Ways to a New Style in Architecture
GA 286
7 June 1914, Dornach
4. The Acanthus Leaf
A thought that may often arise in connection with this building is that of our responsibility to the sacrifices which friends have made for its sake. Those who know how great these sacrifices have been, will realise that the only fit response is a strong sense of responsibility, for the goal at which we must aim is the actual fulfilment of the hopes resting in this building. Anyone who has seen even a single detail—not to speak of the whole structure, for no conception of that is possible yet—will realise that this building represents many deviations from other architectural styles that have hitherto arisen in the evolution of humanity and have been justified in the judgment of man. An undertaking like this can of course only be justified if the goal is in some measure attained. In comparison to what might be, we shall only be able to achieve a small, perhaps insignificant beginning. Yet, may be, this small beginning will reveal the lines along which a spiritual transformation of artistic style must come about in the wider future of humanity. We must realise that when the building is once there, all kind of objections will be made, especially by so-called ‘experts,’ that it is not convincing, perhaps even dilettante. This will not disconcert us, for it lies in the nature of things that ‘expert’ opinion is least of all right when anything claiming to be new is placed before the world. We shall not, however, be depressed by derogatory criticism that may be levelled at our idea of artistic creation, if we realise, as a compensation for our sense of responsibility, that in our age, the origin of the Arts and of their particular forms and motifs is greatly misunderstood by technical experts. And then, gradually, we shall understand that all we are striving to attain in this building stands much closer to primordial forces of artistic endeavour which are revealed when the eye of the Spirit is directed to the origin of the Arts, than do the conceptions of art claiming to be authoritative at the present time. There is now little understanding of what was once implied by the phrase “true artistic conception.” It need not therefore astonish us if a building like ours, which strives to be in harmony with primordial Will and in accordance with the origin of the arts, is not well or kindly received by those who adhere to the direction and tendency of the present age.
In order to bring home these thoughts to you, I should like to start to-day by considering a well-known motif in art—that of the so-called acanthus leaf—showing the sense in which our aims are in harmony with the artistic endeavours of humanity as expressed in the origin of this acanthus leaf as a decorative motif. Now because our endeavours are separated by many hundreds, nay even thousands of years, from the first appearance of this acanthus motif, they must naturally take a very different form from anything that existed in the days when, for instance, the acanthus leaf was introduced into the Corinthian capital.
If I may be permitted a brief personal reference here, let me say that my own student days in Vienna were passed during the time when the buildings which have given that city its present stamp, were completed—the Parliament Buildings, the Town Hall, the Votivkirche and the Burgtheatre. The famous architects of these buildings were still living: Hanson who revived Greek architecture, Schmidt who elaborated Gothic styles with great originality, Ferstel who built the Votivkirche. It is perhaps not known to you that the Burgtheatre in Vienna was built according to the designs of an artist who in the seventies and eighties of the last century was the leading influence in artistic appreciation and development of form in architecture and sculpture. The Burgtheatre was built according to the designs of the great Architect, Gottfried Semper.
At the Grammar School I myself had as a teacher a gifted admirer and disciple of Gottfried Semper, in the person of Josef Baier, so that I was able to live, as it were, in the whole conception of the world of architectural, sculptural and decorative form as inaugurated by the great Semper.
Now, in spite of all the genius that was at work, here was something that well-nigh drove one to despair in the whole atmosphere of the current conceptions of the historical development of art, on the one side, and of the way to artistic creation on the other. Gottfried Semper was undoubtedly a highly gifted being, but in those days the usual conception of man and the universe was an outcome of the materialistic interpretation of Darwin, and the doctrine of evolution was also apparent in the current ideas of art. Again and again this materialistic element crept into the conceptions of art. It was, above all, considered necessary to possess a knowledge of the technique of weaving and interlacing. Architectural forms were derived in the first place from the way in which substances were woven together, or fences constructed so that the single canes might interpenetrate and hold together. In short, people were saturated with the principle that decoration and ornamentation were forms of external technique. This subject of course might be further elaborated, but I only want to indicate the general tendency which was asserting itself at that time—namely, the tendency to lead everything artistic back to external technique. The standpoint had really become one of ultilitarianism and the artistic element was considered to be an outcome of the use to which things were put. All treatises on the subject of art, and especially on decoration, invariably made mention of the special idiosyncrasies of the different technical experts. This of course was a stream running parallel to the great flood of materialistic conceptions that swept over the 19th century, chief among them being the materialistic conception of art. The extent to which materialism asserted itself in all spheres of life during the second half of the 19th century was enough to drive one to despair. Indeed I still remember how many sleepless nights I had at that time over the Corinthian capital. Now the main feature, the principal decoration of the Corinthian capital—although in the days of which I am speaking it was almost forbidden to speak of such a thing as ‘decoration’—is the acanthus leaf. What could be more obvious than to infer that the acanthus leaf, on the Corinthian capital was simply the result of a naturalistic imitation of the leaf of the common acanthus plant? Now anyone with true artistic feelings finds it very difficult to conceive that a beginning was somewhere made by man taking a leaf of a weed, an acanthus leaf, working it out plastically and adding it to the Corinthian column. Let us think for a moment of the form of the acanthus leaf.  I will draw a rough sketch of the form of the Acanthus Spinoza. This was supposed to have been worked out plastically and then added to the Corinthian column. Now there is, of course, something behind this. Vitruvius, the learned compiler of the artistic traditions of antiquity, quotes a well-known anecdote, which led to the adoption of the “basket hypothesis” in connection with the Corinthian column. The expression is a good one, for what, according to the materialistic conception of art, was the origin of the decoration on the Corinthian capital? Little baskets of acanthus leaves that were carried about! When we enter more deeply into these things we realize that this is both symptomatic and significant. It becomes evident that their understanding of the finer spiritual connections of the evolutions of humanity has led investigators to a basket, to basket-work, and as a kind of token of it we have the “basket hypothesis” of the Corinthian column. Vitruvius says that Callimachos, the Corinthian Sculptor, once saw a little basket standing on the ground somewhere, with acanthus plants growing around it, and he said to himself: There is the Corinthian capital! This is the very subtlest materialism imaginable. Now let me show you the significance of this anecdote narrated by Vitruvius. The point is that in the course of the modern age the inner principle, the understanding of the inner principle of artistic creation has gradually been lost. And if this inner principal is not re-discovered, people simply will not understand what is meant and desired in the forms of our building, its columns and capitals. Those who hold fast to the basket hypothesis—in a symbolical sense of course—will never be able rightly to understand us.
I will draw a rough sketch of the form of the Acanthus Spinoza. This was supposed to have been worked out plastically and then added to the Corinthian column. Now there is, of course, something behind this. Vitruvius, the learned compiler of the artistic traditions of antiquity, quotes a well-known anecdote, which led to the adoption of the “basket hypothesis” in connection with the Corinthian column. The expression is a good one, for what, according to the materialistic conception of art, was the origin of the decoration on the Corinthian capital? Little baskets of acanthus leaves that were carried about! When we enter more deeply into these things we realize that this is both symptomatic and significant. It becomes evident that their understanding of the finer spiritual connections of the evolutions of humanity has led investigators to a basket, to basket-work, and as a kind of token of it we have the “basket hypothesis” of the Corinthian column. Vitruvius says that Callimachos, the Corinthian Sculptor, once saw a little basket standing on the ground somewhere, with acanthus plants growing around it, and he said to himself: There is the Corinthian capital! This is the very subtlest materialism imaginable. Now let me show you the significance of this anecdote narrated by Vitruvius. The point is that in the course of the modern age the inner principle, the understanding of the inner principle of artistic creation has gradually been lost. And if this inner principal is not re-discovered, people simply will not understand what is meant and desired in the forms of our building, its columns and capitals. Those who hold fast to the basket hypothesis—in a symbolical sense of course—will never be able rightly to understand us.
The basis of all artistic creation is a consciousness that comes to a standstill before the portals of the historical evolution of humanity as depicted by external documents. A certain consciousness that was once active in man, a remnant of the old clairvoyance, belonged to the fourth Post-Atlantean period, the Graeco-Roman. Although Egyptian culture belongs to the third Post-Atlantean epoch, all that was expressed in Egyptian art belongs to the fourth epoch. In the fourth epoch this consciousness gave rise to such intense inner feeling in men that they perceived how the movement, bearing and gestures of the human being, nay even the human form itself, develop outwards into the physical and etheric. You will understand me if you realise that in those times, when there was a true conception of artistic aim, the mere sight of a flower or a tendril was of much less importance than the feeling: ‘I have to carry something heavy; I bend my back and generate with my own form the forces which make me, as a human being, able to bear the weight.’ Men felt within themselves what they must bring to expression in their own postures. This was the sense in which they made movements when it was a question of taking hold of something or of carrying something in the hand. They were conscious of a sense of carrying, of weight, where it was necessary to spread the hands and finger outwards. Then there arose the lines and forms which passed over into artistic creation. It is as though one felt in humanity itself how man can indeed go beyond what he sees with his eyes and perceives with his other senses:—he can go beyond it when he enters into and adapts himself to a larger whole. Even in this case of a larger whole, when a man no longer merely lets himself go as he walks along, but is obliged to adapt himself to the carrying of a load—already here he enters into the organism of the whole universe. 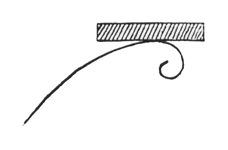 And, from the feeling of the lines of force which man has to develop in himself, arose the lines that gave birth to artistic form. Such lines are nowhere to be found in external reality. Now spiritual research is often confronted by a certain wonderful akashic picture; it represents the joining together of a number of human beings into a whole, but a harmonious, ordered joining together. Imagine a kind of stage, and as an amphitheatre around it, seats with spectators; certain human beings are now to pass in a procession round and inside the circle. Something higher, super-sensible—not naturalistic—is to be presented to man.
And, from the feeling of the lines of force which man has to develop in himself, arose the lines that gave birth to artistic form. Such lines are nowhere to be found in external reality. Now spiritual research is often confronted by a certain wonderful akashic picture; it represents the joining together of a number of human beings into a whole, but a harmonious, ordered joining together. Imagine a kind of stage, and as an amphitheatre around it, seats with spectators; certain human beings are now to pass in a procession round and inside the circle. Something higher, super-sensible—not naturalistic—is to be presented to man.
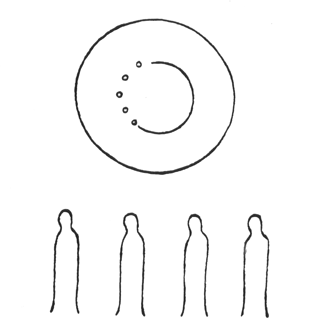
I have drawn it diagrammatically, from the side view: a number of men are walking one behind the other. They form the procession which then passes round inside the circle; others are sitting in the circle looking on. 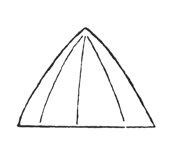 Now the persons (in the procession) are to portray something of great significance, something that does not exist on the Earth, of which there are only analogies on the Earth; they are to represent something that brings man into connection with the great sphere of the cosmos. In those times it was a question of representing the relationship between the earthly forces and the sun forces. How can man come to feel this relationship of the earthly forces to the sun forces? By feeling it in the same way as, for instance, the state of carrying a load. He can feel it in the following way: all that is earthly rests upon the surface of the earth and as it rises away from the earth (this is only to be thought of in the sense of force) it runs to a point. So that man felt the state of being bound to the earth expressed in a form with a wide base, running upwards to a point. It was this and nothing else, and when man sensed this working of forces, he said to himself: ‘I feel myself standing on the earth.’
Now the persons (in the procession) are to portray something of great significance, something that does not exist on the Earth, of which there are only analogies on the Earth; they are to represent something that brings man into connection with the great sphere of the cosmos. In those times it was a question of representing the relationship between the earthly forces and the sun forces. How can man come to feel this relationship of the earthly forces to the sun forces? By feeling it in the same way as, for instance, the state of carrying a load. He can feel it in the following way: all that is earthly rests upon the surface of the earth and as it rises away from the earth (this is only to be thought of in the sense of force) it runs to a point. So that man felt the state of being bound to the earth expressed in a form with a wide base, running upwards to a point. It was this and nothing else, and when man sensed this working of forces, he said to himself: ‘I feel myself standing on the earth.’
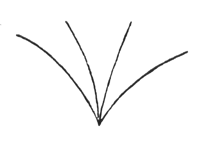 In the same way he also became aware of his connection with the sun. The sun works in upon the earth and man expressed this by portraying the lines of forces in this way. The sun, in its apparent journey round the earth, sends its rays thus, running downwards to a point.
In the same way he also became aware of his connection with the sun. The sun works in upon the earth and man expressed this by portraying the lines of forces in this way. The sun, in its apparent journey round the earth, sends its rays thus, running downwards to a point.
If you think of these two figures in alternation, you have the earth-motif and the sun-motif that were always carried by the people who formed the procession. This was one thing that in olden times was presented in circling procession. The people sat around in a circle and the actors passed around in a procession. Some of them carried emblems representing man's connection with the sun; and they alternated: earth-sun, sun-earth and so on:
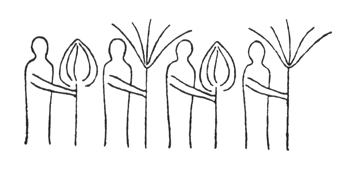
Man sensed this cosmic power: earth-sun, and then he began to think how he could portray it. The best medium for purposes of art proved to be a plant or tree whose forms runs upwards to a point from a wider base. This was alternated with palms. Plants having a form like a wide bud were alternated with palms. Palms represented' the sun forces; bud-forms running upwards to a point, the earth forces.
Feeling his place in the cosmos, man created certain forms, merely using the plants as a means of expression. He used plants instead of having to invent some other device. Artistic creation was the result of a living experience of cosmic connections; this is in accordance with the evolution of the creative urge in man and the process is no mere imitation of outer phenomena of nature. The artistic representation of the elements of outer nature only entered into art later on. When men no longer realised that palms were used to express the sun forces, they began to think that the ancients simply imitated the palm in their designs. This was never the case; the ancients used the leaves of palms because they were typifying the sun forces. Thus has all true artistic creation arisen, from a ‘superabundance’ of forces in the being of man—forces which cannot find expression in external life, which strive to do so through man's consciousness of his connection with the universe as a whole. Now all contemplation and thought both in the spheres of natural science and art, have been misled and confused by a certain idea which it will be very difficult to displace. It is the idea that complexity has arisen from simplicity. Now this is not the case. The construction of the human eye, for instance, is much more simple than that of many of the lower animals. The course of evolution is often from the complex to the simple; it often happens that the most intricate interlacing finally resolves itself into the straight line. In many instances, simplification is the later stage, and man will not acquire the true conception of evolution unless he realises this.
Now all that was presented to the spectators in those ancient times, when it was always a question of portraying living cosmic forces, was later on simplified into the decoration, the lines of which expressed man's living experience when he presented these things. 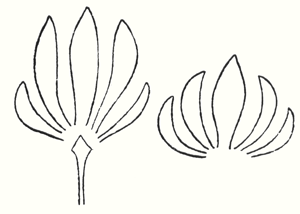 I might make the following design in order to express how man, from his conception of the course of evolution from the complex to the simple, developed the lines into a decoration. If you think of the lines in alternation you have a simplified reproduction of the circling procession of Sun-motif—Earth-motif, Sun-Motif—Earth-motif. That is what man experienced in the decorative motif. This decorative motif was already a feature of Mesopotamian art and it passed over into Greek art as the so-called Palmette, either in this or in a similar form, resembling the lotus petal.
I might make the following design in order to express how man, from his conception of the course of evolution from the complex to the simple, developed the lines into a decoration. If you think of the lines in alternation you have a simplified reproduction of the circling procession of Sun-motif—Earth-motif, Sun-Motif—Earth-motif. That is what man experienced in the decorative motif. This decorative motif was already a feature of Mesopotamian art and it passed over into Greek art as the so-called Palmette, either in this or in a similar form, resembling the lotus petal.
This alternation of Sun-motif, Earth-motif, presented itself to the artistic feeling of mankind as a decorative motif in the truest sense. Later on man no longer realised that he must see in this decorative motif a reproduction that had passed into the subconscious realm, of a very ancient dance motif, a ceremonial dance. This was preserved in the palmette motif. Now it is interesting to consider

the following:—On the decorations of certain Doric columns one often finds a very interesting motif which I will sketch thus.
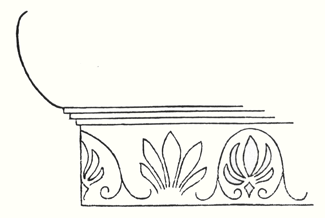 Underneath what has to bear the capital we find
the following. Here we have the torus of the Doric column,
but underneath this we find, in certain Doric columns,
introduced as a painting around the pillar, the Earth-motif
somewhat modified, and the Sun-motif. Up above we have the
Doric torus and the decorative motif below as an ornament. We
actually find the palmette motif on certain Doric columns,
carried out in such a way that it forms a procession:
Sun-Earth, Sun-Earth and so on.
Underneath what has to bear the capital we find
the following. Here we have the torus of the Doric column,
but underneath this we find, in certain Doric columns,
introduced as a painting around the pillar, the Earth-motif
somewhat modified, and the Sun-motif. Up above we have the
Doric torus and the decorative motif below as an ornament. We
actually find the palmette motif on certain Doric columns,
carried out in such a way that it forms a procession:
Sun-Earth, Sun-Earth and so on.
In Greece, that wonderful land where the fourth Post-Atlantean period was expressed in all its fulness, there was a union of what came over from Asia with all that I have now described and which, as an after-image is there, on Doric columns together with the truly dynamic-architectonic principle of weight-bearing. This union came about because it was in Greece that the Ego was fully realised within the human body, and therefore this motif could find expression in Greek culture. 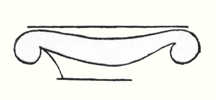 The Ego, when it is within the body, must grow strong if it has to bear a load. It is this strengthening process that is felt in the volute. We see the human being, as he strengthens his Ego in the fourth Post-Atlantean period, expressed in the volute. Thus we come to the basic form of the Ionic pillar; it is as if Atlas is bearing the world, but the form is still undeveloped in that the volute becomes the weight bearer.
The Ego, when it is within the body, must grow strong if it has to bear a load. It is this strengthening process that is felt in the volute. We see the human being, as he strengthens his Ego in the fourth Post-Atlantean period, expressed in the volute. Thus we come to the basic form of the Ionic pillar; it is as if Atlas is bearing the world, but the form is still undeveloped in that the volute becomes the weight bearer.
Now you need only imagine what is merely indicated in the Ionic pillars, the middle portion, developing downwards to the perfect volute and you have the Corinthian column. 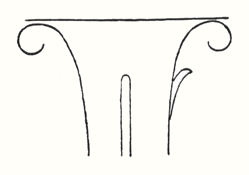 The middle portion is simply extended downward, as it were, so that the character of weight bearing becomes complete. And now think of this weight bearing in the form of a plastic figure and you have the human force bent into itself—the Ego bent round, in this case bearing a weight. An artistic principle is involved when we reproduce in miniature anything that is worked out on a large scale, and vice-versa. If you now think of an elaboration of the Corinthian column with the volute bearing the abacus here, and repeat this artistic motif lower down where it only serves as a decoration, you have plastically introduced in the decoration something that is really the whole column. Now imagine that the Doric painting which grew out of the decorative representation of a very ancient motif, is united with what is contained in the Corinthian column and the intuition will arise that the decoration around it is the same as an earlier painting. The painting on the Doric column was worked out plastically—I can illustrate this to you by the diagram of the motif containing the the palmette—and the urge arose to bring the palmette into the later decorative motif. Here it was not a motif representing the bearing of a load; what was mere painting in the Doric column (and therefore flat) was worked out plastically in the Corinthian column and the palm leaves are allowed to turn downwards. To the left I have drawn a palmette and on the right the beginning of it that arises when the palmette is worked out plastically.
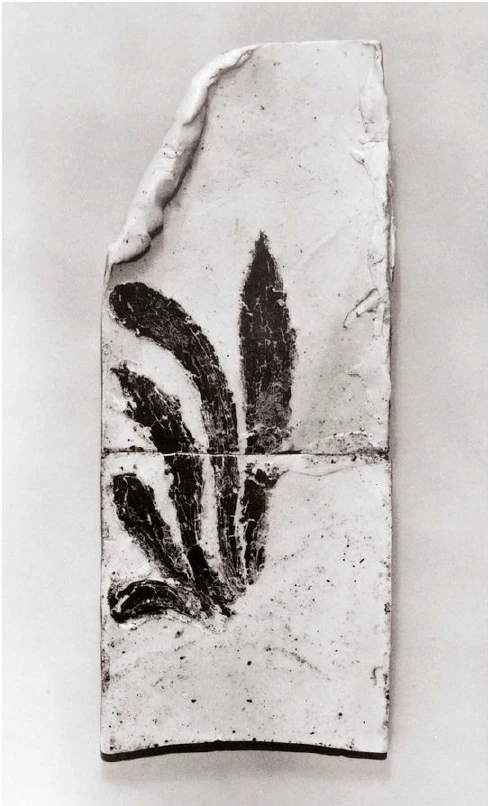
The middle portion is simply extended downward, as it were, so that the character of weight bearing becomes complete. And now think of this weight bearing in the form of a plastic figure and you have the human force bent into itself—the Ego bent round, in this case bearing a weight. An artistic principle is involved when we reproduce in miniature anything that is worked out on a large scale, and vice-versa. If you now think of an elaboration of the Corinthian column with the volute bearing the abacus here, and repeat this artistic motif lower down where it only serves as a decoration, you have plastically introduced in the decoration something that is really the whole column. Now imagine that the Doric painting which grew out of the decorative representation of a very ancient motif, is united with what is contained in the Corinthian column and the intuition will arise that the decoration around it is the same as an earlier painting. The painting on the Doric column was worked out plastically—I can illustrate this to you by the diagram of the motif containing the the palmette—and the urge arose to bring the palmette into the later decorative motif. Here it was not a motif representing the bearing of a load; what was mere painting in the Doric column (and therefore flat) was worked out plastically in the Corinthian column and the palm leaves are allowed to turn downwards. To the left I have drawn a palmette and on the right the beginning of it that arises when the palmette is worked out plastically. 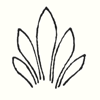 If I were now to continue, the painted Doric palmette would thus pass over into the Corinthian plastic palmette. If I did not paint the palmette we should in each case have the acanthus leaf. The acanthus leaf arises when the palmette is worked out plastically; it is the result of an urge not to paint the palmette but to work it out plastically. People then began to call this form the acanthus leaf; in early times, of course, it was not called by this name. The name has as little to do with the thing portrayed as the expression ‘wing’ has to do with the lungs and lobes or ‘wings’ of the lungs. The whole folly of naturalistic imitation in the case of the acanthus leaf is exposed, because, in effect, what is called the acanthus leaf decoration did not arise from any naturalistic imitation of the acanthus leaf, but from a metamorphosis of the old Sun motif in the palmette that was worked out plastically instead of being merely painted. So you see that these artistic forms have proceeded from an inner perception and understanding of the postures of the human etheric body (for the movement of a line is connected with this)—postures which man has to set up in his own being.
If I were now to continue, the painted Doric palmette would thus pass over into the Corinthian plastic palmette. If I did not paint the palmette we should in each case have the acanthus leaf. The acanthus leaf arises when the palmette is worked out plastically; it is the result of an urge not to paint the palmette but to work it out plastically. People then began to call this form the acanthus leaf; in early times, of course, it was not called by this name. The name has as little to do with the thing portrayed as the expression ‘wing’ has to do with the lungs and lobes or ‘wings’ of the lungs. The whole folly of naturalistic imitation in the case of the acanthus leaf is exposed, because, in effect, what is called the acanthus leaf decoration did not arise from any naturalistic imitation of the acanthus leaf, but from a metamorphosis of the old Sun motif in the palmette that was worked out plastically instead of being merely painted. So you see that these artistic forms have proceeded from an inner perception and understanding of the postures of the human etheric body (for the movement of a line is connected with this)—postures which man has to set up in his own being.
The essential forms of art can no more arise from an imitation of nature than music can be created by an imitation of nature. Even in the so-called imitative arts, the thing that is imitated is fundamentally secondary, an accessory as it were. Naturalism is absolutely contrary to true artistic feeling. If we find that people think our forms here are grotesque we shall be able to comfort ourselves with the knowledge that this kind of artistic conception sees in the acanthus motive nothing but a naturalistic imitation. The acanthus motif, as we have seen, was created purely from the spirit and only in its late development came to bear a remote resemblance to the acanthus leaf. Artistic understanding in future ages will simply be unable to understand this attitude of mind which in our time influences not only the art experts who are supposed to understand their subject, but all artistic creation as well. The materialistic attitude of mind in Darwinism also confronts us in artistic creation, in that there is a greater and greater tendency to make art into a mere imitation of nature. My discovery of these connections in regard to the acanthus leaf has really been a source of joy to me, for it proves circumstantially that the primordial forms of art have also sprung from the human soul and not from imitation of external phenomena.
I was only able really to penetrate to the essence of art after I had myself moulded the forms of our building here. When one moulds forms from out of the very well-springs of human evolution, one feels how artistic creation has arisen in mankind. It was a strange piece of karma that during the time when I was deeply occupied with following up a certain artistic intuition (this was after the forms for the buildings had already been made)—an intuition that had arisen during the General Congress in Berlin—it happened that I began to investigate what I had created in these forms, in order to get a deeper understanding. One can only think afterwards about artistic forms; if one “understands” them first and then carries them out, they will have no value. If one creates from concepts and ideas nothing of value will ensue, and the very thing that I perceived so clearly in connection with the acanthus leaf, and have shown to be erroneous, is an indication of the inner connections of the art in our building.
I came upon a remarkable example which is purely the result of clairvoyant investigation. At one point I discovered a curious point of contact with Rigl, a fellow-countryman of mine. It is a curious name, not very aristocratic, but typically Austrian. This man Rigl did not achieve anything of great importance but while he was Curator of an Architectural Museum in Vienna he had an intuitive perception of the fact that these architectural decorations had not arisen in the way described by “Semperism” at the end of the 19th century. Rigl hit upon certain thoughts which are really in line with the metamorphosis of the palmette motif into that of the acanthus leaf. Quite recently, therefore, I have discovered a perfect connection between the results of occult investigation, and external research which has also hit upon this development of the so-called acanthus motif from the palmette. ‘Palmette’ is of course merely a name; what is really there in the palmette is the Sun-motif. In the first place, of course, one feels in despair about an idea like that of Rigl. He simply could not realise whence the palmette motif had originated and that it was connected with forces working and moving in man. Rigl remonstrates with the learned art critics who have brought Semper's ideas into everything and are for the most part mere naturalists, but in spite of this he did not get very far. He says that in regard to the acanthus leaf the learned art critics are still feeding upon the old anecdote quoted by Vitruvius. (It cannot be said that they are all feeding upon it, but it is true that they constantly quote it.) Rigl, however, only mentions this anecdote briefly; he does not think it worth while to go into all the details because it is too well known. What he leaves out is very characteristic. He says that Callimachos had seen a basket surrounded by acanthus leaves and that then the idea of the Corinthian column came to him. Rigl, too, leaves something out and this very thing shows that the typical conceptions of our age must despair of ever having real knowledge in this sphere. He leaves out the most important factor in the whole anecdote, which is that what Callimachos saw was over the grave of a Corinthian girl. That is the important thing, for it implies no less than that Vitruvius, although he wisely holds his tongue about it, intends to indicate that Callimachos was clairvoyant and saw, over a girl's grave, the Sun-motif struggling with the Earth-motif, and above this the girl herself, hovering in her etheric body. Here indeed is a significant indication of how the motifs of Sun and Earth came to be used on the capitals of columns. If we are able to see clairvoyantly what is actually present in the etheric world above the grave of a girl who had died, we realise that the palmette motif has arisen out of this, growing, as it were, around the etheric body that is rising like the sun. It seems as though men have never really understood the later Roman statues of Pytri-Clitia for they are nothing else than a clairvoyant impression that can be received over the graves of certain people; in these statues, the head of an extraordinarily spiritual, though not virginal Roman woman, seems to grow upwards as if from a flower chalice. Some time, my dear friends, we shall understand what really underlies the anecdote quoted by Vitruvius, but not until we grow out of the unfortunate habit which makes us perpetually ask, ‘What is the meaning of this or that?’ and is always looking for symbolic interpretations such as, ‘this signifies the physical body, that the etheric body, this or that the astral body.’ When this habit is eliminated from our Movement we shall really come to understand what underlies artistic form—that is to say, we shall either have direct perception of true spiritual movement, or of the corresponding etheric phenomenon.
It is actually the case that in clairvoyant vision the acanthus leaf can be seen, in its true form, above a grave.
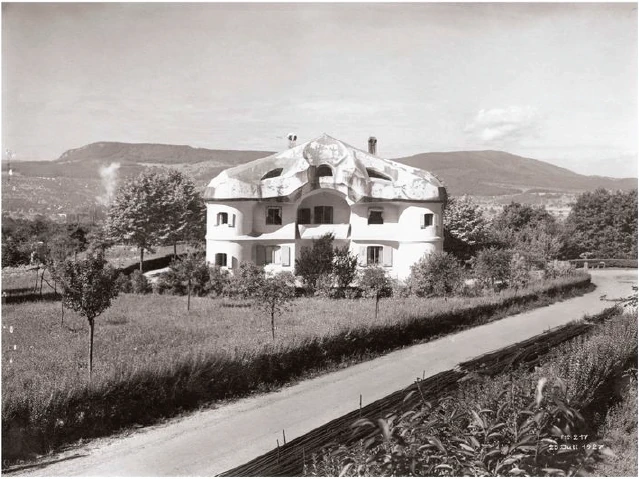
If you will consider all these things; my dear friends, you will realise how important it is to understand the forms in the interior of our building, the forms that should adorn it, and to know the artistic principle from which they have arisen. On previous occasions I used a somewhat trivial comparison, but it is only a question of understanding the analogy. Although it is trivial, it does, nevertheless, convey what it is intended to convey. When we are trying to understand what will be placed in the interior of the building in these two different sized spaces, we may with advantage think of the principle of the mould in which German cakes are baked. 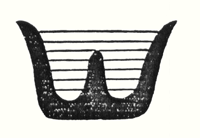 The cake rises in the mould and when it is taken out its surface shows all the forms which appear on the sides of the mould in negative. The same principle may be applied in the case of the interior decoration of our building, only that of course there is no cake inside; what must live there is the speech of Spiritual Science, in its true form. All that is to be enclosed within the forms, all that is to be spoken and proclaimed, must be in correspondence, as the dough of the cake corresponds to the negative forms of the baking mould. We should feel the walls as the living negative of the words that are spoken and the deeds that are done in the building. That is the principle of the interior decoration. Think for a moment of a word, in all its primordial import, proceeding from our living Spiritual Science and beating against these walls. It seems to hollow out the form which really corresponds to it. Therefore I at least was satisfied from the very outset that we should work in the following way: with chisel and mallet we have a surface in mind from the beginning, for with the left hand we drive the driving chisel in the direction which will eventually be that of the surface. From the very outset we drive in this direction. On the other hand we hold the graver's chisel at right angles to the surface.
The cake rises in the mould and when it is taken out its surface shows all the forms which appear on the sides of the mould in negative. The same principle may be applied in the case of the interior decoration of our building, only that of course there is no cake inside; what must live there is the speech of Spiritual Science, in its true form. All that is to be enclosed within the forms, all that is to be spoken and proclaimed, must be in correspondence, as the dough of the cake corresponds to the negative forms of the baking mould. We should feel the walls as the living negative of the words that are spoken and the deeds that are done in the building. That is the principle of the interior decoration. Think for a moment of a word, in all its primordial import, proceeding from our living Spiritual Science and beating against these walls. It seems to hollow out the form which really corresponds to it. Therefore I at least was satisfied from the very outset that we should work in the following way: with chisel and mallet we have a surface in mind from the beginning, for with the left hand we drive the driving chisel in the direction which will eventually be that of the surface. From the very outset we drive in this direction. On the other hand we hold the graver's chisel at right angles to the surface.
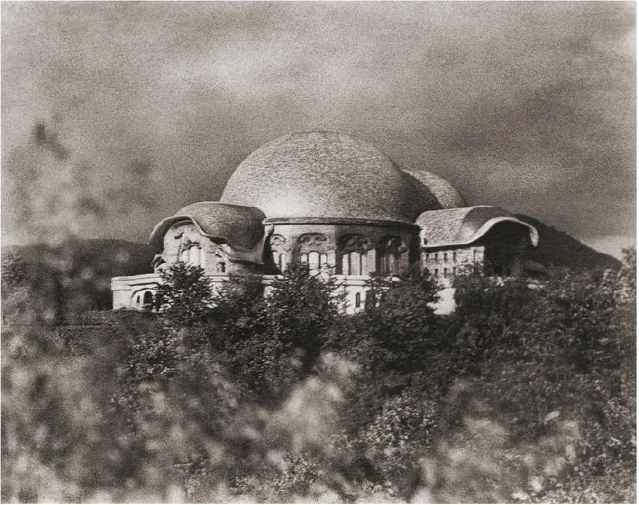
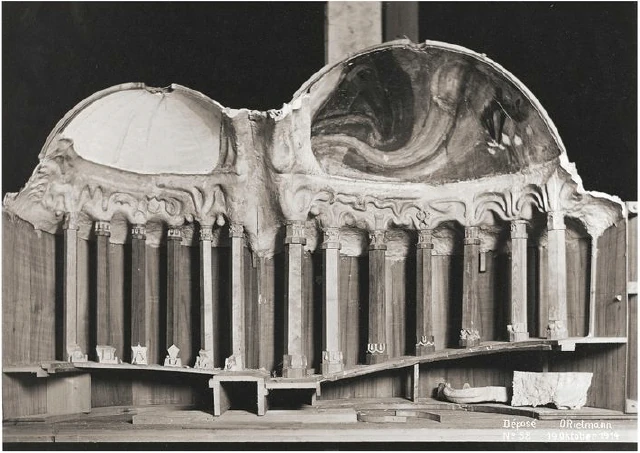
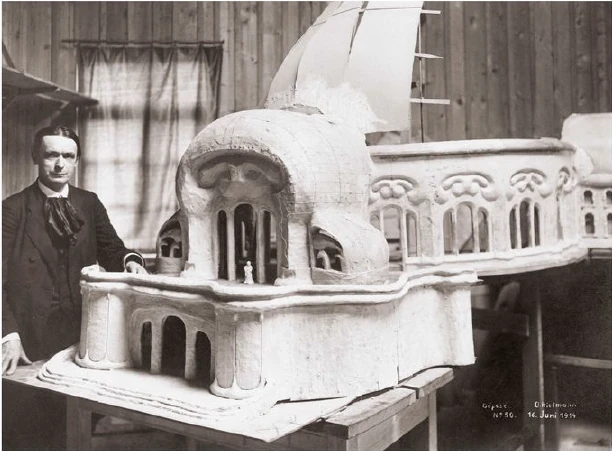
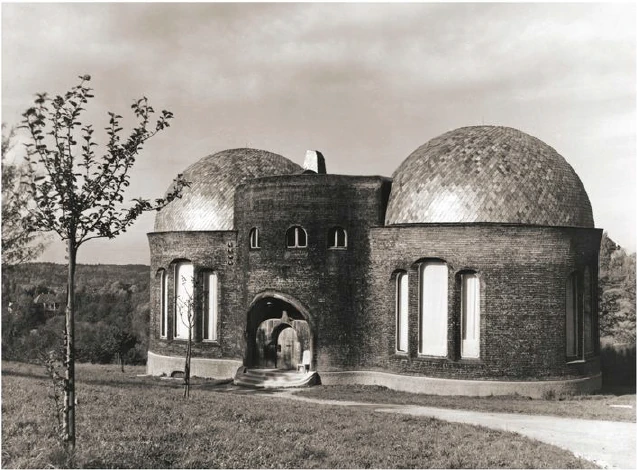
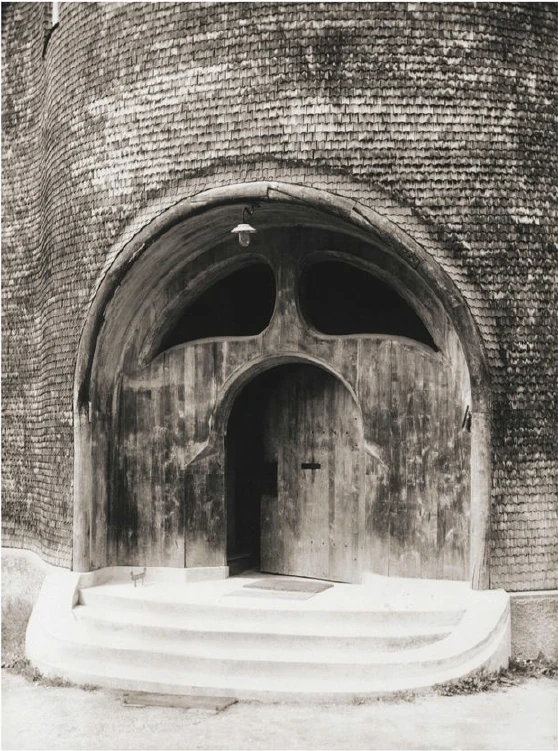
It would have been my wish—only it was not to be—that we should have had no such surfaces as these (pointing to an architrave). They will only be right—when something is taken away from them. This roundness here must be eliminated. It would have been better if from the very beginning we had worked with the graver's chisel for then there would have been no protuberance but only a surface. What we must do is to feel from the models how the interior decoration is the plastic vesture for the Spiritual Science that is given its in the building. Just as the interior decoration has the quality of being ‘in-carved,’ so the outer decoration will seem as though it is ‘laid on.’ The interior decoration must always have the character of being in-carved. One can feel this in the model, for the essential thing is a true inner feeling for form in space. It is this that leaves one unsatisfied even in such writings as those of a man like Hildebrandt. He has a certain idea of the workings of form but what he lacks is the inner feeling of form—the inner feeling that makes one live wholly within the form. He simply says that the eye should feel at home when it looks at form. In our building we must learn to experience the forms inwardly, so that, holding the chisel in a particular way, we learn to love the surface we are creating—the surface that is coming into being under the mallet. I, for my part, must admit that I always feel as if I could in some way caress such a surface. We must grow to love it, so that we live in it with inner feeling and not think of it as something that is merely there for the eye to look at.
Just recently someone told me after a lecture that a certain very clever man had accused us of straining after ‘externalities,’ as instanced by the fact that different kinds of wood have been used for the columns in the interior. This shows how little our work has been understood. Such a thing is considered to be a dreadful externality. This very intelligent man, you see, simply cannot realise that the columns must be of different woods. The real reason why he cannot understand, is that he has not paused to consider what answer he would have to make if he were asked: ‘Why must there be different strings on a violin? Would it not be possible simply to stretch four A strings instead?’ The use of different woods is a reality in just the same sense. We could no more use only one kind of wood than we could have only A strings on a violin. Real inner necessities are bound up with this. One can never do more than mention a few details in these matters. The whole conception of our building and what must be expressed in it, is based upon deep wisdom, but a wisdom that is at the same time very intimate. Of course there will be forms which are nowhere to be found in the outer physical world. If anything bears an apparent resemblance to a form in the animal or human body, this is simply due to the fact that higher Spirits who work in nature, create according to these forces; nature is expressing the same things as we are expressing in our building. It is not a question of an imitation of nature, but of the expression of what is there as pure etheric form. It is as though a man were to ask himself: ‘What idea must I have of my own being when I look away from the outer sense-world, and try to find an environment that will express my inner being in forms?’ I am sure that everyone will be struck by the plastic forms on the capitals and in the rest of the interior. Not a single one of these forms is without its own raison d'étre. Suppose anyone is carving the column just here (pointing to an architrave motif). At another place he will carve more lightly or deeper down into the wood. It would be nonsense to demand symmetry. There must be living progression, not symmetry. The columns and architraves in the interior are a necessary consequence of the two circular buildings with the two incomplete domes. And I cannot express this any more precisely than by saying that if the radius of the small dome were at all larger or smaller in proportion to the large dome, each of these forms would have to be quite different, just as the little finger of a dwarf is different from that of a giant. It was not only the differences in dimension, but the differences in the forms that called forth the overwhelming feeling of responsibility while we were erecting the building; down to the smallest detail it could not be other than it is. Each single part of a living organism has to exist within and in accordance with the whole living organism. It would be nonsense to say: I want to change the nose and put a different organ in the place where the nose now is.' It is a matter of actual fact that the big toe, and the small toe as well, would have to be different if the nose were different. Just as nobody in his senses would wish to re-model the nose, so it is impossible that the form here should be other than it is. If this form were different, the whole building would have to be different, for the whole is conceived in living, organic form. The advance we must make is this: all that was, in the early days of art, a kind of instinctive perception of a human posture transformed into artistic form must now enter with consciousness into the feeling life of man. In this way we shall have, in our interior decorations, etheric forms that are true and living, and we shall feel them to be the true expression of all that is to live in our building. It simply cannot be otherwise.
Now the other day I received two letters from a man who, ten years ago, it is true, did belong to the Anthroposophical Movement, but who since then has left it. He asked me if he could be allowed to make the windows, for he was so well qualified for the work. He was really very insistent. But when you see the windows you will understand that they could only be made by somebody who has followed our work right up to the present. Suppose I were to press my hand into a soft substance: the impress could only be that of my hand, it could not be the head of an ox for instance! It is Spiritual Science that must be impressed into the interior decoration; and Spiritual Science must let in the sunlight through the windows in a way that harmonises with its own nature. The whole building is really constructed—forgive this analogy—according to the principle of the cake mould, only of course instead of a rising cake, it is filled with Spiritual Science and all the sacred things that inspire us. This was always the case in art, and above all it was so in the days when men perceived in their dim, mystical life of feeling the alternation of the principles of earth and sun in the living dance and then portrayed the dance in the palmette motif. So it must be when it is a question of penetrating the outer sense- veil of natural and human existence and expressing in forms things that lie behind the realm of sense perception—if, that is to say, we are fortunate enough to be able to carry this building through. How inner progress is related to the symptoms of onward-flowing evolution—this is what will be expressed in the building, in the dimensional proportions, forms, designs and paintings.
I wanted to place these thoughts before you in order that you may not allow yourselves to be misled by modern conceptions of art, which have put all true understanding on one side. A good example of this is the belief that the Corinthian capital arose primarily from the sight of a little basket with acanthus leaves around it. The truth is that something springing from the very depths of human evolution has been expressed in the Corinthian capital. So also we shall feel that what surrounds us in our building is the expression of something living in the depths of human nature behind the experiences and events of the physical plane.
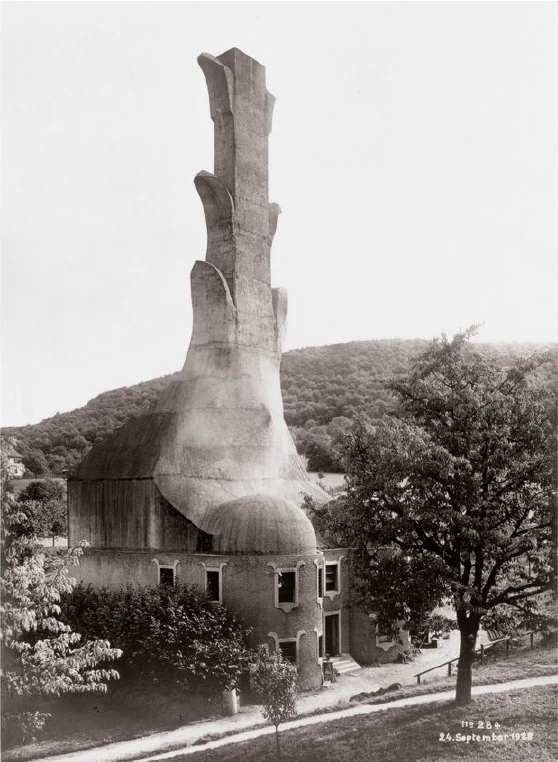
To-day I only wanted to speak of this particular detail in connection with our building and with a certain chapter in the history of art.
There may be opportunities during the coming weeks to speak to you of other things in connection with some of the motifs in the building. I shall seize every available opportunity to bring you nearer to what is indeed full of complexity, but yet absolutely natural and necessary, in a spiritual sense, for our building.
In our days it is not at all easy to speak about problems of art, for naturalism, the principle of imitation, really dominates the whole realm of art. So far as the artist himself is concerned, naturalism has arisen out of a very simple principle; so far as other people are concerned it seems to have arisen from something less simple. The artist, when he is learning must, of course, copy the productions of his master; he must imitate in order to learn. Man now imitates nature out of instinct—for he has made the principle of pupil into that of master and has then put the master on one side because he will brook no authority. This principle is very convenient for artists, for they do not want to get beyond an artistic reproduction of the models before them. The layman to-day understands the principle of naturalism as a matter of course. Where can he find anything to take hold of when he sees forms like those in our building? How are these forms to stimulate any thought at all? He will tear his hair and ask, with a shrug of his shoulders: ‘Whatever is this?’ And he will be lucky if he finds anything at all to take hold of, for instance, if he discovers that some detail has a slight resemblance, maybe to a nose! Although this may be negative, he is delighted that he has discovered anything at all. To-day the layman is pleased if when he finds in the different arts something that transcends the purely naturalistic element, he can say: ‘This has a resemblance to something or other.’ Art will most certainly be misunderstood if people continue to think that it is only legitimate to express things that resemble something or other in the external world. Real art does not ‘resemble’ anything at all; it is something in itself, sufficient unto itself. And again from this point of view it was despairing to find that as a result of the materialism of the second half of last century, painters (not to speak of sculptors) were asking themselves for instance: ‘How am I to get the effect of that mist in the distance?’ And then all kinds of attempts were made to reproduce nature by pure imitation. It really was enough to drive one to despair! Ingenious things were produced, it is true, but what is the value of them? It is all far better in nature herself. The artists were wasting their time in their efforts to imitate, for nature has it all in a much higher form. The answer to this problem is to be found in the Prologue to “The Portal of Initiation.” [The first of Dr. Steiner's Mystery Plays.]
Not long ago we happened to be going through the Luxemburg Gallery in Paris, and we saw a statue there. At first sight it was exceedingly difficult to make out what it was supposed to be, but by degrees it dawned on one that perhaps it was meant to represent a human figure. It was so distorted .... I will not imitate the posture, for it would be too much of a strain on the shoulders and knees! It is an absolutely hideous production, but I assure you that if it were to meet one in nature it would be much easier to understand than this “work of art.” People to-day do not realise the absurdity of giving plastic form to a motif that has been thought out, for there is, as a matter of fact, no real necessity to give it plastic form. That which is to be given plastic form must from the very beginning be there in itself and only conceived of plastically. No true sculptor will say that Rodin's productions are an expression of true plastic art. Rodin models non-plastic motifs very well, in an external sense, but true artistic feeling will always be prompted to ask if it amounts to anything, for true plastic conception is entirely lacking. All these things are connected, my dear friends. I have told you what happened in my young days, when I was about 24 or 25 years old, when I absorbed the doctrines of Semper. Already then they were enough to drive one to despair and their influence has not been got rid of yet. Therefore I ask you—and more particularly those who are working so devotedly and unselfishly at our building with all the sacrifices that their work entails—always to try to proceed from inner feeling for what this building ought to contain and to feel in life itself the forms which must arise, in order that we may free ourselves from the trammels of much so-called modern “art.” We must realise, in a new sense, that art is born from the depths of man's being. So greatly is this prone to be misunderstood in our age that people have taken the metamorphosis of of the Earth and Sun motifs to be an imitation of the acanthus leaf. If people will stop believing the anecdote quoted by Vitruvius, that Callimachos saw a basket strewn around with acanthus leaves and then used it as a motif on columns, and will listen to what he says about Callimachos having had a vision over the grave of a Corinthian girl, they will also realise that he had clairvoyant sight and they will have a better understanding of the evolution of art. They will realise that development of clairvoyance leads man to the realm lying behind the world of sense. Art is the divine child of clairvoyant vision—although it only lives as unconscious feeling in the soul. The forms that are seen by the clairvoyant eye in the higher worlds cast their shadow pictures, as it were, down to the physical plane.
When people understand all that lives in the Spirit—the Spirit which has the power to impress itself into what surrounds us here in our building, finding its expression in the outer framework around us—they will also understand the goal we have set ourselves, and see in the forms of art the impress of what has to be accomplished and proclaimed in living words in our building. It is a living word this building of ours!
Now that I have tried, scantily, it is true, to indicate something in regard to the interior we shall, before very long, be able to speak of the painting and also of the outside of the building.








4. Der Gemeinsame Ursprung der Dornacher Bauformen und des Griechischen Akanthusornamentes
Meine lieben Freunde! Ein Gedanke, der uns bei diesem Bau wohl oftmals kommen kann, das ist der Gedanke der Verantwortung, die wir zu tragen haben gegenüber den opferwillig dargebrachten Werten, welche unsere lieben Freunde zu diesem Bau zur Verfügung gestellt haben. Diejenigen, die sich einmal bekannt gemacht haben damit, wie groß eigentlich nach und nach diese Werte geworden sind, werden begreifen, daß gegenüber solcher Opferwilligkeit das richtige Äquivalent ein wirklich starkes Gefühl der Verantwortlichkeit sein muß, dahingehend, daß auch zustande gebracht wird dasjenige, was man erhoffen darf von diesem Bau.
Nun, jeder, der, ich möchte sagen, nur einmal einen Blick geworfen hat, gar nicht auf das Ganze, das man ja noch nicht überschauen kann, sondern nur auf das Einzelne, wird sich klar sein darüber, daß dieser Bau abweicht eigentlich von allem, was sich in der bisherigen Entwickelung der Menschheit als dieser oder jener Baustil darstellt, der nun einmal vor dem Urteil der Menschheit gerechtfertigt ist. Rechtfertigen kann ja eine solche Unternehmung selbstverständlich nur die Tatsache, daß das Gewollte annähernd gelingt. Aber jeder erste Anfang kann ja naturgemäß nichts anderes sein, als daß sozusagen das Gelingen nur in recht primitiver Weise eintreten kann. Gegenüber dem, was man etwa wollen könnte, wird dasjenige, was uns möglich sein wird zu vollbringen, nur ein kleiner, vielleicht winzig zu nennender Anfang sein. Aber man wird vielleicht doch in diesem Anfange die Linie sehen, nach welcher eine spirituelle Umgestaltung künstlerischer Stilmäßigkeit sich in der weiteren Zukunft der Menschheit vollziehen muß.
Allerdings müssen wir uns darauf gefaßt machen, meine lieben Freunde, daß wenn die Sache einmal fertig sein wird, insbesondere von sogenannter fachmännischer Seite die mannigfaltigsten Vorwürfe kommen werden und das hier Gemachte unsachgemäß, vielleicht sogar dilettantisch gefunden werden wird. Das alles wird uns aber nicht beirren können, denn es ist nur in der Natur der Tatsachen gelegen, daß fachmännische Urteile am wenigsten dann zurechtkommen, wenn irgend etwas als etwas Neues in die Welt gestellt worden ist. Wir werden uns aber nicht bedrückt fühlen gegenüber abfälliger Kritik, die gegenüber unserem künstlerischen Wollen auftreten könnte, wenn wir - ich möchte sagen, für uns selbst wie einen Trost für unser Verantwortlichkeitsgefühl - den Gedanken uns vor Augen führen, daß gerade in unserer Zeit im Grunde genommen die Entstehung der Künste, die Entstehung der einzelnen Formen und Motive der Künste, von fachmännischer Seite recht stark mißverstanden wird. Und da wird uns allmählich das Verständnis kommen, daß wir mit dem, was wir hier wollen mit diesem Bau, den, ich möchte sagen, «Urkräften künstlerischen Wollens» - wie es einem entgegentreten kann, wenn man auf die Entstehung der Künste einmal das geistige Auge lenkt - viel näher kommen, als ihm dasjenige nahekommt, was so vielfach als künstlerische Auffassung in der Gegenwart sich geltend macht. Man versteht heute wenig mehr von dem, was eigentlich einmal mit der künstlerischen Auffassung gemeint war im Entwickelungsgang der Menschheit. Daher braucht es nicht zu überraschen, wenn so etwas wie unser Bau, der wiederum im Einklang sein will mit dem Urwollen, mit der Entstehung der Künste, vielleicht gerade von denjenigen, die der Richtung und der Tendenz der Gegenwart huldigen, nicht gerade wohlwollend aufgenommen wird.
Ich möchte heute, um den Gedanken, den ich angedeutet habe, Ihnen näherzubringen, ausgehen von der Betrachtung eines sehr bekannten künstlerischen Motivs, des sogenannten Akanthusblattes, und möchte zeigen, wie das, was wir wollen, im vollen Einklang steht mit jenem Wollen sagen wir künstlerischem Wollen - der Menschheit, das sich ausdrückt in der Entstehung des Akanthusblattes. Nur muß das, was wir wollen, weil es selbstverständlich viele Jahrhunderte, ja Jahrtausende nach der Entstehung des Akanthusblattes liegt, eben etwas ganz anderes werden, als es damals geworden ist, da man das Akanthusblatt in die konrinthische Säule zum Beispiel eingefügt hat.
Meine lieben Freunde, wenn ich dabei kurz etwas Persönliches berühren darf, so möchte ich sagen, daß meine eigene Wiener Studienzeit gerade in diejenige Zeit der Wiener Entwickelung fiel, in welcher die großen Bauten, die Wien sein gegenwärtiges Gepräge gegeben haben - das Parlamentsgebäude, das Rathaus, die Votivkirche, das Burgtheater - ihre Vollendung gefunden haben. Die großen Baumeister dieser Bauten lebten noch: Hansen, der Regenerator, der Erneuerer der griechischen Architektur, Schmidt, der eigenartige Ausgestalter der Gotik, Ferstel, der die Votivkirche gebaut hat. Und bekannt wird ja vielleicht sein, daß das Burgtheater in Wien gebaut worden ist nach den Plänen desjenigen Künstlers, welcher dazumal in den siebziger, achtziger Jahren des vorigen Jahrhunderts für künstlerische Empfindung und künstlerische Ausgestaltung architektonischer, plastischer Formen tonangebend geworden ist: das Burgtheater ist ausgeführt nach den Plänen des großen Architekten Gottfried Semper. An der Hochschule hatte ich selbst zum Lehrer einen genialen Verehrer und Anhänger Gottfried Sempers in dem ausgezeichneten Ästhetiker Joseph Bayer, so daß ich dazumal leben durfte sozusagen in der ganzen Auffassung der Formenwelt, der architektonischen und plastischen Formenwelt und der Ornamentik, wie sie inauguriert worden ist durch den genialen Gottfried Semper.
Sehen Sie, meine lieben Freunde, es war dazumal etwas, ich möchte sagen, in der ganzen Atmosphäre der Anschauungen, die sich geltend machten auf der einen Seite, um zu begreifen das kunstgeschichtliche Werden, auf der andern Seite, um sich hineinzufinden in künstlerisches Gestalten, es war in der Atmosphäre der Auffassungen und Empfindungen dazumal etwas, das ich kurz so aussprechen möchte: es konnte einen zur Verzweiflung bringen trotz aller Genialität, die damals wirkte. Gottfried Semper war gewiß eine geniale Persönlichkeit, allein es hatte dazumal auch die ganze künstlerische Auffassung derjenige Zug der allgemeinen Menschheits- und Weltauffassung ergriffen, der hervorging aus der materialistischen Deutung des Darwinismus und der Entwickelungslehre. Und so konnte man immer wiederum das Materialistische auch in der Kunstauffassung dazumal hervortreten sehen. Da mußte man vor allen Dingen sich gut bekanntmachen mit den äußeren Techniken des Flechtens und Webens. Und aus der Art, wie, ich will sagen, Stoffe gewebt oder wie Zäune geflochten wurden, so daß man die einzelnen Stöcke in gewisser Weise ineinander zu stecken hatte, damit sie hielten und sich ineinander fügten, wurden erst abgeleitet die architektonischen Formen; so daß man förmlich eingepfropft bekam den Satz: das Ornament ist eine Form der äußeren Technik.
Ich deute damit etwas an, was weiter ausgeführt werden könnte, doch jetzt will ich nur auf merksam machen auf den Zug der Zeit, der sich damals geltend machte: alles, was künstlerisch ist, schließlich zurückzuführen auf das Äußere der Technik. Ich möchte sagen, man war auf einen gewissen Utilitätsstandpunkt gekommen, und das Künstlerische sah man an wie eine Weiterführung desjenigen, was sich ergab aus dem, wie man die Dinge gebrauchte. Daher hörte man in der damaligen Zeit auf Schritt und Tritt, wo es um künstlerische Themata sich handelte, besonders um Themata des Ornamentes, immer wiederum von den Eigenarten der Techniken sprechen.
Nun, das alles war gewissermaßen nur eine Nebenströmung der großen materialistischen Strömung, die im 19. Jahrhundert waltete und die man nennen könnte: die materialistische Auffassung des Künstlerischen überhaupt. Wie sich das Materialistische eben in der zweiten Hälfte des 19. Jahrhunderts auf allen Gebieten besonders geltend machte, das war eine Auffassung, die einen in der Tat zur Verzweiflung brachte. Denn wirklich, ich erinnere mich noch, wie viele schlaflose Nächte in jener Zeit mir das korinthische Kapital gemacht hat. Nicht wahr, dieses korinthische Kapital, das hat ja zu seinem Hauptteil, zu seinem Hauptschmuck sagen wir - obwohl es in der Zeit, von der ich spreche, fast verboten war, von Schmuck zu sprechen - das Akanthusblatt. Was lag selbstverständlich näher als zu sagen: Nun, das Akanthusblatt, auch das der korinthischen Säule, ist einfach entstanden durch naturalistische Nachahmung des Blattes der Akanthuspflanze, die man ja überall findet. - Nun, für denjenigen, der künstlerisches Empfinden hat, ist es wirklich ein hartes Stück, sich vorzustellen, daß irgendeinmal begonnen worden sein soll damit, daß man sozusagen ein Unkrautblatt genommen habe, eben ein Akanthusblatt, und daß man das plastisch ausgestaltet und an die korinthische Säule angeklebt habe.
Nehmen wir einmal, um uns zu orientieren, die Form des Akanthusblattes. Ich möchte es gewissermaßen schematisch aufzeichnen, dieses Akanthusblatt. So etwa ist dieses Blatt von Acanthus spinosus, der gewöhnlichen Bärenklaue, geformt:

Das soll also dazu gedient haben, plastisch ausgestaltet und in dieser Ausgestaltung an die korinthische Säule geklebt zu werden.
Nun kommt allerdings etwas anderes noch dazu. Nämlich Vitruv, der bedeutende Bearbeiter der künstlerischen Traditionen des Altertums, bringt eine Anekdote, die sehr bekannt ist, und diese Anekdote hat mit dazu geführt, die «Korbhypothese» des korinthischen Säulenkapitäls zu begründen. Man kann sie schon so nennen, denn wozu wurden nach und nach für die materialistische Kunstauffassung die Kapitale der korinthischen Säulen? Zu Körbchen, die ringsherum von Akanthusblättern getragen waren. Man kann, wenn man den Dingen genauer nachgeht, den Eindruck bekommen, daß hier etwas Symptomatisches, Bedeutsames vorliegt. Denn gerade an diesem Punkte zeigt es sich, daß das Verständnis der feineren spirituellen Zusammenhänge der Menschheitsentwickelung den nachforschenden Menschen einen «Korb» gegeben hat und gleichsam wie eine Art Denkmal dieses «Korbes»> steht diese Korbhypothese der korinthischen Säulenkapitäle da.
Was erzählt Vitruv denn eigentlich? Er erzählt, daß Kallimachos, der korinthische Bildhauer, einmal ein irgendwie zufällig dastehendes Körbchen gesehen habe, und am Grunde dieses Körbchens seien ringsherum diese Akanthusblätter gewachsen. - Also sagt man: Kallimachos habe angeschaut ein Körbchen, umgeben von Akanthusblättern, und habe gesagt: Ja, das gibt das korinthische Kapital. - Das ist der reinste Materialismus, den man sich denken kann. Nun, ich werde gleich nacher sagen, wie es sich mit dieser Vitruvanekdote eigentlich verhält, was sie für eine Bedeutung hat.
Die Hauptsache, die hier zugrunde liegt, ist diese, daß man allmählich - und im Laufe der neueren Zeit im Grunde genommen ganz - verloren hat das Verständnis für das innere Prinzipielle des künstlerischen Schaffens. Und wenn man dieses innere Prinzipielle des künstlerischen Schaffens nicht wieder finden wird, wird man eigentlich das, was mit den Formen gewollt ist, was den Formen unserer Kapitale, ja den Formen unseres ganzen Baues zugrunde liegt, niemals verstehen. Die Menschen, welche - jetzt symbolisch gesprochen - der «Korbhypothese» huldigen, werden uns niemals richtig verstehen können.
Dasjenige, was allem künstlerischen Schaffen zugrunde liegt, ist ein Bewußtsein, welches, ich möchte sagen, vor den Pforten der historischen Entwickelung der Menschheit - der äußeren historischen Entwickelung, die durch äußere Dokumente festgelegt ist - haltmacht. Ein gewisses Bewußtsein, das vor den Pforten dieser historischen Entwickelung im Menschen tätig war, und das noch ein Überbleibsel des alten Hellsehertums der Menschheit war, das war etwas, was ebenso dem vierten nachatlantischen Zeiträume angehörte. Wenn auch die ägyptische Kultur dem dritten nachatlantischen Zeiträume angehört, so ist doch das, was zur Kunst hintendiert in der ägyptischen Kultur, dem vierten nachatlantischen Zeiträume angehörig. Im vierten nachatlantischen Zeiträume hat sich dieses Bewußtsein so geltend gemacht, daß inneres Gefühl, innere Empfindung des Menschen Platz gegriffen hat, - so Platz gegriffen hat, daß man fühlte, wie die Bewegung des Menschen, wie Haltung und Geste die menschliche Form und die menschliche Figur herausentwickeln aus dem Ätherischen ins Physische.
Sie werden mich verstehen, wenn Sie sich darüber klar sind, daß für jene Zeiten mit einer, ich möchte sagen, richtigen Auffassung des künstlerischen Wollens, viel wichtiger als die Anschauung einer Blume oder einer Ranke das Gefühl war: ich muß etwas tragen, schwer tragen; ich beuge den Rücken und mache mit meiner menschlichen Figur die Kraftentwickelung, die mich Menschen nötigt, mich so zu bilden, um die Last zu tragen.

Man fühlte in sich gewissermaßen das gebildet, was man in der eigenen Geste ausführen muß. Und so führte man die Greifbewegung, so zum Beispiel auch das Tragen mit der Hand, aus. Man fühlt dieses Tragen mit den Händen, wo man nötig hat, die Hände nach auswärts zu spreizen. Da entstanden die Linien und Formen, die ins künstlerische Gestalten übergingen. Man fühlt sozusagen an der eigenen Menschlichkeit, wie der Mensch über das, was er mit den Augen sieht und mit den übrigen Sinnen wahrnimmt, hinausgehen kann, wenn er sich einfügt einem Allgemeinen. Und ich möchte sagen: schon bei diesem Allgemeinen, wenn man nicht mehr bloß hinzuschlendern braucht, sondern genötigt ist, sich zu fügen dem Tragen einer Last, da ordnet man sich ein dem Organismus der ganzen Welt. Und aus dem Fühlen solcher Linien, die man in sich selber zu bilden hat, entstanden jene Linien, die zur künstlerischen Gestalt führten. Das sind Linien, die nicht in der äußeren Wirklichkeit zu finden sind.
Nun tritt einem in der spirituellen Forschung eines oftmals entgegen. Ich möchte sagen, wie ein wunderbares Akashabild tritt einem immer wiederum entgegen das Einfügen einer Anzahl von Menschen in ein Ganzes, aber ein gesetzmäßiges, harmonisches Einfügen von Menschen in ein Ganzes. Denken Sie sich das etwa so: Wir hätten eine Art Bühne, rings herum, wie amphitheatralisch, Sitze, wo Zuschauer sind, und es würden Menschen einen Umgang formieren. Die gehen herum im Innern, sie haben einen Umgang zu formen. Nicht etwas naturalistisch Gebildetes, sondern etwas Höheres, Übersinnliches sollte vor des Menschen Auffassung treten. Denken Sie sich, das ist in der Aufsicht gezeichnet:
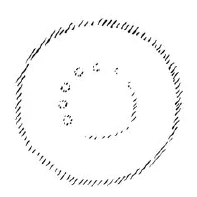
Ich zeichne es nun in der Seitenansicht, also schematisch: Eine Anzahl von hintereinander gehenden Menschen. Die bilden sozusagen den Umzug, der da im Kreise herumgeht; die andern sitzen im Kreise und schauen zu.

Nun handelt es sich darum, daß diese Personen etwas Wichtiges darstellen, etwas, was es sozusagen nicht ausgebildet gibt auf der Erde, sondern wovon es auf der Erde nur Analogien gibt, daß sie etwas darstellen, was den Menschen in Zusammenhang brachte mit dem großen Weltenzusammenhang. Und da liegt nun ja nahe, vor diesen Menschen der damaligen Zeit darzustellen das Verhältnis der Erdenwirkungen zu den Sonnenwirkungen. Wie kann der Mensch fühlen das Verhältnis der Erdenwirkungen zu den Sonnenwirkungen? Wenn er es ähnlich fühlt, wie man fühlen kann zum Beispiel das Getragensein, das heißt, wenn man eine Last trägt. Man kann also fühlen das Verhältnis der Erden- zu den Sonnenwirkungen so: Alles Irdische steht nur eben auf der Bodenfläche der Erde auf, und indem es sich von der Erde entfernt - das alles ist eigentlich nur in Kräften gedacht -, spitzt es sich zu. Also man fühlte sozusagen das Verbundensein des Menschen mit der Erde dadurch, daß man ein nach unten Breites und nach oben sich Zuspitzendes darstellte. Gar nichts anderes! Das heißt, indem man diese Kraftwirkung so fühlte, sagte man: ich fühle mich stehen auf der Erde.
Nun wurde der Mensch ebenso gewahr seine Zugehörigkeit zur Sonne. Dieses Hereinwirken der Sonne auf die Erde, man fühlte es, indem man die Kraftlinien eben so gestaltete, daß die Sonne, indem sie um die Erde herumgeht, in dieser Weise ihre Strahlen der Reihe nach hereinsendet, sie nach unten zuspitzend, weil die Sonne scheinbar um die Erde herumgeht.

Denken Sie sich diese beiden Darstellungen in Abwechslung, so können Sie sehen das Erdenund das Sonnenmotiv, das von diesen umhergehenden Menschen immer getragen wurde. Das gehörte zu dem, was in alten Zeiten im Umgang vorgeführt wurde. Da saßen die Menschen herum, und da gingen herum die Darsteller. Die einen trugen das Erdenmotiv, die andern gleichsam dasjenige, was man als Hinaufleben zur Sonne darstellte, denn so konnte man das Hereinstrahlen des Sonnenmäßigen auch darstellen. Und sie wechselten ab: Erde - Sonne, Erde - Sonne, und so weiter.

Diese Kraft, ich möchte sagen, diese kosmische Kraft: Erde - Sonne, fühlte man. Dann erst dachte man darüber nach, wie man das nun am besten machen könnte. Und da stellte sich heraus, daß man als Mittel, gleichsam als ein Kunstmittel, um das am besten zu machen, am besten eine solche Pflanze oder einen solchen Baum verwendet, der seine Wipfelentfaltung nach oben so hat, daß er unten breit ist und nach oben spitz zuläuft, und daß man dann abwechselt mit Palmen. So daß sich herausbildete das Hintereinandertragen von solchen Pflanzen, die etwas wie breite Knospen darstellen, welche sich nach oben zuspitzen, und von Palmen. Palmen als Entfaltung der sonnenhaften Kräfte, und nach oben sich zuspitzende Knospen als charakteristisch für die Erdenkräfte.
Man produzierte sozusagen, indem man fühlen lernte das Hineingestelltsein in den Kosmos als Mensch, gewisse Formzusammenhänge, und man benützte nur die pflanzlichen Mittel zur Darstellung. Man griff dabei, um das nicht künstlerisch erst fabrizieren zu müssen, zu den pflanzlichen Mitteln. Aus dem lebendigen Erfühlen des Weltenzusammenhanges heraus ist das künstlerische Schaffen entstanden, das deshalb auch einem Entfalten des Schaffensdranges entspricht, der im Menschen liegt, und nicht einer bloßen Nachahmung irgendeines bloß äußerlich Natürlichen entspricht. Alles äußerlich Natürliche ist lediglich, indem es künstlerisch nachgeahmt wurde, erst später in die Kunst hineingekommen. Als man nicht mehr gewußt hat, daß man Palmen genommen hat, um Sonnenkräfte auszudrücken, da hat man, indem man einen solchen Zweig aufgemalt hat, geglaubt, die Alten hätten die Absicht gehabt, eine Palme zu kopieren. Das war aber niemals der Fall, sondern sie haben die Palmen verwendet, weil sie die Sonnenkräfte darstellten. So ist alles wirkliche künstlerische Schaffen hervorgehend aus einer in der menschlichen Natur steckenden Überfülle von Kräften, die im äußeren Leben nicht zum Ausdruck kommen können, die sich daher ausleben wollen, indem der Mensch sich bewußt wird seines Zusammenhanges mit dem Weltenganzen.
Nun beirrte alles Nachdenken und Empfinden - sowohl gegenüber der Naturwissenschaft, wie auch gegenüber dem Künstlerischen -, es beirrte alles Empfinden und Vorstellen ein Gedanke, der aus der Menschheit recht schwer auszutreiben sein wird. Das ist der Gedanke, daß alles Komplizierte aus Einfachem entsteht. Das ist nicht wahr! Das menschliche Auge zum Beispiel ist in seiner Konstruktion viel einfacher als das Auge vieler niederer Tiere. Die Entwickelung geht vielfach so vonstatten, daß das Komplizierte vereinfacht wird, daß das Verschlungene zur geraden Linie abgerundet wird. Das Vereinfachte ist vielfach in der Entwickelung das Spätere. Erst wenn man das einsehen wird, wird man einen richtigen Begriff von wahrer Entwickelung erlangen.
Dasjenige, was sich nun damals den Menschen darbot, und was alles für die Zuschauer ringsherum dargestellt wurde und durchaus die Darstellung von lebendigen kosmischen Kräften war, das wurde später vereinfacht zu jenem Ornamente, in dessen Linie man zusammenfaßte dasjenige, was damals der Mensch, indem er diese Dinge darstellte, lebendig erfühlte. Und wenn ich darstellen wollte, wie man zusammengefaßt hat aus dem Komplizierten der Menschheitsentwickelung ins Einfache die Linie zu einem Ornament, das zum Schmucke dienen soll, so könnte ich mich folgender Zeichnung bedienen:

Denken Sie sich das abwechselnd, so haben Sie die vereinfachte Wiedergabe jenes Umganges, den ich angeführt habe als Erdenmotiv, Sonnenmotiv - Erdenmotiv, Sonnenmotiv. Da haben Sie das, was der Mensch erlebt hat, zusammengefaßt in das ornamentartige Motiv. Dieses ornamentartige Motiv figurierte schon in der mesopotamischen Kunst und ist auch in die griechische Kunst herübergekommen als die sogenannte Palmette, in dieser oder einer ähnlichen Form, die dem Lotosblatt ähnlich ist.
Diese Abwechslung von Erden- und Sonnenmotiv, die bot sich sozusagen dem menschlichen Empfinden dar als Schmuckmotiv, als richtiges ornamentales Schmuckmotiv. Daß man in diesem ornamentalen Schmuckmotiv eine ins Unbewußte übergegangene Nachbildung eines uralten Tanzmotives, eines feierlichen Tanzes zu sehen hat, das wußte man später nicht mehr. Aber erhalten hat sich das im Palmettenmotiv.
Nun ist es interessant, das Folgende ins Auge zu fassen. Wenn Sie gewisse dorische Säulen betrachten, so finden Sie da, wo die dorischen Säulen bemalt worden sind, ein höchst interessantes Motiv, das ich in dieser Weise zeichnen möchte. Unter dem, was das Kapital zu tragen hat, finden wir folgendes: Hier würde der obere Wulst der dorischen Säule sein, hier unten aber finden wir bei gewissen dorischen Säulen als Malerei rund um die Säule herum nur etwas modifiziert angebracht das Erdenmotiv und das Sonnenmotiv. Oben haben Sie den dorischen Wulst, unten ringsherum gemalt die ornamentalen Motive zum Schmuck der Säulen. So sehen Sie tatsächlich an gewissen dorischen Säulen unten gemalt die Palmette, so ausgeführt, daß sie wirklich einen Umgang gibt: Erde - Sonne, Erde - Sonne und so fort.
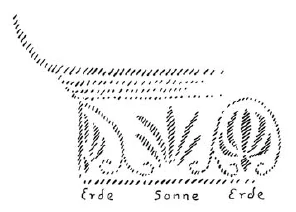
In Griechenland, dem vorzüglichsten Gebiete, in dem der vierte nachatlantische Zeitraum zu seinem vollen Ausdruck kam, vermählte sich nun das, was aus Asien herüberkam, mit all dem, was ich jetzt erzählt habe, und was in Griechenland an dorischen Säulen in Nachbildung sichtbar ist, mit dem eigentlich dynamisch-architektonischen Prinzip des Tragens, weil in Griechenland zunächst die Erfassung des Ich im menschlichen Leibe in vollkommenster Weise zum Ausdruck kam. Und deshalb war es in Griechenland, wo ein solches Motiv zum Ausdruck kommen konnte: daß das Ich, wenn es im Leibe ist, sich verstärken muß, wenn es eine Last trägt. Das Ganze fühlt man in der Volute:

Dieses Starkmachen, das ist dasjenige, was man in der Volute fühlt. Den Menschen, indem er sein Ich verstärkt im vierten nachatlantischen Zeitraum, den sehen wir ausgedrückt in der Volute. Und so gewinnen wir die Grundform der ionischen Säule, ich möchte sagen, wie wenn der Atlas die Welt trägt, aber noch unausgebildet, indem die Volute zum Träger wird.
Nun brauchen Sie sich nur vorzustellen, daß das, was in der ionischen Säule nur angedeutet ist, das Mittelstück, nach unten sich zur vollständigen Volute ausbildet, dann haben Sie die korinthische Säule: nichts anderes, als die Mittelstücke gleichsam nach unten ausgedehnt, so daß die Natur des Tragens zur Vollständigkeit wird. Und nun denken Sie sich dieses Tragende als plastisches Gebilde, dann haben Sie gleichsam die in sich gekrümmte Menschenkraft. Das Ich umgebogen, hier Last tragend.
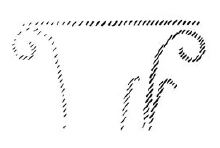
Ein künstlerisches Prinzip liegt nun darin, meine lieben Freunde, daß man dasjenige, was irgendwie ausgebildet ist im Großen, im Kleinen, en miniature wiederholt, oder umgekehrt. Wenn Sie sich nun die korinthische Säule so ausgebildet denken, daß sie hier die haupttragende Volute hat, und Sie wiederholen nun dieses künstlerische Motiv hier, wo es nur zum Schmuck dient, so haben Sie gleichsam plastisch eingefügt dasjenige, was das ganze Kapital ist, noch ringsherum im Schmuck. Und jetzt denken Sie sich, daß sich vermählt das dorische Malmotiv, das hervorgegangen ist aus der ornamentalen Nachmalerei des vorgeführten uralten Sonnenmotivs, vermählt mit dem, was an der korinthischen Säule angebracht ist, denken Sie sich, daß die Intuition entsteht, das, was ringsherum ist, ähnlich zu gestalten dem, was man früher gemalt hat: und man hat das Gemalte der dorischen Säule plastisch ausgestaltet. Ich kann das dadurch versinnlichen, daß ich das plastische Motiv zunächst Ihnen zeige, an das ich angemalt habe die Palmette [siehe Abbildung 8]. Der Drang ist entstanden, die Palmette zu sehen an dem Motiv, das sich hier so ergeben hat. Es ist aber nicht zu einem solchen Anmalen dieses Tragmotivs gekommen, sondern es ist dazu gekommen, daß man, was man dorisch bloß gemalt hat, korinthisch plastisch gestaltet hat; das heißt, man hat hier plastisch ausgestaltet, und ließ das Palmettenblatt bis unten hin gehen. Links habe ich gezeichnet eine Palmette [siehe Abbildung], rechts den Anfang, der entsteht, wenn die Palmette plastisch ausgestaltet wird. Da würde, wenn ich weiter fortfahren würde, die dorische gemalte Palmette in die korinthische plastische Palmette ausgestaltet. Und so würden wir, wenn ich nicht die Palmette malen würde, überall bekommen das Akanthusblatt.
Das Akanthusblatt entsteht, indem die Palmette plastisch umgewandelt wird. Also aus dem Drang, hier die Palmette nicht aufzumalen, sondern sie plastisch zu gestalten, ergibt sich diese Form; und aus dem bloßen Träger wird, indem man immer mehr in Komplikationen übergeht, dasjenige, wovon es einem Menschen ein Gefühl sein kann zu sagen: das hat eine gewisse Ähnlichkeit mit dem Akanthusblatt. Und man hat diese Sache, die man früher selbstverständlich nicht Akanthusblatt genannt hat, von da an Akanthusblatt genannt. Aber der Name hat mit dem, was dargestellt wurde, ebensoviel zu tun wie mit der Lunge und den Lungenflügeln der Ausdruck «Flügel». Und das ganze Unsinnige der naturalistischen Nachahmung des Akanthusblattes entfällt, weil dasjenige, was man Akanthusblatt nennt, gar nicht entstanden ist aus der naturalistischen Nachbildung des Akanthusblattes, sondern durch Umbildung des alten Sonnenmotivs, der Palmette, die man plastisch gemacht, statt daß man sie gemalt hat. So sehen Sie, daß aus einem inneren Erfassen desjenigen, was mit der Geste des menschlichen Ätherleibes zusammenhängt — denn damit hängt die Bewegung einer Kraftlinie zusammen, die man an sich selbst auszuführen hat -, durch die Wahrnehmung dessen, was aus dem menschlichen Ätherleib fließt, wirklich diese künstlerischen Formen geflossen sind.
Meine lieben Freunde, was an der Kunst künstlerisch ist, das hat mit Naturnachahmung so wenig zu tun, wie etwa in der Musik man mit Naturnachahmung etwas machen kann. Auch in den sogenannten nachahmenden Künsten ist dasjenige, was nachgeahmt wird, etwas im Grunde genommen Nebensächliches, Sekundäres, etwas Zweitrangiges. Daher ist alles naturalistische Empfinden dem wahren künstlerischen Empfinden eigentlich schnurstracks zuwiderlaufend. Und wenn man unsere Formen vielleicht grotesk finden wird, so werden wir uns damit trösten können, daß diejenige künstlerische Auffassung, welche diese Formen grotesk findet, es glücklich dazu gebracht hat, das Akanthus-Kapitälmotiv, das rein aus dem Geiste heraus geschöpft ist und in seiner weiteren Fortbildung eine entfernte Ähnlichkeit mit dem Bärenklaublatt erlangte, dieses Motiv aufzufassen gerade als naturalistische Nachahmung des Bärenklaublattes. Künftige Zeiten künstlerischer Auffassung werden solche Dinge gar nicht mehr verstehen können, die in unserer Zeit nicht nur etwa die Kunstgelehrten beherrschen, welche die Kunst verstehen sollten, sondern die wirklich auch das künstlerische Schaffen beherrschen. Dasjenige, was im materialistischen Darwinismus nachwirkt als materialistische Auffassung, das tritt auch im künstlerischen Schaffen uns entgegen, indem man die Kunst immer mehr zur bloßen Nachahmung des Natürlichen machen will. Ich möchte sagen, meine lieben Freunde, ich fühle mich glücklich in der Einsicht dieses Zusammenhanges gegenüber dem Akanthusblatte; denn es gibt dieses tatsächlich Aufklärung darüber, daß auch die Urformen des künstlerischen Schaffens aus der menschlichen Seele herausgequollen und nicht durch Nachahmung eines Äußeren entstanden sind.
Im Grunde genommen konnte ich so gründlich hineinsehen in die Urform des Künstlerischen auch erst, nachdem ich selber unsere Formen hier gebildet habe. Wo man solche Formen fühlt, wo man aus dem Urquell des Menschentums Formen zu schaffen hat, da fühlt man, wie im Grunde genommen in derselben Weise auch das künstlerische Schaffen in der Menschheitsentwickelung seinen Anfang genommen hat. Es ist ein eigentümliches Karma, daß während ich tief beschäftigt war - aber nachdem schon die Formen unseres Baues fertig waren -, eine künstlerische Intuition zu verfolgen - die sich im Jahre 1912 während der Berliner Generalversammlung ergeben hatte -, daß ich da, während ich sie in der Anlage verfolgte, nun, um mehr zu verstehen, dasjenige untersuchte, was ich mit den Formen gemacht habe. Denken über das, was als künstlerische Form entstehen soll, kann man erst hinterher. Wenn man sie erst versteht und nachher ausführt, dann werden sie sicher nichts nutzen. Schafft man aus Begriffen und Ideen heraus, dann wird es ganz gewiß nichts wert sein. Aber gerade das, was ich so recht anschaute und anschaulich machte an dem Akanthusblatte, und was ich an diesem als Irrtum zeigte, das gibt auch den inneren Zusammenhang dessen, was hier geisteswissenschaftlich walten wird, mit dem, was künstlerisch ausgedrückt wird mit unserem Bau.
Einen merkwürdigen Fall [von Übereinstimmung mit der äußeren Kunstforschung] fand ich, der allerdings nicht mit der Entwickelung zusammenhängt, wie ich sie eben gegeben habe. Sie ist nirgends zu finden, sie hat sich mir ergeben aus der hellseherischen Forschung heraus. Aber in einem Punkte fand ich hinterher einen merkwürdigen Zusammenhang mit meinem Landsmann im weiteren Sinne, Riegl. Er trägt schon den eigentümlichen Namen Riegl, der zwar nicht vornehm, aber um so österreichischer klingt. Dieser Riegl ist nicht auf sehr viel gekommen; aber als Konservator gerade eines Ornamentenmuseums in Wien hat sich ihm immerhin die Anschauung ergeben, daß diese Ornamente nicht so entstanden sind, wie es sich der «Semperismus» am Ende des 19. Jahrhunderts gedacht hat. Er kam auf Gedanken, die wirklich in der Linie liegen, in der die Umwandlung des Palmettenmotivs in das Akanthusmotiv liegt, so daß wirklich für diesen Punkt ein vollständiger Zusammenhang sich ergibt zwischen der okkulten Forschung, die sich mir ergeben hat in den letzten Tagen, und der äußeren Kunstforschung, die auch schon stößt auf diese Entstehung des sogenannten Akanthusblattes aus der Palmette. «Palmette» ist natürlich ebenso nur ein Wort; es ist in Wahrheit das Sonnen-Erdenmotiv, um das es sich handelt.
Natürlich bringt einen so etwas, was Riegl gegeben hat, erst recht wieder zur Verzweiflung. Denn er kann nicht einsehen, woher das Palmettenmotiv kommt und daß es zusammenhängt mit im Menschen wirkender, bewegender Kraft. Und so ist es denn erklärlich, daß man, ich möchte sagen, selbst im Kleinen bemerken kann, wie [beherrschend die materialistische Kunstauffassung geworden ist, denn wenn auch] der gute Riegl - obwohl er nicht auf sehr viel gekommen ist zwar, wenn ich den Ausdruck gebrauchen darf, «aufmuckt» gegen die Kunstgelehrten, die also gewissermaßen alles «versemperb haben und meistens Naturalisten sind, so sagt er doch, daß in bezug auf das Akanthusblatt alle Kunstgelehrten noch zehren von der alten Vitruvanekdote. Man kann aber nicht sagen, daß alle davon zehren. Man kann auch die Behauptung finden: Die alte Vitruvanekdote gilt nicht einmal als Anekdote, sie ist eine Erfindung des Kallimachos; sie wird aber immer Vitruv nacherzählt. - Bei Riegl wiederum - er deutet die Anekdote nur kurz an, sie sei zu bekannt, als daß er in alle Einzelheiten eingehen wolle - ist nur eine Merkwürdigkeit, und das ist das, was er ausläßt, und das ist nun sehr charakteristisch! Er deutet an - das übrige brauche man nicht auszuführen, es sei zu bekannt -, Kallimachos hätte eben ein Körbchen gesehen; ringsherum waren Bärenklaublätter, und da sei ihm der Gedanke an das korinthische Kapital aufgegangen. - Also auch Riegl läßt eines aus, und das zeigt, wie unsere Zeit zur Verzweiflung an der Erkenntnis auf solchem Gebiete kommen muß, wenn sie wirkliche Einsicht erstrebt; er läßt das aus, was zum Wichtigsten der ganzen Vitruverzählung gehört.
Was das Wichtigste ist, das ist nämlich dies, daß der Kallimachos das, was er sieht, auf dem Grabe eines korinthischen Mädchens sieht. Das ist das Allerwichtigste. Denn das besagt nichts Geringeres, als daß Vitruv, wenn er es auch weise verschweigt, andeuten will, daß Kallimachos ein Hellseher war, der über dem Grabe eines Mädchens aufstreben sah das Sonnenmotiv im Kampfe mit dem Erdenmotiv, und darüber das Mädchen sah, schwebend in reinem, ätherischem Leibe. Ja, da konnte einem eine Andeutung kommen, die man verwenden kann: nämlich das SonnenErdenmotiv zu dem Säulenkapitäl. Wenn man hellseherisch über dem Grabe einer jungfräulich Verstorbenen sieht, was im Ätherischen wirklich vorhanden ist, kann man verstehen, daß von der Palmette das Akanthusblatt geworden ist, ringsherumwachsend um den sonnenmäßig sich erhebenden Ätherleib des jungfräulichen Mädchens. Es ist, als ob die Menschen niemals die spätere römische Plastik der Pytri-Clytia mit verständnisvollem Blick angeschaut hätten, worin nichts anderes zu sehen ist in Wirklichkeit als eine hellseherische Impression, die man haben kann über den Gräbern gewisser Personen, wo, wie aus dem Blütenkelch, der Kopf herauswächst einer, wenn auch nicht jungfräulichen, so doch außerordentlich edlen Römerin.
Wir werden das, was der Erzählung des Vitruv zugrunde liegt, erst verstehen, meine lieben Freunde, wenn bei uns einmal das unglückselige Prinzip überwunden sein wird, das in der Frage liegt: «Was bedeutet dieses oder jenes®» Wenn dieses unglückselige Prinzip, das hinter jedem gleich eine Bedeutung sucht und sagt, das bedeutet den physischen, das den Ätherleib, das den Astralleib und so weiter, und das überall symbolische Bedeutungen sucht, wenn dies aus unserer Bewegung herausgebracht sein wird, dann wird man verstehen, was den künstlerischen Formen wirklich zugrunde liegt: entweder das unmittelbare Erfassen der eigenen geistigen Bewegung, oder die Anschauung des Ätherischen, wobei das eine mit dem anderen übereinstimmt.
In der Tat erscheint einem das Akanthusblatt, das sich richtig ausbildet in dem hellseherischen Bild, wenn es sich in richtiger Weise über einem Grabe zeigen kann.
Wenn Sie das alles zusammennehmen, meine lieben Freunde, werden Sie begreifen, wie notwendig es ist zum Verständnis der Formen, die unseren Innenraum auskleiden, oder, wenn ich das Wort gebrauchen darf, ihn schmücken sollen, daraufzukommen, welchem künstlerischen Prinzip sie entsprungen sind. Ich habe früher einmal den trivialen Vergleich gebraucht — den man nur zu verstehen braucht, wenn er auch trivial ist, so ergibt er doch das, was er geben soll -: Wenn man verstehen will, was in unserem Innenraum sein wird, in diesen zwei zusammengehörenden Halboder Dreiviertelbauten, so möge man sich erinnern an das Prinzip des Gugelhupftopfes, des Topfes, in dem man einen Napfkuchen bäckt.
In diesem Topf entsteht der Napfkuchen, und wenn der Gugelhupf herauskommt, zeigen sich an der Oberfläche des Gugelhupfes alle die Formen, die an den Wänden des Topfes im Negativ

Das Prinzip ist wirklich bei der Innendekoration des Baues richtig anzuwenden, nur daß eben nicht ein Gugelhupf drinnen sein wird, sondern daß lebend und webend drinnen sein soll das lebendige Wort der Geisteswissenschaft in der ihr möglichen Form. Das, was hier umschlossen ist in den Raumformen, was darin gesprochen und getrieben wird, soll sich so anpassen, wie sich der Napfkuchenteig anpaßt der Negativform des Napfkuchentopfes. Fühlen soll man in dem, was an den Wanden ist, das lebendige Negativ dessen, was da gesprochen und getan werden soll. Das ist das Prinzip der Innendekoration. Was ist eine solche Form? Eine solche Form ist nichts anderes als folgendes: Denken Sie sich einen Teil unseres lebendigen geisteswissenschaftlichen Wortes an diese Wände anstoßend, diese Wand in seinem ureigentlichen Wortsinne so aushöhlend - dann entsteht die Form, die dem Worte entspricht. Daher sind diese Innenformen auch so gebildet. Sehen Sie sich sie an. Wenn sie einmal ganz fertig sein werden, dann werden sie aus der Fläche herausgearbeitet sein, das werden die Formen der Baudekorationen. Diese Formen sind alle in die Fläche hineingearbeitet. Daher war es mir wenigstens von Anfang an recht, daß wir so arbeiteten, daß, wenn wir hier mit Hohleisen und Schlegel arbeiten, wir von vorneherein eine Fläche haben, mit der linken Hand das Stemmeisen in der Richtung schlagend, in der die Fläche zuletzt liegen muß. So schlagen wir von vornherein in der Richtung. Andererseits halten wir das Grabeisen so, daß es senkrecht aufsteht.
Es wäre mir sehr lieb gewesen, aber es hat sich nicht durchführen lassen, wenn von Anfang an eine solche Fläche gar nicht entstanden wäre. [Am Architrav gezeigt!] Diese Fläche wird dann erst richtig werden, wenn hier noch etwas fort ist. Die Rundung hier muß noch fort. Es wäre besser gewesen, wenn man von Anfang an mit dem Grabeisen gearbeitet hätte, dann würde diese Rundung nicht entstanden sein, sondern von vorneherein eine Fläche. Worauf es ankommt, ist, daß man nach den Modellen fühlt, wie die Innendekoration die Hülle ist, die nach innen sich plastisch ausbildende Hülle für dasjenige, was uns erfüllt als Geisteswissenschaft in diesen Räumen; und wie die Innendekoration so ist, daß sie eigentlich eingegraben ist, so wird die äußere Dekoration so wer- * den, daß etwas aufgetragen ist. Das Innere muß immer den Charakter des Hineingegrabenen tragen. [Beim Arbeiten] am Modell konnte man es so empfinden, denn es handelte sich wirklich um räumlich formgemäßes innerliches Empfinden.
Das ist dasjenige, was heute unbefriedigt läßt, selbst bei einer solchen Schrift wie die von Adolf Hildebrand. Der Mann hat gewisse Begriffe von Formwirkung; aber das, was ihm fehlt, das ist das innerliche Durchfühlen der Form, so daß man in der Form drinnensteckt, während für Hildebrand das Auge sich der Form gegenüber befindlich fühlen soll. Hier [es wird auf eine Form gedeutet] soll es so sein, daß man die Form innerlich erlebt, so daß man, indem man das Grabeisen in gewisser Weise hält, lieben lernt die Fläche, die man hier ausführt, die man hier mit dem Schlegel entstehen läßt. Und ich muß gestehen, ich kann nicht anders, als eine solche Fläche immer etwas zu streicheln, wenn sie entstanden ist. Es handelt sich darum, daß man sie lieb gewinnen kann, so daß man in ihr lebt mit innerlicher Empfindung und nicht als etwas, was bloß mit dem Auge angeschaut werden soll.
Neulich hat einmal jemand nach einem Vortrag gesagt, ein sehr gescheiter Mensch hätte sich darüber aufgehalten, daß man so nach äußeren Dingen strebe; das habe sich ihm daran gezeigt, wie die Sache aufgefaßt wird; so zum Beispiel, daß die inneren Säulen von verschiedenen Hölzern sind. Das sei doch eine solche Außerlichkeit, da arbeite man mit ungeheuren Äußerlichkeiten. - Sehen Sie, der gescheite Mann kann nicht begreifen, daß die Säulen von verschiedenem Holz sein sollen. Aber der wirkliche Grund, warum er das nicht begreifen kann, ist der, daß er nicht nachdenkt darüber, was er zu denken hätte, wenn ihn jemand fragen würde: Wozu ist es notwendig, daß auf der Violine verschiedene Saiten sind? Man könnte ja bloß vier A-Saiten aufspannen! - Es handelt sich eben um Realitäten auch bei den verschiedenartigen Holzverwendungen. Sowenig wie auf einer Violine nur A-Saiten sein können, sowenig können wir nur eine Holzart haben. Das hängt mit realen inneren Notwendigkeiten zusammen.
Man kann von diesen Dingen immer nur bloß Einzelheiten andeuten. So ist es zum Beispiel etwas ungeheuer Weises und etwas zugleich recht Intimes, was der ganzen Auffassung unseres Baues zugrunde liegt und im Bau zum Ausdruck kommen muß: es kommen selbstverständlich lauter Formen zum Ausdruck, die es in der äußeren physischen Welt gar nicht gibt. Wenn sich etwas an einer Form mit etwas im tierischen oder menschlichen Leibe vergleichen läßt, so beruht das darauf, daß die höheren Geister, die in der Natur formen, nach diesen Kräften schaffen, so daß die Natur dasselbe ausdrückt, was wir ausdrücken hier an diesem Bau. Aber nicht um Nachahmung der Natur handelt es sich, sondern um den Ausdruck dessen, was wirklich als reine ätherische Form vorhanden ist, wie wenn etwa der Mensch sich sagt: Wie muß ich mich selber vorstellen, wenn ich jetzt absehen will von der äußeren Sinnenwelt, wenn ich eine Umgebung haben will, die mir in Formen ausdrücken soll mein Inneres?
Ich bin mir klar darüber, daß die plastischen Formen, die an den Säulenkapitälen und im weiteren Innenraum zum Ausdruck kommen, mancher kritisch anschauen wird, jedoch keine einzige dieser Formen ist ohne Begründung. Derjenige, der hier unten [es wird gezeigt auf ein Säulenmotiv] die Säule an dieser Seite mit Schlegel und Grabmeißel haut, der wird hier [an anderer Stelle] auch so hauen, daß er hier höher haut und hier tiefer. Ganz unsinnig wäre es, hier Symmetrie zu verlangen. Nicht Symmetrie, sondern lebendiger Fortschritt soll drinnen sein. Im Grunde genommen folgt aus der Tatsache, daß wir die zwei runden Bauten mit den zwei unvollkommenen Kuppeln haben, des Zusammenschließens eines größeren und eines kleineren Rundbaues mit Kuppel, auch alles in der inneren Auskleidung mit Säulen und Architraven. Und ich kann das nicht deutlicher aussprechen als indem ich sage: wenn nur der Radius der kleineren Kuppel um ein weniges größer oder kleiner wäre im Verhältnis zur größeren Kuppel, so müßten diese Formen, diese einzelnen Formen ganz anders sein, als sie hier aussehen; geradeso wie der kleine Finger eines Knirpses anders aussieht als der eines riesig gewachsenen Menschen.
Nicht nur die Größenunterschiede, sondern auch die Formunterschiede waren es, die, während wir die Formen zu entwickeln hatten, das ungeheure Verantwortungsgefühl hervorbrachten, daß tatsächlich bis in die Einzelheiten hinein alles so sein muß, wie es ist, genauso wie das einzelne Glied des lebendigen Organismus im lebendigen Organismus drinnen stehen muß und wie niemand sagen könnte: Ich möchte die menschliche Nase umformen, ich möchte da, wo jetzt die Nase ist, ein anderes Organ anbringen. - Sie würden sagen: das hat keinen Sinn. Aber es ist so: Die große Zehe müßte anders sein und die kleine auch, wenn die Nase anders wäre. Wie niemand die Nase umformen will, der bei gesunder Vernunft ist, so kann hier niemand irgendeine andere Form bilden als die, die hier ist. Wäre diese Form anders, so müßte der ganze Bau anders sein, denn das Ganze ist organisch lebendig gedacht in seinen Formen.
Darin besteht allerdings der Fortschritt, meine lieben Freunde, der zu machen ist, daß dasjenige, was in Urzeiten der Kunst gleichsam wie ein gedankenloses Wahrnehmen der menschlichen Geste empfunden worden ist und dann umgesetzt wurde in künstlerische Formen, daß das nunmehr wirklich bewußt in das menschliche Fühlen hereintritt, so daß wir jetzt in den Innendekorationen wirklich lebendige Ätherformen haben und wir empfinden: dasjenige, was leben soll in solchem Räume, muß wirklich hier sich so abdrücken. Wahrhaftig, es kann nicht anders ein.
Sehen Sie, in den letzten Tagen hat mir zweimal ein Mann geschrieben, der jetzt nicht mehr unserer anthroposophischen Bewegung angehört, der zwar früher mit uns verbunden war, aber seit zehn Jahren nicht mehr zu uns gehört. Er hat mir geschrieben, warum er nicht die Fenster machen dürfe, er könnte so etwas außerordentlich gut machen. Und er wurde wirklich recht zudringlich. Aber wenn Sie die Fenster einmal sehen werden, werden Sie einsehen, daß niemand die Fenster machen kann, der nicht bis zum letzten Augenblick, bis zum heutigen Tage mit uns gelebt hat. So wie sich in einer weichen Tonmasse nichts anderes abdrücken kann als meine Hand, wenn ich sie hineindrücke - wie das nicht ein Ochsenkopf sein kann —, so muß sich abdrücken in der Innendekoration dasjenige, was unsere Geisteswissenschaft ist, und so muß diese Geisteswissenschaft durch die Fenster hereinlassen das Sonnenlicht in solcher Weise, wie es dieser Geisteswissenschaft angemessen ist. Der ganze Bau ist wirklich - verzeihen Sie diesen trivialen Vergleich - nach dem Prinzip des Gugelhupfes, des Napfkuchens gebildet, aber so, daß nicht ein Kuchen sich darin bildet, sondern Geisteswissenschaft ihn erfüllt mit all ihrem Heiligen und ihrem Hehren, das uns beseelt. So war es immer wirklich in der Kunst. So war es dazumal, als die Menschen empfunden haben in ihrem dumpfen, mystischen, menschlichen Gefühl die Abwechslung von Erden- und Sonnenprinzip im lebendigen Tanz, beim ornamentalen Darstellen dieses Tanzes im Palmettenmotiv. So ist es auch da, wo durchdrungen werden muß die äußere sinnliche Hülle von Natur- und Menschensein, und wo gerade - wenn wir so glücklich sind, den Bau ausführen zu können - verschiedenes, was hinter dem sinnlich Wahrnehmbaren ist, in den Formen zum Ausdruck kommen soll. Wie das innere Fortschreiten Bezug hat zu den Symptomen, die von Evolution zu Evolution gehen, das wird sowohl an diesen Maß Verhältnissen als an den Formen oder am Zeichnerischen und Malerischen an diesem Bau wahrgenommen werden können.
Ich möchte sagen, deshalb wollte ich diese Betrachtung vor Ihnen anstellen, damit Sie sich nicht verleiten lassen sollen durch das, was moderne Kunstauffassung hervorgebracht hat. Sie hat von dem wirklichen Verständnis einen «Korb» bekommen. Das drückt sich in schöner Weise darin aus, dad man glaubt, daß das korinthische Säulenkapitäl ein von Bärenklaublättern umgebenes Körbchen sein soll. In Wahrheit ist aber etwas tief aus der Menschheitsentwickelung Entsprossenes im korinthischen Säulenkapitäl zum Ausdruck gekommen. So wird man in dem, was uns da umgibt, zum Ausdruck gekommen fühlen etwas, was da lebt in den Tiefen der menschlichen Natur, die hinter den Erlebnissen und Tatsachen des physischen Planes liegen.
Nur über diesen Punkt unseres Baues und im Zusammenhang damit über ein Kapitel der Kunstgeschichte wollte ich heute zu Ihnen sprechen, meine lieben Freunde.
Vielleicht bietet sich weiterhin Gelegenheit in den kommenden Wochen, über ähnliche Dinge in Anknüpfung an dieses oder jenes Motiv unseres Baues in solcher Weise zu Ihnen zu sprechen. Ich werde jede sich bietende Zeit benutzen, jede mögliche Gelegenheit ergreifen, die sich bieten kann, um durch solche Betrachtungen näher zu kommen dem, was wirklich als Kompliziertes, aber durchaus geistig Natürliches und Notwendiges unsern Bauformen zugrunde liegt.
In unserer Zeit ist es ja gar nicht leicht, über Kunstprobleme zu sprechen, da wirklich der Naturalismus, das Imitationsprinzip mit aller Kraft die Kunst beherrscht. Für die Künstler selbst ist der Naturalismus aus etwas höchst Einfachem gekommen - für die Künstler selbst -, für die anderen Menschen allerdings aus etwas weniger Einfachem. Der Künstler muß selbstverständlich, wenn er lernt, die Vorlagen seines Meisters nachbilden, er muß nachbilden, um etwas zu lernen. Und aus einem Instinktiven heraus - indem man das Schülerprinzip zum Meisterprinzip erhoben hat und den Meister beseitigt hat, weil man keine Autorität haben will - macht man das Schülerprinzip zum Meisterprinzip und imitiert die Natur. Für die Künstler ist das sehr bequem, weil die Künstler nicht weiter kommen wollen als bis zur künstlichen Nachahmung dessen, was ihnen ein Vorbild ist. Für den Laien liegt heute das Naturalistische noch viel näher.
Wo soll denn der Laie eigentlich einen Anhaltspunkt haben, was soll er denn um Gottes willen machen für seine naturalistische Beurteilung, um etwas denken zu können, wenn er solche Formen sieht? Hier wird er gezwungen sein, wenn er lauter solche Sachen sieht, sich an den Kopf zu greifen, er muß mit der Schulter zucken. Was ist denn das? wird er fragen. Er wird schon froh sein, wenn er irgendwo wenigstens einen Anhaltspunkt hat. Wenn er zum Beispiel findet: ein bißchen sieht das hier schon einer Nase ähnlich, wenn auch negativ, so ist er doch froh, wenigstens einen geringen Anhaltspunkt zu haben. Der Laie ist heute, wo ihm das fehlt in den verschiedensten Künsten, was hinter dem bloß Natürlichen liegt, unendlich froh, wenn er sagen kann: das sieht dem oder jenem ähnlich, ungeheuer froh ist er dann über das, was er da oder dort erkennt. Warum sollte es dann nicht auch zu der künstlerischen Verwirrung kommen können, dasjenige darzustellen, was nur einem Äußerlichen ähnlich schaut? Aber das wirklich Künstlerische schaut nicht einem andern ähnlich, sondern ist für sich selber etwas.
Und wiederum war es von diesem Gesichtspunkte aus, ich möchte sagen, zum Verzweifeln, als auch die künstlerische Praktik heraufkam infolge der materialistisch-künstlerischen Auffassung der zweiten Hälfte des vorigen Jahrhunderts, daß unsere Maler, von den Bildhauern gar nicht zu reden, sich eigentlich nur die Aufgabe stellten: wie kriege ich das heraus, was zum Beispiel dort als Dunstmasse in der Ferne erscheint?, als man die verschiedensten Versuche machte, herauszukriegen in reiner Imitation, was in der Natur gegeben ist. Es war zum Verzweifeln. Es kamen geniale Sachen zustande, aber wozu denn das alles wirklich? Es ist ja in der Natur trotzdem viel besser da. Die Künstler haben in diesem Bestreben, nachzuahmen, verspielt, es ist wirklich in der Natur besser da. Die Antwort darauf ist in dem Vorspiel zur «Pforte der Einweihung» zu finden.
Wir gingen kürzlich in Paris durch die Ausstellung des Luxembourg. Da stand etwas. Ja, es war zunächst recht, recht schwer zu entziffern, was das eigentlich war. Aber man konnte allmählich dahinter kommen: es soll doch vielleicht eine menschliche Gestalt vorstellen. Aber nun war diese Gestalt in sich so verrenkt - ich werde es nicht nachmachen, da man sich zu sehr anstrengen müßte, um die Schulter nicht mehr vom Knie unterscheiden zu können. Das Ding ist recht häßlich, aber ich kann Ihnen die Versicherung geben, selbst in dem Falle, wenn es einem in der Natur entgegentreten würde, würde es in der Natur noch leichter verständlich sein als in diesem «Kunstwerk». Es ist heute so, wie wenn man wirklich keine Ahnung davon hätte, [was plastisch dargestellt werden kann]; daß zum Beispiel irgendein Motiv, das man sich ausdenkt, ganz unsinnigerweise nun plastisch dargestellt wird, während gar keine Notwendigkeit da ist, das Motiv plastisch darzustellen. Was plastisch dargestellt werden soll, das muß von Anfang an in der Plastik drinnen gedacht sein und rur plastisch gedacht sein. So wird kein wirklicher Plastiker im künstlerischen Sinne zahlreiche von den Dingen, die Rodin gemacht hat, der Plastik zurechnen. Rodin ist ein Bildner von nicht plastischen Motiven, die er äußerlich genial macht, aber die Frage muß jedem künstlerischen Empfinden kommen: wozu das Ganze? - denn es ist nicht plastisch gedacht.
Das hängt alles zusammen, meine lieben Freunde [mit der allgemeinen materialistisch-naturalistischen Kunstauffassung. Erinnern Sie sich an das], was ich erzählt habe aus der Zeit als ich noch jung war. Ich war wirklich noch ein sehr junger Dachs, als ich den Semperismus aufzunehmen hatte, ich war höchstens 24 oder 25 Jahre alt. Aber es war dazumal schon so, daß es einen zur Verzweiflung bringen konnte, und das ist auch heute noch nicht ausgelöscht.
Daher bitte ich Sie, versuchen Sie immer wieder und wiederum, zuwege zu bringen — gerade diejenigen, die so hingebungsvoll, so opfervoll arbeiten an dem Bau, der so viel Opferwilligkeit unserer Freunde fordert -, auszugehen bei aller Formung von innerlicher Empfindung, von innerlichem Nachfühlen dessen, was da werden soll, und wirklich im Leben mitzuempfinden die Formen, die entstehen sollen, um uns frei zu machen von vielem, was man in der Gegenwart Kunst nennt. Dann wird vielleicht auch dasjenige als etwas Fruchtbares sich uns ergeben, daß wir in einem neuen Sinne wissen werden: Das ist Kunst, was in der Entstehung der Kunst aus den Tiefen der menschlichen Wesenheit herausgeboren ist, was man in unserer Zeit so mißverstehen kann, daß man das umgewandelte Erden-Sonnenprinzip als Nachbildung des Bärenklaublattes auf gefaßt hat. Wenn sich die Leute einmal herbeilassen werden, nicht zu glauben, daß die Anekdote des Vitruv darauf beruht, daß Kallimachos ein Körbchen gesehen habe und ringsherum Akanthusblätter, und daß er das, was er sah, an die Säule geklebt hat, sondern wenn man hinhorchen wird, wie Vitruv erzählt, daß Kallimachos das als Gesicht gehabt hat auf dem Grabe eines korinthischen Mädchens, dann wird man auch glauben können, daß er das hellseherisch gesehen hat, dann wird man auch zu besserem Verständnis der Kunstentwickelung kommen. Dann wird man einsehen, daß uns hellseherische Entwickelung hinaufführt in das Gebiet, das hinter dem sinnlichen Gebiete liegt. Und dann wird man auch sehen, daß das göttliche Kind der hellseherischen Anschauung wenn auch nur unbewußt in der Seele als Empfindung getragen - die Kunst ist, und daß diejenigen Gebilde, welche mit dem hellseherischen Auge in den höheren Welten geschaut werden, gleichsam die Schattenbilder herunterwerfen auf den physischen Plan.
Und wenn man an unserem Bau wird erfassen wollen dasjenige, was im Geiste lebt, und was die Kraft hat, daß es sich eindrückt dem, was uns als Hülle umgibt in unserem Bau, wenn man das sehen wird in dem, was ausgedrückt ist rund um uns herum in den äußeren Hüllen, dann wird man verstehen, was wir wollen, denn man wird in den Formen, die als künstlerische - ich möchte sagen - Eindrucksformen uns da umgeben, den Abdruck dessen sehen, was in lebendigen Worten getan, gesagt, gewirkt werden soll in unserem Bau. Ein lebendiges Wort ist es - ist unser Bau!
Habe ich so versucht, etwas, wenn auch nur spärlich, anzudeuten und über das Innere zu sagen, so werden wir demnächst auch etwas andeutend geben können über das Malerische und das Äußere.








4. The common origin of the Dornach building designs and the Greek acanthus ornament
My dear friends! A thought that may often occur to us in connection with this building is the thought of the responsibility we bear for the values that our dear friends have willingly sacrificed and made available for this building. Those who have become aware of how great these values have gradually become will understand that the right equivalent to such willingness to make sacrifices must be a truly strong sense of responsibility, so that what one may hope for from this building will also be achieved.
Well, anyone who has taken even a single glance, not at the whole, which cannot yet be surveyed, but only at the individual parts, will realize that this building actually deviates from everything that has been presented in the development of humanity to date as this or that architectural style, which is now justified in the judgment of humanity. Of course, such an undertaking can only be justified by the fact that what is intended is approximately successful. But every first beginning can naturally be nothing other than that success can only occur in a rather primitive way, so to speak. Compared to what one might want, what we will be able to accomplish will only be a small, perhaps tiny beginning. But perhaps we will nevertheless see in this beginning the line along which a spiritual transformation of artistic style must take place in the further future of humanity.
However, my dear friends, we must be prepared for the fact that once the work is complete, a wide variety of criticisms will be levelled at it, especially by so-called experts, who may find what has been done here inappropriate, perhaps even amateurish. But none of this will be able to deter us, for it is only natural that expert judgments are least apt to be correct when something new has been brought into the world. However, we will not feel depressed by disparaging criticism that may arise in response to our artistic intentions if we—I would like to say, for ourselves, as a consolation for our sense of responsibility—keep in mind that, especially in our time, the emergence of the arts, the emergence of the individual forms and motifs of the arts, is fundamentally misunderstood by experts. And then we will gradually come to understand that what we want to achieve here with this building, which I would describe as the “primordial forces of artistic ambition,” — as it can confront us when we turn our spiritual eye to the emergence of the arts — much closer than what is so often asserted as the artistic conception in the present. Today, we understand little more of what was actually meant by artistic conception in the course of human development. It should therefore come as no surprise that something like our building, which in turn seeks to be in harmony with the primal will, with the emergence of the arts, may not be received with particular goodwill by those who pay homage to the direction and tendency of the present.
Today, in order to bring you closer to the idea I have outlined, I would like to start by looking at a very well-known artistic motif, the so-called acanthus leaf, and show how what we want is in complete harmony with that will – let's say artistic will – of humanity, which is expressed in the emergence of the acanthus leaf. However, because what we want lies many centuries, even millennia, after the creation of the acanthus leaf, it must become something completely different from what it was then, when the acanthus leaf was incorporated into the Corinthian column, for example.
My dear friends, if I may touch on something personal for a moment, I would like to say that my own time as a student in Vienna coincided with the period of Vienna's development in which the great buildings that have given Vienna its present character—the Parliament building, the City Hall, the Votive Church, the Burgtheater—were completed. The great architects of these buildings were still alive: Hansen, the regenerator, the innovator of Greek architecture; Schmidt, the unique designer of Gothic architecture; Ferstel, who built the Votive Church. And it may be well known that the Burgtheater in Vienna was built according to the plans of the artist who set the tone for artistic sensibility and artistic design of architectural and sculptural forms in the 1870s and 1880s: the Burgtheater was built according to the plans of the great architect Gottfried Semper. At university, I myself had a brilliant admirer and follower of Gottfried Semper as my teacher in the excellent aesthetician Joseph Bayer, so that at that time I was able to live, so to speak, in the whole conception of the world of forms, the architectural and sculptural world of forms and ornamentation, as inaugurated by the brilliant Gottfried Semper.
You see, my dear friends, at that time there was something, I would say, in the whole atmosphere of the views that prevailed on the one hand, in order to understand the development of art history, and on the other hand, in order to find one's way into artistic creation, there was something in the atmosphere of the views and feelings at that time that I would like to express briefly: it could drive one to despair despite all the genius that was at work at the time. Gottfried Semper was certainly a brilliant personality, but at that time the entire artistic conception had also been influenced by the general view of humanity and the world that emerged from the materialistic interpretation of Darwinism and the theory of evolution. And so, once again, materialism could be seen to emerge in the artistic conception of that time. Above all, it was necessary to become well acquainted with the external techniques of braiding and weaving. And from the way in which, let us say, fabrics were woven or fences were woven, so that the individual sticks had to be inserted into each other in a certain way in order to hold and fit together, architectural forms were first derived; so that one was literally grafted with the phrase: ornament is a form of external technique.
I am hinting at something that could be elaborated further, but for now I just want to draw attention to the trend of the time: everything artistic can ultimately be traced back to the external aspects of technique. I would say that a certain utilitarian standpoint had been reached, and art was seen as a continuation of what resulted from the way things were used. That is why, at that time, whenever artistic topics were discussed, especially topics related to ornamentation, people always talked about the peculiarities of techniques.
Well, all of this was, in a sense, only a side stream of the great materialistic current that prevailed in the 19th century and which could be called the materialistic conception of art in general. The way in which materialism asserted itself in all areas in the second half of the 19th century was a conception that indeed drove one to despair. For really, I still remember how many sleepless nights the Corinthian capital caused me at that time. Isn't that right, this Corinthian capital, which has as its main part, its main ornament, let's say — although in the time I am talking about it was almost forbidden to speak of ornamentation — the acanthus leaf. What could be more obvious than to say: Well, the acanthus leaf, including that of the Corinthian column, simply arose from a naturalistic imitation of the leaf of the acanthus plant, which can be found everywhere. Well, for those with artistic sensibilities, it is really hard to imagine that it all began with someone taking a weed leaf, an acanthus leaf, so to speak, and sculpting it and sticking it onto the Corinthian column.
Let's take the shape of the acanthus leaf as a guide. I would like to sketch this acanthus leaf schematically, so to speak. This is roughly the shape of the leaf of Acanthus spinosus, the common bear's claw:

This is said to have been sculpted and glued to the Corinthian column in this form.
However, there is something else to consider. Vitruvius, the important editor of the artistic traditions of antiquity, recounts a well-known anecdote, and this anecdote has helped to establish the “basket hypothesis” of the Corinthian column capital. It can be called that, because what did the capitals of Corinthian columns gradually become in the materialistic conception of art? They became baskets surrounded by acanthus leaves. If one examines the matter more closely, one gets the impression that there is something symptomatic and significant here. For it is precisely at this point that it becomes apparent that the understanding of the finer spiritual connections in human development has given the inquiring mind a “basket,” and this basket hypothesis of the Corinthian column capitals stands, as it were, as a kind of monument to this “basket.”
What does Vitruvius actually say? He says that Callimachus, the Corinthian sculptor, once saw a small basket standing there somehow by chance, and at the bottom of this basket acanthus leaves were growing all around. So they say: Callimachus looked at a basket surrounded by acanthus leaves and said: Yes, that's what the Corinthian capital is. That is the purest materialism one can imagine. Well, I will explain in a moment what this anecdote from Vitruvius actually means and what significance it has.
The main point here is that we have gradually—and in recent times, basically completely—lost our understanding of the inner principles of artistic creation. And if we do not rediscover this inner principle of artistic creation, we will never understand what is intended with the forms, what underlies the forms of our capitals, indeed the forms of our entire building. People who — symbolically speaking — subscribe to the “basket hypothesis” will never be able to understand us properly.
What underlies all artistic creation is a consciousness that, I would say, stops at the gates of the historical development of humanity — the external historical development that is determined by external documents. A certain consciousness that was active before the gates of this historical development in human beings, and which was still a remnant of the ancient clairvoyance of humanity, was something that also belonged to the fourth post-Atlantean epoch. Even though Egyptian culture belongs to the third post-Atlantean epoch, what tends toward art in Egyptian culture belongs to the fourth post-Atlantean epoch. In the fourth post-Atlantic epoch, this consciousness asserted itself to such an extent that inner feeling, inner sensation, took hold in human beings — took hold to such an extent that one felt how human movement, posture, and gesture developed the human form and figure from the etheric into the physical.
You will understand me if you are clear about the fact that for those times, with what I would call a correct understanding of artistic will, the feeling was much more important than the view of a flower or a vine: I must carry something, carry something heavy; I bend my back and use my human figure to develop the strength that compels me as a human being to form myself in such a way as to carry the load.

One felt within oneself, as it were, what one had to perform in one's own gesture. And so one performed the grasping movement, for example, or carrying with the hand. One feels this carrying with the hands, where one needs to spread the hands outward. This gave rise to the lines and forms that merged into artistic design. One feels, so to speak, in one's own humanity, how human beings can go beyond what they see with their eyes and perceive with their other senses when they integrate themselves into a universal whole. And I would like to say: already in this universal, when one no longer needs to merely stroll along, but is compelled to submit to carrying a load, one aligns oneself with the organism of the whole world. And from the feeling of such lines, which one has to form within oneself, arose those lines that led to artistic form. These are lines that cannot be found in external reality.
Now, in spiritual research, one often encounters something. I would like to say that, like a wonderful akashic image, one always encounters the integration of a number of people into a whole, but a lawful, harmonious integration of people into a whole. Think of it like this: we have a kind of stage, surrounded by seats for spectators, like an amphitheater, and people are forming a circle. They walk around inside, they have to form a circle. Not something naturalistic, but something higher, something supernatural should appear before the human perception. Imagine that this is drawn from above:

I will now draw it in side view, schematically: a number of people walking in a row. They form, so to speak, the procession that goes around in a circle; the others sit in a circle and watch.

Now, the point is that these people represent something important, something that does not exist on Earth, so to speak, but of which there are only analogies on Earth, that they represent something that connected human beings with the greater context of the world. And so it seems obvious to present to the people of that time the relationship between the effects of the Earth and the effects of the Sun. How can human beings feel the relationship between the effects of the Earth and the effects of the Sun? They can feel it in a similar way to how one feels, for example, when one is carrying a load, that is, when one is carrying a burden. So one can feel the relationship between the effects of the Earth and the effects of the Sun in this way: everything earthly stands only on the surface of the Earth, and as it moves away from the Earth – all this is actually only thought of in terms of forces – it tapers to a point. So one felt, so to speak, the connection of the human being with the earth by representing something broad at the bottom and tapering at the top. Nothing else! That is, by feeling this force in this way, one said: I feel myself standing on the earth.
Now humans also became aware of their connection to the sun. This influence of the sun on the earth was felt by depicting the lines of force in such a way that the sun, as it revolves around the earth, sends its rays in this manner, one after the other, tapering them downward, because the sun apparently revolves around the earth.

If you imagine these two representations in alternation, you can see the Earth and Sun motifs that were always carried by these wandering people. This was part of what was presented in ancient times. People sat around, and the performers walked around. Some carried the Earth motif, others carried what was represented as ascending to the Sun, because this was how the radiance of the Sun could be represented. And they alternated: Earth – Sun, Earth – Sun, and so on.

This power, I would say, this cosmic power: Earth – Sun, could be felt. Only then did people think about how best to do this. And it turned out that the best way to do this, as a means, as an artistic means, so to speak, was to use a plant or tree that had a crown that spread out upwards in such a way that it was broad at the bottom and tapered towards the top, and that one then alternates with palms. So that the carrying out one after the other of such plants, which represent something like broad buds that taper upwards, and of palms, developed. Palms as the unfolding of the sun-like forces, and buds tapering upwards as characteristic of the earth forces.
By learning to feel our place in the cosmos as human beings, we produced certain formal relationships, using only plant materials for representation. In order to avoid having to fabricate them artistically, plant materials were used. Artistic creation arose from a living sense of the world's interconnectedness and therefore corresponds to the unfolding of the creative urge that lies within human beings, rather than merely imitating something that is merely outwardly natural. Everything external and natural only entered into art later, when it was imitated artistically. When people no longer knew that palm trees were used to express the forces of the sun, they believed that the ancients had intended to copy a palm tree when they painted such a branch. But that was never the case; rather, they used palm trees because they represented the forces of the sun. Thus, all true artistic creation arises from an abundance of forces inherent in human nature that cannot be expressed in external life and therefore want to be lived out as human beings become aware of their connection with the whole world.
Now all thinking and feeling – both in relation to natural science and to art – was misled by a thought that will be very difficult to eradicate from humanity. That is the idea that everything complicated arises from something simple. That is not true! The human eye, for example, is much simpler in its construction than the eyes of many lower animals. Development often proceeds in such a way that the complicated is simplified, that the convoluted is rounded off into a straight line. The simplified is often the later stage in development. Only when this is understood will a true concept of real development be attained.
What was presented to people at that time, and what was depicted for the spectators around them, which was entirely the representation of living cosmic forces, was later simplified into that ornament, in whose lines was summarized what people at that time felt vividly when they depicted these things. And if I wanted to illustrate how the complexity of human development was summarized into the simplicity of a line for an ornament intended to serve as decoration, I could use the following drawing:

If you think about this alternately, you have a simplified representation of the approach I have described as Earth motif, Sun motif — earth motif, sun motif. There you have what humans have experienced, summarized in the ornamental motif. This ornamental motif already appeared in Mesopotamian art and also found its way into Greek art as the so-called palmette, in this or a similar form, which resembles the lotus leaf.
This alternation of earth and sun motifs presented itself, so to speak, to human perception as a decorative motif, as a true ornamental decorative motif. Later, people no longer knew that this ornamental decorative motif was a reproduction of an ancient dance motif, a solemn dance, which had passed into the unconscious. But this has been preserved in the palmette motif.
Now it is interesting to consider the following. If you look at certain Doric columns, you will find, where the Doric columns have been painted, a most interesting motif, which I would like to draw in this way. Underneath what the capital has to bear, we find the following: Here would be the upper molding of the Doric column, but here below, on certain Doric columns, we find only a slightly modified version of the earth motif and the sun motif painted around the column. At the top you have the Doric molding, and at the bottom, painted all around, are the ornamental motifs decorating the columns. So you actually see the palmette painted at the bottom of certain Doric columns, executed in such a way that it really gives a procession: earth - sun, earth - sun, and so on.

In Greece, the most distinguished region in which the fourth post-Atlantic period found its full expression, what came over from Asia was now combined with everything I have just described, and what can be seen in Greece in the reproduction of Doric columns, with the actually dynamic architectural principle of support, because in Greece the perception of the ego in the human body was expressed in the most perfect way. And that is why it was in Greece that such a motif could be expressed: that when the ego is in the body, it must strengthen itself when it carries a load. One feels the whole thing in the volute:

This strengthening is what one feels in the volute. We see the human being, strengthening his ego in the fourth post-Atlantean period, expressed in the volute. And so we arrive at the basic form of the Ionic column, I would say, as if Atlas were carrying the world, but still undeveloped, with the volute becoming the support.
Now you only need to imagine that what is only hinted at in the Ionic column, the middle section, develops downwards into a complete volute, and then you have the Corinthian column: nothing other than the middle sections extended downwards, as it were, so that the nature of bearing becomes complete. And now imagine this supporting element as a plastic structure, and you have, as it were, human power curved within itself. The self bent over, bearing a load here.
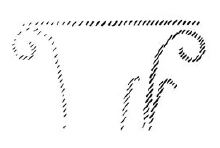
An artistic principle, my dear friends, lies in repeating what is formed in the large in the small, in miniature, or vice versa. If you now imagine the Corinthian column formed in such a way that it has the main supporting volute here, and you repeat this artistic motif here, where it serves only as decoration, you have, as it were, plastically inserted what is the whole capital, still all around in the decoration. And now imagine that the Doric motif, which emerged from the ornamental imitation of the ancient sun motif, is combined with what is attached to the Corinthian column. Imagine that the intuition arises to design what is around it in a similar way to what was painted earlier: and the painting on the Doric column has been sculpturally designed. I can illustrate this by first showing you the sculptural motif to which I have added the palmette [see illustration 8]. The urge arose to see the palmette in the motif that has emerged here. However, this motif was not painted in this way, but instead what had been painted in the Doric style was sculpted in the Corinthian style; that is, it was sculpted here, and the palmette leaf was allowed to extend all the way down. On the left, I have drawn a palmette [see illustration], and on the right, the beginning of what emerges when the palmette is sculpted. If I were to continue, the Doric painted palmette would be transformed into the Corinthian sculpted palmette. And so, if I did not paint the palmette, we would end up with acanthus leaves everywhere.
The acanthus leaf is created by transforming the palmette into a three-dimensional form. So this shape arises from the urge not to paint the palmette, but to give it a three-dimensional form; and by increasingly adding complications, the mere carrier becomes something that a person might say has a certain resemblance to the acanthus leaf. And from then on, this thing, which of course was not called an acanthus leaf before, was called an acanthus leaf. But the name has as much to do with what was depicted as the term “wing” has to do with the lungs and the lobes of the lungs. And the whole absurdity of the naturalistic imitation of the acanthus leaf is eliminated, because what we call the acanthus leaf did not arise from the naturalistic reproduction of the acanthus leaf, but through the transformation of the old sun motif, the palmette, which was made plastic instead of being painted. So you see that these artistic forms really flowed from an inner grasp of what is connected with the gesture of the human etheric body — for this is connected with the movement of a line of force that one has to carry out in oneself — through the perception of what flows from the human etheric body.
My dear friends, what is artistic in art has as little to do with imitating nature as, for example, one can do anything with imitating nature in music. Even in the so-called imitative arts, what is imitated is, in essence, something incidental, secondary, something of secondary importance. Therefore, all naturalistic sensibility is actually directly contrary to true artistic sensibility. And if our forms are perhaps found grotesque, we can console ourselves with the fact that the artistic conception that finds these forms grotesque has happily led it to interpret the acanthus capital motif, which was created purely from the spirit and in its further development attained a distant resemblance to the bear claw leaf, as a naturalistic imitation of the bear claw leaf. Future generations of artistic perception will no longer be able to understand such things, which in our time dominate not only the art scholars who are supposed to understand art, but also those who actually dominate artistic creation. What continues to have an effect in materialistic Darwinism as a materialistic conception also confronts us in artistic creation, in that there is an increasing tendency to make art a mere imitation of nature. I would like to say, my dear friends, I feel happy in my understanding of this connection with the acanthus leaf, for it actually enlightens us that the original forms of artistic creation also sprang from the human soul and did not arise through imitation of the external world.
Basically, I was only able to see so thoroughly into the original form of art after I myself had formed our forms here. When one feels such forms, when one has to create forms from the primordial source of humanity, one feels how, in essence, artistic creation also began in the same way in human development. It is a peculiar karma that, while I was deeply engaged—but after the forms of our building were already complete—I pursued an artistic intuition that had arisen in 1912 during the Berlin General Assembly, that while I was pursuing it in the grounds, I now examined what I had done with the forms in order to understand more. One can only think about what is to emerge as artistic form afterwards. If one first understands it and then executes it, it will certainly be of no use. If you create from concepts and ideas, then it will certainly be worthless. But precisely what I looked at so closely and made clear in the acanthus leaf, and what I showed to be an error in it, also gives the inner connection between what will prevail here in spiritual science and what is expressed artistically in our building.
I found a curious case [of agreement with external art research], which, however, is not related to the development I have just described. It cannot be found anywhere; it came to me through clairvoyant research. But in one respect I subsequently found a remarkable connection with my compatriot in the broader sense, Riegl. He bears the peculiar name Riegl, which, though not distinguished, sounds all the more Austrian for that. This Riegl did not achieve very much; but as curator of an ornament museum in Vienna, he nevertheless came to the conclusion that these ornaments did not originate in the way that “Semperism” had imagined at the end of the 19th century. He came up with ideas that are really in line with the transformation of the palmette motif into the acanthus motif, so that on this point there is a complete connection between the occult research that has come to me in recent days and the external art research, which also encounters this emergence of the so-called acanthus leaf from the palmette. “Palmette” is, of course, just a word; in reality, it is the sun-earth motif that is at stake.
Of course, something like this, as presented by Riegl, only leads to despair. For he cannot see where the palmette motif comes from and that it is connected with the force that works and moves within human beings. And so it is understandable that, I would say, even in small things one can notice how [dominant the materialistic view of art has become, because even if] the good Riegl—although he did not come up with very much, if I may use the expression, “rebels” against the art scholars, who, so to speak, have everything “under control” and are mostly naturalists, he nevertheless says that, with regard to the acanthus leaf, all art scholars still draw on the old Vitruvian anecdote. But one cannot say that all of them draw on it. One can also find the assertion that the old Vitruvian anecdote is not even considered an anecdote, but rather an invention of Callimachus; yet it is always retold as Vitruvian. Riegl, on the other hand, only briefly alludes to the anecdote, saying that it is too well known for him to go into all the details. There is only one peculiarity, and that is what he omits, which is very characteristic! He hints that Callimachus had seen a basket, the rest of which need not be elaborated on as it is too well known, and that there were bear claw leaves all around it, which gave him the idea for the Corinthian capital. So Riegl also leaves something out, which shows how our time is in despair. surrounded by bearberry leaves, and that this gave him the idea for the Corinthian capital. So Riegl also leaves something out, and this shows how our age must despair of knowledge in such a field if it strives for real insight; he leaves out what is most important in the whole of Vitruvius's account.
The most important thing is that Callimachus sees what he sees on the tomb of a Corinthian girl. That is the most important thing. For this means nothing less than that Vitruvius, even though he wisely conceals it, wants to imply that Callimachus was a clairvoyant who saw the sun motif in battle with the earth motif above the tomb of a girl, and above it the girl, floating in a pure, ethereal body. Yes, one could get a hint that could be used: namely, the sun-earth motif for the column capital. If one clairvoyantly sees above the grave of a virgin who has died what is really present in the ether, one can understand that the palmette has become the acanthus leaf, growing all around the sun-like rising etheric body of the virgin girl. It is as if people had never looked at the later Roman sculpture of Pytri-Clytia with an understanding gaze, in which there is really nothing else to see but a clairvoyant impression that one can have over the graves of certain persons, where, as if from the calyx, the head of a Roman woman emerges, who, though not a virgin, is nevertheless extraordinarily noble.
We will only understand what lies at the heart of Vitruvius's narrative, my dear friends, once we have overcome the unfortunate principle that lies in the question: “What does this or that mean?” Once this unfortunate principle, which immediately seeks a meaning behind everything and says, this means the physical body, that means the etheric body, that means the astral body, and so on, and seeks symbolic meanings everywhere, if this is removed from our movement, then we will understand what really underlies artistic forms: either the immediate grasping of one's own spiritual movement, or the perception of the etheric, whereby the one corresponds to the other.
In fact, the acanthus leaf appears correctly formed in the clairvoyant image when it can be shown in the right way above a grave.
When you take all this together, my dear friends, you will understand how necessary it is, in order to understand the forms that line our inner space, or, if I may use the word, adorn it, to discover the artistic principle from which they sprang. I once used a trivial comparison — which only needs to be understood, for even if it is trivial, it still conveys what it is meant to convey —: if you want to understand what will be in our interior space, in these two matching half or three-quarter buildings, remember the principle of the Gugelhupf pot, the pot in which you bake a ring cake.
The ring cake is created in this pan, and when the Gugelhupf comes out, all the shapes on the walls of the pan appear in negative on the surface of the Gugelhupf.

The principle is indeed to be applied correctly in the interior decoration of the building, except that there will not be a Gugelhupf inside, but rather the living word of spiritual science in its possible form, living and weaving inside. What is enclosed here in the forms of the room, what is spoken and done within it, should adapt itself in the same way that the dough adapts to the negative form of the cake pan. One should feel in what is on the walls the living negative of what is to be spoken and done there. That is the principle of interior decoration. What is such a form? Such a form is nothing other than the following: Imagine a part of our living spiritual-scientific word touching these walls, hollowing out this wall in its original sense of the word – then the form that corresponds to the word emerges. That is why these interior forms are also formed in this way. Look at them. Once they are completely finished, they will be carved out of the surface; they will become the forms of the architectural decorations. These forms are all carved into the surface. That is why I was in favor of working in such a way that, when we work here with gouges and mallets, we have a surface from the outset, striking the chisel with the left hand in the direction in which the surface must ultimately lie. So we strike in that direction from the outset. On the other hand, we hold the digging iron so that it stands upright.
I would have liked that very much, but it would not have been possible if such a surface had not been created from the outset. [Shown on the architrave!] This surface will only be correct when something else is removed here. The curve here still needs to be removed. It would have been better to work with the digging iron from the outset, then this curve would not have been created, but a surface from the outset. What is important is that, according to the models, one senses how the interior decoration is the shell, the shell that forms plastically inwardly for that which fills us as spiritual science in these rooms; and just as the interior decoration is actually carved out, so the exterior decoration becomes something that is applied. The interior must always bear the character of being engraved. [When working] on the model, one could feel this, because it was really a matter of spatially form-appropriate inner feeling.
That is what leaves us unsatisfied today, even with a text such as that by Adolf Hildebrand. The man has certain ideas about the effect of form; but what he lacks is an inner feeling for form, so that one is inside the form, whereas for Hildebrand the eye should feel itself to be facing the form. Here [pointing to a form], it should be such that one experiences the form internally, so that by holding the grave iron in a certain way, one learns to love the surface that one is creating here, that one is bringing into being here with the mallet. And I must confess that I cannot help but always caress such a surface once it has been created. The point is that one can grow fond of it, so that one lives in it with an inner feeling and not as something that is merely to be looked at with the eye.
Recently, after a lecture, someone said that a very intelligent person had commented on the fact that people strive for external things; this was evident to him in the way the matter was understood; for example, that the inner columns are made of different types of wood. This is such an external thing, he said, that people work with enormous externalities. You see, the intelligent man cannot understand that the pillars should be made of different types of wood. But the real reason why he cannot understand this is that he does not think about what he would have to think if someone asked him: Why is it necessary for the violin to have different strings? One could just string four A strings! - It is a matter of reality, even when it comes to the different uses of wood. Just as a violin cannot have only A strings, we cannot have only one type of wood. This has to do with real internal necessities.
One can only ever hint at the details of these things. For example, there is something tremendously wise and at the same time quite intimate that underlies our entire conception of construction and must be expressed in the building: naturally, forms are expressed that do not exist at all in the external physical world. If something in a form can be compared to something in the animal or human body, this is because the higher spirits that shape nature create according to these forces, so that nature expresses the same thing that we express here in this building. But it is not a matter of imitating nature, but of expressing what really exists as pure etheric form, as when a person says to themselves: How must I present myself if I now want to disregard the outer sensory world, if I want to have an environment that expresses my inner self in forms?
I am aware that some people will view the sculptural forms expressed in the column capitals and in the interior space with a critical eye, but not a single one of these forms is without justification. The person who is chiseling the column on this side with a hammer and chisel [pointing to a column motif] will also chisel here [in another place] in such a way that he chisels higher here and deeper here. It would be completely nonsensical to demand symmetry here. It should not be symmetry, but lively progress that is inside. Basically, the fact that we have two round buildings with two imperfect domes results in the combination of a larger and a smaller round building with a dome, as well as everything in the interior lining with columns and architraves. And I cannot express this more clearly than by saying: if only the radius of the smaller dome were a little larger or smaller in relation to the larger dome, these forms, these individual forms, would have to be completely different from how they look here; just as the little finger of a child looks different from that of a giant.
It was not only the differences in size, but also the differences in shape that, while we were developing the forms, gave rise to the tremendous sense of responsibility that everything must indeed be as it is, down to the smallest detail, just as the individual limb of a living organism must be inside the living organism and no one could say: I want to reshape the human nose; I want to attach a different organ where the nose is now. You would say: that makes no sense. But it is like this: the big toe would have to be different, and the little toe too, if the nose were different. Just as no one in their right mind would want to reshape the nose, so here no one can form any other shape than the one that is here. If this shape were different, the whole structure would have to be different, for the whole is conceived as organically alive in its forms.
This, my dear friends, is the progress that must be made: that which in the early days of art was perceived as a thoughtless perception of human gestures and then translated into artistic forms, must now consciously enter into human feeling, so that we now have truly living etheric forms in interior decoration and we feel that that what is to live in such rooms must truly leave its mark here. Truly, it cannot be otherwise.
You see, in the last few days I have received two letters from a man who no longer belongs to our anthroposophical movement, who was formerly associated with us but has not been a member for ten years. He wrote to me asking why he was not allowed to make the windows, saying he could do such a thing extremely well. And he became really quite insistent. But when you see the windows, you will understand that no one can make the windows who has not lived with us until the very last moment, until today. Just as nothing other than my hand can leave an imprint in a soft mass of clay when I press it into it—it cannot be an ox's head—so too must our spiritual science leave its imprint on the interior decoration, and so too must this spiritual science allow sunlight to enter through the windows in a manner appropriate to this spiritual science. The whole building is really — forgive this trivial comparison — formed according to the principle of the Gugelhupf, the ring cake, but in such a way that it is not a cake that is formed in it, but spiritual science fills it with all its sacred and sublime qualities that inspire us. This has always been the case in art. This was the case in the past, when people felt in their dull, mystical, human feelings the alternation of the earth and sun principles in a lively dance, in the ornamental representation of this dance in the palmette motif. This is also the case where the outer sensual shell of nature and human existence must be permeated, and where – if we are fortunate enough to be able to carry out the construction – various things that lie beyond the realm of sensory perception should be expressed in the forms. How the inner progression relates to the symptoms that go from evolution to evolution can be perceived both in these proportions and in the forms or in the drawings and paintings in this building.
I would like to say that this is why I wanted to share these thoughts with you, so that you will not be misled by what modern art has produced. It has been given the cold shoulder by true understanding. This is beautifully expressed in the belief that the Corinthian column capital is supposed to be a small basket surrounded by bear claw leaves. In truth, however, something that has sprung from deep within human development has found expression in the Corinthian column capital. Thus, in what surrounds us, we feel something expressed that lives in the depths of human nature, which lies behind the experiences and facts of the physical plane.
It is only about this point of our building and, in connection with it, about a chapter of art history that I wanted to speak to you about today, my dear friends.
Perhaps there will be further opportunities in the coming weeks to speak to you about similar things in connection with this or that motif of our building. I will use every opportunity that presents itself, seize every possible occasion that may arise, to come closer through such reflections to what really lies at the basis of our building forms as something complicated, but thoroughly spiritual, natural, and necessary.
In our time, it is not at all easy to talk about problems of art, since naturalism, the principle of imitation, dominates art with all its might. For the artists themselves, naturalism has come from something very simple—for the artists themselves—but for other people, it has come from something less simple. When learning, the artist must, of course, copy his master's models; he must copy in order to learn something. And out of instinct – by elevating the student principle to the master principle and eliminating the master because one does not want authority – one makes the student principle the master principle and imitates nature. This is very convenient for artists, because artists do not want to go beyond the artificial imitation of their role models. For the layman today, naturalism is even closer.
Where is the layman supposed to find a point of reference, for God's sake, what is he supposed to do for his naturalistic assessment, in order to be able to think something when he sees such forms? When they see nothing but such things, they will be forced to scratch their heads and shrug their shoulders. What is this? they will ask. They will be happy if they can find at least one point of reference somewhere. If, for example, they find that something here looks a little like a nose, even if it is a negative one, they will be happy to have at least a small point of reference. Today, when the layman lacks an understanding of what lies behind the merely natural in the various arts, he is infinitely happy when he can say: this looks like this or that, and he is then immensely happy about what he recognizes here or there. Why, then, should there not also be artistic confusion in depicting that which only looks similar to something external? But the truly artistic does not resemble anything else; it is something in itself.
And again, from this point of view, I would say it was exasperating when artistic practice emerged as a result of the materialistic-artistic conception of the second half of the last century, that our painters, not to mention sculptors, actually set themselves only one task: how do I bring out what appears, for example, as a mass of haze in the distance? when various attempts were made to imitate what is given in nature. It was maddening. Brilliant things were created, but what was the point of it all? It is much better in nature anyway. In their endeavor to imitate, the artists have lost out; it really is better in nature. The answer to this can be found in the prelude to “The Gate of Initiation.”
We recently visited the Luxembourg exhibition in Paris. There was something there. Yes, at first it was quite difficult to decipher what it actually was. But gradually we figured it out: it was supposed to represent a human figure. But now this figure was so contorted—I won't imitate it, because you would have to strain too much to be unable to distinguish the shoulder from the knee. The thing is quite ugly, but I can assure you that even if you encountered it in nature, it would be easier to understand in nature than in this “work of art.” Today, it is as if one really had no idea [what can be represented plastically]; for example, some motif that one thinks up is now represented plastically in a completely nonsensical way, while there is no need at all to represent the motif plastically. What is to be represented plastically must be conceived in the sculpture from the outset and conceived plastically. Thus, no real sculptor in the artistic sense would attribute many of the things Rodin did to sculpture. Rodin is a creator of non-plastic motifs, which he makes outwardly ingenious, but the question must arise in every artistic sensibility: what is the point of it all? – because it is not conceived in a plastic way.
It all hangs together, my dear friends [with the general materialistic-naturalistic conception of art. Remember] what I told you about when I was still young. I was really still a very young badger when I had to take up Semperism; I was at most 24 or 25 years old. But even back then, it was enough to drive one to despair, and that has not been eradicated even today.
Therefore, I ask you to try again and again to bring about — especially those who are so devotedly work so sacrificially on the building that demands so much willingness to sacrifice from our friends — to start from all forms of inner feeling, of inner empathy for what is to come, and to truly empathize in life with the forms that are to emerge in order to free us from much of what is currently called art. Then perhaps that which we will know in a new sense will also yield something fruitful for us: that art is what is born in the depths of human being during the creation of art, which in our time can be so misunderstood that the transformed earth-sun principle has been conceived as a replica of the bear's claw leaf. Once people are willing to believe that Vitruvius' anecdote is not based on Callimachus seeing a basket surrounded by acanthus leaves and that he stuck what he saw onto the column, but if one listens to Vitruvius' account that Callimachus had this vision on the grave of a Corinthian girl, then one will also be able to believe that he saw it clairvoyantly, and then one will also come to a better understanding of the development of art. Then one will realize that clairvoyant development leads us up into the realm that lies beyond the sensory realm. And then one will also see that the divine child of clairvoyant perception, even if only unconsciously carried in the soul as a feeling, is art, and that those forms which are seen with the clairvoyant eye in the higher worlds cast their shadow images down onto the physical plane.
And if one wants to grasp in our building that which lives in the spirit and has the power to impress itself upon that which surrounds us as a shell in our building, if one sees this in what is expressed around us in the outer shells, then one will understand what we want, for one will see in the forms that surround us as artistic — I would like to say - forms of impression, one will see the imprint of what is to be done, said, and accomplished in living words in our building. It is a living word - our building!
If I have thus attempted to hint at something, albeit sparsely, and to say something about the interior, we will soon be able to give some indication of the painterly and the exterior as well.









