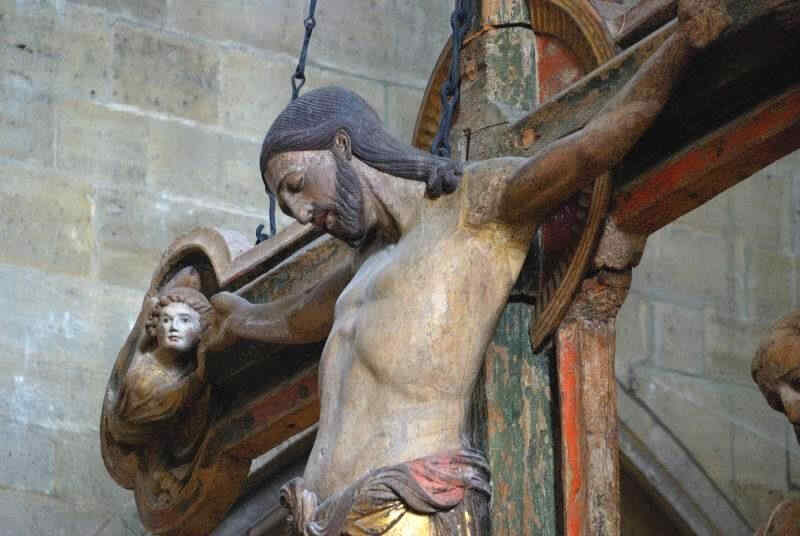
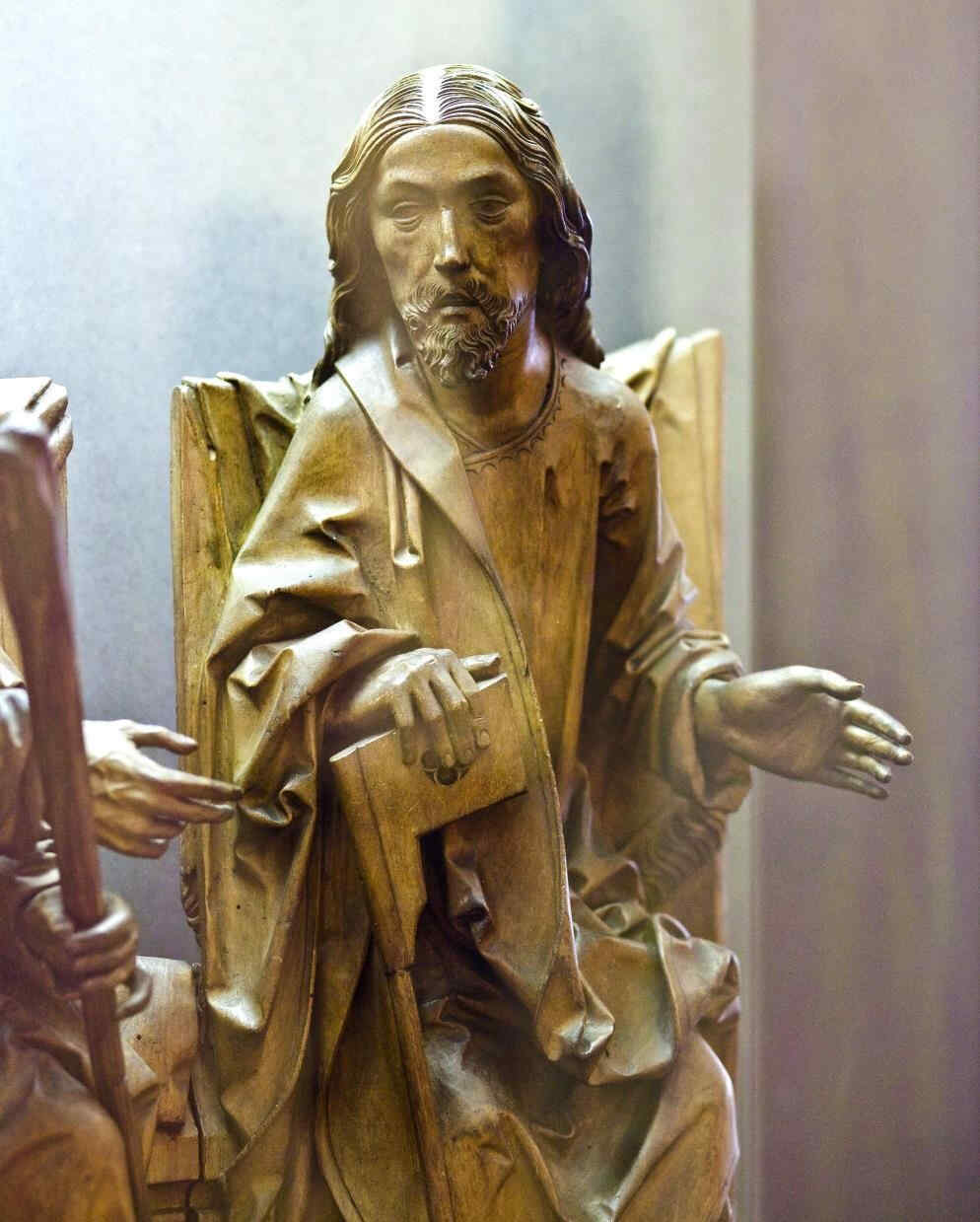
This, too, is in the wood, and dates from the first third of the 13th century. None the less, you will see in it a wonderful progression from the former group whose subject is so similar. Observe the communion of soul between the Mary and the Christ-Figure. See how the faith in the Christian world-conception, deeply united with the human soul, appears in the St. John and in the Mary-Figure, as the power that overcomes all things. The Christian world-conception had entered into the souls of these people so as to become an universal historic conception of all earthly evolution. See how Adam, down here, receives the Blood of the Redeemer dropping downward from the Cross. Study the face of Adam, how he is touched by the influence of Grace which he can now receive inasmuch as he may catch the Blood of the Redeemer flowing from the Cross. You will realise with what infinite depths Christianity had found its may into the lives of these people. It had risen to a universal and truly Cosmic conception.
Angels carry the Cross. God the Father descends with the Dove, setting His seal upon the fact that what He had given to the Earth in His Son gives, at this moment, the whole Earth its meaning. In this group with all its artistic perfection we see how deeply Christianity had found its way into Middle Europe,because they tried again and again to permeate it with the human heart and feeling,—to permeate it from within the human soul.
On the other hand, in the South, it was permeated by fancy and imagination, thus producing that peculiar permeation, so free from the moral element—(or shall we say, in order not to give offence, so free from moral cant)—which comes to expression in the Renaissance in the South.
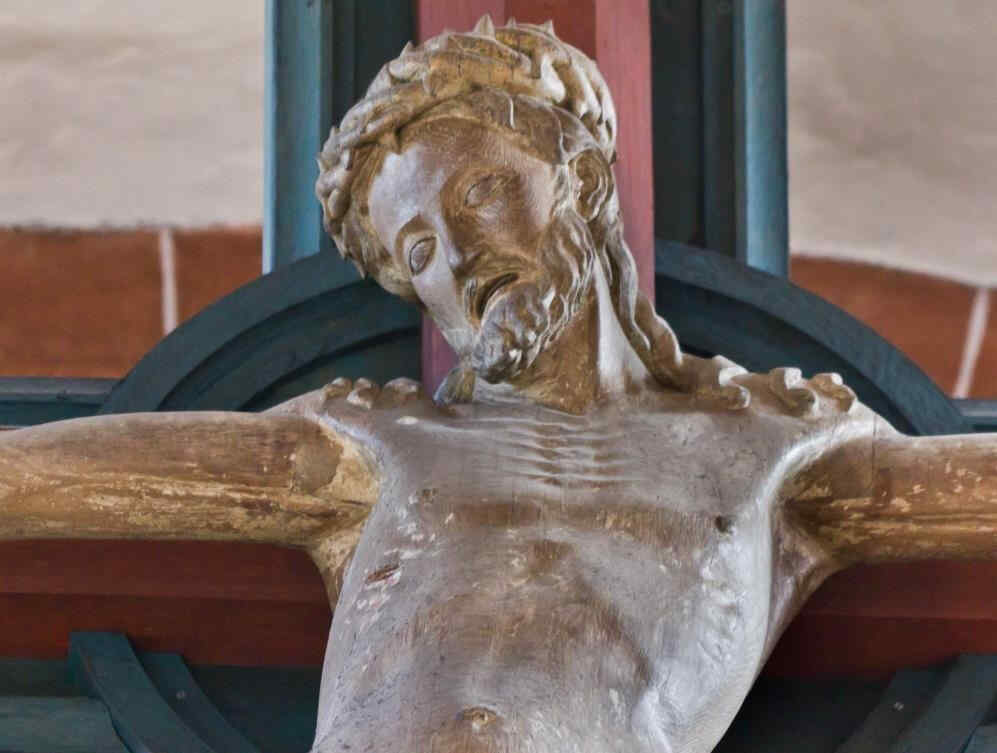
If you were to make a study of the progress in the representation of the Christ-Figure, this Head of Christ would be an important station. Also the Head of Christ in the Cathedral of Amiens, and afterwards, the Head of Christ by Albrecht Dürer.
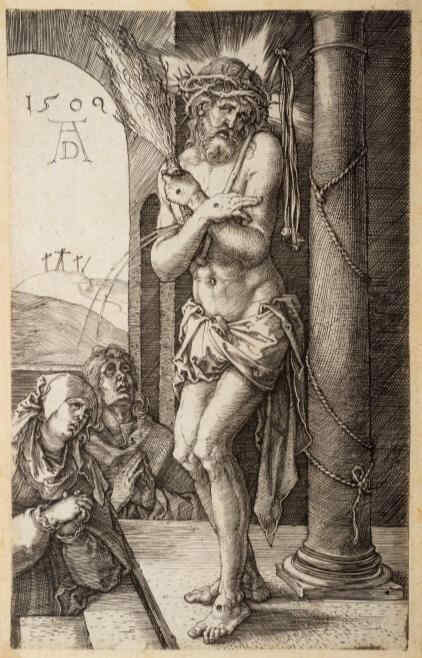



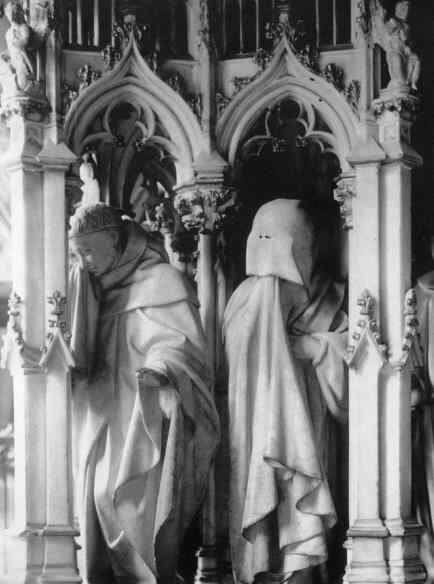
We now pass to some sculptures which are found at Freiburg in Saxony, also dating from the first third of the 13th century. They show an altogether different aspect, though here, too, it is the sacred history, and a deep striving for inwardness. It is not too much to say that one loves to dwell on every single face. The next picture:
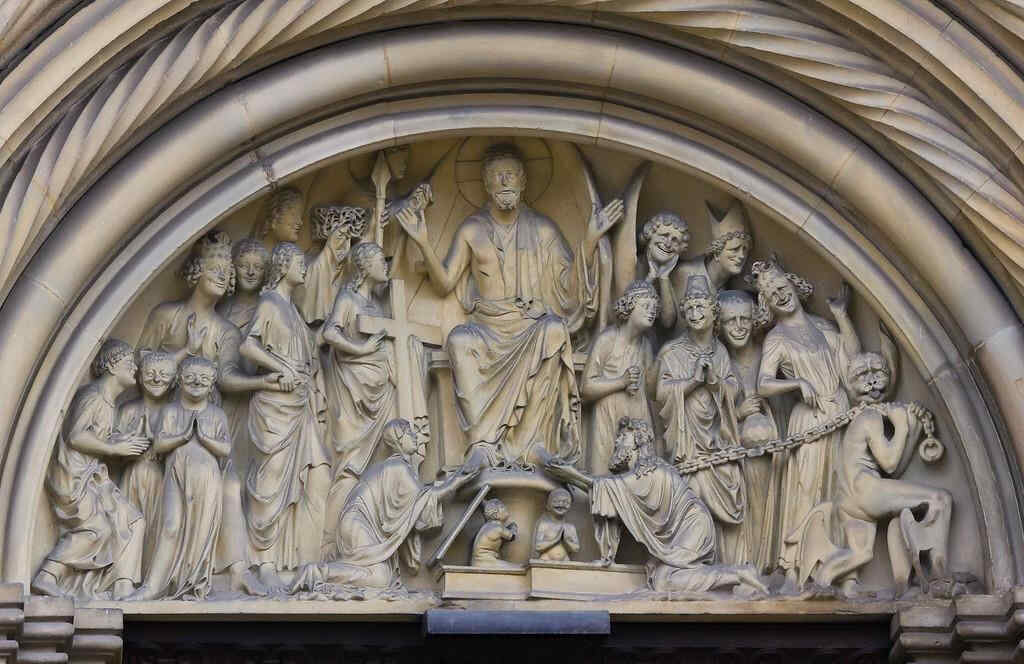

(St. Mary's Cathedral, Freiburg.)
shows us two figures. The one, the figure of a woman, is hard to interpret. Perhaps she is an “Ecclesia.” The other is said to be Aaron. These things are not essential. The figures are undoubtedly connected, allegorically or in some other way, with the Christian world-conception. Once more, observe the deepening of the soul's life. The contrast of expression between the face on the left, and that on the right is particularly fascinating from this point of view.
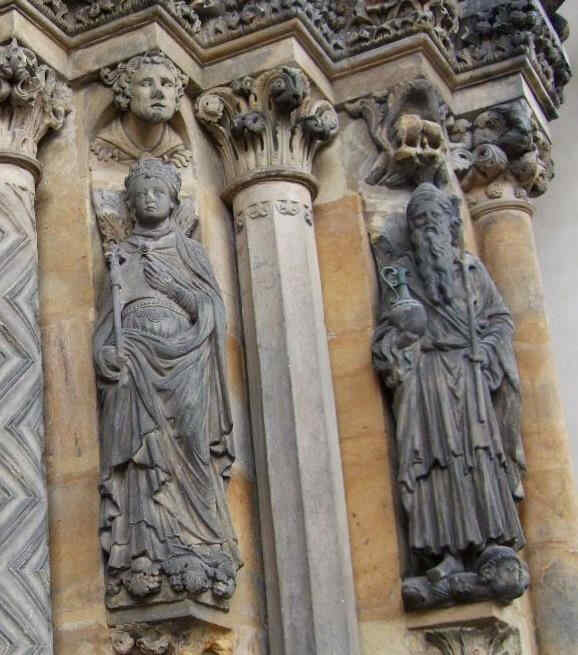

Supplementing what we showed last time of the Cathedrals at Naumburg and Strasburg, we will now show some sculptures from the Cathedral at Bamberg. Here, to begin with, we have two.
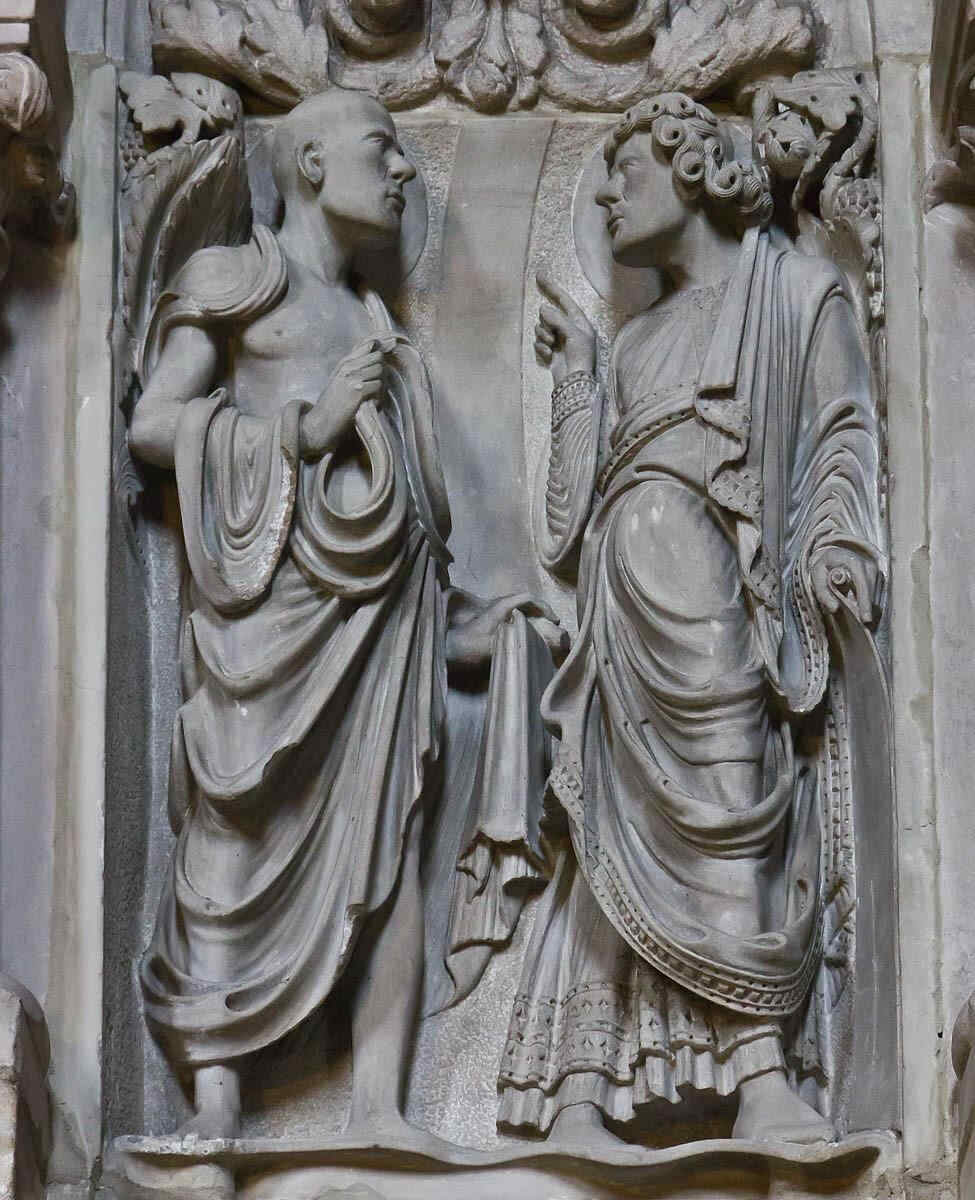

See how directly the dramatic element, the living movement of soul, is expressed in the attitudes, representing the interchange between one soul and another. C. single moment is presented to us, while at the same time the two contrasting characters are well expressed.

The composition is by no means great, but the expressiveness of soul is marvellous. He must remember that this dates from about 1240. Spiritual scientific research will in course of time be confirmed, in that it does not suggest—as many people still do today—that the Mid-European element, in its presentation of the Christian world-conception, was in any high degree influenced by the Southern. That, indeed, is not the case. On the contrary, the very opposite is true.
The different streams are not as yet clearly seen by external history. It is not seen, for instance, what I pointed out the other day—how the Northern impulses worked down even into the creations of Raphael and Michelangelo. Artistically, this conception is altogether a product of the Northern spirit.

This example shows how the worldly and the religious elements played into one another. This was, indeed, the case, especially at the time with which we are now dealing. The worldly and the religious were brought together in the effort which I characterised just now. The souls of men had to be won over; the individual souls must first be called—must by some means be gathered together, if they are to look up in community, in congregation, to the spiritual world. Likewise, they must first be called if they are to express reverence in one way or another, for something in the outer worldly sphere.
Hence the worldly is brought together with the ecclesiastical element. Here, then, we see the Emperor Heinrich, the Empress Kunigunde, and, on the left, St. Stephen.
Needless to say, these things presuppose, as a rule, the naivete of the common people, their blind devotion and dependence. Today, in the fond belief of our contemporaries, these things are overcome. Inwardly, they are present all the more. On the part of the great lords themselves there is very frequently the underlying idea (not unconnected with very human qualities, which shall be nameless), that they themselves stand just a little nearer to the various Saints and supersensible powers than ordinary mortals do.
We will now show a detail, the middle figure of this picture.



The Old and the New Testament were always conceived in unison, as the promise and the fulfilment. Follow the detail of these figures.



And now another figure from the same Cathedral.
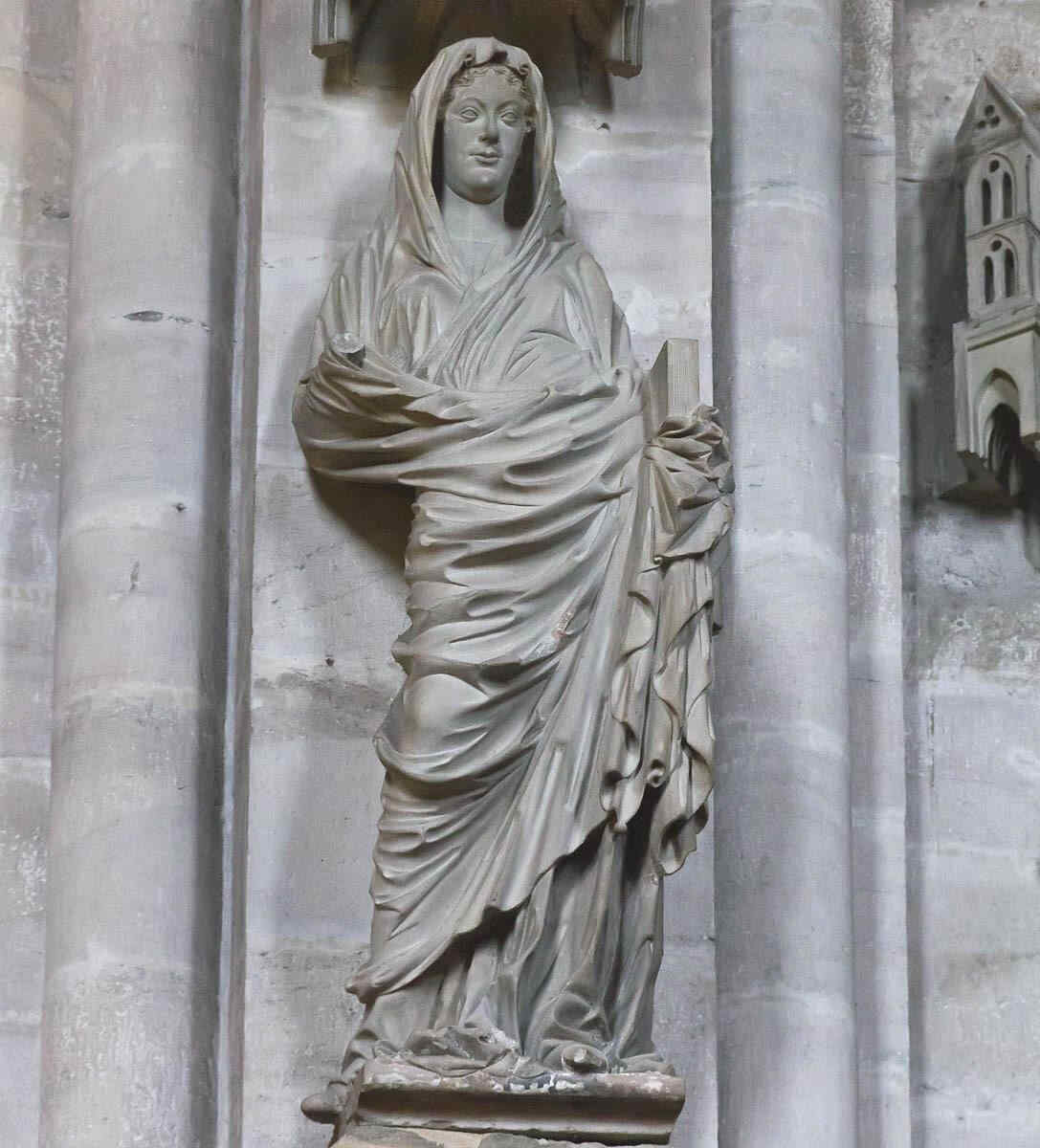

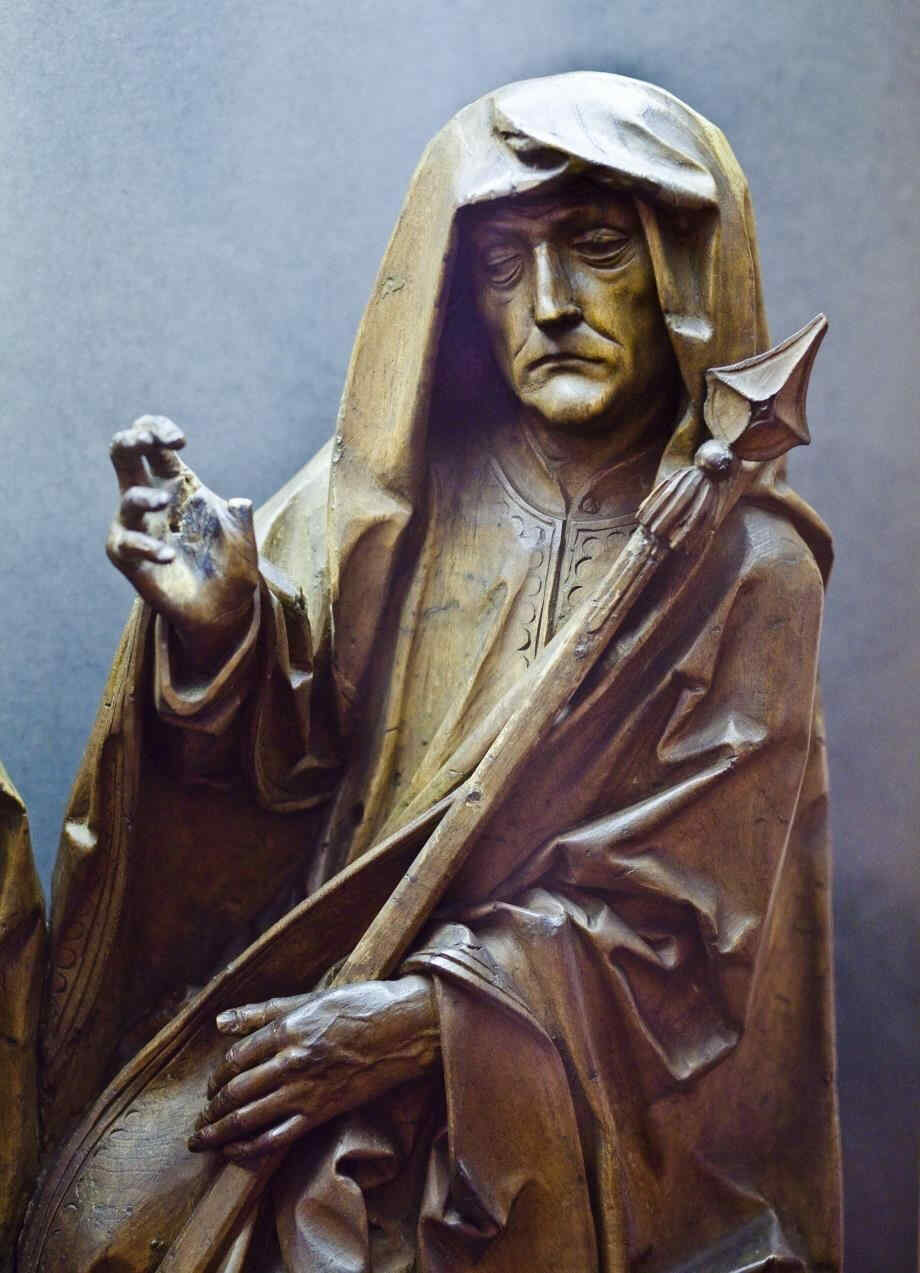
A figure of Mary, showing—from whatever point of view you may consider it—how richly the qualities which I described before, come to expression in this stream of Art. You must remember that this was done about the year 1245. What would you look for in the South at that time? The next Picture, from the Cathedral at Bamberg again, represents the figure of:
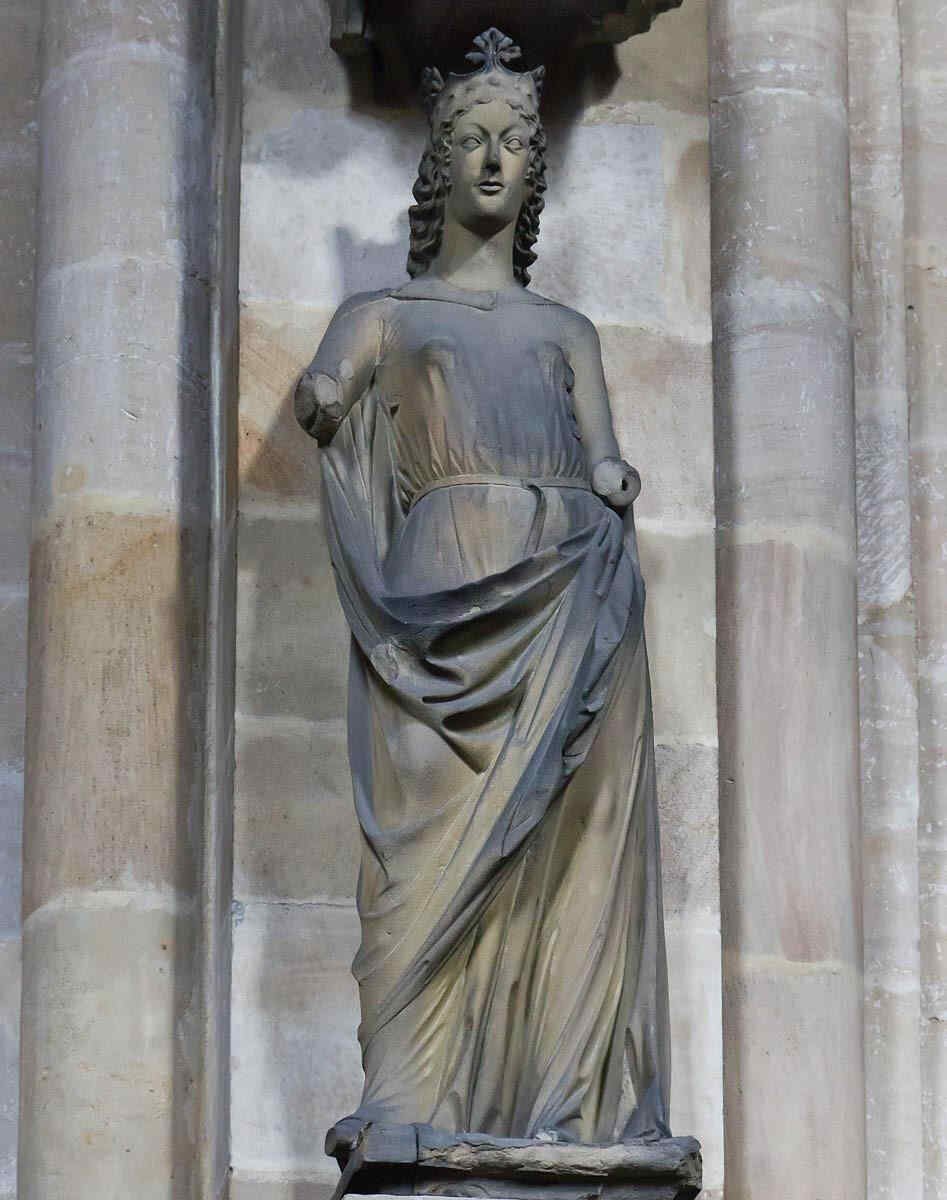

A favorite representation at that time. Last time we saw the corresponding figure from the Cathedral at Strasburg. The figure of the Church is conceived with a certain inner freedom. Her soul is free, she gazes freely far into the world, with wisdom.

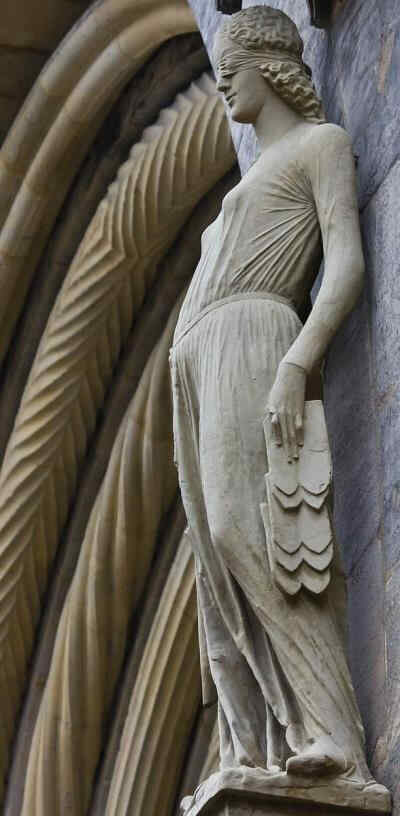
This figure is in contrast, as we saw last time, with the Synagogue, who is represented once more with bound and downcast eyes. The whole posture is intended to represent this contrast in every detail, even to the sweep of the drapery.
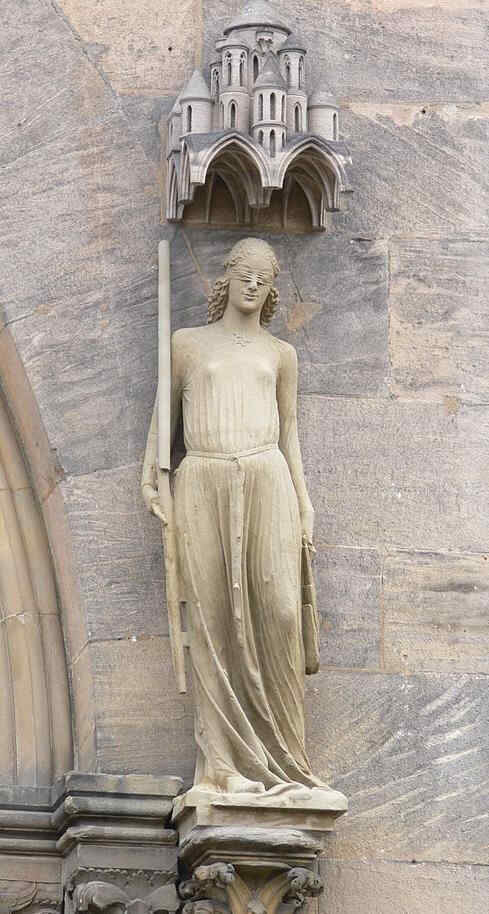



Look at the lower portion of the dress, how well it is adapted to the movement of the soul. We will insert the 'Church' once more, in order that you may compare the draperies:


And now a worldly, or secular figure from the same Cathedral.

Study the expression well. The head, which we will now show in detail, is most wonderful:

We now pass on to the 14th century, and see what had occurred by that time. We have a few figures from the Cathedral at Cologne, first half of the 14th century.


It is easy to see that a certain decline had taken place. The next picture is also from Cologne:
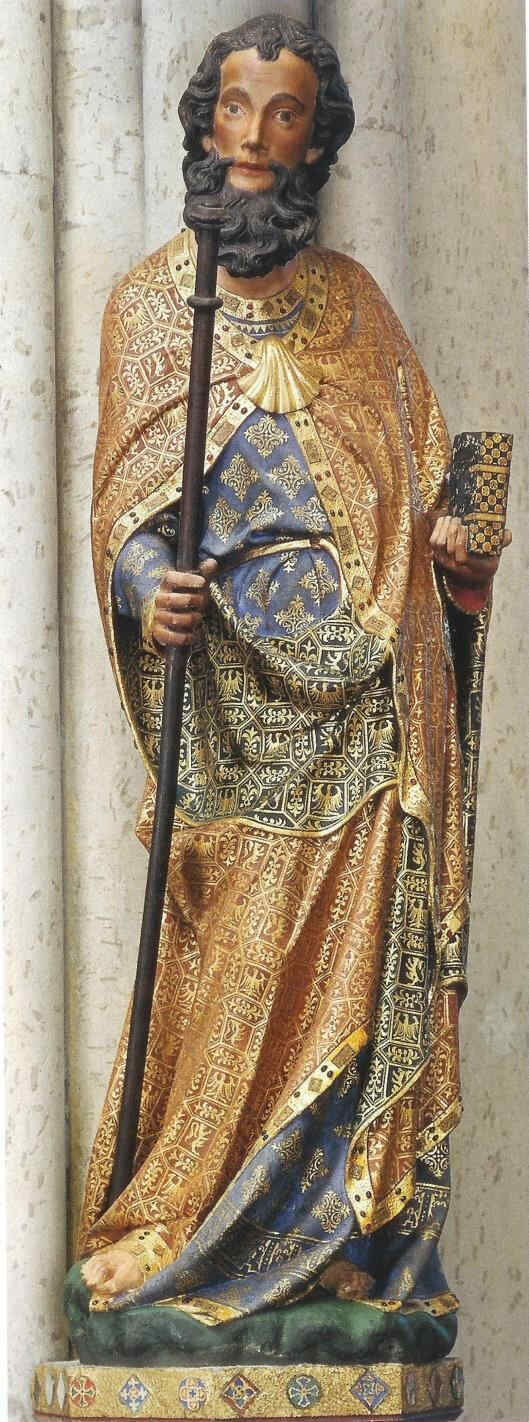
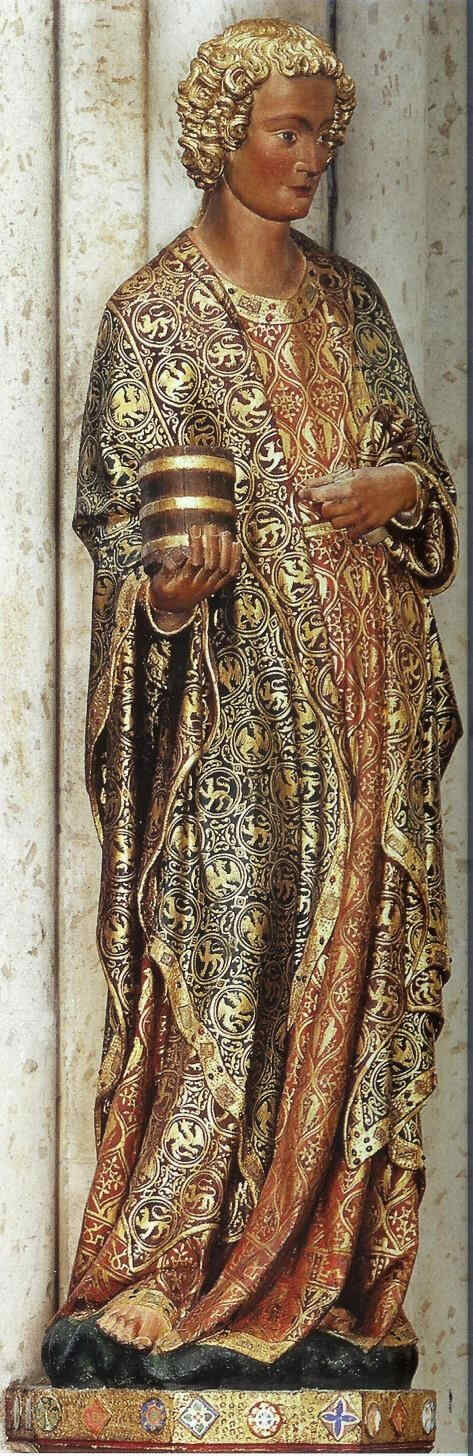


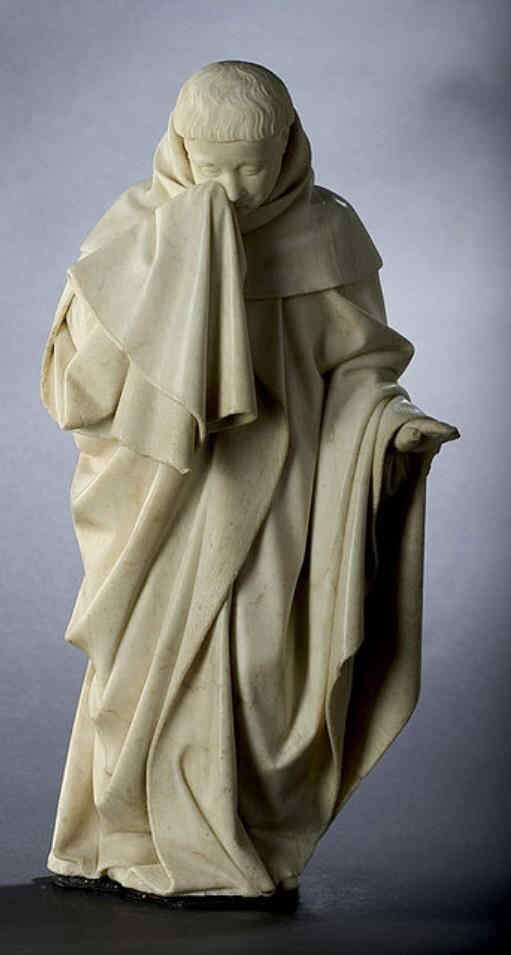
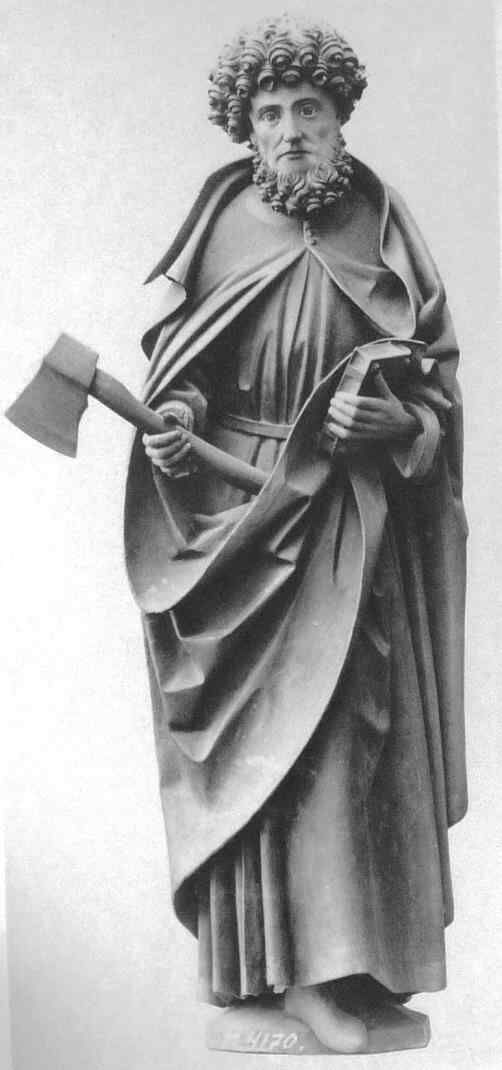
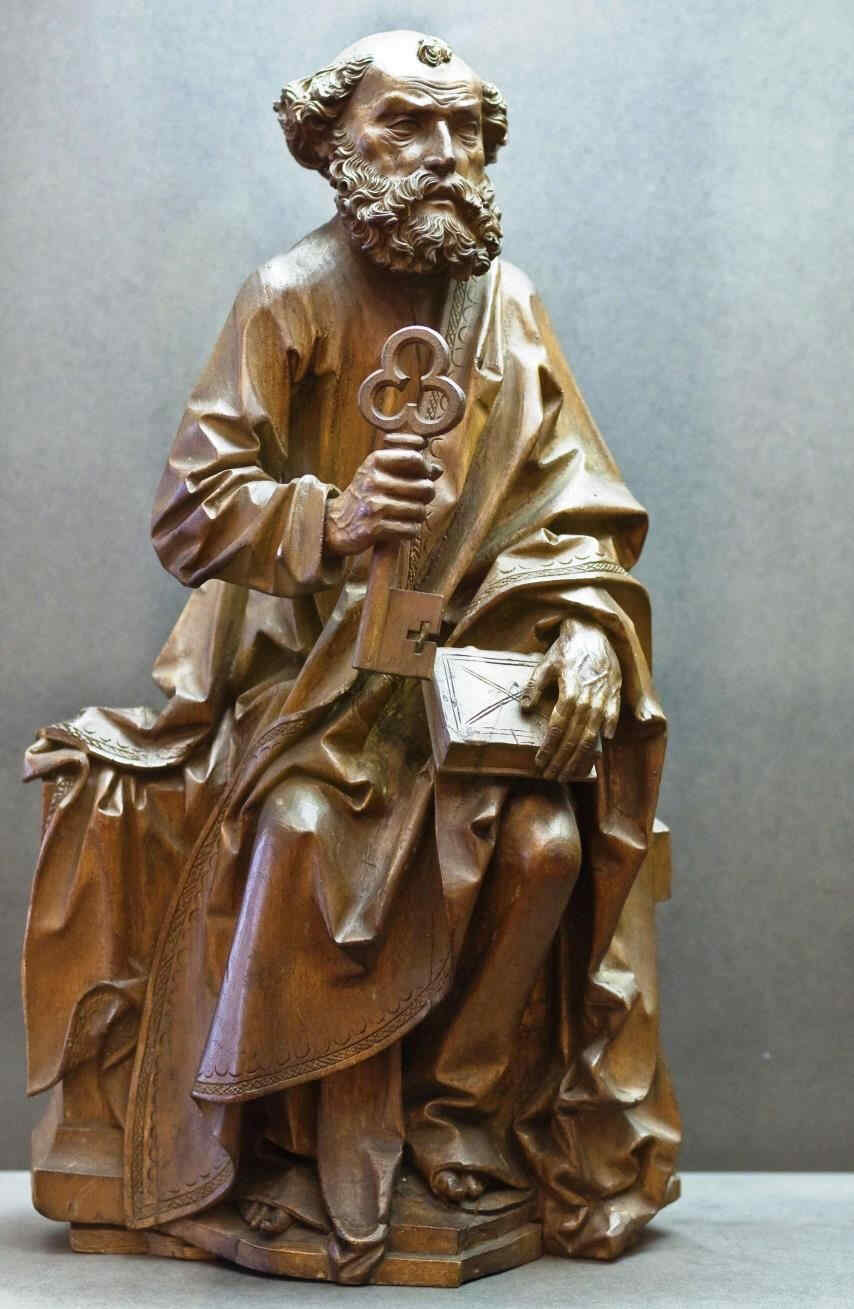
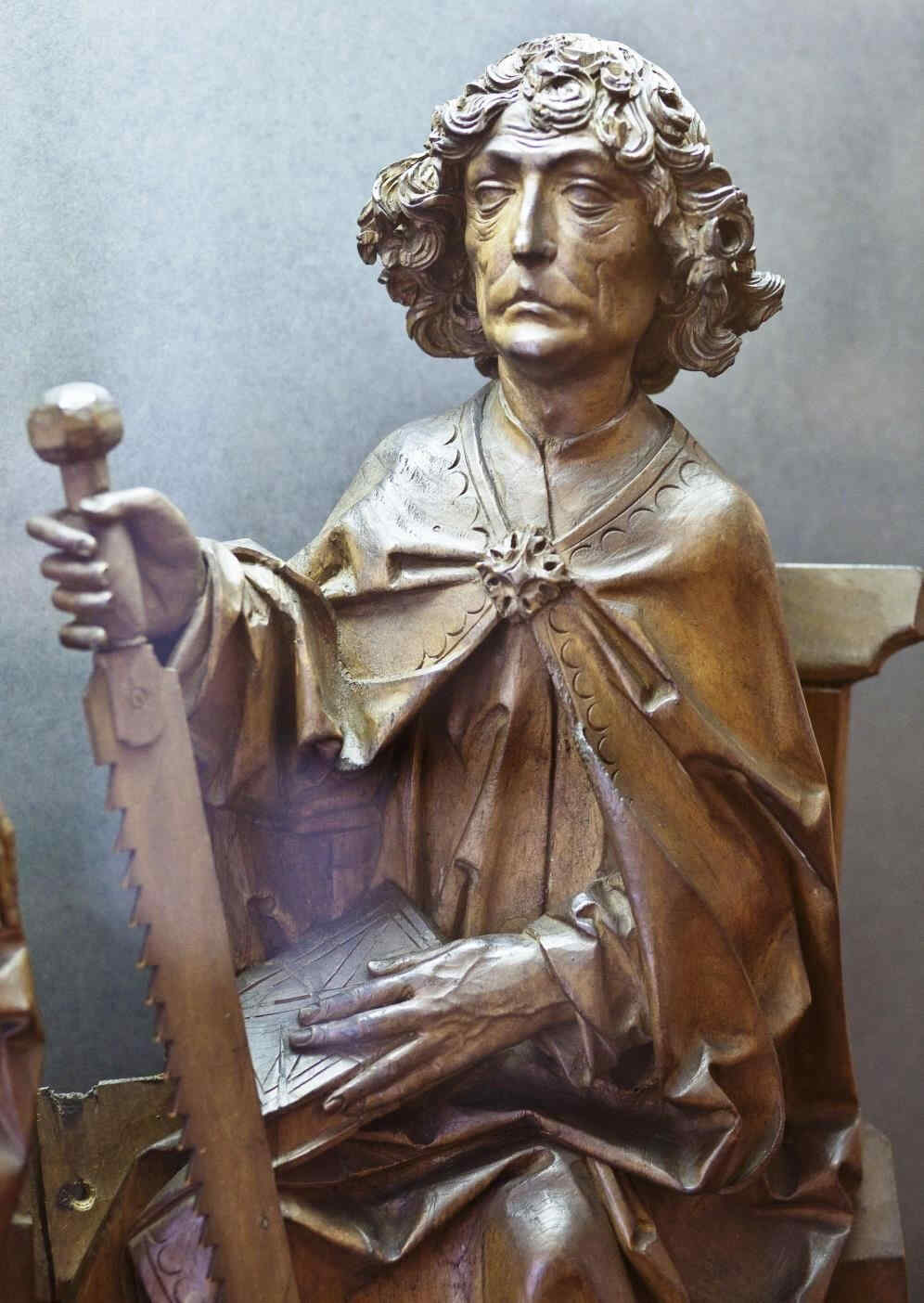
Going further in the 14th century we now come to a figure of St. Paul by a master known as the “Master of the Clay Figures.” These figures were executed in burnt earthenware.
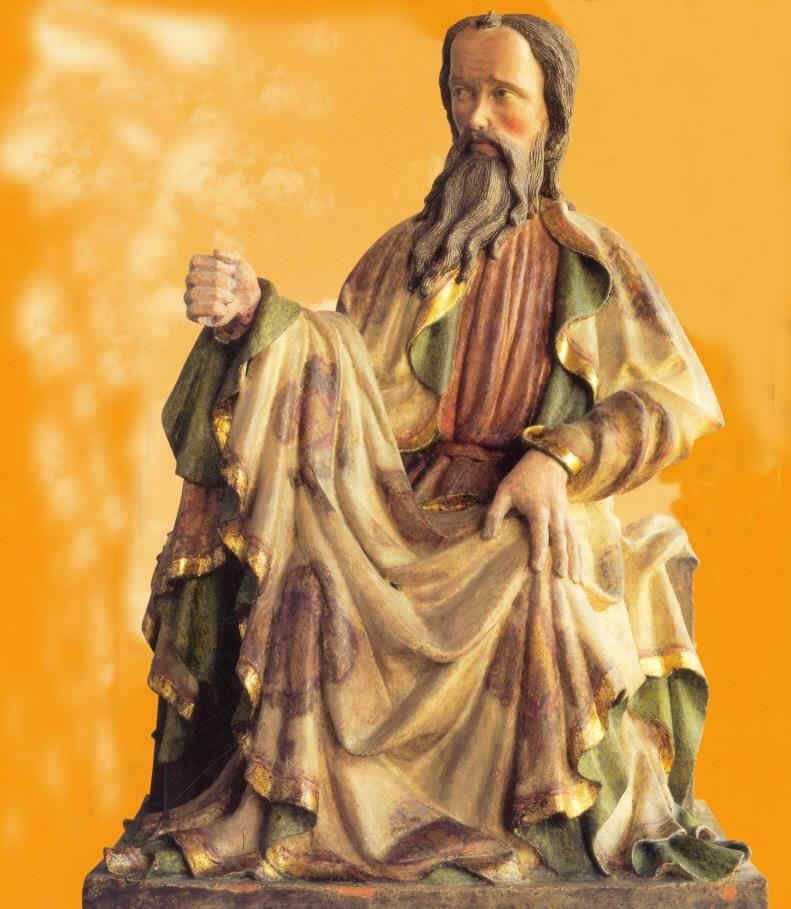

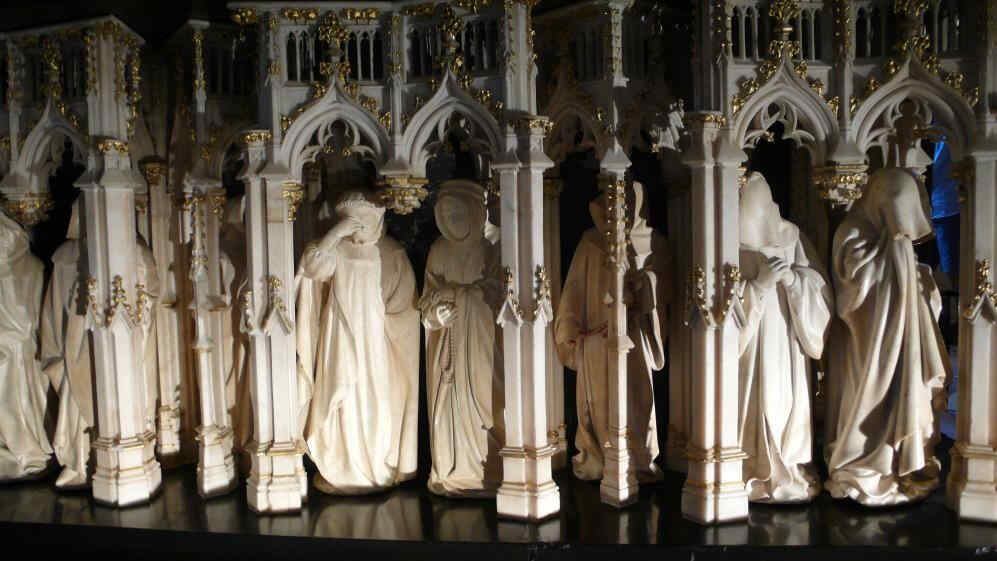
Having now shown the rise, and to some extent the decline of a stream of evolution complete in itself, we will give a series of pictures from the Chartreuse de Champmol at Dijon, which are really great of their kind. Most, if not all of them are the independent work of the Dutch sculptor, Sluter, or else done under his direction. He brought to the Chartreuse at Dijon, from the Netherlands, an almost unique power of individual characterisation. From many points of view we see this individualising tendency in his work.
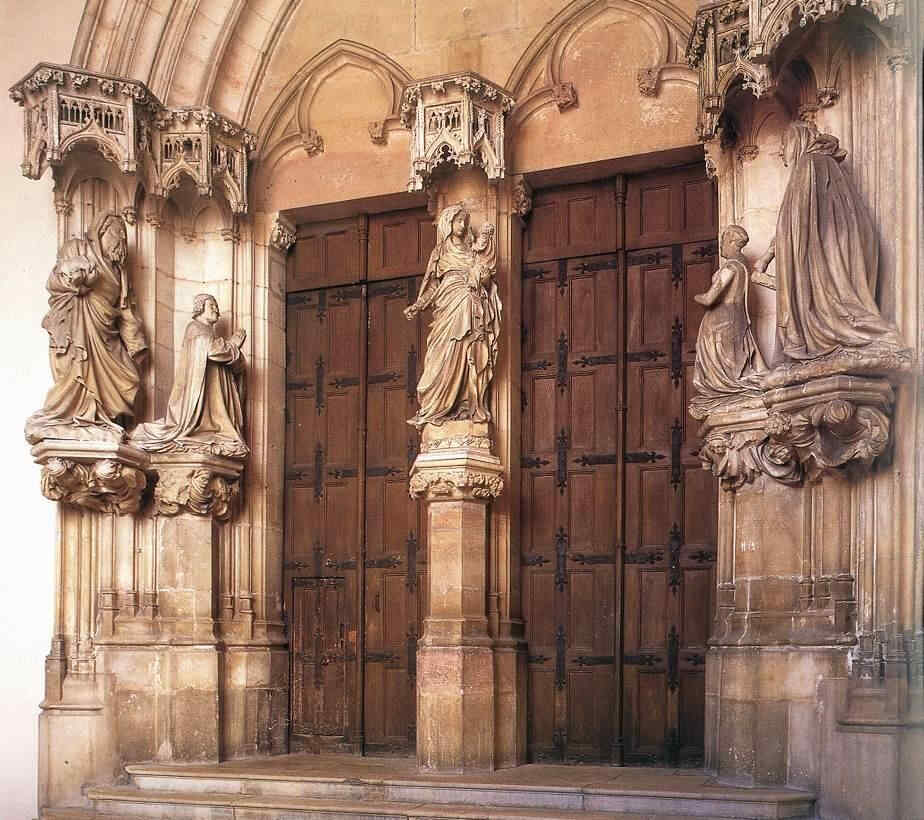
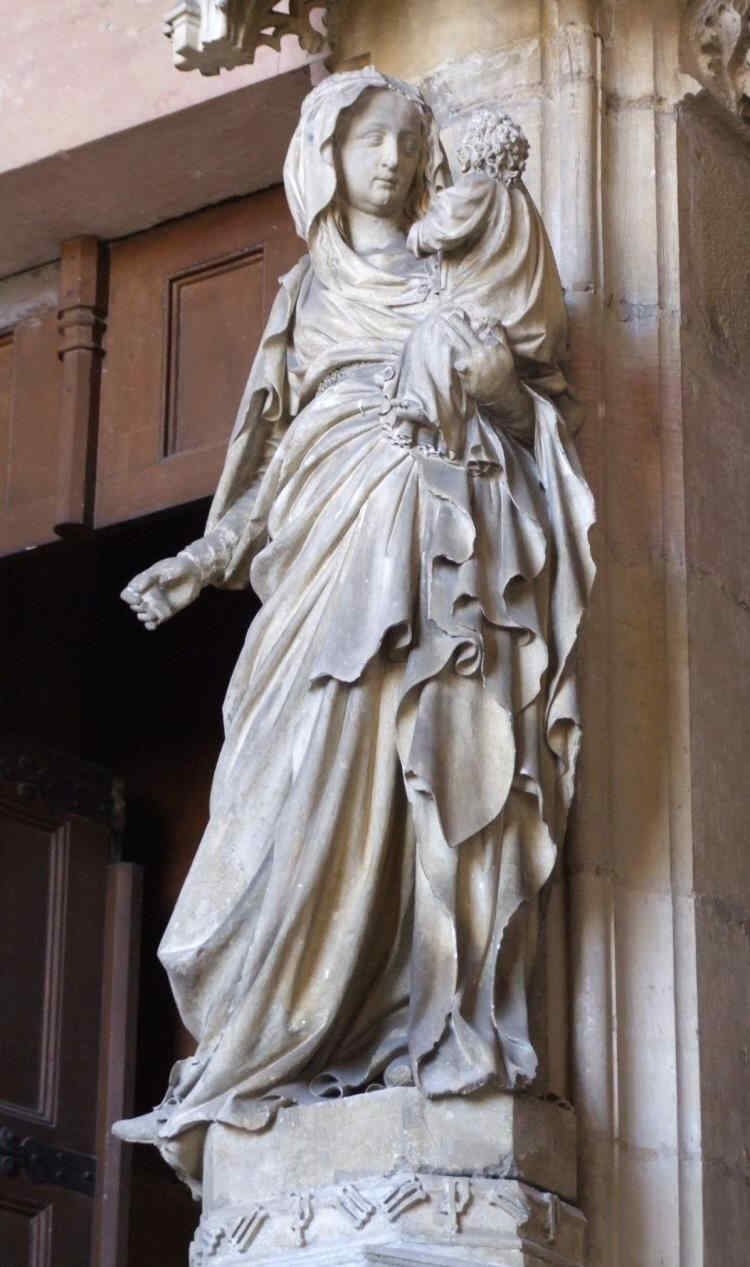



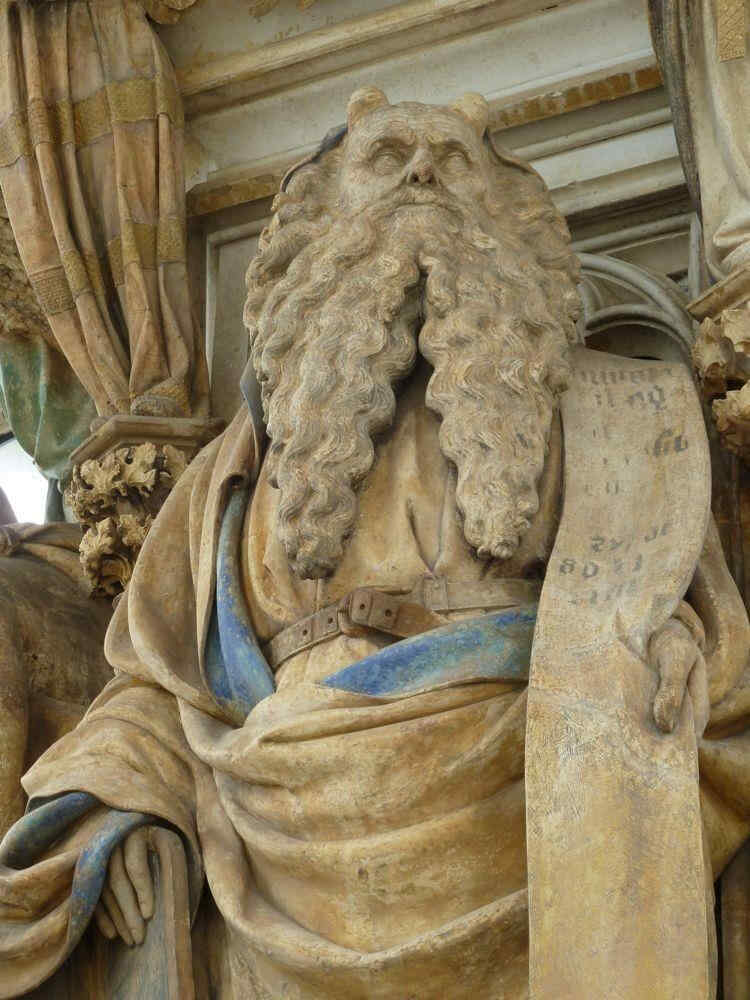
Here especially you see the Art of individual characterisation. Compare this Madonna and Child of Sluter's with the next picture (Moses) and realise the power of one and the same man to characterise these two.

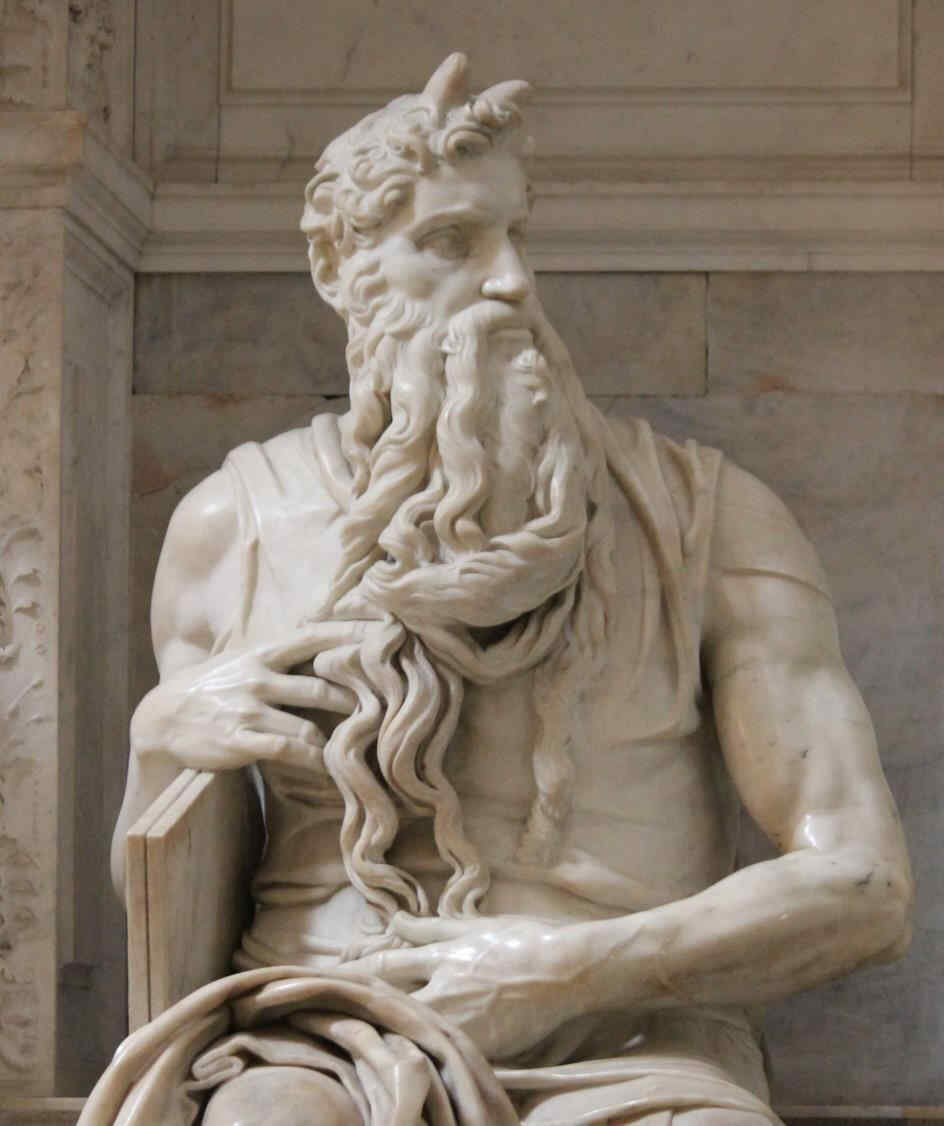
Remember that this Chartreuse at Dijon was built in 1306 to 1334; it was therefore the beginning of the 14th century. Compare this with Michelangelo's Moses—for why should these things not be placed together—they are, indeed, comparable.

And now by the same artist as before—Sluter.
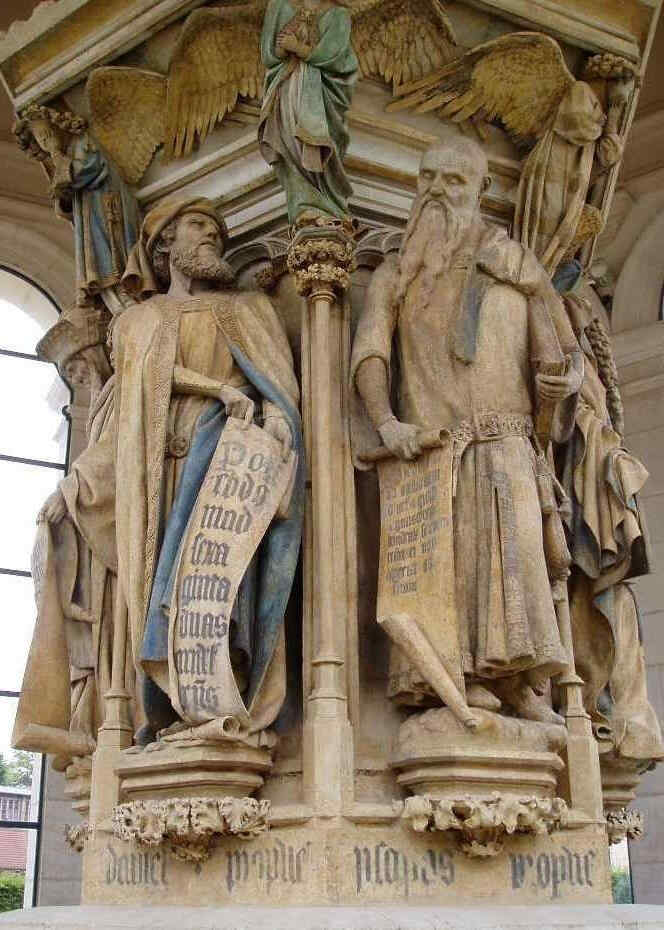



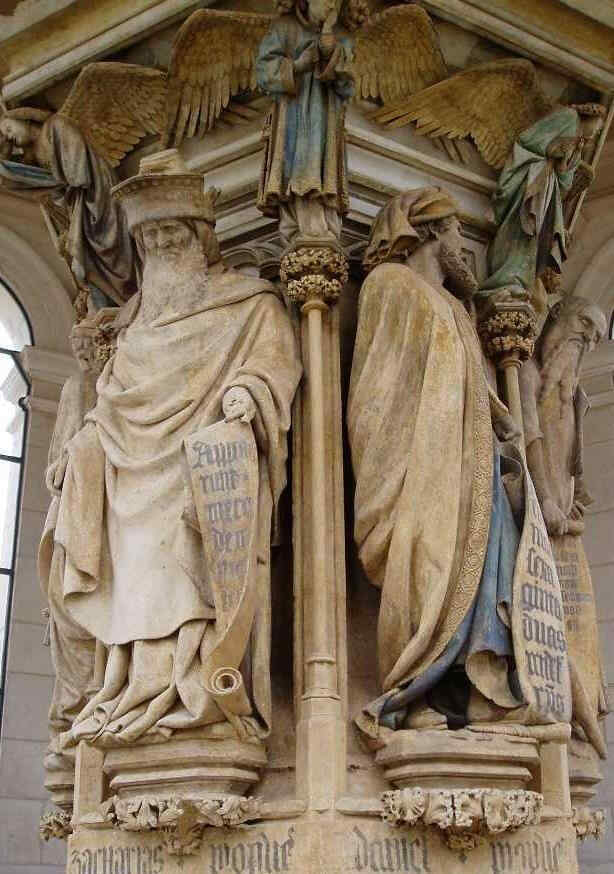
To live with the prophetic figures so as to achieve this degree of individualisation, was, indeed, most wonderful. We will now show one of the figures in detail:



These are by the same artist. The age was especially great in the creation of tomb monuments. We will show the detail of the upper part:


The figures round the base of the tomb which were formerly so small, are wonderfully executed when you come to see them in detail.



Such is the individual characterisation of all the single figures round the base of the tomb. Here is another group.


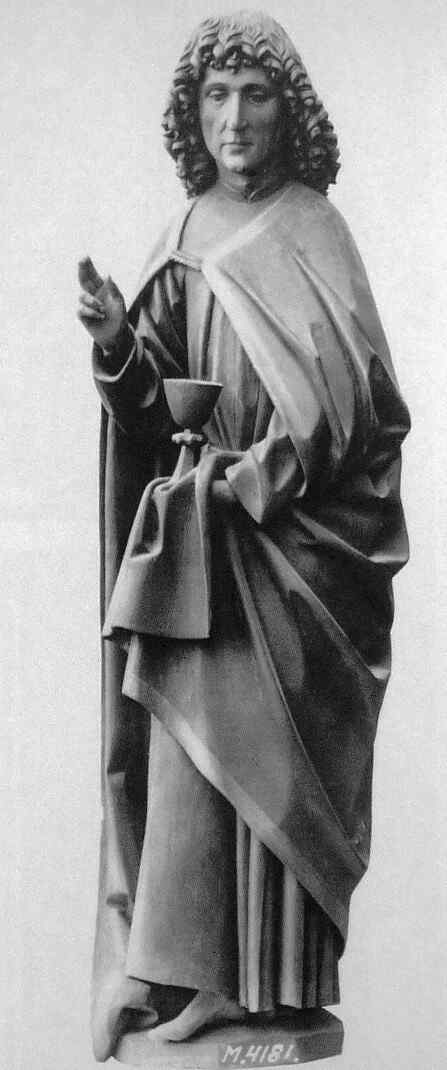
We now go on to an artist of the 15th century. (We must go according to the pictures we possess at the moment.) The last pictures, you remember, were by an artist of the early 14th century. With the Cologne Master, and the Master of the Clay Figures who made the group we saw before, we came to the 14th century. We now pass on into the 15th. Here, then, we have two figures by Hans Multscher:
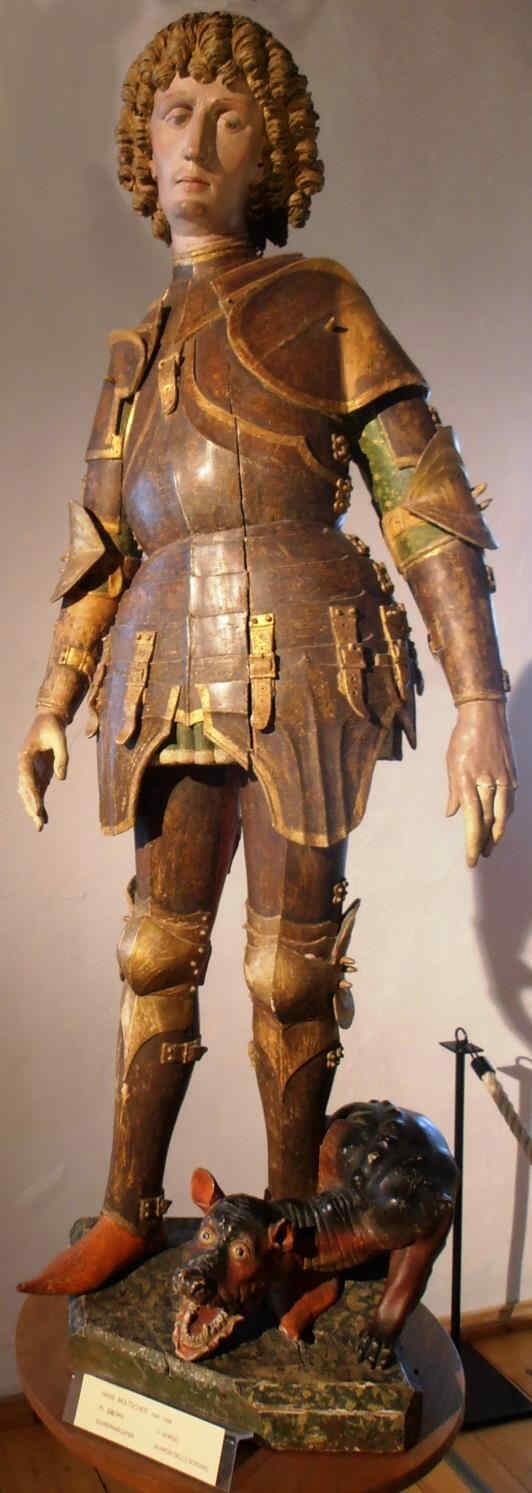
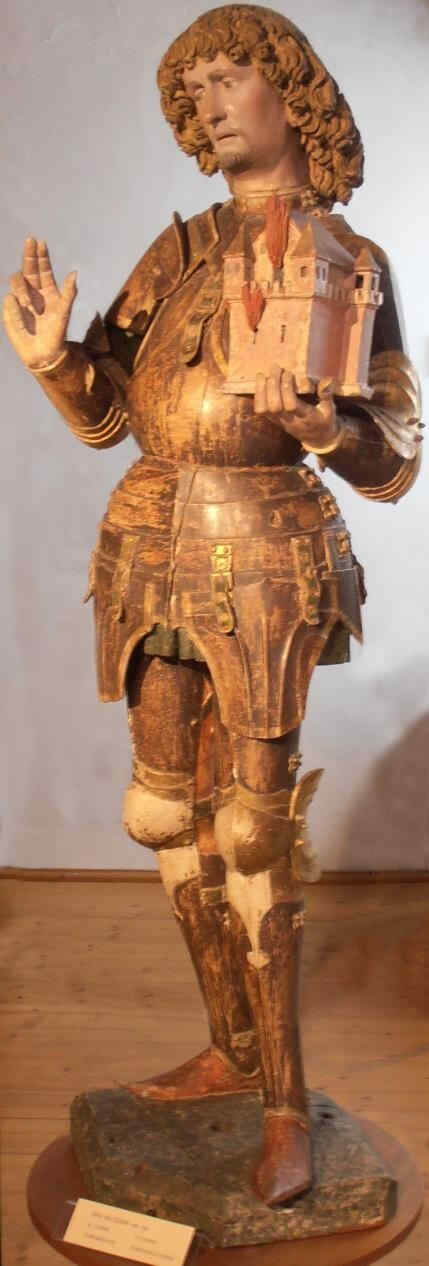


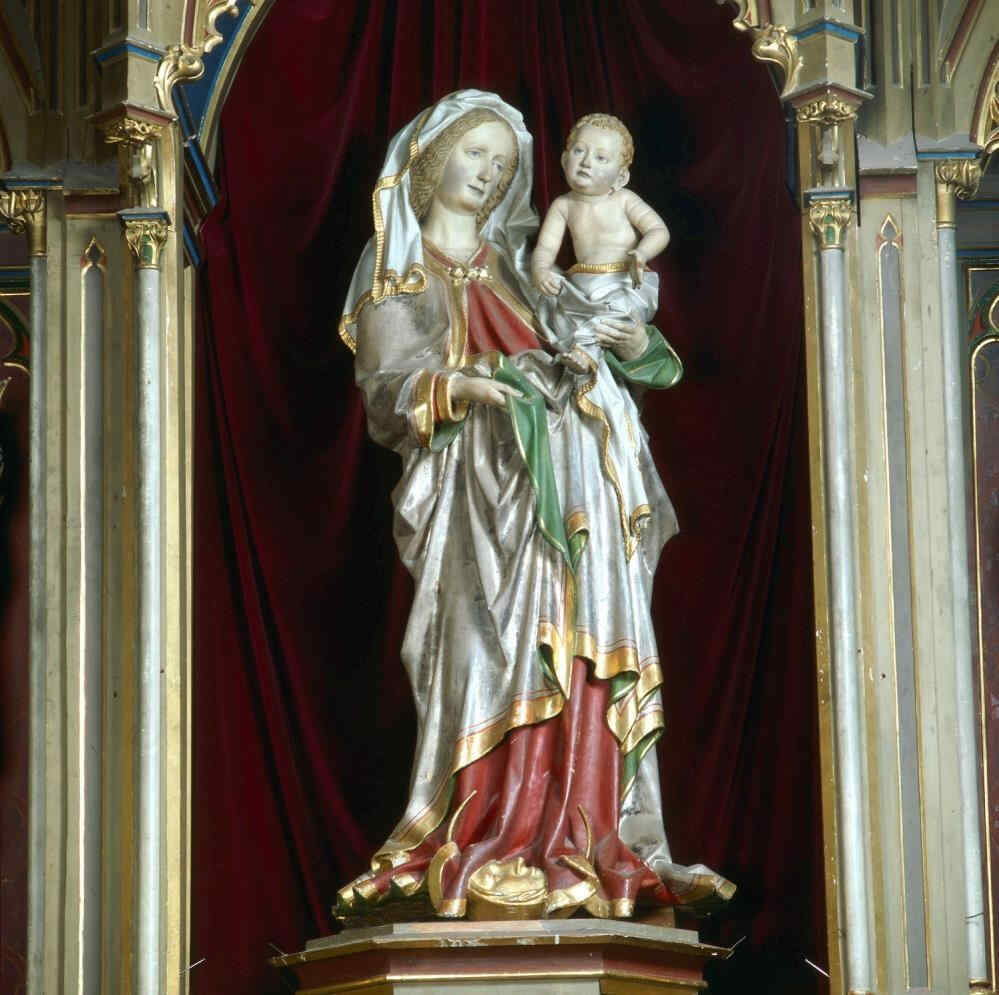
This is about the middle of the 15th century. The next is a Madonna, by the same artist (Multscher).

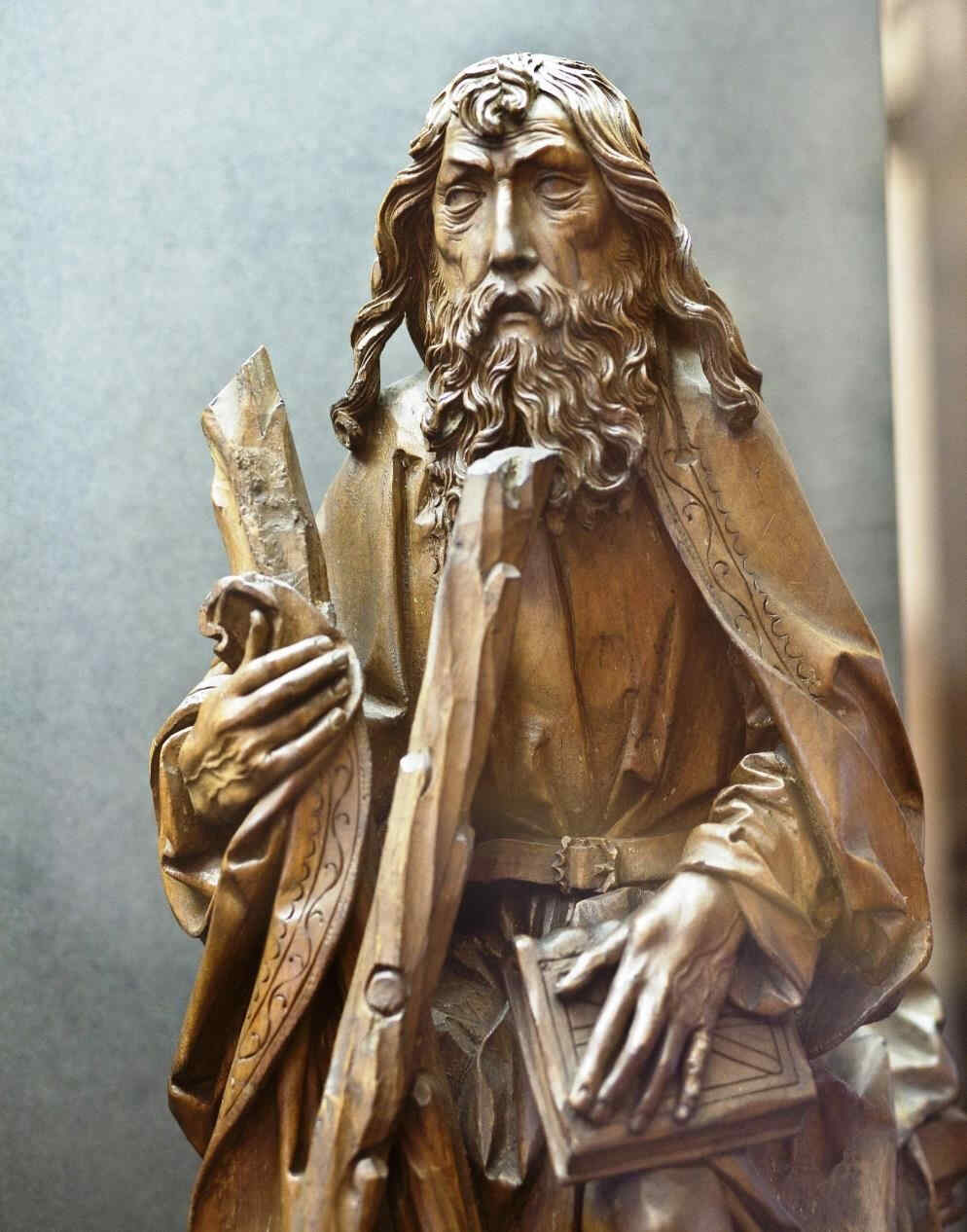
And now we go further and further in what I described just now as the elaboration of the Christian subjects with deep inwardness of soul. The following are figures carved in wood, at Blutenburg (end of the 15th century). The art of characterisation has, indeed, attained its ideal to a marvellous extent.
The figure of Mary, carved in wood—end of the 13th century:



This, then, is the time when Michelangelo and Raphael were born. The next picture, too, is from Blutenburg.



The time when these highly individual figures were created was also especially great in wood-carving, with which they decorated the Choristers' seats in their churches. We will give two examples from the Frauenkirche in Munich, end of the 15th century.
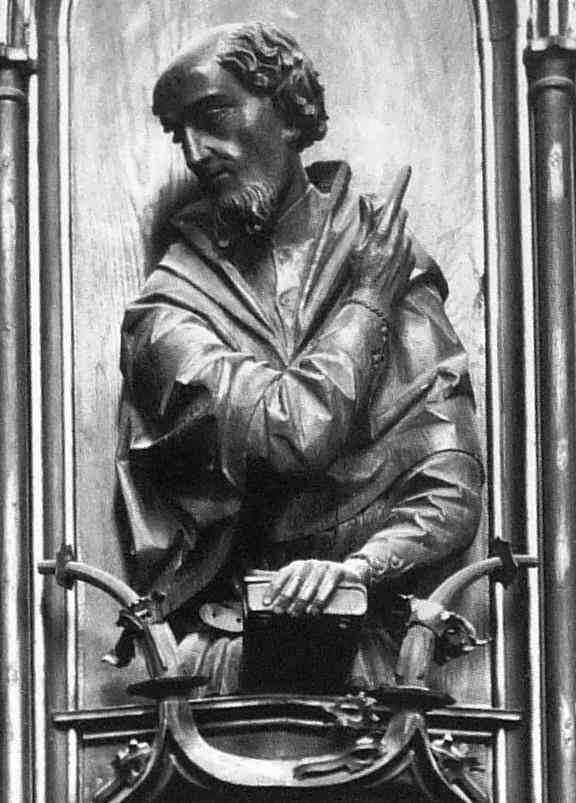


We now come to the sculptor who worked at the end of the 15th century.





And this was the time when the High Renaissance in Italy had not as yet begun. These works were created about 1490–1495.
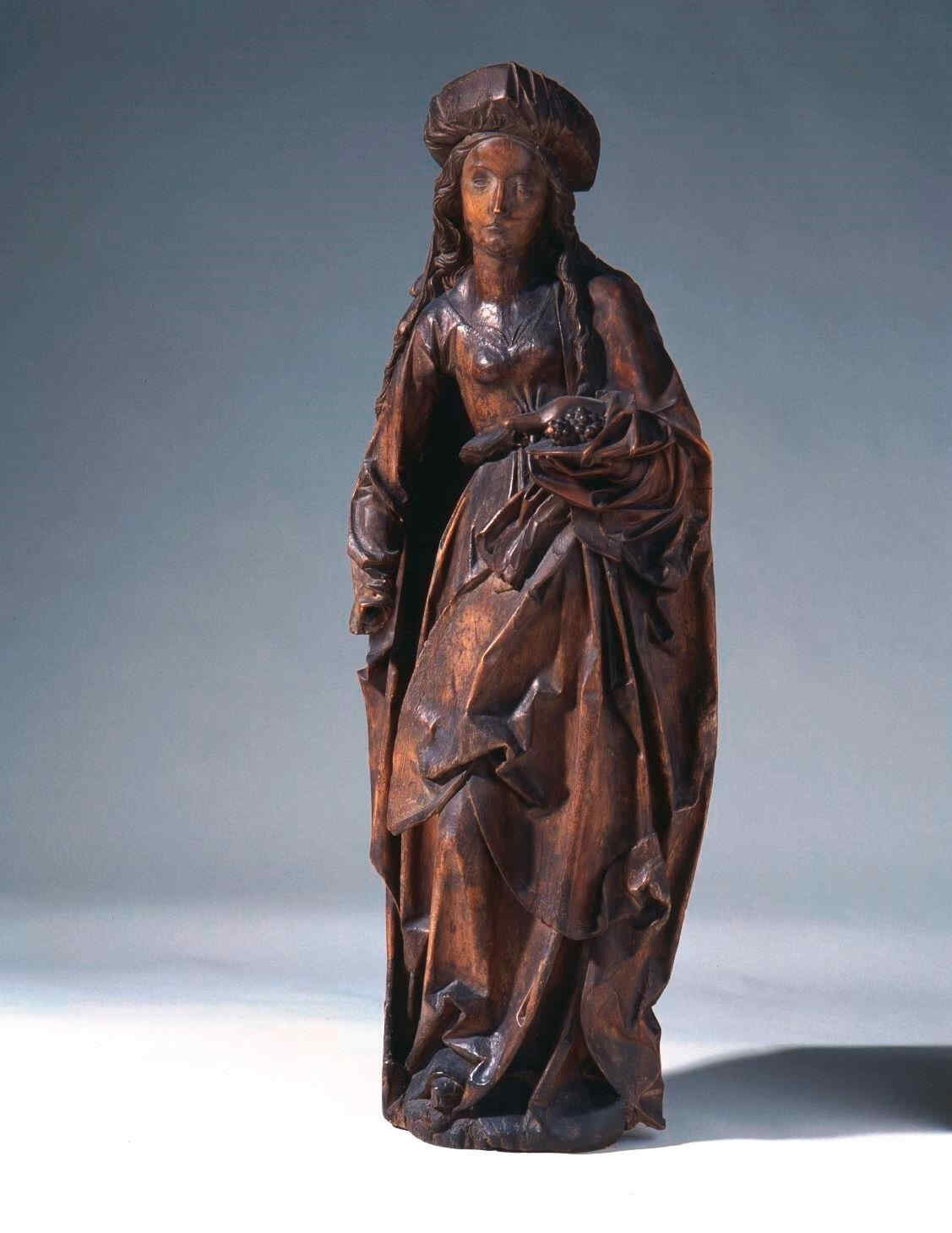

This St. Elizabeth—created in the early 16th century—is now in the (Germanisches Museum, at Nuremberg.)
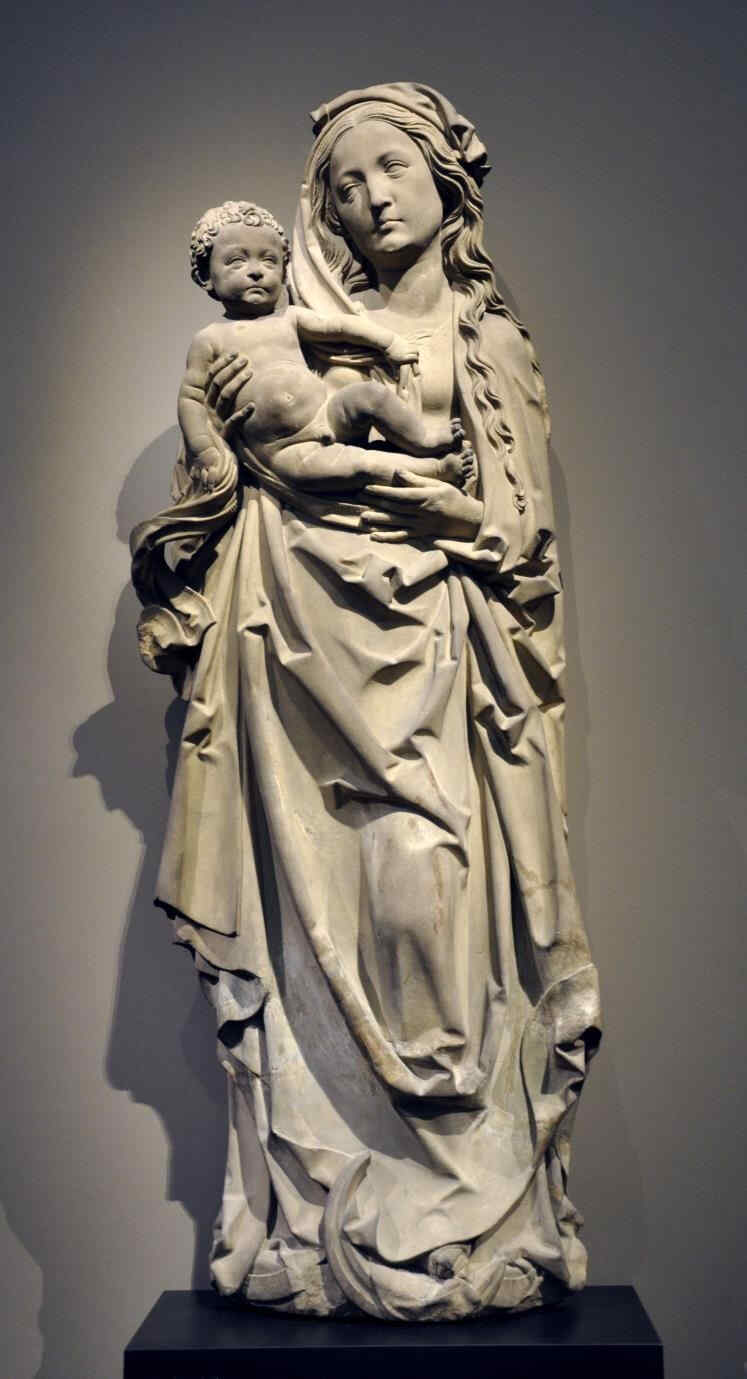

This, too, dates from the beginning of the 16th century.




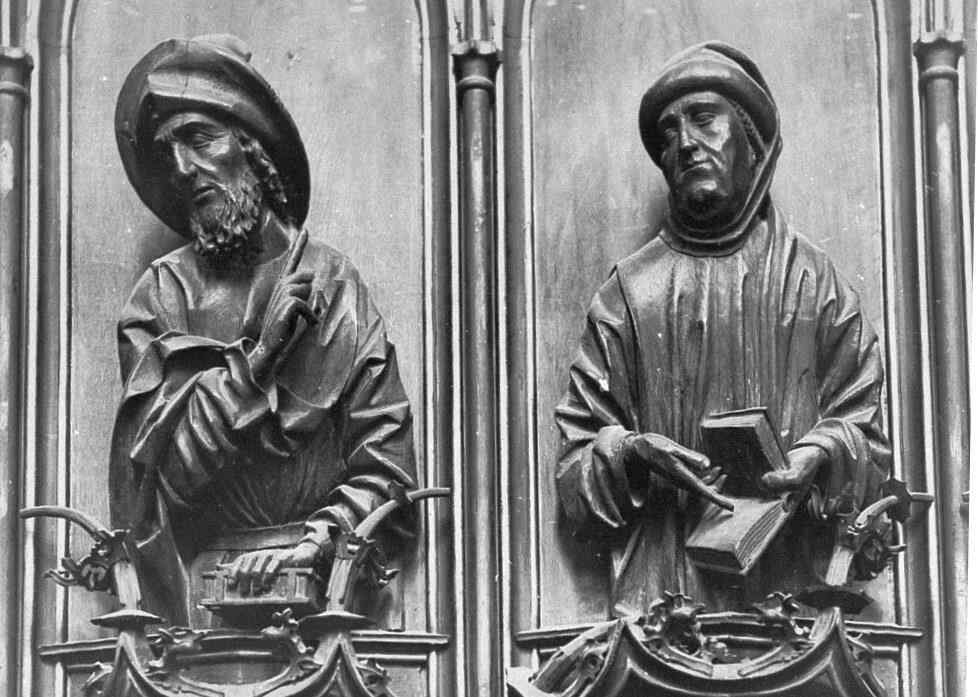
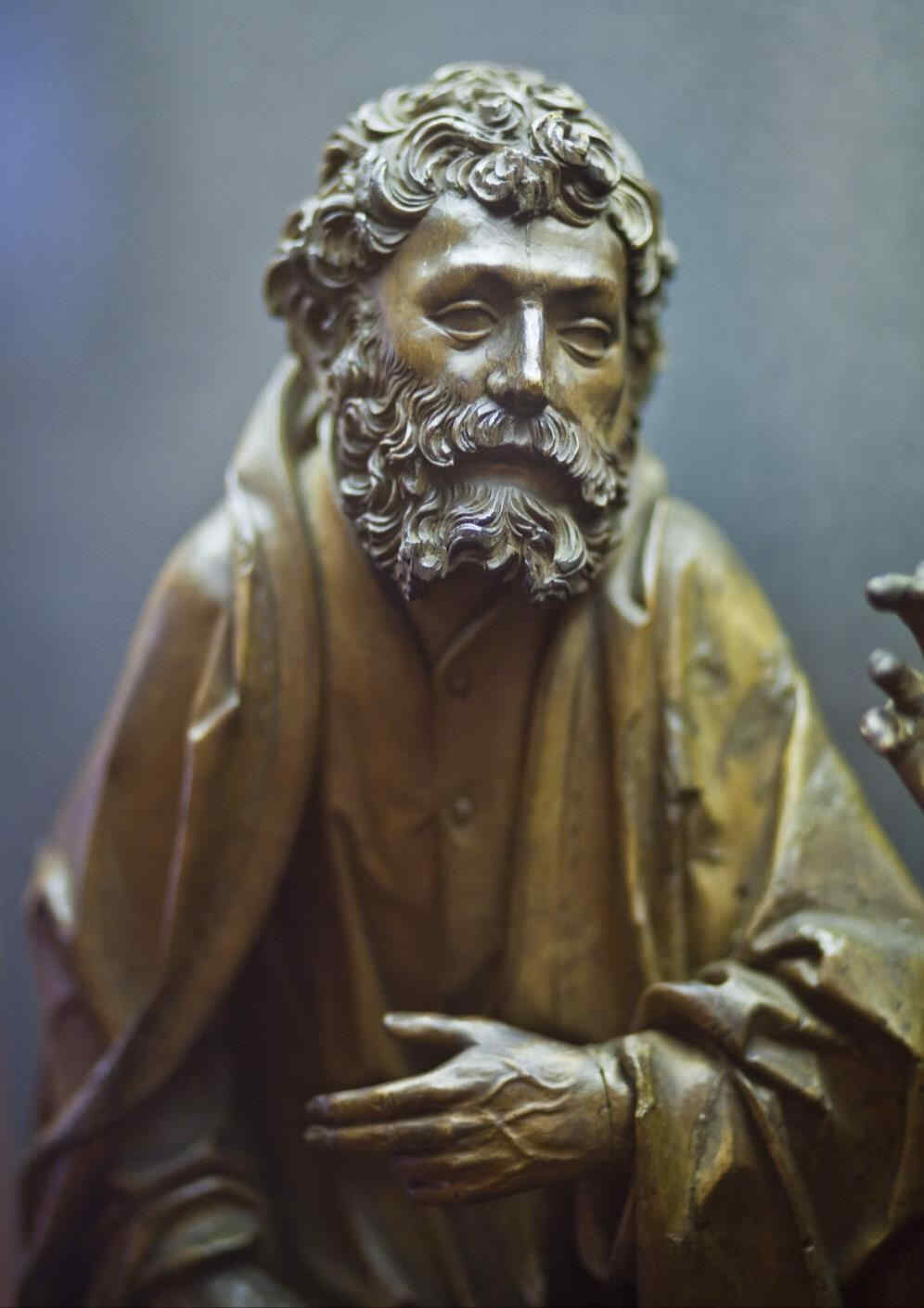
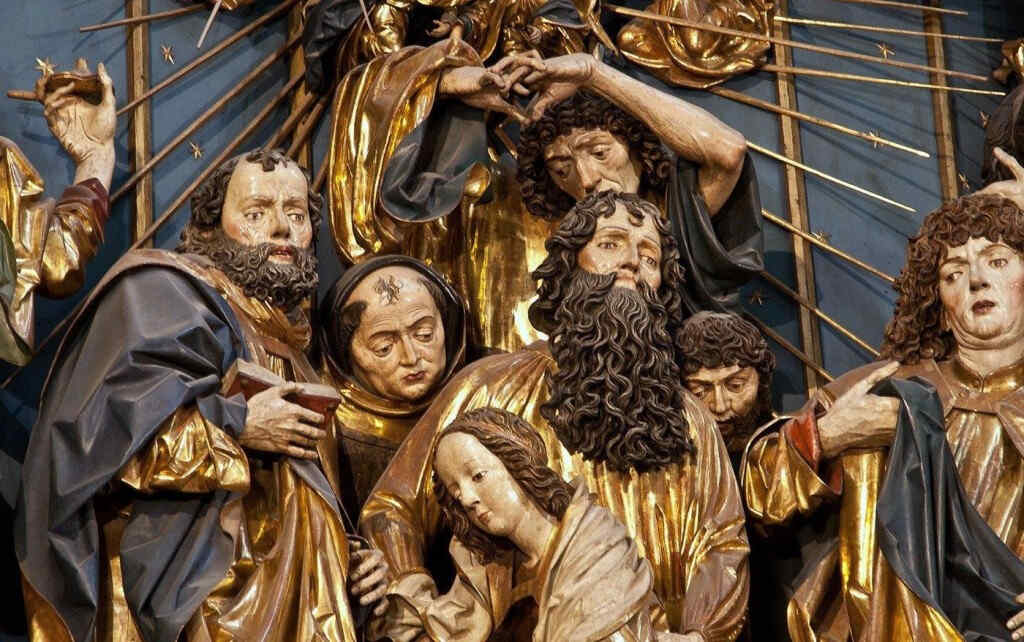
There are wonderful types among these twelve Apostles; one would like to study every single head alone:
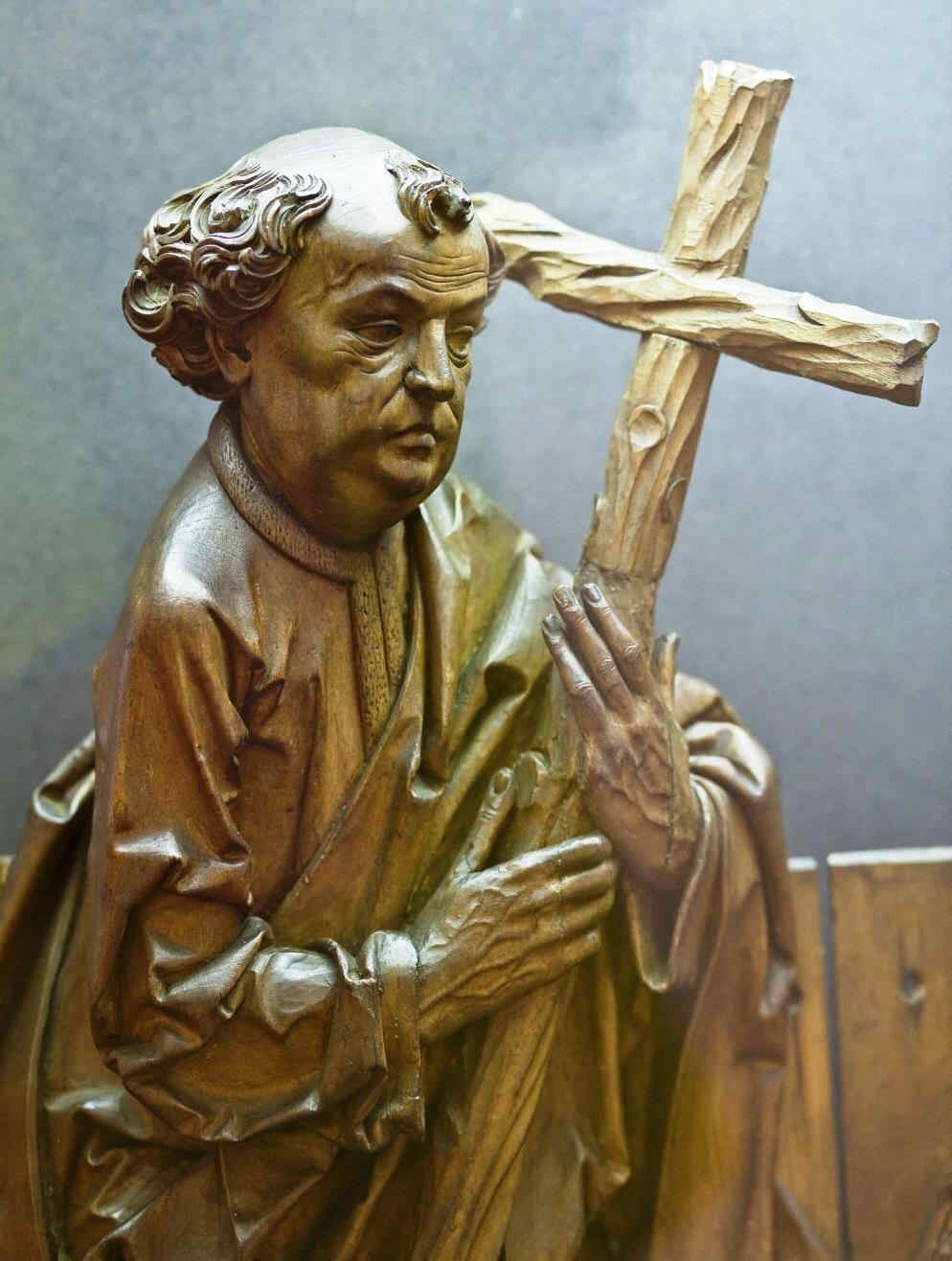
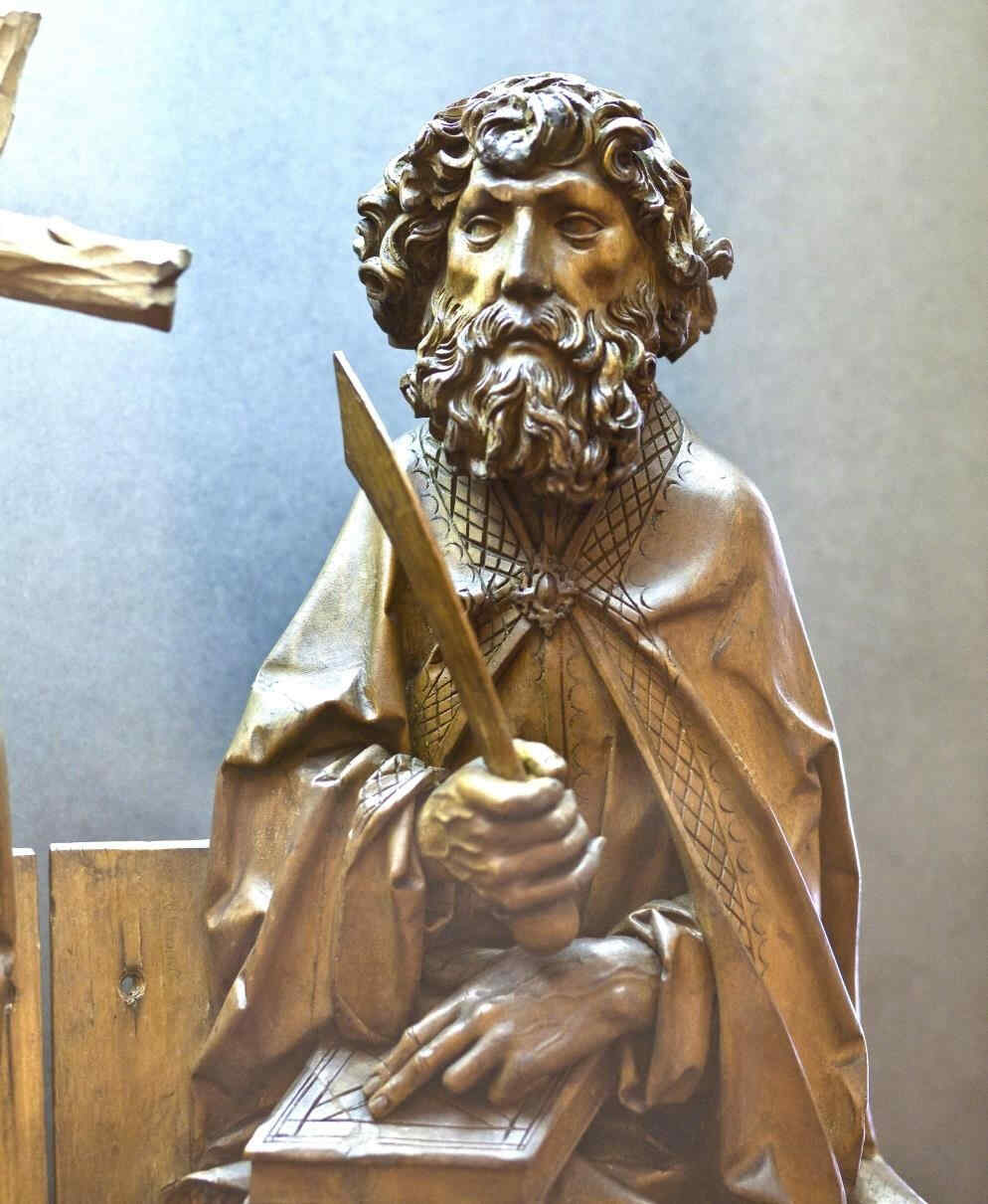
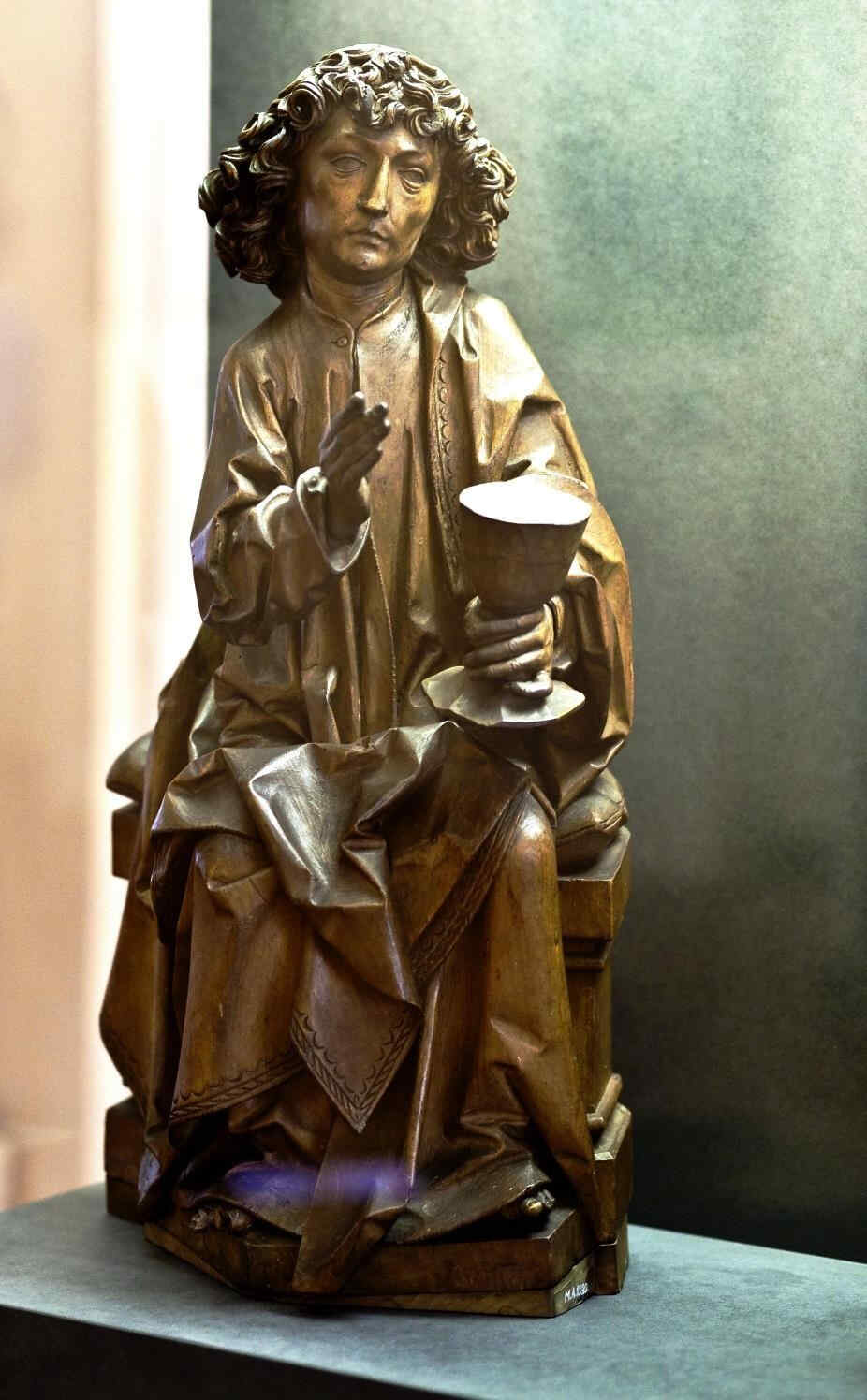
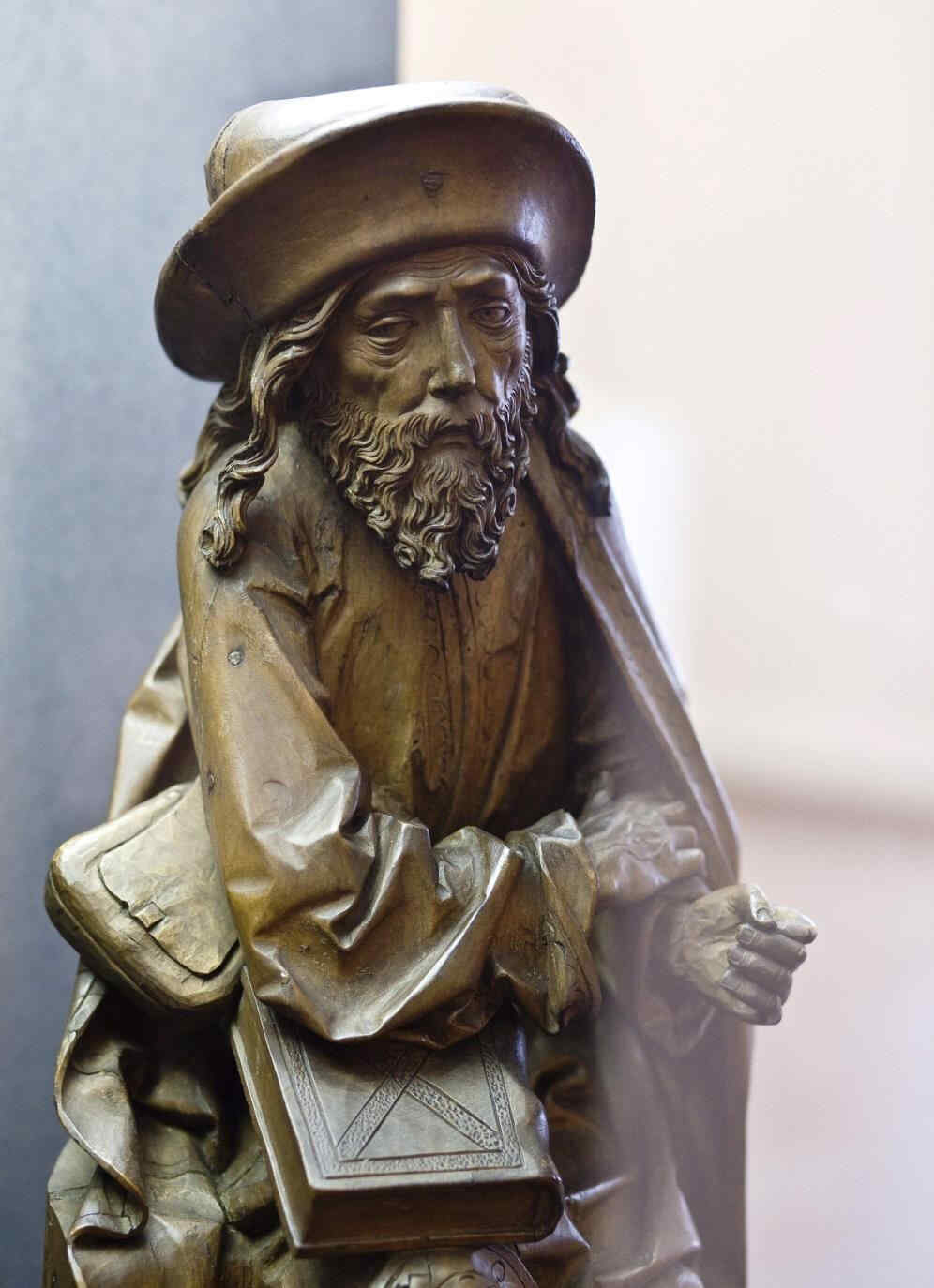












Finally, we give two examples of the sculptor—Veit Stoss—early 16th century, who worked in Cracow and also in Southern Germany, creating his plastic works in many different materials.


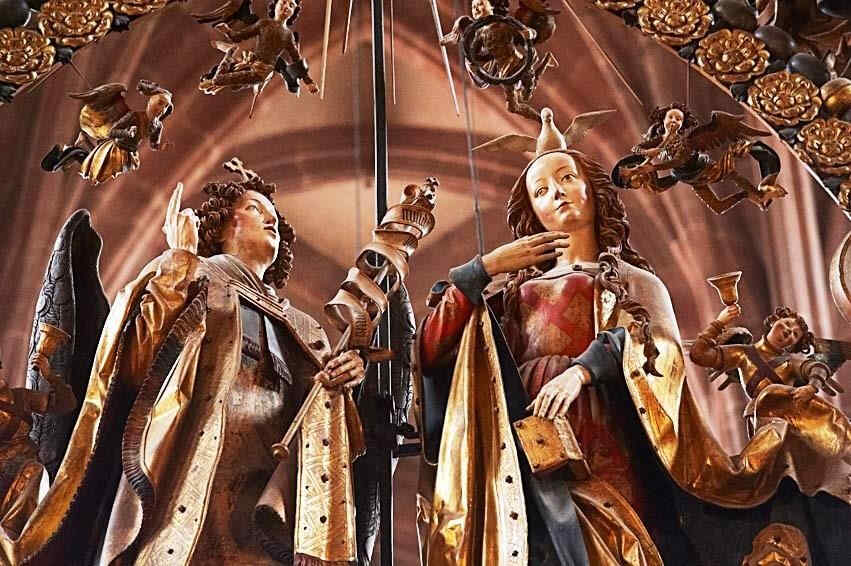
The next picture is in Nuremberg,. “The Angel's Greeting,” it is called.


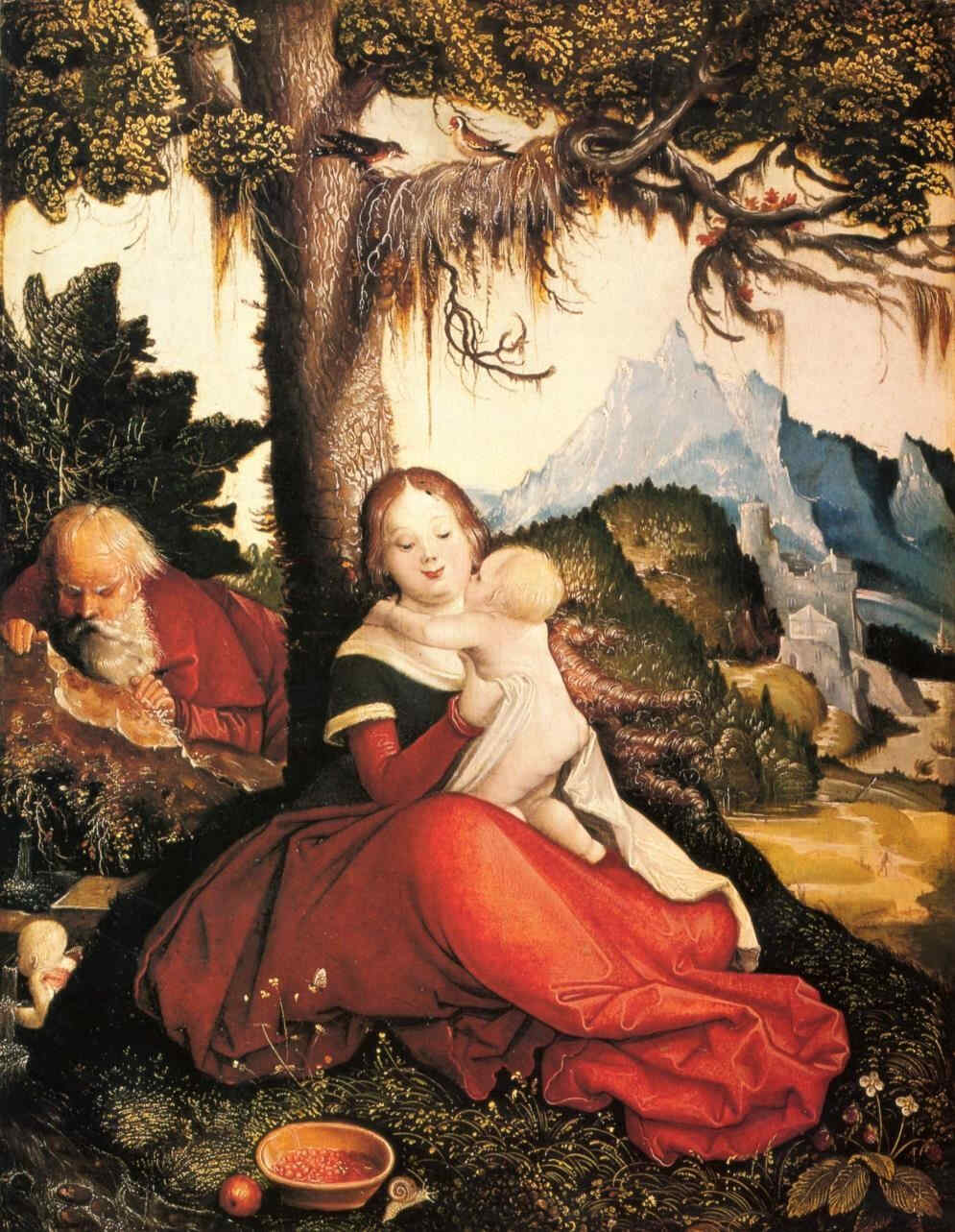
I will also show three paintings by Hans Baldung, also known as Hans Grun, who worked in Dürer's workshop at the beginning of the 16th century—about 1507–1509.

His pictures reveal once more, in the sphere of painting, how everything is turned towards the life of the soul.
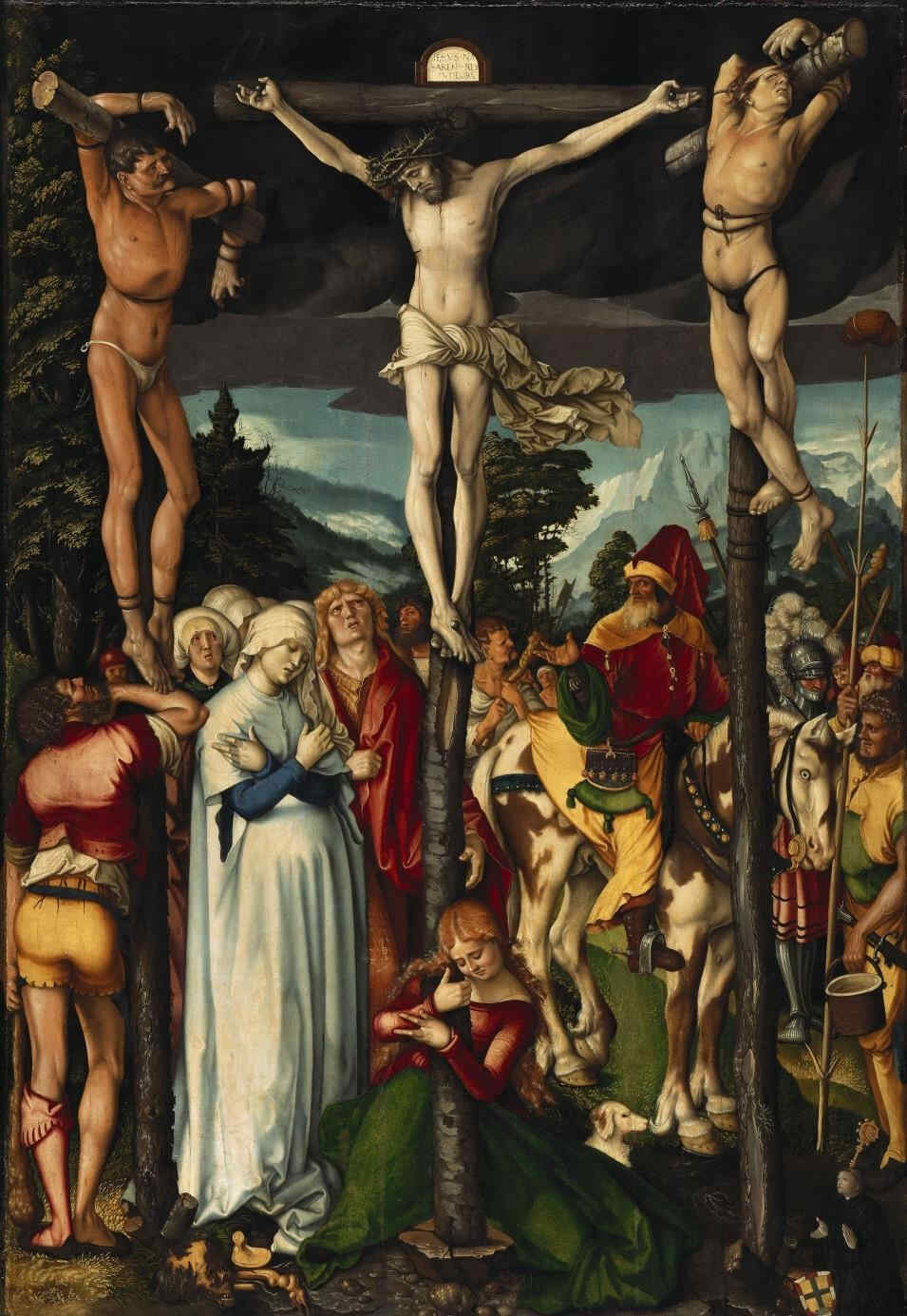

Hans Baldung was also a portrait painter of no mean order. Here you have an example.
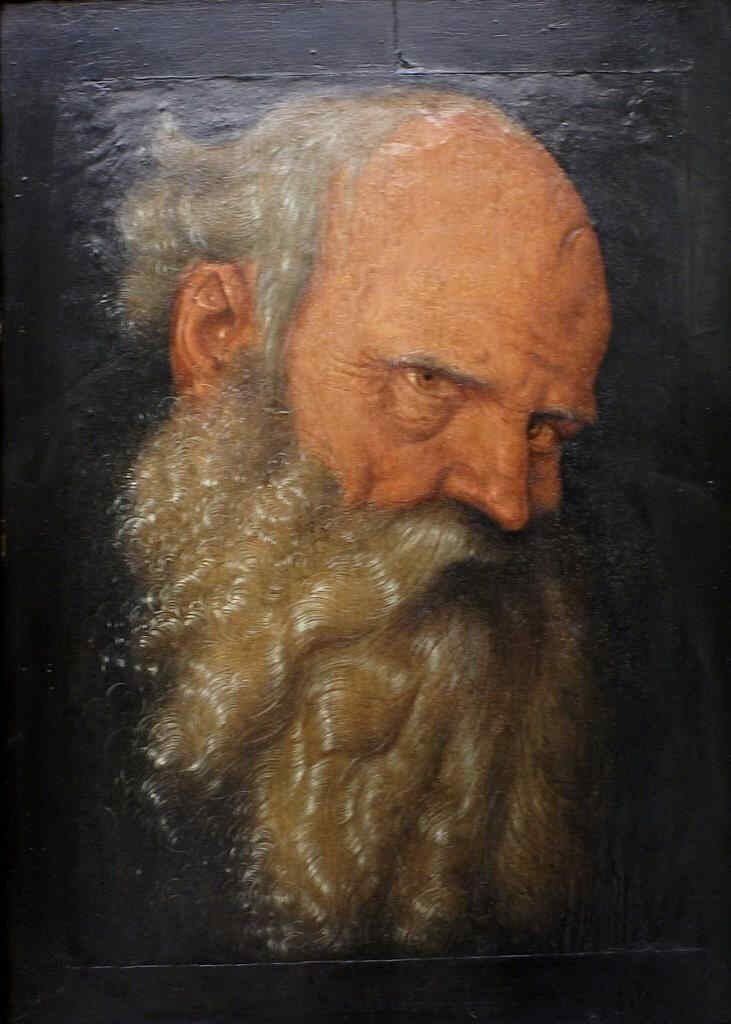

Here you see how the same master cultivated the art of portraiture. He was a pupil of Dürer's, who subsequently lived at Strasburg, and at Freiburg in Breisgau. He did some wonderful paintings of the Life of Christ, and of the Mother of Christ. You will find a picture by him at Basel—“Christ on the Cross.”
This picture, then, is of the early 16th century—the time of Raphael and Michelangelo in Rome.
My dear Friends, the more we multiply these pictures, the more should we see, from this juxtaposition of the Northern and Southern Art, what an immense revolution took place at the turn of the fourth and fifth Post-Atlantean Epochs. And the more should we realise how infinitely rich in content is the simple statement that at that historic moment Civilisation passed from the development of the Intellectual, or Feeling Soul into that of the Spiritual Soul. Infinitely much is contained in such a simple statement. But we only learn to understand these things of Spiritual Science rightly when we follow them into the several and detailed domains of human life.
In conclusion, my dear Friends, I still wish to speak a word of solemn remembrance to you on this day. The day after tomorrow is the anniversary of the death of our dear friend, Fraulein Stinde, and in our hearts we will not forget to think on that day of all that came into our Movement through the work of this dear and valued member.
And we will also turn our thoughts to her soul as she works on in the Spiritual Worlds—deeply and lovingly connected as she is with our Movement. On this day especially we will deepen the thoughts and feelings of our hearts which are directed to her.
I only wished to add this word of remembrance to remind you of the day after tomorrow.
In memory of all that unites us with our dear friend—with the soul of our dear Sophie Stinde—let us now rise from our seats.
4. Deutsche und Niederländische Plastik. Michelangelo
Das selbständig Großartige des nördlichen Kunstschaffens neben der Renaissance-Kunst Italiens:
Im Fortgange unserer Betrachtungen über Kunstwerke werden wir Ihnen heute Ergänzungen geben zu dem, was wir in der vorigen Woche hier vorgeführt haben, und aus diesem Grunde wird das, was ich vorgesehen habe, im wesentlichen auch Ergänzendes sein zu dem, was ich in dem Vortrag auszuführen versuchte über den Zusammenhang und Gegensatz der mitteleuropäischnordischen Kunst und der südlichen Kunst. Sie werden sich ja erinnern, daß ich da gerade versucht habe zu zeigen, wie das spezifisch künstlerische Element durch den Charakter des Südens und des Nordens beeinflußt ist, wie aber auf der anderen Seite fortwährend Übereinanderschichtungen der südlichen Impulse und der mitteleuropäischen Impulse stattgefunden haben und es daher heute noch außerordentlich schwierig ist, die Dinge in ihrem richtigen Zusammenwirken zu erkennen. Geisteswissenschaftliche Forschungen werden in diese Dinge nach und nach auch immer mehr und mehr Licht bringen. Heute möchte ich auf diesen Gegensatz von einigen anderen Gesichtspunkten aus aufmerksam machen. Sie erinnern sich, wie ich betont habe, daß aus gewissen Impulsen des mitteleuropäischen Geisteslebens heraus sich dasjenige herausbildet, was man die Kunst des Willens- und auch des VerstandesAusdruckes nennen kann, die Kunst des beweglichen seelischen Elementes. Die Seele in Bewegung — das ist es, wohin der mitteleuropäische Impuls zielt, während der südliche Impuls, der aber sehr früh beeinflußt wird von dem mitteleuropäischen, mehr auf dasjenige geht, was in die Anschauung herein kommt, in die Anschauung herein wirkt aus dem geistig-göttlichen Elemente der Welt und was sich in über das Menschliche ins Übermenschliche hineingehendem Ausdruck charakterisiert und auch in dem kompositionellen Element. Nun ist es, möchte ich sagen, eine Unart der heutigen Zeit, daß man die Kunst auf der einen Seite ja auch da, wo sie bildende Kunst ist, zu stark nach ihrem eigentlich novellistischen Inhalte beurteilt und zu wenig Verständnis hat für das Spezifische dessen, was in der Kunst eigentlich zum Ausdruck kommt.
Eine andere Unart aber ist diese, daß man die Kunst heute vielfach, ich möchte sagen wie ein eigenlebiges Element absondert von dem gesamten Kulturleben. Das ist durchaus unsinnig. Sobald man nur Gefühl und Empfindung und Verständnis hat für das spezifisch Künstlerische, für das, was in Form und Farbe, in Komposition und so weiter wirkt, und nicht immer den Drang hat, symbolisch oder in irgendeiner anderen Weise auszudeuten, sobald man nur diese Empfindung hat, daß zum Beispiel in einem solchen Bilde wie dem Dürerschen «Heiligen Hieronymus» (292) oder demjenigen, das «Die Melancholie» heißt (293), sobald man Verständnis dafür hat, daß etwas unendlich Tieferes in dem geheimnisvollen Weben und Wogen der Lichtmasse wirkt als in irgendeiner symbolischen Ausdeutung, dann kann man auch sehen, wie dieses spezifisch Künstlerische, das sich zum Ausdruck bringt, wiederum in dem allgemeinen Kulturleben doch lebt, wie der Künstler aus dem Allgemeinempfinden seiner Zeit heraus gerade in das Formgebende, in das Farbengebende, in das Ausdruckverleihende herein arbeitet, wie die Zeit durch die Seele des Künstlers arbeitet und wie die Gesamtkultur einer Zeit sich in den wirklich charakteristischen Kunstwerken zum Ausdruck bringt.
Nun haben wir wohl das letztemal schon gesehen, daß gewissermaßen das mitteleuropäische Element sich mehr oder weniger selbständig heraufarbeitet, indem es sich aber vermählt mit dem, was durch die Kirche, durch das Christentum von der romanischen Seite her gebracht wird. Und so sehen wir, daß bis ins 12., 13. Jahrhundert hinein in einer einzigartigen Weise, könnte man sagen, sich ausbildet in Mitteleuropa ein künstlerisches Leben, welches vermählt Romanisches mit individueller Gestaltung des Bewegten der Menschenseele, des in der Menschenseele bewegt Lebenden. Man versteht, was da eigentlich vorgegangen ist bis in das 12. Jahrhundert, bis in das 13. Jahrhundert hinein — man versteht das nicht richtig, wenn man nur in Erwägung zieht, was man hat kennenlernen können über die Ausbreitung des Christentums in der Folgezeit und bis in unsere Tage herein. Die Ausbreitung des Christentums ist ja eine ganz andere geworden; in jenen älteren Jahrhunderten war die Sache wirklich ganz anders. All das starr Dogmatische, das abstoßende Dogmatische ist ja im Grunde genommen so recht erst später gekommen, wenn selbstverständlich auch alle möglichen Ausschreitungen des Christentums auch in jenen Jahrhunderten bis zum 12. Jahrhundert vorhanden waren. Und wenn in Mitteleuropa das Systematisieren darin, das Formale des romanischen Elementes immer wie ein Fremdkörper verspürt worden ist, so ist doch vorhanden ein wunderbares Sich-Einleben der christlichen Impulse gerade in die mehr unterbewußten, gefühlsmäßigen Elemente des Seelenlebens in Mitteleuropa. Und das insbesondere bringt sich in der nach Gestaltung ringenden Kunst zum Ausdruck: dieses Sich-Einleben des Christentums. Da darf man hinweisen auf etwas, was sich mit zwei Sätzen charakterisieren läßt, mit zwei Sätzen, die weittragend, ungeheuer weittragend sind. Man kann nämlich fragen: zu was spricht denn eigentlich die Kunst bei dem Südlichen? Zu was sprach sie schon im Altertum, zu was sprach sie im Grunde genommen auch sonst im Süden, auch da, wo sie im Niedergange war, und da, wo sie wieder zum Aufgange kommt von der Frührenaissance in die Spätrenaissance hinein, wozu spricht in südlichen Gegenden die Kunst? - Sie spricht zur Phantasie. Und in diesem Satze liegt eigentlich unendlich Weitgehendes. Sie spricht zur Phantasie, welche in dieser südlichen Menschenseele lebt mit einem gewissen Anfluge Anfluge, sage ich - von sanguinischem Temperament in bezug auf diese Dinge. Und so sehen wir, daß sich die christlichen Vorstellungen und christlichen Ideen vor allen Dingen in diesen südlichen Gegenden in das Phantasieleben hineinschieben und von der Phantasie künstlerisch geboren werden. Natürlich darf man einen solchen Satz nicht pressen, sondern ich möchte sagen: man muß ihn selbst künstlerisch verstehen. Nur damit konnte es dahin kommen, daß in der Zeit der Renaissance die künstlerische Phantasie es zu einer schwindelnden Höhe in der Kunstentwickelung brachte und das Moralische, wie wir ja dargestellt haben in dem Vortrage, der hier über die Renaissance gehalten worden ist, eben in eine solche Situation kam, wie sie sich zeigt in den Angriffen zuerst von Franz von Assisi und dann in den Angriffen, in den flammenden Angriffen von Savonarola. Die ganze Situation steht ja vor uns, wenn wir die vergeblichen flammenden Angriffe Savonarolas kontrastieren mit dem unendlich reichen Ausleben der christlichen Anschauung in den Bildwerken Donatellos, Michelangelos, Raffaels, Lionardos und vieler anderer.
Anders spricht im Norden die Kunst zu anderem Seelenelement: zu dem Seelenelement des Gemütes, zu dem Seelenelement der Empfindung. Wiederum, wir dürfen die Dinge nicht pressen; aber wir müssen wissen, daß in solchen Sätzen Leitlinien gegeben sind für das Verständnis ganzer Zeitalter, für die Äußerungen ganzer Zeitalter. Und so können wir sagen: Wenn man glaubt, daß im Christentum ein besonderer seelischer, moralisch-religiöser Impuls lebt, so muß man sagen: Der hat sich nicht in den Phantasie-Impuls hineingezogen in die südliche Kultur, die in der Renaissance eine solch schwindelnde Höhe erreicht hat. Aber man kann sagen: Die Jahrhunderte bis in das 12. Jahrhundert hinein, selbst bis in den Anfang des 13. Jahrhunderts, sie zeigen uns fortschreitend das Sprechen des Christentums zu Gemüt und Empfindung auch im künstlerischen Ringen, im künstlerischen Schaffen das Einleben des Christentums, namentlich der tragischen Elemente des Christentums. Während die Renaissancekunst dahin strebt, sagen wir: das Antlitz des Christus selber so schön als möglich zu gestalten - das ist ja das eigentliche Element der Renaissancekunst -, sehen wir, wie die Jahrhunderte, auf die ich hingedeutet habe, in Mitteleuropa dem Bestreben gewidmet sind, die Passionsgeschichte, die Leidensgeschichte mit all ihrem tragischen, dramatischen Elemente zu verstehen, wie das Bestreben dahin geht, sich anzueignen diese Passionsgeschichte in der eigenen Seele, im eigenen Herzen. Und während man sagen kann, daß selbst zur Zeit der karolingischen Herrschaft in Mitteleuropa noch überall das mitteleuropäisch-heidnische Element im Gemütsleben durchbricht, sehen wir von der karolingischen Zeit bis in die Zeit, deren Grenzen ich angegeben habe, aufleben wie aus der eigenen Seele Mitteleuropas heraus ein christlich gehaltenes Verständnis allen Menschenlebens. Das ist das Eigentümliche. Und merkwürdig ist es, daß nach dem 13. Jahrhundert, vom 13. Jahrhundert ab, ein gewisser Abstieg allerdings zu bemerken ist - ich habe ja das auch das letztemal charakterisiert —, daß aber selbst in dieser Zeit, in der ein anderes Element wiederum überwuchert, das Bestreben dahin geht, dasjenige, was man sich angeeignet hat, still, im stillen Seelenleben zu verarbeiten. Und eigentlich ist es doch eine kontinuierliche Arbeit vom 13. bis ins 15., 16. Jahrhundert hinein, was da vorgeht, vorgeht bei den besten Seelen.
Dasjenige, was ich eben charakterisiert habe bis in das 13. Jahrhundert hinein als das Einleben des Christentums, wir können es ja auch sehen, könnten es vielmehr sehen, wenn erhalten wären die bis in das 13. Jahrhundert wirklich sich immer mehr und mehr vertiefenden Darstellungen dramatischer Art. Was wir jetzt ausgraben, was spätere Weihnachts-, Osterspiele, Dreikönigsspiele sind, das ist ja nur ein schwacher Abglanz derjenigen Spiele, die älteren Datums sind und die mehr sogar auf eine universellere Aneignung der christlichen Weltanschauung gehen. Das schon im 12. Jahrhundert entstandene «Spiel von dem Antichrist», das in Tegernsee gefunden worden ist, ein späteres «Spiel von den zehn Jungfrauen» — das sind nur schwache Nachklänge von Spielen, die überall aufgeführt worden sind und welche zeigten die heilige Geschichte und auch die legendarische Geschichte in einem dramatischen Zusammenhange. Und aus diesem Gesamterfassen der christlichen Weltanschauung heben sich auch die bildnerischen Kunstwerke wie einzelne Sterne heraus, wie wir sie dann heute wiederum - ergänzend das Vorige — sehen werden.
Aber dann ist es, ich möchte sagen: ein stilles, langsames Arbeiten in der Vertiefung des Seelenlebens und seiner künstlerischen Ausgestaltung. Und wirklich seinen Ausdruck findet das ja - und es wird mir eine gewisse Befriedigung sein, wenn wir Ihnen das später auch noch werden vorführen können - in der «Passionsgeschichte», wie sie Dürer erklärt hat, und namentlich in dem Christus-Antlitz, wie es durch Dürer und andere geworden ist. Dazu haben wir jetzt noch nicht Bilder; hoffentlich werden wir sie bekommen. Wenn man vorschreitend gerade die künstlerische Bewältigung des ChristusAntlitzes bis zu Dürer und anderen hin studiert, studiert auf allen Gebieten des künstlerischen Schaffens, dann wird man finden, wie wirklich in dieser Zeit in Mitteleuropa erreicht wird eine gewisse Reife im seelischen Ausdruck — eine ungeheure Reife im seelischen Ausdruck. Es hängt mit intimen Verschiedenheiten des mitteleuropäisch-nordischen Lebens und des südlichen Lebens zusammen, daß das alles so gekommen ist. Wir müssen uns ja da denn man versteht die Dinge sonst durchaus nicht - besinnen auf den großen Unterschied, der gegeben ist zu dem südlichen Leben, das, ich möchte sagen die letzte Phase ausbildet des vierten nachatlantischen Zeitraums — wenn auch der fünfte nachatlantische Zeitraum hereinscheint in der Renaissance -, das südliche Leben, das auslebt in den intimsten Empfindungen die letzte Phase des vierten nachatlantischen Zeitraumes, während sich in Mitteleuropa, im Norden vorbereitete der fünfte nachatlantische Zeitraum so, daß aus dunklen Seelentiefen sich dasjenige heraufarbeitet, was später zum Ausdruck des Individuellen, des Beweglichen der Menschenseele, Beweglichen und Bewegten der Menschenseele werden soll. Das ganze Leben der beiden Erdengebiete ist dabei durchaus in seiner Verschiedenheit ins Auge zu fassen. Man erinnere sich nur, wieviel zusammenhängt in der südlichen Kunst damit, daß man da noch eine lebendige atavistische Anschauung hatte von dem, was aus geistigen Regionen hereinspielt in das Sinnliche. Das hat sich ja dann erhalten in alledem, was man die byzantinischen Kunstformen nennt, erhalten in alledem, was durchdringt durch die suggestiven Gestaltungen, was so suggestiv wirkt in der Mosaikkunst, bei Cimabue und alledem, was an den Namen Cimabue sich anschließt. Da wirkt mehr der Christus, die Christus-Gestalt. Für Mitteleuropa wird das Jesusleben dasjenige, was dargestellt wird, weil aus dem unmittelbar Seelischen heraus die künstlerische Gestalt dargestellt wird. Ebenso übermenschlich, wie der byzantinische Christus-Typus ist, ebenso innermenschlich ist der Christus-Typus, den später Dürer herausarbeitet.
Der vierte nachatlantische Zeitraum mit dieser seiner Nachblüte hat durchaus daher doch auch etwas Hinaufsehendes nach dem ÜbermenschlichTypischen, nach dem Übermenschlich-Gattungsseelenhaften, nach dem, was abstreift das Individuell-Menschliche. Und indem die südlichen Völker in einem viel höheren Grade — wenn man diese Dinge einmal genau verstehen wird, wird man das schon bewahrheitet finden — das Alte, Antike in ihrer Kunst aufleben ließen, das Übermenschlich-Gattungsseelenhafte, sehen wir das entschieden Sich-individuell-Heraufarbeiten, das aus jeder einzelnen Menschenseele Sich-Heraufarbeiten in der nordischen Kunst, in der nördlichen Kunst.
Und so sehen wir, wie das südliche Leben, ich möchte sagen die Menschheit noch immer als ein Ganzes hat. Man erinnere sich dabei, in welchem Sinne so ein Athener Athener, ein Spartaner Spartaner war, mit welchem Rechte Aristoteles den Menschen ein «Zoon politikon», ein politisches Tier nannte, und wie dann ausgebildet worden ist dieses Zoon politikon zu seiner höchsten Höhe im Römertum. Da lebt der Mensch, ich möchte sagen auf der Straße mehr als in seinem Hause; er lebt auch mit seiner Seele mehr in dem, was ihn umgibt, als in dem Gehäuse seiner Seele selbst. Die Phantasie, die das Räumliche umschweift, will so angeregt sein.
Und aus diesem, ich möchte sagen politischen Zusammenleben, da heraus entsteht auch das Künstlerische. Das, was ich jetzt eben gesagt habe, durchdringt die südliche Kunst wie ein ihr durchaus gemeinsamer Zug. Man kann die Kirchen ausschmücken, man kann die Plätze ausschmücken, man sieht überall, daß damit gerechnet ist, daß das Volk gern zuläuft, gern in die Kirchen läuft, gern zuläuft auf die Plätze, weil es vermöge seines Temperamentes dahin gezogen wird und dasjenige sucht, was ihm da hingestellt wird. Es braucht, um sein Seelenleben ganz zu haben, dieses Leben in der Außenwelt, dieses Zusammenleben mit dem Gruppenseelenmäßigen, mit dem im eminentesten Sinne Politischen.
Das ist in Mitteleuropa anders. In Mitteleuropa lebt der Mensch in sich. In Mitteleuropa sucht der Mensch seine Erlebnisse in seinem Hause, auch in seinem Seelenhause, und er will, wenn er sich dem Gruppenhaften weihen soll, erst erobert sein; er will erst gerufen sein. In dem, was ich jetzt ausgesprochen habe, steckt viel von den Entstehungsimpulsen der gotischen Baukunst. Die gotische Baukunst führt Gebäude auf, die nicht dastehen, weil die Leute schon hineinlaufen, sondern die dastehen, weil sie die Leute erst rufen müssen, weil sie die Leute erst, ich möchte sagen: durch die geheimnisvollen suggestiven Zusammenhänge zusammenbringen müssen. Und das liegt selbst in den Formen der gotischen Baukunst ausgedrückt. Das Individuelle will erst zum Gruppenmäßigen zusammengerufen werden. Das liegt auch in der ganzen Verwendung von Licht und Finsternis, wie ich sie neulich charakterisiert habe. Man will in dem elementarischen Weben und Schweben des Lichtes und der Finsternis dasjenige sehen, in das man sich hineinstellt, wenn man loskommt von seinem Individuellen, aber in das man auch sein Individuelles hineintragen kann, weil dieses Elementarische mit dem Seelenhaften verwandt ist. In all diesen Dingen liegt das Unterscheidende der nordischen Kunst von der südlichen Kunst. Daher dieses Streben, dieses glückliche Streben der nordischen Kunst nach dem Ausdrucke der Innerlichkeit. Man braucht sich ja nur zu erinnern an Bildnisse von van Eyck, an Madonnenbilder zum Beispiel. Diese Madonnenbilder mit ihrem ganz aus Verinnerlichung des menschlichen Seelenlebens herausgeholten Gesichtsausdruck, dieses Sprechen überhaupt aus seelischer Vertiefung in Geste und Antlitz, das würde Raffael niemals gemalt haben. Raffael hebt das, was er malt, über das Menschliche hinaus; van Eyck hebt hinein das Menschliche in das Vertieft-Menschliche, damit die menschliche Empfindung und das menschliche Gemüt ergriffen werden können. Es ist auch da ein Erobern der menschlichen Seele.
Mit dieser Eigentümlichkeit der menschlichen Seele Europas wußte die Geistlichkeit bis zum 12., 13. Jahrhundert hin wohl zu rechnen, und sie wußte zusammenzuwirken mit dem Volksgemüt. Und sicherlich ist vieles von dem, was da entstanden ist im künstlerischen Ringen, im Zusammenwirken der Geistlichkeit mit dem charakterisierten Weben und Leben des Volksgemütes zustande gekommen. Man muß schon verstehen, daß diese nördlichere Eigentümlichkeit des künstlerischen Schaffens eng zusammenhängt mit der protestierenden Volksseele des Nordens, die sich auflehnt gegen den Romanismus. Luther ging nach Rom und sah von all der schwindelnden Höhe nichts, sondern nur die moralische Versumpfung Roms. Darinnen liegt sehr viel. Er hätte gewiß begegnen können - ist gewiß manchem der großen Maler Roms auf dem Petersplatze begegnet. Was gingen ihn diese Leute an, die aus einer ganz anderen Seelenverfassung heraus etwas schufen, dem er ganz verständnislos gegenüberstand! Aber schließlich ist die radikale Einseitigkeit Luthers eben nach einer anderen Richtung herausgekommen aus dem, was nun in Mitteleuropa, ich möchte sagen sein Ringen, sein höchstes Ringen fand in dem plastischen, in dem bildnerischen Ausdruck und was doch auch eine künstlerische Höhe erreicht, die in einer gewissen Beziehung — man braucht ja keine Vergleiche anzustellen, die sind immer trivial - eben durchaus etwas Selbständiges, großartig Selbständiges darstellt neben der italienischen Renaissance-Kunst.
Und so wollen wir Ihnen denn heute eben zu dem, was wir Ihnen die vorige Woche vorführten, einige Ergänzungen hinzufügen. Zuerst wollen wir aus der Kunst ganz vom Anfang des 13. Jahrhunderts, ein holzgeschnitztes plastisches Werk aus dem Dom in Halberstadt zeigen:
364 Dom zu Halberstadt Innenaufnahme des Chors mit der Kreuzigungsgruppe
365 Dom zu Halberstadt Kreuzigungsgruppe, Mittelteil
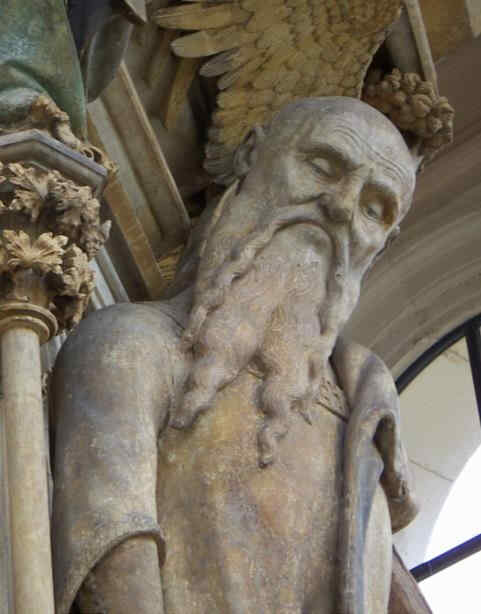
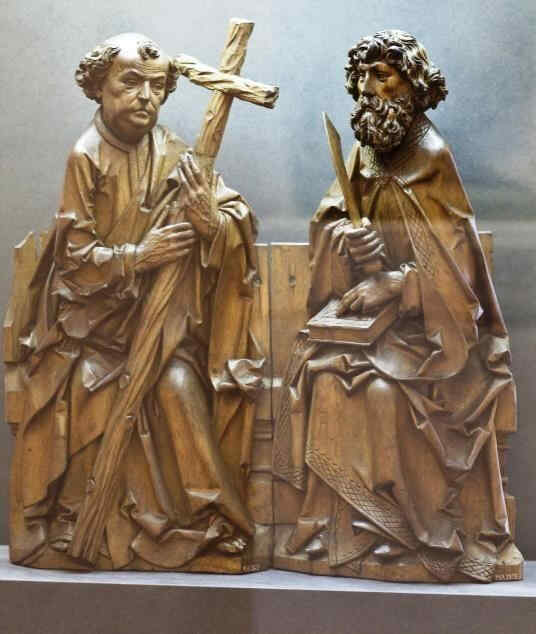
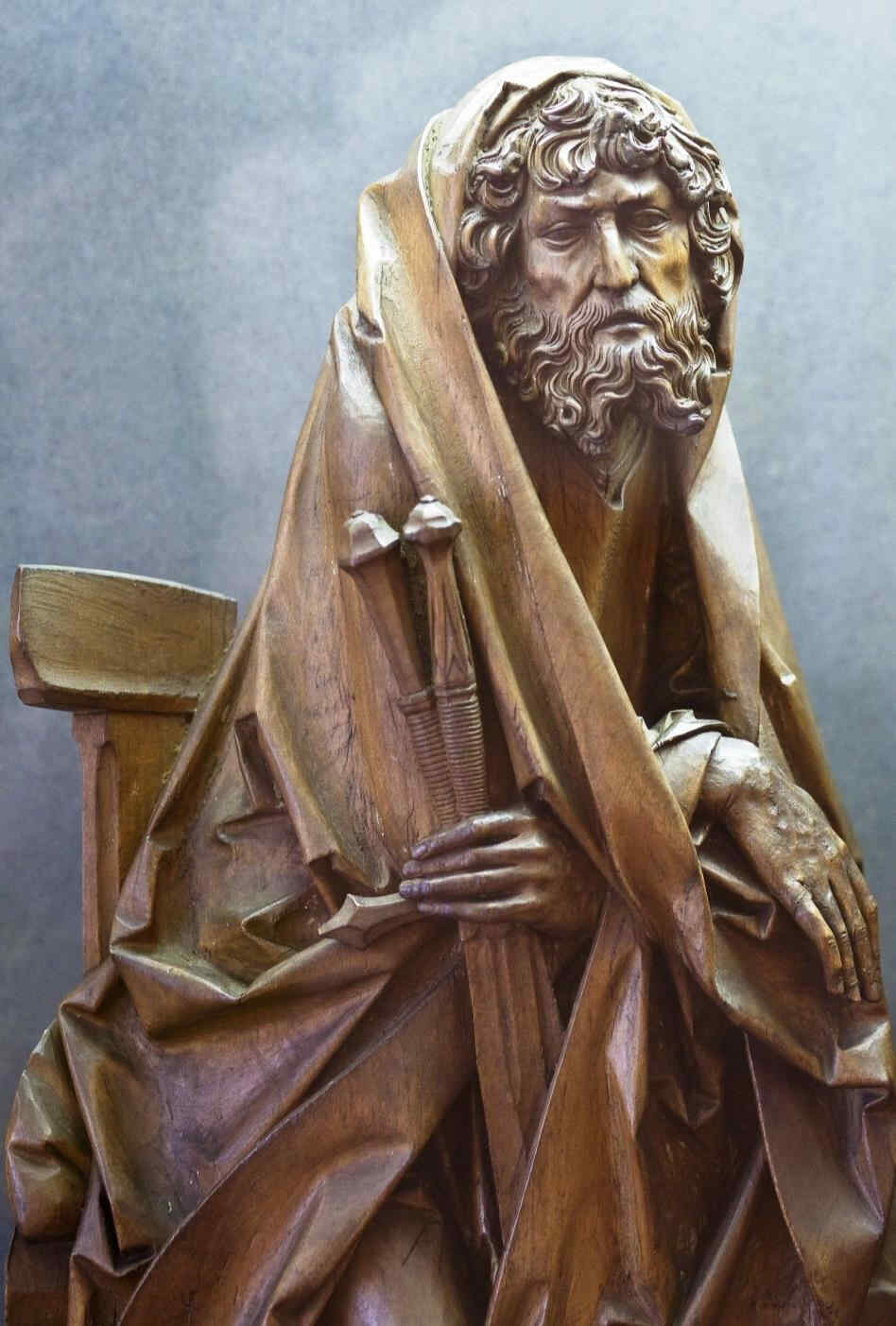
Sehen Sie sich diese Kreuzigungsgruppe an. Ich will nur sagen, was hier besonders bedeutsam wird, das ist, daß nun gerade an dieser Plastik zu sehen ist, wie die Passionsgeschichte sich bis zu diesem Zeitraum voll eingelebt hat.
Maria, Johannes, in der Mitte zu Maria herabblickend der Christus. Würde man das Antlitz sehen,
366 Dom zu Halberstadt Kreuzigungsgruppe, Teil: Christus
so würde man es sehen mit dem Ausdruck unendlicher Vertiefung, seelisch vertieft, ungeheuer. In Maria würde man — wir werden nachher gerade dieses Marienantlitz im Detail zeigen können — unmittelbar erkennen, wenn man dafür Empfindung hat, direkt das Zusammenfließen der romanisch-geistigen Anschauung mit der mitteleuropäischen Gemütsinnigkeit. Gerade an diesem Antlitz ist das in wunderbarer Weise zu sehen, so daß man sagen kann: Gerade diese Gruppe zeigt, wie man aus dem spezifischen Schaffensimpulse Mitteleuropas heraus es dazu gebracht hat, das Christentum, das sich erobert hatte dieses Mitteleuropa, aus eigenem Sceelenimpuls heraus zu gestalten. Nun wollen wir das Detail, die Maria, zeigen.
367 Dom zu Halberstadt Kreuzigungsgruppe, Teil: Maria
Es ist dieser ungemein charakteristische Gesichtsausdruck, der so ganz ineinander webt dasjenige, was man im südlichen Ausdruck hat, bei dem die Augen mehr, viel mehr in die Welt hinausschauen, als daß die Seele in das Auge sich hineinschiebt von innen. Hier haben Sie beides geradezu miteinander vereinigt, so daß hier über einer romanischen Rundung, möchte ich sagen, schwebt leise, wunderbar das Seelische im Ausdrucke.
Natürlich, alle diese Dinge dürfen nicht gepreßt werden; aber ich bitte Sie, bei allem Folgenden darauf zu achten, wie ganz anders die Gewandung verwendet wird in der mitteleuropäischen Kunst als in der südlichen Kunst. Gewiß dürfen solche Dinge nicht geprefßt werden; aber wahr ist es doch, daß alle südliche Kunst die Gewandung uns zeigt als den Menschenleib umhüllend, einhüllend, sich an den Menschenleib anschließend, gewissermaßen fortsetzend die Formen des Menschenleibes. Die Gewandung der mitteleuropäischen Kunst ist anders; sie geht aus der Bewegung der Seele hervor, und je nach der Geste der Hand, je nach der ganzen Haltung setzt sich das Bewegliche der Seele in die Gewandung hinein fort, die viel weniger sich anschließt an den Leib, viel weniger die Formen des Leibes verhüllen oder ausdrücken will wie bei der südlichen Kunst, sondern gewissermaßen wie eine Fortsetzung des seelischen Erlebens ist. Das werden Sie immer deutlicher und deutlicher wahrnehmen, wenn wir gerade in den folgenden Jahrhunderten fortschreiten.
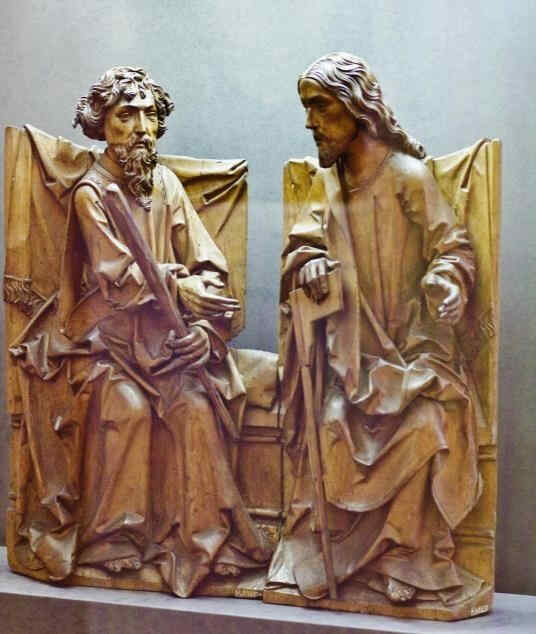
Nun kommen wir zu der berühmten «Kreuzigungsgruppe» in Wechselburg in Sachsen,
368 Schloßkirche Wechselburg Kreuzigungsgruppe
die auch in Holz geschnitzt ist, auch aus dem ersten Drittel des 13. Jahrhunderts stammt und die Ihnen in einer großartigen Weise dennoch einen Fortschritt zeigt, einen gewaltigen Fortschritt gegenüber der ja ein ähnliches Motiv zeigenden vorigen Gruppe (364). Wenn Sie hier jene seelische Kommunikation zwischen der Maria und dem Christus beobachten, wenn Sie das mit dem Johannes-Gesichte, mit dem ganzen Johannes-Ausdruck vergleichen, wenn Sie vergleichen, wie der Glaube, der mit der Seele verbundene Glaube an die christliche Weltanschauung sich in dem Johannes und der Maria als Überwinder darstellt und wenn Sie sich nun sagen, wie diese christliche Weltanschauung wirklich sich so eingelebt hat, daß sie zur universellen historischen Auffassung des Erdenwerdens geworden ist, wenn Sie sehen, wie Adam hier unten auffängt das von dem Kreuz herabträufelnde Blut des Erlösers, und wenn Sie in dem Antlitz Adams studieren, wie er berührt wird von der gnadevollen Wirkung, die er empfangen kann dadurch, daß er auffangen darf das Erlöserblut, das herunterträufelt vom Kreuze, so sehen Sie, wie unendlich tief das Christentum sich eingelebt hat in diesem Jahrhundert. Zur universellen kosmischen Auffassung schwingt es sich auf. Engel tragen das Kreuz; Gottvater kommt mit der Taube herunter, besiegelnd in diesem Momente, daß der Erde den Sinn gibt dasjenige, was er in seinem Sohne der Erde gegeben hat. Man sieht in einer solchen Gruppe, die eine hohe künstlerische Vollendung zeigt, wie sich das Christentum dadurch eingelebt hat in Mitteleuropa, daß es überall von der Seele aus zu durchziehen versucht worden ist von Gemüt und Empfindung aus, während es im Süden von der Phantasie durchdrungen worden ist und dadurch jene, ich möchte sagen eigentümliche, sagen wir, damit wir nicht verletzen: «moralinfreie» Durchdringung bewirkt hat, die im Renaissanceleben, im südlichen Renaissanceleben zum Ausdruck gekommen ist.
Wenn man studieren würde den Fortgang der Darstellungen des ChristusTypus, so würde dieser Christus-Kopf hier
369 Schloßkirche Wechselburg Kreuzigungsgruppe, Teil: Kopf des Christus
eine wichtige Station darstellen, ebenso wie der Christus-Kopf der Kathedrale von Amiens
371 Kathedrale zu Amiens Christus (Le Beau Dieu) eine wichtige Station darstellt, und später der Dürer-Kopf:
37la Albrecht Dürer Der Schmerzensmann, Kupferstich-Passion
Dagegen der Adams-Kopf aus der Gruppe in Wechselburg.
370 Schloßkirche Wechselburg Kreuzigungsgruppe, Teil: Kopf des Adam
Wir gehen jetzt über zu einigen Darstellungen, die sich in Freiberg in Sachsen finden und die ebenfalls aus dieser Zeit sind, aus dem ersten Drittel des 13. Jahrhunderts:
372 Freiberger Marienkirche Bogenfeld der «Goldenen Pforte»: Die Anbetung der Könige
Sie haben eine ganz andere Seite, aber eben doch auch die Auffassung der Heiligen Geschichte - alles strebend nach Innerlichkeit. Man wird wirklich nicht zuviel sagen, wenn man sagt, daß man sich gern vertieft in jedes einzelne Antlitz. - Eine andere Darstellung, die wir davon haben:
373 Freiberger Marienkirche Gewände der «Goldenen Pforte»:
Ecclesia und Aaron
Die eine, die weibliche Gestalt ist schwer zu deuten; vielleicht ist sie eine «Ecclesia», die andere, rechte Gestalt soll den Propheten Aaron darstellen. Aber auf alles das kommt es nicht an. Es sind gewisse Gestalten, die entweder allegorisch oder sonst irgendwie mit der Weltanschauung des Christentums zusammenhängen, und die wir wieder studieren wollen auf die seelische Vertiefung hin. Für denjenigen, der diese Dinge studieren will, ist ja die Kontrastierung des linken und des rechten Antlitzes, die dem Ausdrucke zugrunde liegt, gerade das, was besonders reizvoll ist.
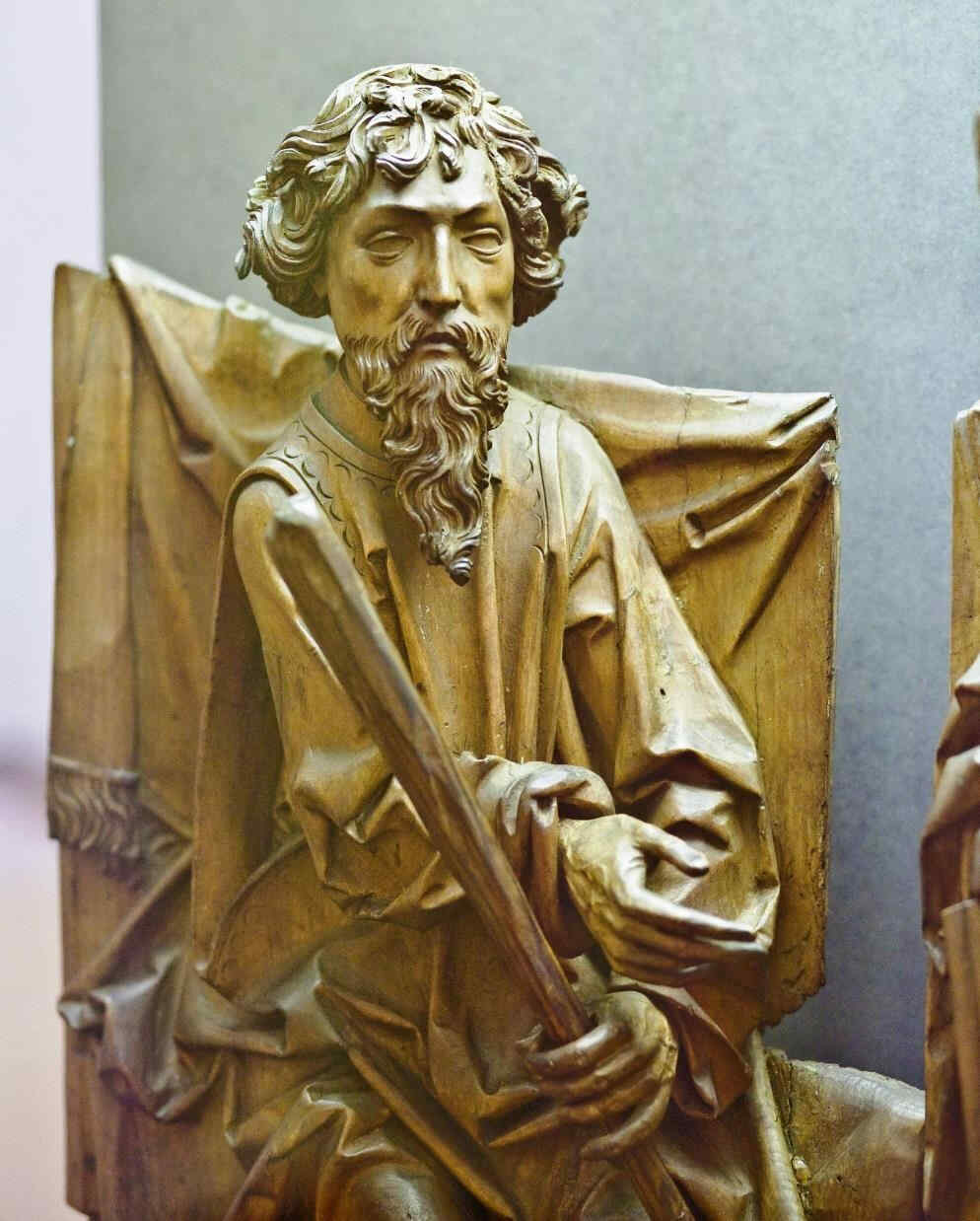
Und nun werden wir, ergänzend dasjenige, was wir das letztemal dargestellt haben am Naumburger Dom und am Straßburger Münster, die Plastiken des Bamberger Domes zeigen. Hier haben wir zunächst zwei Propheten,
374 Bamberger Dom Chorschranke: Zwei Propheten: Jonas und Hosea
wobei Sie sehen, wie, ich möchte sagen das dramatische Element, das SeelischBewegte gerade hier sich geltend macht in dem Versuch, den Seelenaustausch direkt darzustellen, Seelenaustausch, sowohl darstellend einen momentanen Seelenmoment wie zwei gegensätzliche Charaktere.
Und nun dieses «Jüngste Gericht» vom Fürstenportal in Bamberg:
375 Bamberger Dom Bogenfeld des «Fürstenportals»: Das Jüngste Gericht
Nicht eine großartige Komposition, aber im seelischen Ausdruck etwas Ungeheures. Und in Berücksichtigung muß gezogen werden, daß das Relief etwa entstanden ist vielleicht so um das Jahr 1240, so daß man später der geisteswissenschaftlichen Forschung schon recht geben wird, die nicht sprechen wird — was heute noch viele tun — davon, daß in der Darstellung der christlichen Weltanschauung das mitteleuropäische Element von dem südlichen in hohem Grade beeinflußt worden wäre. Das ist nicht der Fall; gerade das Umgekehrte ist der Fall. Aber es werden heute noch nicht in der äußeren Geschichte die Strömungen so gesehen, daß bis in die Schöpfungen Raffaels und Michelangelos namentlich, wie das tatsächlich der Fall ist und ich schon neulich andeutete, hineinwirken die nördlichen Impulse; denn diese Auffassung des «Jüngsten Gerichtes» ist, soweit das Künstlerische in Betracht kommt, durchaus eine aus dem nördlichen Geiste heraus geborene.
Das soll nun ein Beispiel dafür sein — wiederum vom Bamberger Dom -, wie das weltliche und das religiöse Element immer ineinanderspielen. Es ist ja nun schon so, daß gerade für diese Zeit, mit der wir es jetzt zu tun haben, das Weltliche und das Religiöse durchaus zusammenspielen. Sie finden sich zusammen in dem Gemeinsamen, das ich vorhin charakterisierte, nämlich darin, daß die menschliche Seele erobert sein will, die individuelle Seele zusammengerufen werden soll, zusammengefaßt werden soll, wenn sie verehrend zu dem Übersinnlichen hinaufschauen will in Gemeinschaft, aber auch gerufen sein will, wenn sie in irgendeiner Weise etwas im Weltlichen draußen zu verehren hat, daher verbindet man mit dem Kirchlichen das Weltliche.
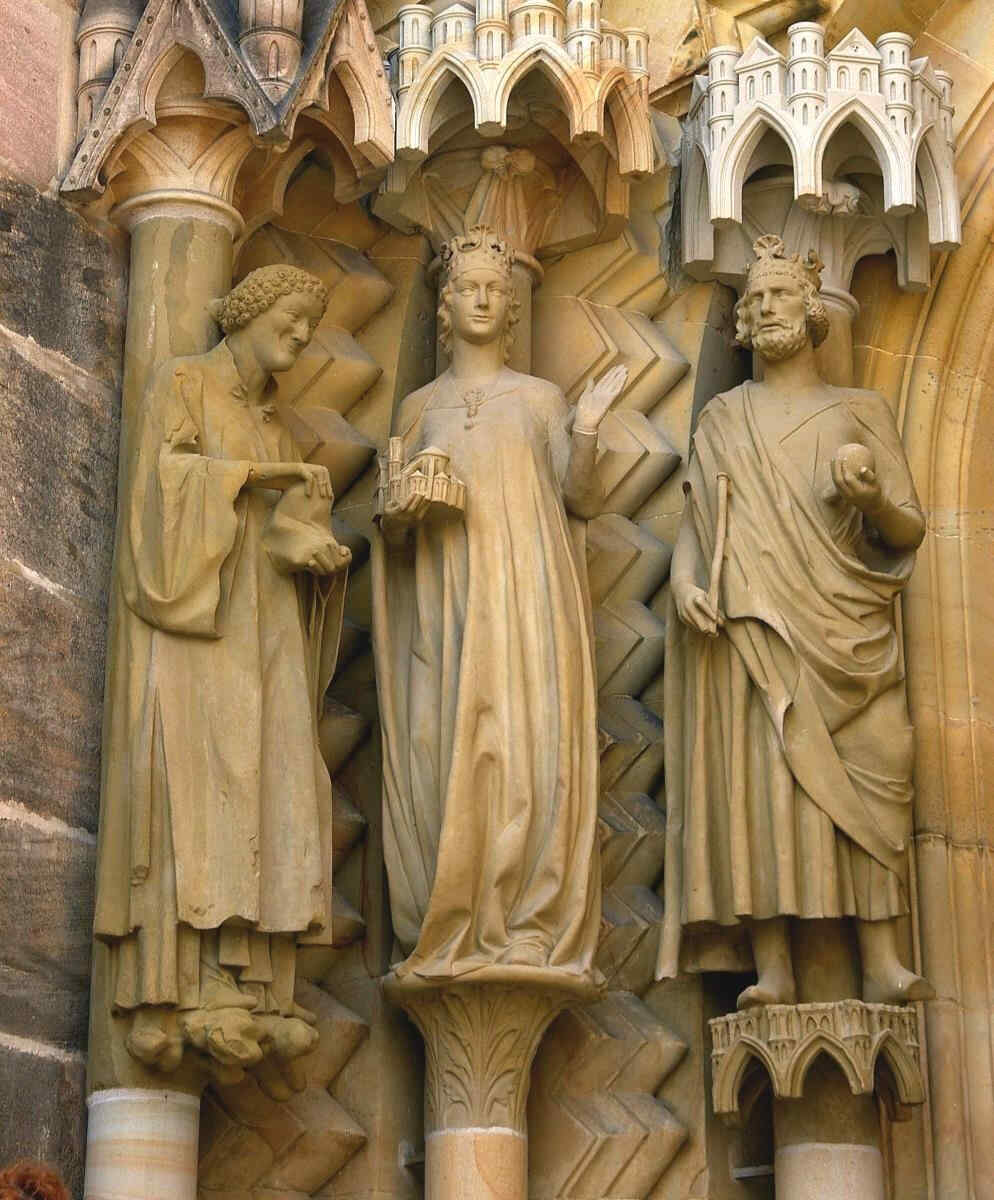
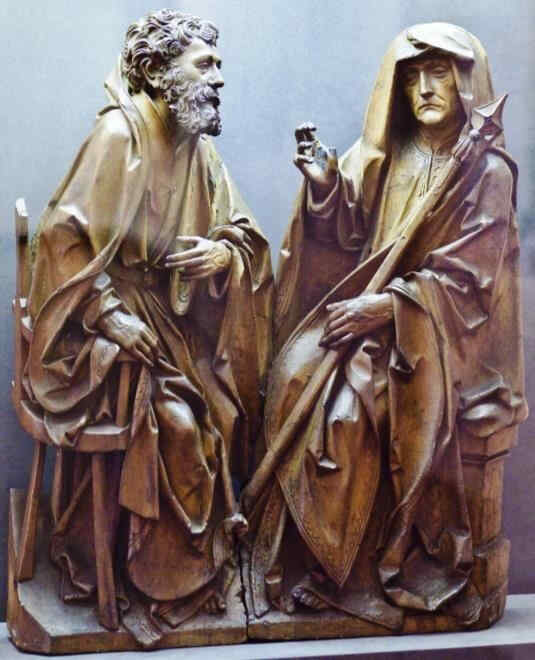
Hier sehen wir dargestellt Stephanus, Kaiserin Kunigunde, Kaiser Heinrich:
376 Bamberger Dom Linkes Gewände der «Adamspforte»: Stephanus, Kaiserin Kunigunde, Kaiser Heinrich
Dabei liegt ja selbstverständlich gewöhnlich von seiten des Volkes die Naivität zugrunde: die blinde Anlehnung, das Hinaufschauen. Nur heute ist dies in der Phantastik der Mitwelt überwunden, innerlich aber um so mehr vorhanden; und von seiten der hohen Herren liegt ja selbstverständlich sehr häufig der mit allerlei menschlichen Eigenschaften verquickte Glaube zugrunde, den verschiedenen Heiligen und anderen übersinnlichen Mächten etwas näherzustehen als andere Sterbliche.
Nun ein Detail daraus, die mittlere Gestalt vom vorigen Bilde:
377 Bamberger Dom Kaiserin Kunigunde, Teil von 376
Es werden in dieser Zeit immer das Alte Testament und das Neue Testament im Einklange miteinander gedacht, wie Versprechung und Erfüllung. Nun ein Detail daraus:
380 Bamberger Dom Kopf des Adam, Teil von 378
Ein anderes Detail:
379 Bamberger Dom Kopf der Eva, Teil von 378
Nun eine Figur an demselben Dom:
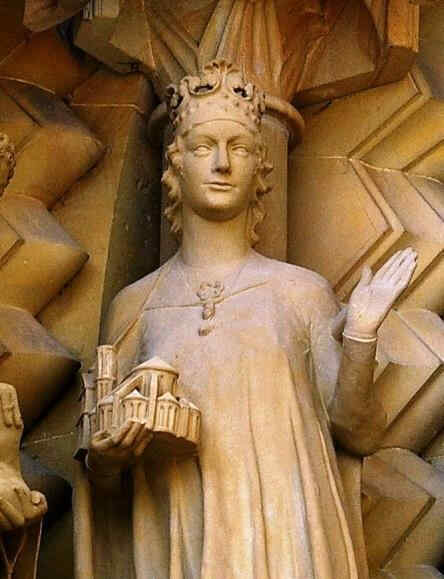
381 Bamberger Dom Maria
Eine Maria-Gestalt, die, ich möchte sagen überall, von jedem Gesichtspunkte aus aufgefaßt, zeigt, wie dasjenige wirklich nun zum Ausdruck kommt in dieser Kunstströmung, das vorhin besprochen worden ist. Dabei bitte ich Sie, zu berücksichtigen bei all diesen Dingen, daß zum Beispiel diese «Maria» ungefähr im Jahre 1245 entstanden ist, und sich zu erinnern, was Sie in dieser Zeit etwa im Süden suchen wollten.
Von demselben Dom die Gestalt der Kirche:
382 Bamberger Dom «Fürstenportal»: Die Kirche
Das war eine beliebte Darstellung. Wir haben Ihnen schon neulich die Darstellung der Kirche, wie sie sich am Straßburger Münster befindet, gezeigt, hier haben Sie sie vom Bamberger Dom. Die Gestalt der Kirche, die innerlich frei, von freier Seele gedacht, dargestellt wird, frei in die Welt hinausblickend, weise, und die kontrastiert wird mit der Synagoge, was wir auch neulich gesehen haben. Das ist nun ein Detail, der Kopf der Kirche:
385 Bamberger Dom Kopf der Kirche, Teil von 382
Sie wird kontrastiert mit der Synagoge. Sie sehen diese immer wieder dargestellt mit verbundenen, niedergeschlagenen Augen; und vergleichen Sie die ganze Haltung! Die Haltung der Synagoge soll auch hier wiederum bis in den Faltenwurf des Gewandes hinein den Gegensatz darstellen:
383 Bamberger Dom «Fürstenportal»: Die Synagoge
Sehen Sie sich namentlich das Untergewand hier an, wie es der Seelenbewegung voll angepaßt ist. Jetzt wollen wir noch einmal betrachten die Kirche, damit Sie das Untergewand vergleichen können mit dem Untergewand der Synagoge:
Bamberger Dom, «Fürstenportal»:
382 Die Kirche
384 Die Synagoge, Seitenansicht
386 Kopf der Synagoge
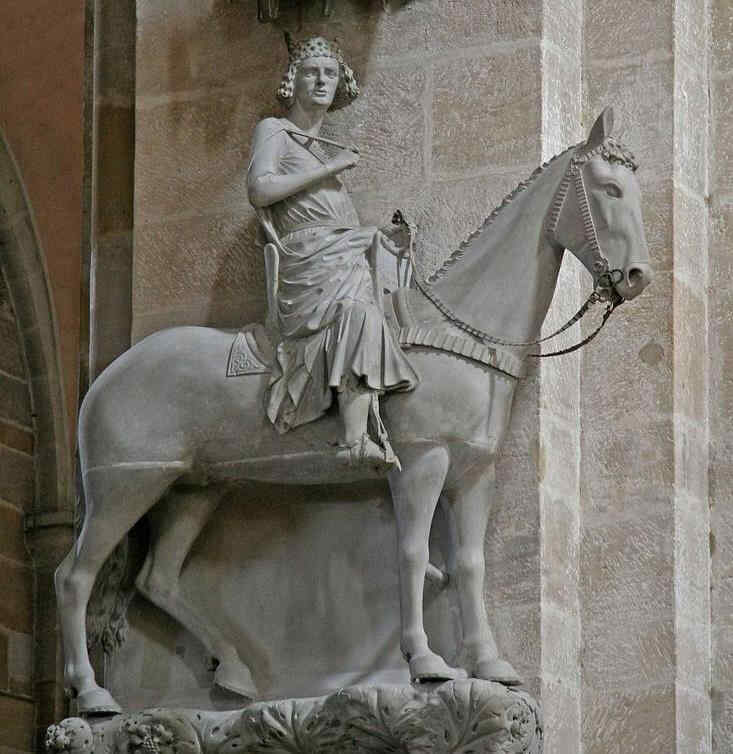
Nun wiederum eine weltliche Figur aus demselben Dom; eine Reiterstatue irgendeines Königs:
387 Bamberger Dom Der Reiter (sog. «Bamberger Reiter»)
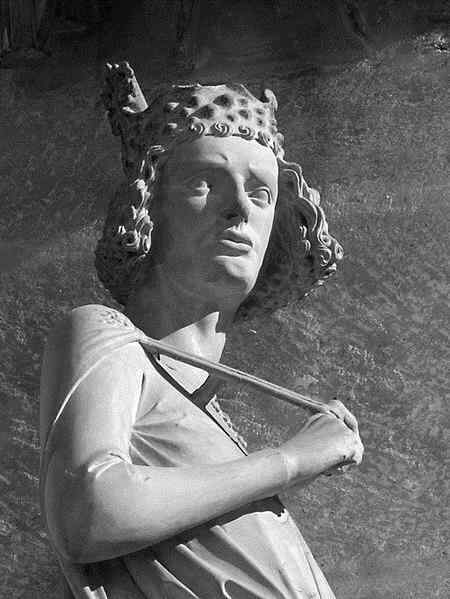
Sie werden den Ausdruck gut studieren können gerade an dem Kopf der Reiterstatue, der wundervoll ist:
388 Bamberger Dom Brustbild des Reiters, Teil von 387
Es ist ein wunderbarer Kopf!
Nun gehen wir von da ins 14. Jahrhundert hinein und sehen uns an, was nun geworden ist, indem wir einige Figuren des Kölner Domes betrachten, die in der ersten Hälfte des 14. Jahrhunderts entstanden sind: 389 Kölner Dom Maria
Es ist unschwer zu erkennen, daß nunmehr ein gewisser Rückgang stattgefunden hat.
Dann, ebenfalls vom Kölner Dom:
390 Kölner Dom Johannes
391 Kölner Dom Jakobus d.Ä.
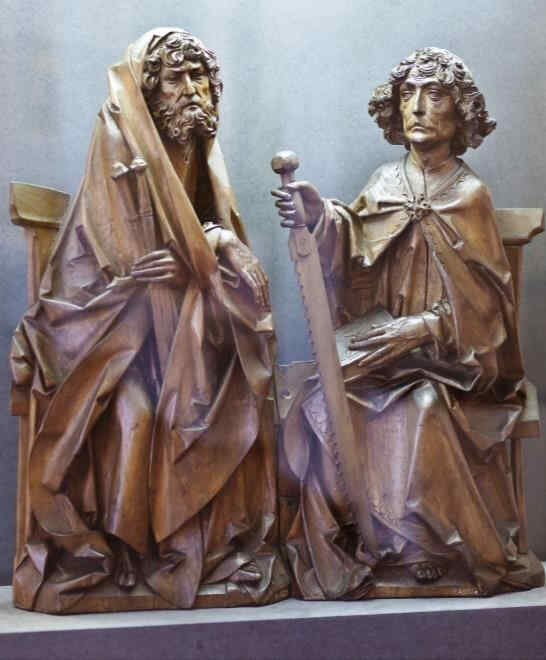
Wir gehen nun im 14. Jahrhundert weiter und kommen zu einem Meister, der der «Meister der Tonapostel» genannt wird, weil diese Figuren in gebranntem Ion ausgeführt sind:
392 Meister der Tonapostel Paulus
Und nun, nachdem wir, ich möchte sagen Aufstieg und etwas Abfall einer geschlossenen Linie, geschlossenen Entwickelungsströmung uns vorgeführt haben, betrachten wir etwas, was in seiner Art wirklich ganz groß ist, nämlich eine Reihe von Bildwerken aus der Kartause in Dijon, die Ende des 14. und zu Beginn des 15. Jahrhunderts entstanden sind und ausgeführt wurden von dem Niederländer Claus Sluter oder unter seiner Anleitung. An allen diesen Figuren werden Sie sehen, wie hier von den Niederlanden hereinströmt in diese Dijoner Kartause wirklich individuellste Charakteristik in einer ganz einzigen Weise, so daß von den verschiedensten Seiten her gesehen werden kann, wie das Individualisierende, das aus der Seele heraus charakteristisch Individualisierende auftritt.
Zunächst haben wir da das Portal der Kartause:
Claus Sluter, Portal der Chartreuse de Champmol Dijon
393 Madonna mit Stiftern
Nun einige Figuren von diesem Portal:
394 Madonna mit dem Kinde
395 Philipp der Kühne, Johannes der Täufer
Überall ist gerade hier zu sehen diese individuelle CharakterisierungsKunst. Wenn Sie diese Fähigkeit eines und desselben Menschen, die Madonna so zu charakterisieren mit dem Kinde, mit dem vergleichen, was nun gleich nachkommt,
397 Claus Sluter Moses, vom Sockel des «Mosesbrunnen» in der Chartreuse de Champmol Dijon
wie er nun wiederum den Moses charakterisiert, dann bitte ich Sie zu beach ten, daß die Kartause von Dijon gebaut ist in den Jahren 1383 bis 1388, daß das also der Anfang - 1400/1401 - des 15. Jahrhunderts ist. Und warum sollte man nicht solche Sachen zusammenstellen, denn sie sind zusammenzustellen:
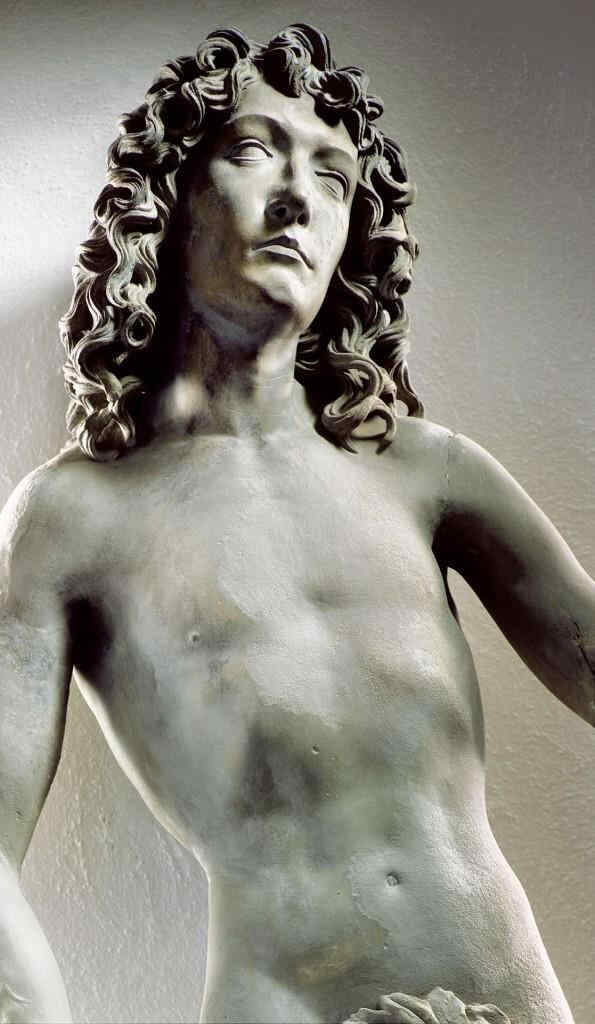
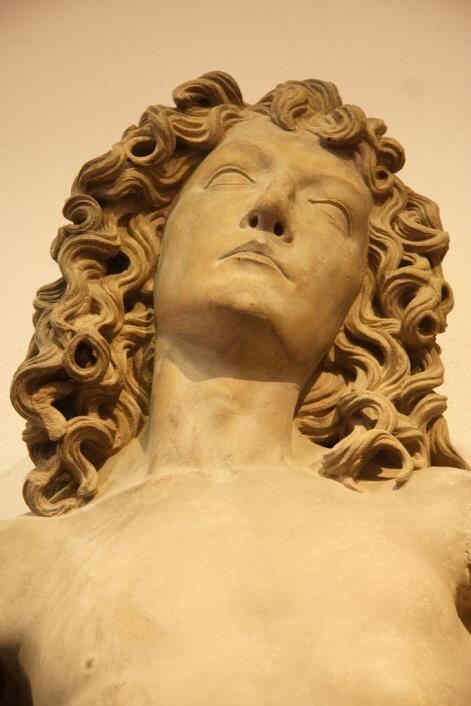
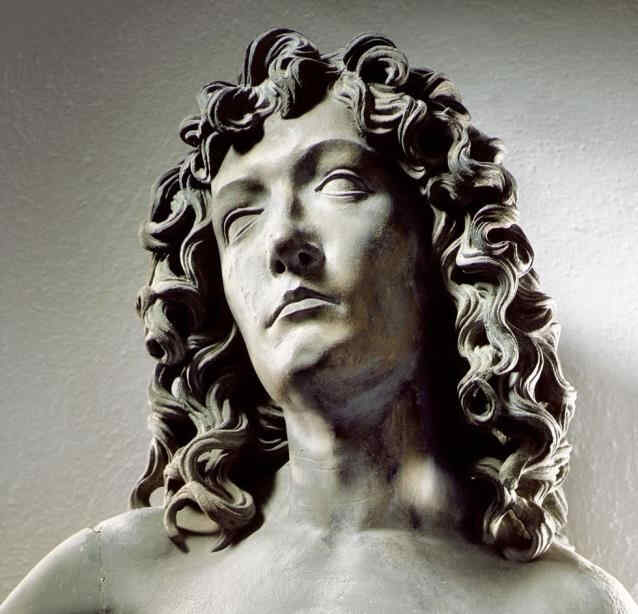
diesen Moses vom Anfang des 15. Jahrhunderts zum Beispiel mit dem Moses von Michelangelo [1516].
398 Michelangelo Moses, Teil von 174
Nun noch einige weitere Arbeiten von Sluter:
Claus Sluter, Dijon, Chartreuse de Champmol, Sockel des «Mosesbrunnen»
399 David, Jeremias
400 Zacharias, Daniel, Jesaias
Dieses Miterleben mit den Prophetengestalten bis zu einer solchen Individualisierung ist natürlich etwas ganz Wunderbares. Nun wollen wir den «Jesaias» herausheben:
396 Brustbild des Jesaias, Teil von 400
Dann von demselben Künstler —- wenigstens teilweise:
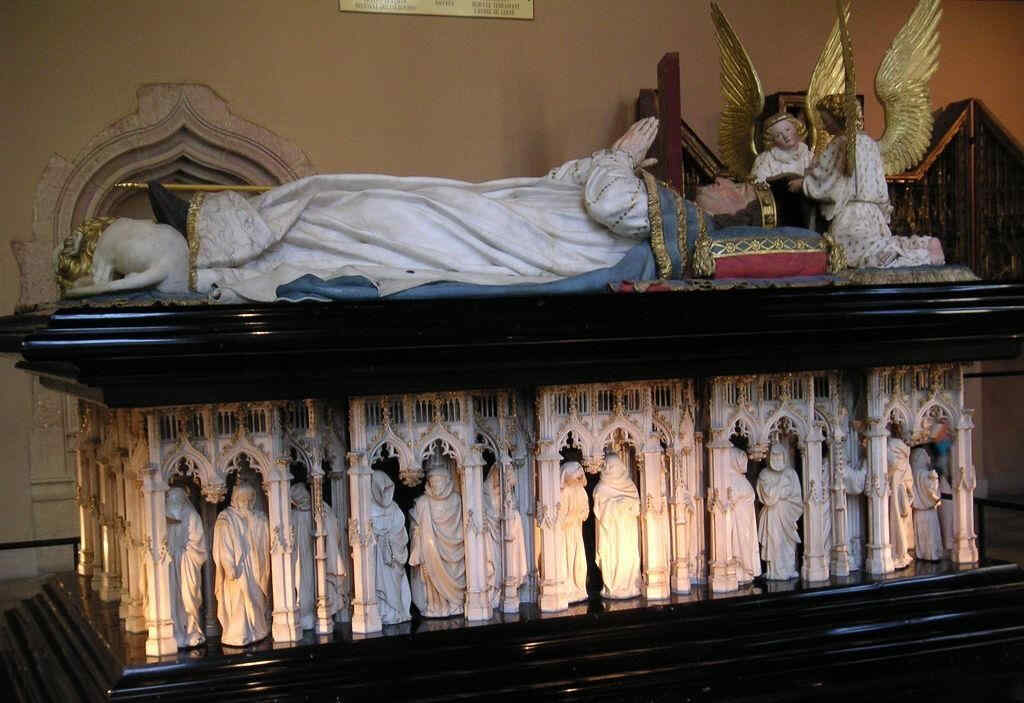
401 Claus Sluter Grabmal Philipps des Kühnen
Die Zeit ist überhaupt sehr bedeutend in der Schaffung von Grab-Denkmälern. Wir werden, nachdem dieses hier im Überblick gegeben ist, den oberen Teil im Detail vorführen:
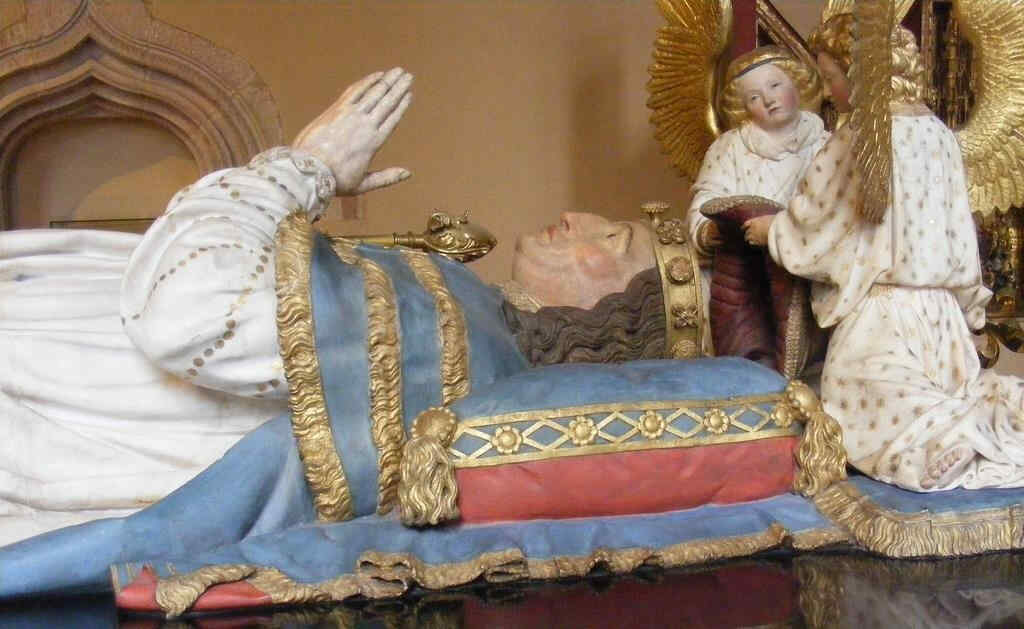
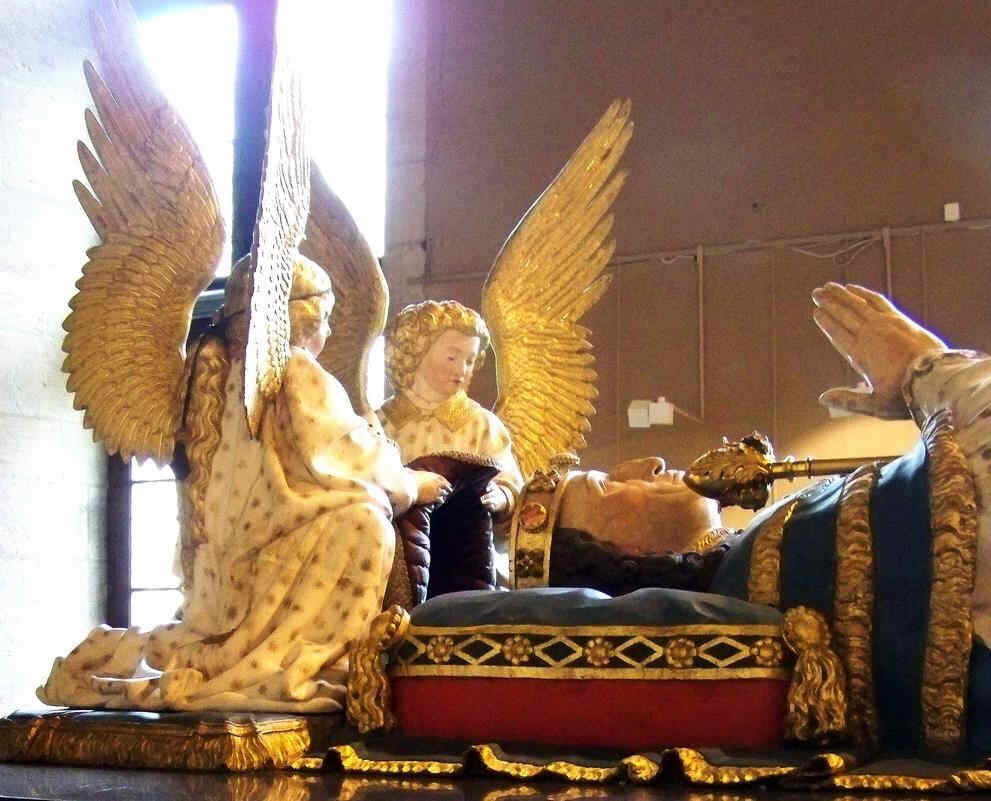
402 Claus Sluter Philipp der Kühne mit zwei Engeln, Teil von 401
Sie werden dann auch sehen, daß die einzelnen Figuren, die vorhin nur so klein erschienen am Sockel, wirklich im einzelnen wunderbar ausgeführt sind:
403 Claus Sluter Trauernde Mönche, Teil von 401
In dieser individuellen Charakteristik sind diese einzelnen Figuren um den Sockel herum ausgeführt:
404 Claus Sluter Trauernde Mönche, Teil von 401
Und nun gehen wir -— wir müssen uns einrichten nach dem, was wir an Bildern haben - zu einem Künstler aus der ersten Hälfte des 15. Jahrhunderts. Bedenken Sie bitte: Bei allem, was wir zuletzt vor uns gehabt haben, hatten wir zu tun mit einem Künstler von der Wende des 14. zum 15. Jahrhundert. Nun gehen wir in das 15. Jahrhundert hinein. Indem wir die Kölner Meister und den «Meister der Tonfiguren» gehabt haben, der um 1400 diese Gruppe in eingebranntem Ton fabrizierte, waren wir bis zum Ende des 14. Jahrhunderts gekommen.
Wir gehen also jetzt weiter ins 15. Jahrhundert, zu Hans Multscher. Von ihm haben wir zunächst eine «Madonna».
405 Hans Multscher Madonna mit dem Kind
Dann von demselben Künstler Sankt Georg und Sankt Florian,
406 Hans Multscher St. Georg
407 St. Florian
beide aus der Spitalkirche in Sterzing, etwa aus der Mitte des 15. Jahrhunderts.
So kommen wir immer weiter in dem, was ich charakterisiert habe: Herausarbeiten der christlichen Motive innerlich-seelisch. Und so kommen wir zu den holzgeschnitzten Figuren vom Ende des 15. Jahrhunderts aus Blutenburg bei München:
408 Blutenburger Schloßkapelle Matthias
Da erreicht es in der Tat in einem ungeheuren Grade die Kunst der Charakteristik.
409 Blutenburger Schloßkapelle Maria
410 Thomas
Das ist also die Zeit, in der Michelangelo, Raffael geboren sind.
411 Blutenburger Schloßkapelle Johannes
Das ist also alles aus Blutenburg.
Sehr bedeutend war auch diese Zeit, gerade diese Zeit, aus der diese so sehr individualisierenden Gestalten sind, in der Ausarbeitung von Holzplastiken für Chorstühle in Kirchen. Davon wollen wir nun auch eine Probe haben aus der Frauenkirche in München vom Ende des 15. Jahrhunderts:
412 Münchner Frauenkirche Baruch, Markus, Job (Chorgestühl)
Nun gehen wir zu einem anderen Künstler, der am Ende des 15. Jahrhunderts gewirkt hat, zu einer Reihe von Werken des «Rosenkranz»-Bildschnitzers, Tilman Riiemenschneider:
Tilman Riemenschneider, Figuren vom Südportal der Marien-Kapelle Würzburg
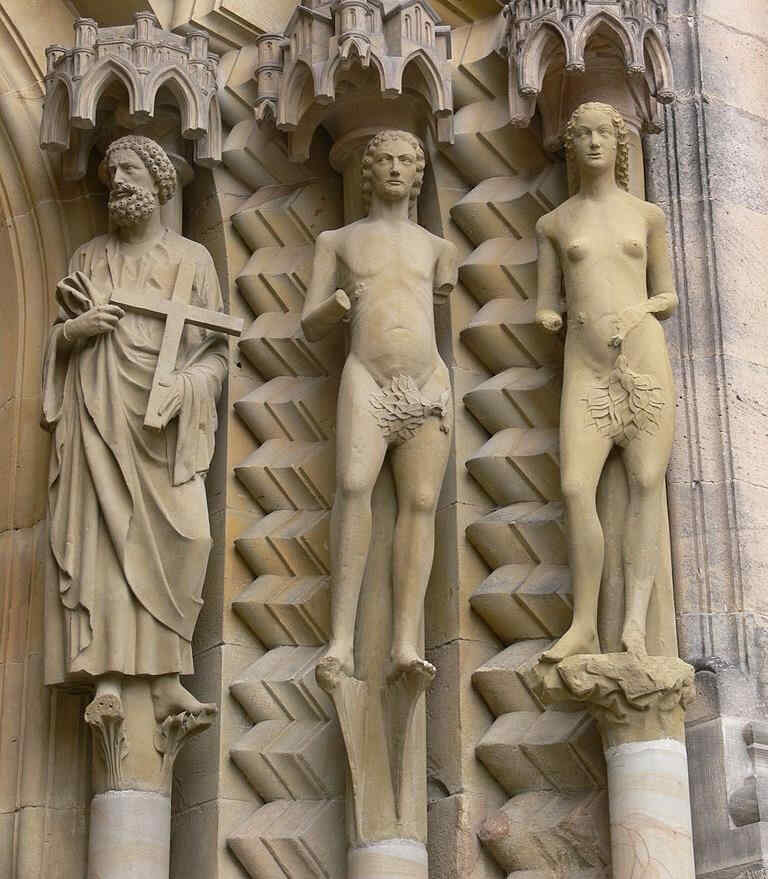
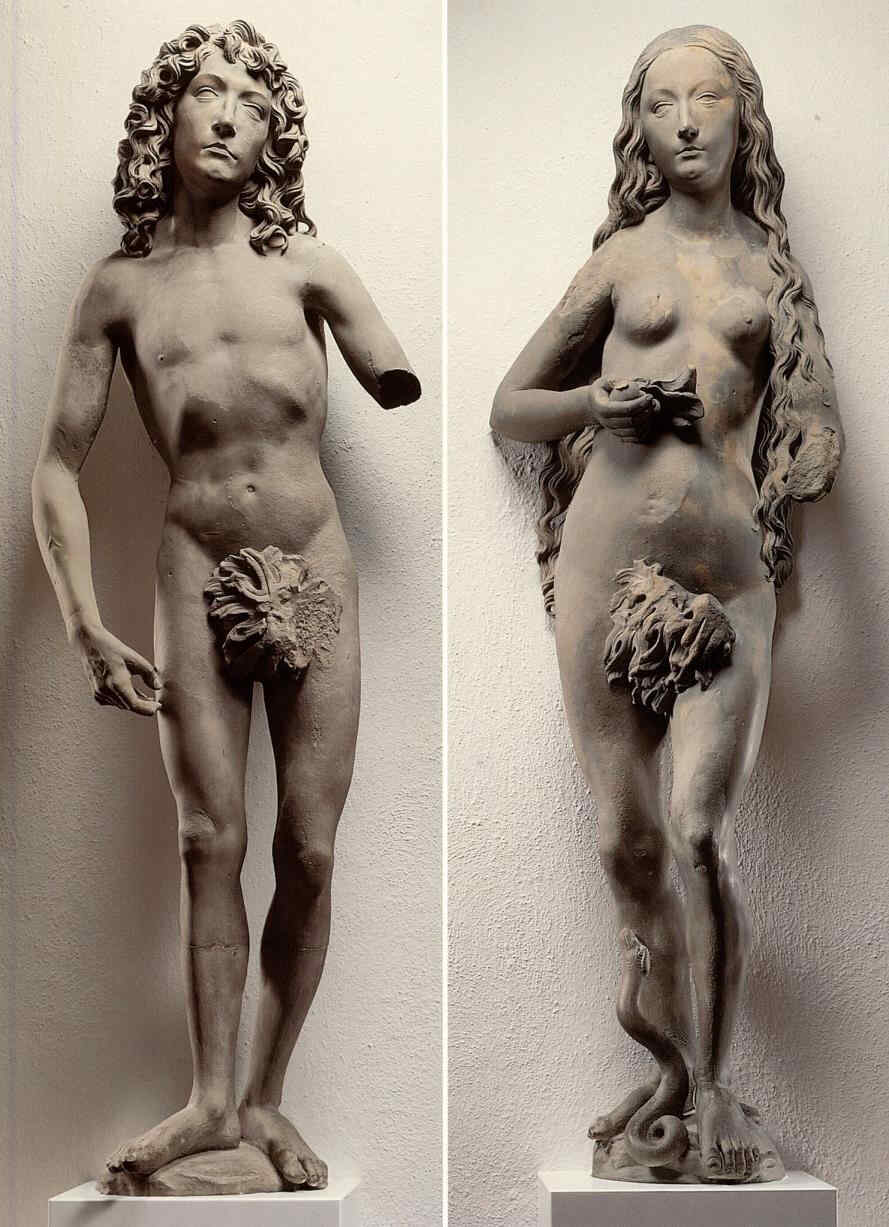
413 Adam
415 Kopf des Adam, Teil von 413
Das ist also immerhin aus der Zeit, in der die Hochrenaissance in Italien noch nicht begonnen hat. Diese Dinge sind etwa geschaffen um das Jahr 1493.
414 Eva
416 Kopf der Eva, Teil von 414
Eine heilige Elisabeth, die jetzt im Germanischen Museum in Nürnberg ist,
417 Tilman Riemenschneider Hl. Elisabeth
im Anfang des 16. Jahrhunderts geschaffen.
418 Tilman Riemenschneider Madonna mit dem Kinde
Eine Madonna mit dem Kinde, auch Anfang des 16. Jahrhunderts.
Und von demselben Künstler:
Tilman Riemenschneider, Die zwölf Apostel
419 Petrus 423 Philippus 427 Paulus
420 Judas Thaddäus 424 Bartholomäus 428 Simon
421 Jakobus d.]. 425 Johannes 429 Matthias
422 Andreas 426 Jakobus d. Ä. 430 Thomas
Es sind wunderbare Typen dabei bei diesen zwölf Aposteln, wobei man jeden einzelnen Kopf studieren möchte.
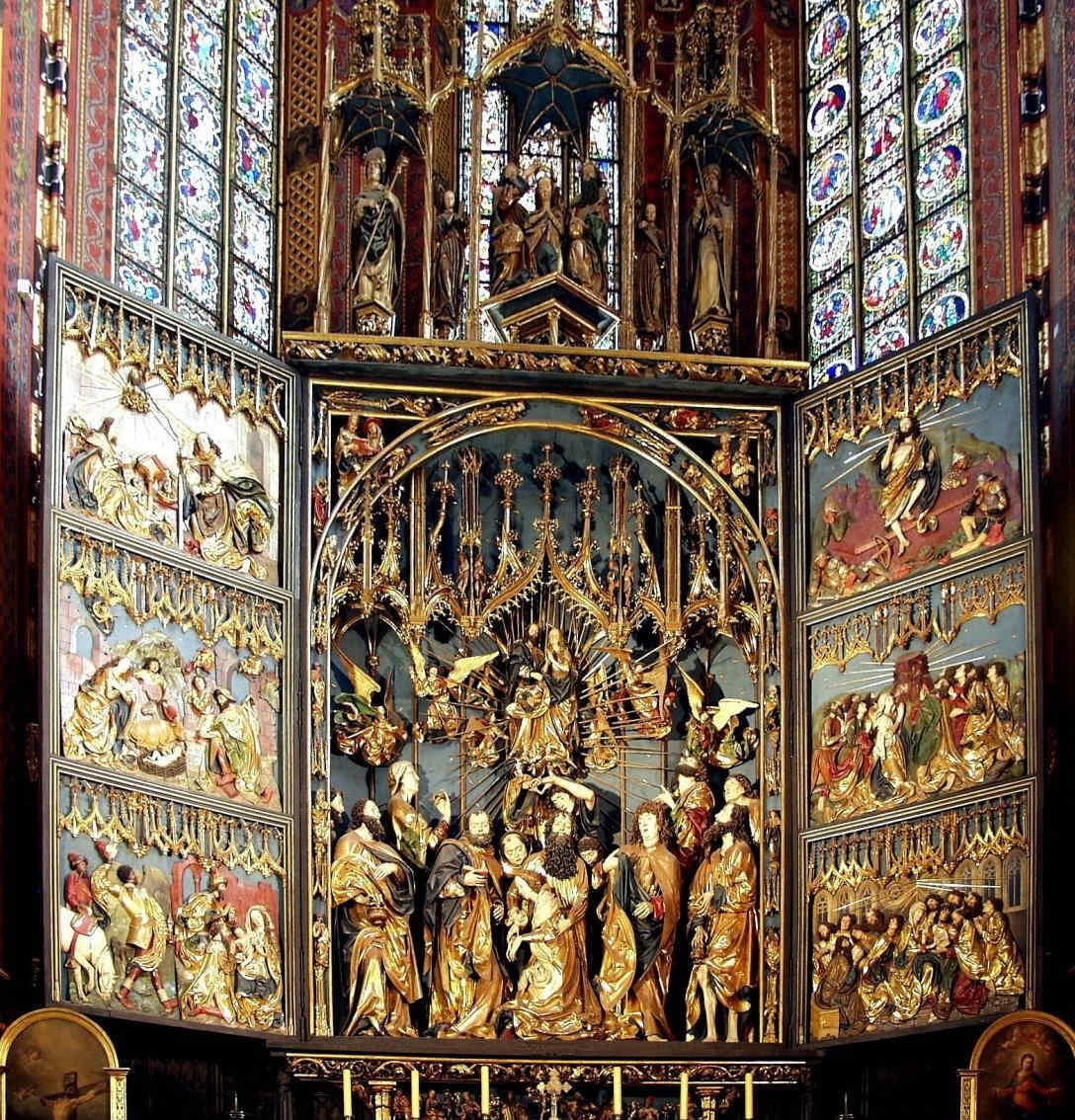
Nun noch zwei Proben von dem dem Ende des 15. Jahrhunderts, Anfang des 16. Jahrhunderts angehörigen Künstler Veit Stoß, der in Krakau und auch in Süddeutschland in den verschiedensten Materialien seine bildnerischen Dinge zum Ausdruck brachte:
431 Veit Stoss Mittelschrein des Marien-Altars, Marienkirche Krakau
Die andere Gruppe stellt einen «Englischen Gruß» dar
432 Veit Stoss Der Englische Gruß
und befindet sich in der Lorenzkirche in Nürnberg.
Und nun möchten wir Ihnen noch einige malerische Kunstwerke vorführen von dem Maler Hans Baldung, der auch unter dem Namen Hans Grien bekannt ist und der im Anfange des 16. Jahrhunderts — etwa 1507 bis 1509 in der Werkstatt von Dürer gearbeitet hat:
327 Hans Baldung Grien Die Ruhe auf der Flucht
Er hat zumeist Bilder gemalt, die im Gebiete der Malerei eben zeigen im Beginne des 16. Jahrhunderts, wie auch da durchaus im ähnlichen Sinne eine Verseelung stattgefunden hat.
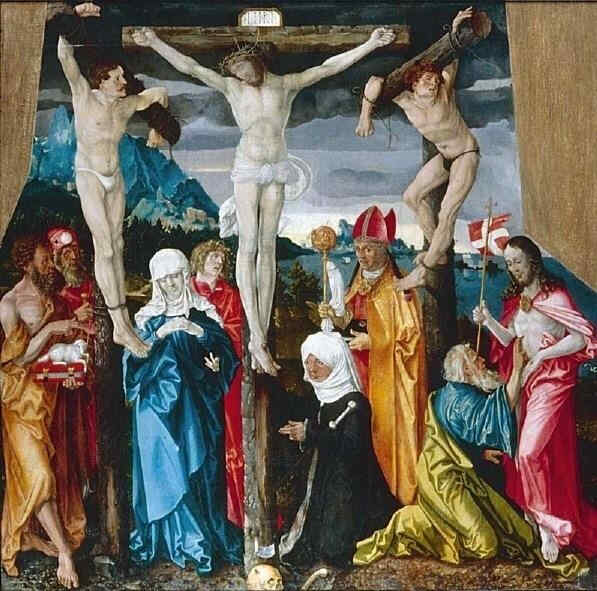
329 Hans Baldung Grien Die Kreuzigung (Berlin)
Hans Baldung - Hans Grien - war auch ein ganz bedeutender Porträtist. Hier haben Sie eine Probe,
328 Hans Baldung Grien Kopf eines bärtigen Greises
wobei wir sehen können, wie die Porträtkunst bei diesem Meister gepflegt worden ist. Er war also ein Schüler Dürers, lebte später in Straßburg, auch in Freiburg im Breisgau, hat wunderbare Tafeln geschaffen zum Leben Christi und der Mutter Christi. Sie finden ein Bild «Christus am Kreuz» von ihm auch in Basel:
330 Hans Baldung Grien Die Kreuzigung (Basel)
Sie können also diese Bilder durchaus in den Beginn des 16. Jahrhunderts setzen, in die Zeit, als Raffael, Michelangelo in Rom waren.
Je mehr wir die Bilder häufen würden, desto mehr würden wir sehen, wie an dieser Grenzscheide des vierten und fünften nachatlantischen Zeitraums uns gerade diese Zusammenstellung der südlichen mit der nördlichen europäischen Kunst zeigen würde, welcher Umschwung stattgefunden hat, und wie reich der einfache Satz ist, daß dazumal die Kultur aus der Verstandes- oder Gemütsseele heraus in die Kultur der Bewußstseinsseele hineinging mit alledem, was damit zusammenhing - wie reich dieser Satz eigentlich ist, und wie man diese Dinge nur kennenlernt, wenn man sie auf den einzelnen Gebieten des menschlichen Daseins betrachtet.
4. German And Dutch Sculpture. Michelangelo
The independent greatness of northern art alongside Italian Renaissance art:
Continuing our reflections on works of art, today we will provide you with additions to what we presented here last week, and for this reason, what I have planned will essentially be a supplement to what I attempted to explain in my lecture on the connection and contrast between Central European-Nordic art and Southern art. You will remember that I tried to show how the specific artistic element is influenced by the character of the South and the North, but how, on the other hand, there has been a continuous overlapping of southern and Central European impulses, making it extremely difficult even today to recognize the true interplay between them. Spiritual scientific research will gradually shed more and more light on these matters. Today I would like to draw attention to this contrast from a few other points of view. You will remember how I emphasized that certain impulses of Central European spiritual life give rise to what can be called the art of the expression of the will and also of the intellect, the art of the mobile soul element. The soul in motion — that is what the Central European impulse aims at, while the southern impulse, which is influenced very early on by the Central European impulse, is more directed toward what enters into perception, what enters into perception from the spiritual-divine element of the world and is characterized by an expression that goes beyond the human into the superhuman, and also in the compositional element. Now, I would say that it is a bad habit of our time that, on the one hand, even where art is visual art, it is judged too strongly on the basis of its actual novelistic content and too little understanding is shown for the specific nature of what is actually expressed in art.
Another bad habit, however, is that today art is often isolated, I would say, as an element with a life of its own, separate from cultural life as a whole. That is completely nonsensical. As soon as one has feeling and sensitivity and understanding for the specifically artistic, for what is effective in form and color, in composition and so on, and does not always have the urge to interpret symbolically or in any other way, as soon as one has this feeling that, for example, in a picture such as Dürer's “Saint Jerome” (292) or the one called “Melancholy” (293), as soon as one has an understanding that something infinitely deeper is at work in the mysterious weaving and surging of the light masses than in any symbolic interpretation, then one can also see how this specifically artistic element that expresses itself lives on in general cultural life, how the artist works from the general sensibility of his time into the shaping, the coloring, the expression, how the time works through the soul of the artist, and how the overall culture of a time expresses itself in truly characteristic works of art.
Now, we have already seen last time that, in a sense, the Central European element develops more or less independently, but in doing so it marries itself to what is brought in from the Roman side through the Church and Christianity. And so we see that, up until the 12th and 13th centuries, an artistic life developed in Central Europe in a unique way, one might say, combining the Romanesque with the individual expression of the movements of the human soul, of what lives and moves within the human soul. One understands what actually happened up to the 12th century, up to the 13th century — one does not understand this properly if one only considers what one has been able to learn about the spread of Christianity in the following period and up to the present day. The spread of Christianity has become something completely different; in those earlier centuries, things were really quite different. All the rigid dogmatism, the repulsive dogmatism, basically came later, although of course all kinds of excesses of Christianity were also present in those centuries up to the 12th century. And if in Central Europe the systematization, the formalism of the Roman element, has always been felt as a foreign body, there is nevertheless a wonderful settling in of Christian impulses, especially in the more subconscious, emotional elements of the soul life in Central Europe. And this is particularly evident in art struggling for form: this settling in of Christianity. Here we can point to something that can be characterized in two sentences, two sentences that are far-reaching, immensely far-reaching. One may ask: what does art actually speak to in the South? What did it speak to in ancient times, what did it speak to in the South in general, even where it was in decline, and where it is rising again from the early Renaissance into the late Renaissance? What does art speak to in southern regions? It speaks to the imagination. And this statement actually has infinite implications. It speaks to the imagination that lives in the southern human soul with a certain touch—I say touch—of sanguine temperament in relation to these things. And so we see that Christian concepts and Christian ideas, especially in these southern regions, enter into the life of the imagination and are artistically born from the imagination. Of course, one must not press such a statement, but I would like to say: one must understand it artistically oneself. Only in this way could it come about that, during the Renaissance, artistic imagination brought art to dizzying heights of development and morality, as we have described in the lecture on the Renaissance given here, came to be in such a situation as is evident in the attacks first by Francis of Assisi and then in the attacks, the fiery attacks of Savonarola. The whole situation is clear to us when we contrast Savonarola's futile, fiery attacks with the infinitely rich expression of the Christian view in the works of Donatello, Michelangelo, Raphael, Leonardo, and many others.
In the North, art speaks to a different element of the soul: the element of the mind, the element of feeling. Again, we must not force things, but we must know that such statements provide guidelines for understanding entire eras, for the expressions of entire eras. And so we can say: If one believes that a special spiritual, moral-religious impulse lives in Christianity, then one must say: it did not draw itself into the imaginative impulse of southern culture, which reached such dizzying heights in the Renaissance. But one can say: The centuries up to the 12th century, even up to the beginning of the 13th century, show us progressively the expression of Christianity in the mind and feelings, also in artistic struggle, in artistic creation, the settling in of Christianity, namely the tragic elements of Christianity. While Renaissance art strives, let us say, to depict the face of Christ himself as beautifully as possible — which is, after all, the actual element of Renaissance art — we see how the centuries I have referred to in Central Europe are devoted to the endeavor to understand the Passion, the story of suffering with all its tragic, dramatic elements, how the endeavor is to appropriate this Passion in one's own soul, in one's own heart. And while it can be said that even during the Carolingian rule in Central Europe, the Central European pagan element still breaks through everywhere in the emotional life, we see from the Carolingian period to the period whose boundaries I have indicated, a Christian understanding of all human life reviving as if from the very soul of Central Europe. That is what is peculiar. And it is remarkable that after the 13th century, from the 13th century onwards, a certain decline can indeed be observed – I also characterized this last time – but that even in this period, in which another element once again prevails, the endeavor is to quietly process what has been acquired in the quiet life of the soul. And actually, what is happening here is a continuous work from the 13th to the 15th and 16th centuries, happening in the best souls.
What I have just characterized as the establishment of Christianity up to the 13th century, we can also see, or rather could see, if the dramatic representations that really became more and more profound up to the 13th century had been preserved. What we are now excavating, what later Christmas, Easter, and Epiphany plays are, is only a faint reflection of those plays that are older and that even more so aim at a more universal appropriation of the Christian worldview. The “Play of the Antichrist,” which originated in the 12th century and was found in Tegernsee, and a later “Play of the Ten Virgins” are only faint echoes of plays that were performed everywhere and which presented sacred history and legendary history in a dramatic context. And from this comprehensive understanding of the Christian worldview, works of art stand out like individual stars, as we will see again today, complementing what we have seen before.
But then it is, I would say, a quiet, slow work of deepening the soul life and its artistic expression. And this really finds its expression — and it will give me a certain satisfaction if we can show you this later — in the “Passion story,” as Dürer explained it, and especially in the face of Christ, as it has been portrayed by Dürer and others. We do not yet have any pictures of this; hopefully we will get them. If one studies the artistic mastery of the face of Christ up to Dürer and others, studying all areas of artistic creation, one will find how a certain maturity in spiritual expression was truly achieved in Central Europe at that time — an enormous maturity in spiritual expression. The fact that all this came about is connected with intimate differences between Central European-Nordic life and southern life. We must reflect on the great difference that exists between southern life, which, I would say, forms the last phase of the fourth post-Atlantic period — even though the fifth post-Atlantic period dawns in the Renaissance — southern life, which lives out the last phase of the fourth post-Atlantic period in its most intimate feelings, while in Central Europe, in the north, the fifth post-Atlantic period was preparing itself in such a way that from the dark depths of the soul there arose what was later to become the expression of the individual, the mobile, the moving and the moved in the human soul. The whole life of the two regions of the earth must be considered in its diversity. One need only remember how much in southern art is connected with the fact that there was still a living atavistic view of what comes in from the spiritual regions into the sensual. This was then preserved in all that is called Byzantine art forms, preserved in all that permeates the suggestive designs, which have such a suggestive effect in mosaic art, in Cimabue and in all that is associated with the name Cimabue. Here, Christ, the Christ figure, has a greater effect. For Central Europe, the life of Jesus becomes what is depicted, because the artistic form is represented directly from the soul. Just as superhuman as the Byzantine Christ type is, just as inner-human is the Christ type that Dürer later elaborates.
The fourth post-Atlantic period, with its late flowering, therefore also has something that looks up to the superhuman type, to the superhuman soul of the species, to that which strips away the individual human. And in that the southern peoples revived the ancient, the antiquity in their art to a much greater degree — once these things are understood precisely, this will be found to be true — the superhuman, the generational soul, we see the decisive working up of the individual, the working up of each individual human soul in Nordic art, in northern art.
And so we see how southern life, I would say, still has humanity as a whole. Remember in what sense an Athenian was an Athenian, a Spartan a Spartan, with what right Aristotle called man a “zoon politikon,” a political animal, and how this zoon politikon was then developed to its highest level in Roman culture. Man lives, I would say, more on the street than in his home; he also lives more with his soul in what surrounds him than in the shell of his soul itself. The imagination, which roams around the spatial, wants to be stimulated in this way.
And from this, I would say political coexistence, the artistic also emerges. What I have just said permeates southern art as a feature common to all of it. One can decorate churches, one can decorate squares, one sees everywhere that it is expected that the people will gladly flock there, gladly run into the churches, gladly run to the squares, because their temperament draws them there and they seek what is placed there for them. In order to have a complete spiritual life, they need this life in the outside world, this coexistence with the group soul, with the political in the most eminent sense.
This is different in Central Europe. In Central Europe, people live within themselves. In Central Europe, people seek their experiences in their homes, including their spiritual homes, and if they are to devote themselves to the group, they first want to be conquered; they first want to be called. Much of the impetus behind the emergence of Gothic architecture is contained in what I have just said. Gothic architecture creates buildings that do not stand there because people already run into them, but because they first have to call people, because they first have to bring people together, I would say, through mysterious, suggestive connections. And this is expressed even in the forms of Gothic architecture. The individual first wants to be called together into a group. This is also evident in the entire use of light and darkness, as I recently characterized it. In the elemental weaving and floating of light and darkness, one wants to see that into which one steps when one breaks away from one's individuality, but into which one can also carry one's individuality, because this elemental is related to the soul. In all these things lies the difference between Nordic art and Southern art. Hence this striving, this happy striving of Northern art for the expression of inner life. One need only remember the portraits of van Eyck, the Madonna paintings, for example. These Madonna paintings, with their facial expressions drawn entirely from the inner life of the human soul, this expression of soulful depth in gesture and countenance, Raphael would never have painted. Raphael elevates what he paints beyond the human; van Eyck elevates the human into the deeply human, so that human feelings and the human mind can be moved. There, too, is a conquest of the human soul.
The clergy knew how to reckon with this peculiarity of the European human soul until the 12th and 13th centuries, and they knew how to work together with the popular mind. And certainly much of what arose there in artistic struggle came about through the interaction of the clergy with the characteristic weaving and life of the popular mind. One must understand that this northern peculiarity of artistic creation is closely related to the protesting spirit of the people of the North, who rebelled against Romanism. Luther went to Rome and saw nothing of its dizzying heights, but only the moral decay of Rome. There is a great deal in this. He could certainly have encountered some of the great painters of Rome in St. Peter's Square. But what did he care about these people, who created something from a completely different state of mind, something he found completely incomprehensible! But ultimately, Luther's radical one-sidedness emerged in a different direction from what is now in Central Europe, I would say his struggle, his highest struggle found its expression in the plastic, in the pictorial expression, and yet also reached an artistic height which, in a certain respect—there is no need to make comparisons, they are always trivial—represents something entirely independent, magnificently independent alongside Italian Renaissance art.
And so today we would like to add a few supplements to what we showed you last week. First, we would like to show you a wooden sculpture from the very beginning of the 13th century, from the cathedral in Halberstadt:
364 Halberstadt Cathedral Interior view of the choir with the crucifixion group
365 Halberstadt Cathedral Crucifixion group, center section
Take a look at this crucifixion group. I just want to say that what is particularly significant here is that this sculpture shows how the Passion story had become fully established by this period.
Mary, John, and Christ looking down at Mary in the middle. If you could see his face,
366 Halberstadt Cathedral Crucifixion group, part: Christ
one would see it with an expression of infinite depth, spiritually profound, immense. In Mary — we will be able to show this face of Mary in detail later — one would immediately recognize, if one has the sensitivity for it, the direct confluence of the Romanesque spiritual view with Central European emotionality. This is particularly evident in this face, so that one can say: this group in particular shows how, out of the specific creative impulse of Central Europe, Christianity, which had conquered this Central Europe, was shaped out of its own spiritual impulse. Now let us show the detail, Mary.
367 Halberstadt Cathedral Crucifixion group, detail: Mary
It is this extremely characteristic facial expression that so completely interweaves what one finds in the southern expression, where the eyes look more look out into the world much more than the soul pushes itself into the eyes from within. Here you have both united, so that above a Romanesque curve, I would say, the soul floats quietly and wonderfully in the expression.
Of course, all these things must not be forced; but I ask you to pay attention to how differently clothing is used in Central European art than in Southern art. Certainly, such things must not be forced; but it is true that all Southern art shows us clothing as enveloping the human body, enveloping it, adjoining the human body, continuing the forms of the human body, as it were. The clothing in Central European art is different; it arises from the movement of the soul, and depending on the gesture of the hand, depending on the whole posture, the movement of the soul is continued in the clothing, which is much less attached to the body, much less intended to cover or express the forms of the body as in Southern art, but is, in a sense, a continuation of the soul's experience. You will perceive this more and more clearly as we progress through the following centuries.
Now we come to the famous “Crucifixion Group” in Wechselburg in Saxony,
368 Wechselburg Castle Church Crucifixion Group
which is also carved in wood, also dates from the first third of the 13th century, and yet shows you in a magnificent way a step forward, a tremendous step forward compared to the previous group (364), which shows a similar motif. If you observe the spiritual communication between Mary and Christ here, if you compare it with the face of John, with John's entire expression, if you compare how faith, the faith in the Christian worldview connected with the soul, is represented in John and Mary as conquerors, and if you now say to yourself how this Christian worldview has really become so established that it has become the universal historical conception of earthly existence, when you see how Adam here below catches the blood of the Redeemer dripping from the cross, and when you study the face of Adam, how he is touched by the gracious effect he can receive by being allowed to catch the Savior's blood dripping down from the cross, then you see how infinitely deeply Christianity has become established in this century. It rises to a universal cosmic conception. Angels carry the cross; God the Father descends with the dove, sealing at this moment that the earth gives meaning to what he has given to the earth in his Son. In such a group, which shows a high degree of artistic perfection, one can see how Christianity has become established in Central Europe by trying to permeate it everywhere from the soul, from the mind and from feeling, while in the south it has been permeated by the imagination and has thus brought about that, I would say peculiar, let us say, so as not to offend, “moral-free” permeation, which found expression in Renaissance life, in southern Renaissance life.
If one were to study the progression of representations of the Christ type, this head of Christ here would represent an important stage, just as the head of Christ in the cathedral of Amiens
369 Wechselburg Castle Church Crucifixion group, detail: head of Christ
represent an important stage, as does the head of Christ in Amiens Cathedral
371 Amiens Cathedral Christ (Le Beau Dieu) represents an important stage, and later the head by Dürer:
37la Albrecht Dürer The Man of Sorrows, copperplate engraving of the Passion
In contrast, the head of Adam from the group in Wechselburg.
370 Wechselburg Castle Church Crucifixion group, part: Head of Adam
We now move on to some depictions found in Freiberg in Saxony, which are also from this period, from the first third of the 13th century:
372 Freiberg St. Mary's Church Arch field of the “Golden Gate”: The Adoration of the Kings
They have a completely different side to them, but they also convey the concept of sacred history – all striving for inwardness. It is no exaggeration to say that one likes to immerse oneself in each individual face. - Another representation we have of this:
373 St. Mary's Church in Freiberg, jamb of the “Golden Gate”:
Ecclesia and Aaron
The female figure is difficult to interpret; perhaps she is “Ecclesia,” while the other figure on the right is supposed to represent the prophet Aaron. But none of that matters. These are certain figures that are either allegorical or otherwise connected in some way with the Christian worldview, and which we want to study again with a view to spiritual deepening. For those who want to study these things, the contrast between the left and right faces, which underlies the expression, is precisely what is particularly appealing.
And now, to supplement what we presented last time at Naumburg Cathedral and Strasbourg Cathedral, we will show the sculptures of Bamberg Cathedral. Here we first have two prophets,
374 Bamberg Cathedral choir screen: Two prophets: Jonah and Hosea
where you can see how, I would say, the dramatic element, the emotional turmoil, comes into play here in the attempt to directly depict the exchange of souls, depicting both a momentary soul moment and two contrasting characters.
And now this “Last Judgment” from the Princes' Portal in Bamberg:
375 Bamberg Cathedral Arch field of the “Princes' Portal”: The Last Judgment
Not a great composition, but something tremendous in its emotional expression. And it must be taken into account that the relief was probably created around 1240, so that later spiritual scientific research will be proven right in not saying—as many still do today—that the Central European element was greatly influenced by the Southern element in the representation of the Christian worldview. That is not the case; quite the opposite is true. But even today, the currents in external history are not yet seen in such a way that, as is actually the case and as I recently indicated, northern impulses have an influence on the creations of Raphael and Michelangelo in particular; for this conception of the “Last Judgment,” as far as the artistic aspect is concerned, is entirely born of the northern spirit.
This is an example — again from Bamberg Cathedral — of how the secular and religious elements always interact. It is already the case that, especially for the period we are now dealing with, the secular and the religious definitely interact. They come together in the commonality that I characterized earlier, namely in the fact that the human soul wants to be conquered, the individual soul wants to be called together, wants to be united, if it wants to look up in reverence to the supernatural in community, but also wants to be called when it has something to worship in the secular world in some way, which is why the secular is connected with the ecclesiastical.
Here we see depicted Stephen, Empress Kunigunde, Emperor Henry:
376 Bamberg Cathedral Left jamb of the “Adam's Gate”: Stephen, Empress Kunigunde, Emperor Henry
Of course, this is usually based on naivety on the part of the people: blind adherence, looking up. Only today has this been overcome in the imagination of the contemporary world, but it is all the more present internally; and on the part of the high lords, of course, it is very often based on a belief, combined with all kinds of human characteristics, that they are closer to the various saints and other supernatural powers than other mortals.
Now a detail from this, the middle figure from the previous image:
377 Bamberg Cathedral Empress Kunigunde, part of 376
During this period, the Old Testament and the New Testament are always thought of in harmony with each other, as promise and fulfillment. Now a detail from this:
380 Bamberg Cathedral Head of Adam, part of 378
Another detail:
379 Bamberg Cathedral Head of Eve, part of 378
Now a figure in the same cathedral:
381 Bamberg Cathedral Mary
A figure of Mary, which, I would say, can be understood from every point of view, shows how what was discussed earlier is now truly expressed in this art movement. In considering all these things, I ask you to bear in mind that this “Mary,” for example, was created around 1245, and to remember what you might have been looking for in the south at that time.
From the same cathedral, the figure of the church:
382 Bamberg Cathedral “Princely Portal”: The Church
This was a popular representation. We recently showed you the representation of the church as it appears on Strasbourg Cathedral, and here you have it from Bamberg Cathedral. The figure of the church, depicted as free inside, conceived by a free soul, looking out freely into the world, wise, and contrasted with the synagogue, as we saw recently. This is now a detail, the head of the church:
385 Bamberg Cathedral Head of the church, part of 382
It is contrasted with the synagogue. You see this depicted again and again with bound, downcast eyes; and compare the whole posture! The posture of the synagogue is again intended to represent the contrast, even in the folds of the robe:
383 Bamberg Cathedral “Princes' Portal”: The Synagogue
Take a look at the undergarment here, how it is fully adapted to the movement of the soul. Now let us look at the church again so that you can compare the undergarment with that of the synagogue:
Bamberg Cathedral, “Princely Portal”:
382 The Church
384 The synagogue, side view
386 Head of the synagogue
Now again a secular figure from the same cathedral; an equestrian statue of some king:
387 Bamberg Cathedral The horseman (known as the “Bamberg Horseman”)
You will be able to study the expression well, especially on the head of the equestrian statue, which is wonderful:
388 Bamberg Cathedral Bust of the horseman, part of 387
It is a wonderful head!
Now let's move on to the 14th century and see what has become of it by looking at some figures from Cologne Cathedral that were created in the first half of the 14th century: 389 Cologne Cathedral Mary
It is not difficult to see that a certain decline has now taken place.
Then, also from Cologne Cathedral:
390 Cologne Cathedral John
391 Cologne Cathedral James the Elder
We now move on to the 14th century and come to a master who is called the “Master of the Tonapostel” because these figures are made of fired clay:
392 Master of the Tonapostel Paulus
And now, after we have seen, I would say, the rise and slight decline of a closed line, a closed stream of development, let us consider something that is truly great in its own way, namely a series of sculptures from the Carthusian monastery in Dijon, which were created at the end of the 14th and beginning of the 15th centuries and executed by the Dutchman Claus Sluter or under his guidance. In all these figures, you will see how the most individual characteristics flow in from the Netherlands into this Dijon Carthusian monastery in a very unique way, so that from the most diverse sides, one can see how the individualizing, the characteristic individualizing that comes from the soul, appears.
First, we have the portal of the Carthusian monastery:
Claus Sluter, portal of the Chartreuse de Champmol Dijon
393 Madonna with donors
Now some figures from this portal:
394 Madonna with Child
395 Philip the Bold, John the Baptist
This individual art of characterization can be seen everywhere here. If you compare this ability of one and the same person to characterize the Madonna with the Child with what comes next,
397 Claus Sluter Moses, from the base of the “Moses Fountain” in the Chartreuse de Champmol Dijon
how he characterizes Moses, then please note that the Carthusian monastery in Dijon was built between 1383 and 1388, which is the beginning of the 15th century – 1400/1401. And why shouldn't such things be compared, because they can be compared:
this Moses from the beginning of the 15th century, for example, with Michelangelo's Moses [1516].
398 Michelangelo Moses, part of 174
Now a few more works by Sluter:
Claus Sluter, Dijon, Chartreuse de Champmol, base of the “Moses Fountain”
399 David, Jeremiah
400 Zacharias, Daniel, Isaiah
This experience of witnessing the prophets in such individualized form is, of course, something quite wonderful. Now let us highlight “Isaiah”:
396 Bust of Isaiah, part of 400
Then, by the same artist—at least in part:
401 Claus Sluter Tomb of Philip the Bold
Time is very important in the creation of tomb monuments. After giving an overview of this one, we will show the upper part in detail:
402 Claus Sluter Philip the Bold with two angels, part of 401
You will then also see that the individual figures, which appeared so small on the pedestal earlier, are really wonderfully executed in detail:
403 Claus Sluter Mourning monks, part of 401
These individual figures around the base are executed with these individual characteristics:
404 Claus Sluter Mourning Monks, part of 401
And now we move on—we have to make do with the images we have—to an artist from the first half of the 15th century. Please bear in mind: In everything we have seen recently, we have been dealing with an artist from the turn of the 14th to the 15th century. Now we are moving into the 15th century. With the Cologne masters and the “Master of the Clay Figures,” who produced this group in fired clay around 1400, we had reached the end of the 14th century.
So now we move on to the 15th century, to Hans Multscher. First, we have a “Madonna” by him.
405 Hans Multscher Madonna and Child
Then, by the same artist, Saint George and Saint Florian,
406 Hans Multscher St. George
407 St. Florian
both from the hospital church in Sterzing, dating from around the middle of the 15th century.
This brings us further into what I have characterized as the inner, spiritual elaboration of Christian motifs. And so we come to the wood-carved figures from the end of the 15th century from Blutenburg near Munich:
408 Blutenburg Castle Chapel Matthias
Here, indeed, the art of characterization reaches an extraordinary degree.
409 Blutenburg Castle Chapel Mary
410 Thomas
So this is the period in which Michelangelo and Raphael were born.
411 Blutenburg Castle Chapel John
So this is all from Blutenburg.
This period was also very significant, precisely this period from which these highly individualized figures originate, in the development of wooden sculptures for choir stalls in churches. Let us now look at an example from the Frauenkirche in Munich from the end of the 15th century:
412 Munich Frauenkirche Baruch, Mark, Job (choir stalls)
Now we turn to another artist who was active at the end of the 15th century, to a series of works by the “Rosary” woodcarver, Tilman Riemenschneider:
Tilman Riemenschneider, figures from the south portal of the Marienkapelle in Würzburg
413 Adam
415 Head of Adam, part of 413
So this is from a time when the High Renaissance had not yet begun in Italy. These pieces were created around 1493.
414 Eve
416 Head of Eve, part of 414
A Saint Elizabeth, now in the Germanisches Museum in Nuremberg,
417 Tilman Riemenschneider St. Elizabeth
created at the beginning of the 16th century.
418 Tilman Riemenschneider Madonna and Child
A Madonna with Child, also from the early 16th century.
And by the same artist:
Tilman Riemenschneider, The Twelve Apostles
419 Peter 423 Philip 427 Paul

