| 115. Wisdom of Man, of the Soul, and of the Spirit: The Position of Anthroposophy in Relation to Theosophy and Anthropology
23 Oct 1909, Berlin Translated by Samuel P. Lockwood, Loni Lockwood |
|---|
| Here in Berlin, as well as in other localities where our Society has spread, much has been discussed that concerns the comprehensive realm of theosophy, that emanates, so to speak, from the high regions of clairvoyant consciousness, and it is natural that a desire should have arisen to do something toward a serious and adequate substantiation of our spiritual current. |
| Observing the human being in this anthroposophical sense, we ask what it is that must first engage our interest. It is his senses, and it is through these that he acquires knowledge of the physical-sensory world. |
| We will now list the human senses according to their real significance, and we will endeavor in the following to start laying the foundations of an anthroposophical doctrine of the senses. The first sense in question is the one that in spiritual science can be called the sense of life. |
| 115. Wisdom of Man, of the Soul, and of the Spirit: The Position of Anthroposophy in Relation to Theosophy and Anthropology
23 Oct 1909, Berlin Translated by Samuel P. Lockwood, Loni Lockwood |
|---|
Here in Berlin, as well as in other localities where our Society has spread, much has been discussed that concerns the comprehensive realm of theosophy, that emanates, so to speak, from the high regions of clairvoyant consciousness, and it is natural that a desire should have arisen to do something toward a serious and adequate substantiation of our spiritual current. The present General Assembly, which brings our members together here at the seventh anniversary of our German Section, may be taken as the proper occasion for contributing something toward strengthening the foundations of our cause. This I shall attempt to do at this time in the four lectures on Anthroposophy. The lectures in Kassel on The Gospel of St. John, those in Düsseldorf on the hierarchies, those in Basel on The Gospel of St. Luke, and those in Munich on the teachings of oriental theosophy, were all occasions for rising to high altitudes of spiritual research and for bringing back spiritual truths difficult of access. What occupied us there was theosophy and, at least in part, its ascent to exalted spiritual peaks of human cognition. It does not seem unjustifiable, given a gradually acquired feeling in the matter, to see something deeper in what is called the cyclical course of world events. At the time of our first General Assembly, when the German Section was founded, I delivered lectures to an audience composed only in part of theosophists; those lectures may be characterized as the historical chapter of anthroposophy. Now, after a lapse of seven years that constitute a cycle, the time seems ripe for speaking in a more comprehensive sense on the nature of anthroposophy. First, I should like to make clear through a comparison what should be understood by the term anthroposophy. If we wish to observe a section of country, together with all that is spread out there in the way of fields, meadows, woods, villages, roads, we can do so by going about from village to village, through streets and meadows and woods, and we will always have a small section of the whole region in view. Again, we can climb to a mountain top and from there overlook the whole landscape. The details will be indistinct for the ordinary eye, but we have a comprehensive view of the whole. That approximately describes the relation between what in ordinary life is called human cognition or human science, and what theosophy stands for. While the ordinary search for human knowledge goes about from detail to detail in the world of facts, theosophy ascends to a high vantage point. This extends the visible horizon, but without the employment of quite special means the possibility of seeing anything at all would vanish. In my book, Knowledge of the Higher Worlds and Its Attainment, is set forth how one can reach this ideal peak without losing the power of clear vision. But there is a third possibility, lying between the two described. It is to ascend part way, remaining half-way up. At the bottom you cannot survey the whole; you observe only details and see the top from below. At the top, everything is beneath you, and above you have only the divine heavens. In the middle you have something above and something below you, and you can compare the two views. Any comparison lags and limps, but all that was intended at the moment was to place before you the manner in which in the first instance theosophy differs from anthroposophy. The latter stands in the middle, the former on the summit: it is the point of departure that is different. Thus far the comparison is helpful, but it is inadequate in characterizing what follows. Devotion to theosophy necessitates rising above human points of view, above the middle, from self to higher self, and it implies the ability to see with the organs of this higher self. The peak attained by theosophy lies above man, ordinary human knowledge, below, and what lies half-way between, that is the human being himself: between nature and the spiritual world. What is above reaches down to him; he is permeated by the spirit. In contemplating the world from a purely human angle, he does not take his point of departure from the summit, but he can see it—see the spirit above. At the same time he sees what is merely nature beneath him; it reaches into him from below. There is a risk connected with theosophy; unless the above-mentioned means are employed to see with the higher self—not with the ordinary self—there is danger of losing contact with the human element, and this results in forfeiting the ability to see anything at all adequate, of recognizing reality below. This danger disappears, however, as soon as those means are employed. Then we can say that theosophy is what comes to light when the God within man says, “Let the God within you speak; what He reveals of the world is theosophy.” Take your stand between God and Nature and let the human being in you speak. Speak of what is beneath as well as what is above you, and you have anthroposophy. It is the wisdom spoken by man. This wisdom will prove an important fulcrum, a key to the whole realm of theosophy. After a period of immersion in theosophy, nothing could be more profitable than seriously to seek the firm center of gravity provided by anthroposophy. All that has been said so far can be historically substantiated in many directions. We have, for example, the science calling itself anthropology. As it is practised, anthropology comprises not only the human being, but everything pertaining to him; all that can be gleaned from nature, everything necessary for understanding man. This science is based on moving about among objects, passing from detail to detail, observing the human being under a microscope. In short, this science, which in the widest circles is regarded as the only one dealing authoritatively with man, takes its view from a point beneath human capacities. It is chained to the ground; it fails to employ all the faculties at the disposal of man, and for this reason it cannot solve the riddles of existence. Now contrast all this with what you encounter as theosophy. There one searches the most rarefied regions for answers to the burning questions of life. But all those who are unable to keep pace, whose standpoint is anthropology, consider theosophy an air-castle, lacking foundation. They are not able to understand how the soul can ascend step by step to that summit from which all is spread out beneath it. They cannot rise to the planes of imagination, inspiration, and intuition. They cannot ascend to the peak that is the final goal of human evolution. Thus we find anthropology on the lowest step, theosophy on the summit. What becomes of theosophy when it wants to reach the top but is not in a position to do so with the right means? We can find the answer in the historic example of the German theosophist, Solger, who lived from 1770–1819. Conceptually, his views are theosophical, but what means does he employ to attain the summit? Philosophical concepts, concepts of human cerebration long since sucked dry and emaciated! That is like climbing a mountain for the purpose of observation, and forgetting to take your field-glasses; you can distinguish nothing whatever down below. In our case the field-glasses are spiritual, and they are called imagination, inspiration, and intuition. Man's ability to reach that peak diminished more and more through the centuries—a fact that was clearly felt and acknowledged as early as the Middle Ages. Today it is felt too, but not acknowledged. In olden times that capacity to ascend existed, as you know, though only to a minor degree. It was based on a clairvoyant twilight condition in man. There really was an ancient theosophy of that sort, but it was written that such revelations from the summit should come to a close, that they should no longer be open to the ordinary means of cognition. This old theosophy, which considers revelation a thing of the past, became theology, and thus we find theology running parallel with anthropology. Theology's ambition is to climb the heights, but for its means it depends upon something that was once revealed, was then handed down, and is now rigid; something incapable of continually revealing itself anew to the striving soul. Throughout the Middle Ages, anthropology and theology frequently opposed without rejecting each other, but in recent times the contrast is sharp. Nowadays theology is admitted along with anthropology as something scientific, but no bridge is found between the two. If we do not stop with the details but ascend half-way, we can establish anthroposophy by the side of theosophy. Within modern spiritual life attempts have been made to practise anthroposophy, among other things, but again, as in the case of theosophy, with the wrong, inadequate means of a defunct philosophy. The meaning of philosophy can really no longer be understood by philosophers—only by theosophists. Historical contemplation alone yields this understanding. Philosophy can be comprehended only by contemplating its origin, as can be seen by an illustration. In former times there were the so-called Mysteries, abodes where the higher spiritual life was cultivated, where the neophytes were guided by special methods to spiritual vision. One such Mystery, for example, was in Ephesus, where the neophytes could learn through their training the secrets of Diana of Ephesus; they learned to look into the spiritual worlds. As much of such matters as could be made public was communicated to the profane and received by them, but not all of these realized that higher secrets had been revealed to them. One of those to whom such communications from the Mysteries of Ephesus had penetrated was Heraclitus. He then proclaimed these, by means of his partial initiation, in a way that could be generally understood. In reading the doctrines of Heraclitus, “The Obscure,” we still find immediate experience, the experience of the higher worlds, shining through between the lines. Then came his successors who no longer realized that those doctrines originated in direct experience. They no longer understood them, so they began to improve them, to spin them out in concepts. They began to speculate intellectually, and this method persisted through the generations. Everything we have in the way of philosophy today is but a heritage of ancient doctrines squeezed out and sucked dry of all life, leaving only the skeleton of the concepts. Yet the philosophers take that skeleton for a living reality, for something created by human thinking. There is, as a matter of fact, no such thing as a philosopher who can think creatively without having recourse to the higher worlds. Just such a skeleton of concepts was all that the philosophers of the nineteenth century had to work with when they took up what may be called anthroposophy. The term actually occurred. Robert Zimmermann wrote a so-called Anthroposophy, but he constructed it of arid, empty concepts. Indeed, everything that has attempted to transcend anthropology without employing the right means has remained a shriveled web of concepts no longer connected with the subject. Like philosophy, anthroposophy too must be deepened through theosophy; the latter must provide the means for recognizing reality within the spiritual life. Anthroposophy takes the human, the middle standpoint, not the subhuman, as does anthropology. A theosophy, on the other hand, as practised by Solger, though spiritual in its point of view, employs only inflated concepts, and when Solger arrives at the summit he sees nothing. That is spinning at the loom of concepts, not living, spiritual observation. It is something we do not intend to do. We aim in these lectures to confront the reality of human life in its entirety. We shall encounter the old subjects of observation, now illuminated, however, from a different point whence the view is both upward and downward. The human being is the most important subject of our observation. We need but to contemplate his physical body to realize what a complicated being he is. In order to gain a sentient understanding of anthroposophy's aims, let us first ponder the following. The complicated physical body as we encounter it today is the product of a long evolution. Its first germinal potentiality came into being on old Saturn, and it evolved further on the old Sun, the old Moon, and the Earth. The etheric body was added to it on the Sun, the astral body on the Moon. Now, these members of the human being have changed in the course of evolution, and what we encounter today as the complicated physical human body, with heart, kidneys, eyes, ears and so forth, is the product of a long development. It has all grown out of a simple germinal form that originated on Saturn. Through millions and millions of years it has continually changed and been transformed in order that it might achieve its present perfection. If today we wish to understand a member or an organ of this physical body—say, the heart or the lungs—we can do so only on the basis of this evolution. Nothing of what we encounter today as the heart existed on the old Saturn. Only gradually did these organs assume their present form, one being developed and incorporated earlier, another later. Some organs we can actually designate Sun-organs, as having first appeared during the Sun evolution, others Moon-organs, and so on. If we would understand the present physical body of man we must assemble our concepts from the whole Universe—that is the theosophical method of observation. How does anthropology set to work? Theosophy ascends to the ultimate heights and from this spiritual summit examines individual phenomena. Anthropology remains on the ground, takes its point of departure from the details, and now even investigates individual cells in their juxtaposition. Everything is mechanically lined up and the cells are studied individually, but this does not reveal their relative age. Yet, far from being immaterial, it is important to know whether a given group of cells developed on the Sun or on the Moon. Much more could be said concerning these complicated conditions. Consider, for example, the human heart. True, as constituted today it evolved late, but as regards its first germinal potentiality it is one of the oldest human organs. During the period of the old Sun, the heart was dependent upon the forces governing there. During the Moon period its development continued; then the Sun withdrew from the Moon, with which it had been united, and henceforth its forces acted upon the heart from without. Here the heart underwent a different development, so that from then on a Sun element and a Moon element can be observed in its tendencies. Then Earth, Sun, and Moon were united again and worked upon the heart. After a pralaya the Earth evolution followed, during which the Sun first withdrew again. This separation resulted in an intensification of the Sun's influence from without. Then the Moon withdrew as well and also acted upon the heart from without. So, being among the oldest human organs, the heart comprises a Sun element, a Moon element, a second Sun element during the Earth evolution, a second Moon element during the Earth evolution, and finally, after the withdrawal of the Earth, an Earth element—all corresponding to cosmic evolution. If these elements of the heart accord, as in the cosmic harmony, the heart is healthy; if any one element preponderates, it is sick. All human sickness derives from disharmony among the elements within the organ in question while their cosmic counterparts are in harmony. All healing depends upon strengthening the element that lacks its share, or subduing superfluous activity, as the case may be, thereby bringing the elements into harmony again. But talking about this harmony is not enough. In order to effect it one must really penetrate into the wisdom of the universe; one must be able to recognize the different elements in each organ. That will suffice to give an idea of genuine occult physiology and anatomy, which comprehend the whole human being out of the whole cosmos and explain the details out of the spirit. Occult physiology speaks of Sun and Moon elements of the heart, larynx, brain, and so forth, but since all these elements are at work upon man himself, something in him confronts us today in which all these elements are consolidated. If we look into the human being himself and understand these elements, we also understand the etheric body, the astral body, etc., the sentient soul, the intellectual soul and the consciousness soul, as man is constituted today. That is anthroposophy, and in anthroposophy, too, we must start at the lowest step, gradually ascending to the highest. Man's lowest member is the physical body that he has in common with the sensory world that is perceived through the senses and the sensory-physical mind. The theosophical point of view, starting from the universe, contemplates man in his cosmic contexts. In the matter of the sensory-physical world, anthroposophy must start from man, in so far as he is a sensory being. Only then can we deal appropriately with the etheric body, then the astral body, the ego, and so forth, and what is to be learned from them. Observing the human being in this anthroposophical sense, we ask what it is that must first engage our interest. It is his senses, and it is through these that he acquires knowledge of the physical-sensory world. Starting from the physical plane, it is therefore these that anthroposophy must consider first. Let the study of the human senses then constitute our first chapter. Thereafter we will ascend to the study of the individual spiritual regions in man's nature. Beginning with the study of the human senses, we at once find anthroposophy invading the territory of anthropology, for anthroposophy must invariably start from all that the senses tell us is real. But it must keep in mind that what is spiritual, influences man from above. In this sense it is genuine anthropology. Ordinary anthropology has thrown everything pertaining to the human senses into complete confusion, groping its way from detail to detail and examining only what is on the ground, so to speak. Important matters are disregarded because men have no Ariadne-thread to lead them out of the labyrinth of facts into the light. Anthropology cannot find its way out of this maze and must fall a victim to the Minotaur of illusion, for the saving thread can be spun only by spiritual research. Even in the matter of the human senses, anthroposophy has a different story to tell than has external observation. At the same time it is interesting to note how external science has lately been forced by material facts to go to work more thoroughly, seriously and carefully. There is nothing more trivial than the enumeration of the five senses: feeling (touch), smell, taste, hearing, and sight. We shall see what confusion reigns in this enumeration. Science, it is true, has now added three more senses to the list, but as yet doesn't seem to know what to do about them. We will now list the human senses according to their real significance, and we will endeavor in the following to start laying the foundations of an anthroposophical doctrine of the senses. The first sense in question is the one that in spiritual science can be called the sense of life. That is a real sense and must be as fully acknowledged as the sense of sight. What is it? It is something in the human being of which, when it functions normally he is not aware. He feels it only when it is out of order. We feel lassitude, or hunger and thirst, or a sense of strength in the organism; we perceive these as we do a color or a tone. We are aware of them as an inner experience. But as a rule we are conscious of this feeling only when something is out of order, otherwise it remains unobserved. The sense of life furnishes the first human self-perception; it is the sense through which the whole inner man becomes conscious of his corporeality. That is the first sense, and it must figure in the list just as does hearing or smell. Nobody can understand the human being and the senses who knows nothing of this sense that enables him to feel himself an inner entity. We discover the second sense when we move a limb—say, raise an arm. We would not be human beings if we could not perceive our own movements. A machine is not aware of its own motion; that is possible only for a living being through the medium of a real sense. The sense of perceiving our own movements—anything from blinking to walking or running—we call the sense of our own movements. We become aware of a third sense by realizing that the human being distinguishes within himself between above and below. It is dangerous for him to lose this perception, for in that case he totters and falls over. The human body contains a delicate organ connected with this sense: the three semicircular canals in the ear. When these are injured we lose our sense of balance. This third sense is the static sense, or sense of balance. (In the animal kingdom there is something analogous: the otoliths, tiny stones that must lie in a certain position if the animal is to maintain its equilibrium.) These are the three senses through which man perceives something within himself, as it were; by their means he feels something within himself. Now we emerge from the inner man to the point at which an interaction with the outer world begins. The first of such reciprocal relations arises when man assimilates physical matter and, by doing so, perceives it. Matter can be perceived only when it really unites with the body. This cannot be done by solid or fluid matter, but only by gaseous substances that then penetrate the bodily matter. You can perceive smell only when some body sends out gaseous matter that penetrates the organs of the mucous membrane of the nose. The fourth sense, then, is the sense of smell, and it is the first one through which the human being enters into reciprocal relationship with the outer world. When we no longer merely perceive matter but take the first step into matter itself, we have the fifth sense. We enter into a deeper relationship with such matter. Here matter must be active, which implies that it must have some effect upon us. This takes place when a liquid or a dissolved solid comes in contact with the tongue and unites with what the tongue itself secretes. The reciprocal relationship between man and nature has become a more intimate one. We become aware not only of what things are, as matter, but of what they can induce. That is the sense of taste, the fifth sense. Now we come to the sixth sense. Again there is an increase in the intimacy of the interaction. We penetrate still deeper into matter, things reveal more of their essence. This can only occur, however, through special provisions. The sense of smell is the more primitive of these two kinds of senses. In the case of smell, the human body takes matter as it is and makes no effort to penetrate it. Taste, where man and matter unite more intimately, is more complicated; then, matter yields more. The next step offers the possibility of penetrating still more deeply into the outer world. This takes place by reason of an external material substance being either transparent or opaque, or by the manner in which it permits light to pass through it, that is, how it is colored. An object that rays out green light is internally so constituted that it can reflect green light and no other. The outermost surface of things is revealed to us in the sense of smell, something of their inner nature in taste, something of their inner essence in sight. Hence the complicated structure of the eye, which leads us much deeper into the essence of things than does the nose or the tongue. The sixth sense, then, is the sense of sight. We proceed, penetrating still deeper into matter. For example, when the eye sees a rose as red, the inner nature of the rose is proclaimed by its surface. We see only the surface, but since this is conditioned by the inner nature of the rose we become acquainted, to a certain extent, with this inner nature. If we touch a piece of ice or some hot metal, not only the surface and thereby the inner nature are revealed, but the real consistency as well because what is externally cold or hot is cold or hot through and through. The sense of temperature, the seventh, carries us still more intimately into the fundamental conditions of objects. Now we ask ourselves if it is possible to penetrate into the nature of objects still more deeply than through this seventh sense. Yes, that can be done when objects show us not only their nature through and through, as in the case of temperature, but their most inner essence; that is what they do when they begin to sound. The temperature is even throughout objects. Tone causes their inner nature to vibrate, and it is through tone that we perceive the inner mobility of objects. When we strike an object its inner nature is revealed to us in tone, and we can distinguish among objects according to their inner nature, according to their inner vibration, when we open our inner ear to their tone. It is the soul of objects that speaks to our own soul in tones. That is the eighth sense, the sense of hearing. If we would find an answer to the question as to whether there exist still higher senses, we must proceed cautiously. We must beware of confusing what is really a sense with other terms and expressions. For example, in ordinary life—down below, where much confusion exists—we hear of a sense of imitation, a sense of secrecy, and others. That is wrong. A sense becomes effective at the moment when we achieve perception and before mental activity sets in. We speak of a sense as of something that functions before our capacity for reasoning has come into action. To perceive color you need a sense, but for judging between two colors you do not. This brings us to the ninth sense. We arrive at it by realizing that in truth there is in man a certain power of perception—one that is especially important in substantiating anthroposophy—a power of perception not based on reasoning, yet present in him. It is what men perceive when they understand each other through speech. A real sense underlies the perception of what is transmitted to us through speech. That is the ninth sense, the sense of speech. The child learns to speak before he learns to reason. A whole people has a language in common, but reasoning is a matter for the individual. What speaks to the senses is not subject to the mental activity of the individual. The perception of the meaning of a sound is not mere hearing because the latter tells us only of the inner oscillations of the object. There must be a special sense for the meaning of what is expressed in speech. That is why the child learns to speak, or at least to understand what is spoken, before he learns to reason. It is, in fact, only through speech that he learns to reason. The sense of speech is an educator during the child's first years, exactly like hearing and sight. We cannot alter what a sense perceives, cannot impair anything connected with it. We perceive a color, but our judgment can neither change nor vitiate it; the same thing is true of the sense of speech when we perceive the inner significance of the speech sound. It is indispensable to designate the sense of speech as such. It is the ninth. Finally we come to the tenth sense, the highest in the realm of ordinary life. It is the concept sense, which enables us perceptively to comprehend concepts not expressed through speech sounds. In order to reason we must have concepts. If the mind is to become active, it must first be able to perceive the concept in question, and this calls for the concept sense, which is exactly as much a sense by itself as is taste or smell. Now I have enumerated ten senses and have not mentioned the sense of touch. What about it? Well, a method of observation lacking the spiritual thread confuses everything. Touch is usually tossed in with our seventh sense, temperature. Only in this meaning, however, as the sense of temperature, has it in the first instance any significance. True, the skin can be called the organ of the temperature sense—the same skin that serves also as the organ of the touch sense. But we touch not only when we touch [TRANSLATOR'S NOTE: The verb tasten can mean “to touch.” Indeed, the sense of touch is der Tastsinn, but more often it signifies something like our “groping,” as one gropes in the dark by means of the sense of touch: “feeling around for something.” In this sentence the first “touch” is to be understood in this sense, the second (berühren) as meaning “to come in contact with.”] the surface of an object. We touch when the eye seeks something, when the tongue tastes something, when the nose smells something. Touching is a quality common to the fourth to seventh senses. All of these are senses of touch. Up to and including the sense of temperature we can speak of touching. Hearing we can no longer describe as touching; at least, the quality is present only to a small degree. In the senses of speech and concepts it is wholly absent. These three senses we therefore designate as the senses of comprehension and understanding. The first three senses inform us concerning the inner man. Reaching the boundary between the inner and the outer world, the fourth sense leads us into this outer world, and by means of the other three we penetrate it ever more deeply. Through the senses of touch we perceive the outer world on the surface, and through those of comprehension we learn to understand things, we reach their soul. Later we will deal with other senses transcending these. Below the sense of smell, then, there are three senses that bring us messages out of our own human inner being. The sense of smell is the first to lead us into the outer world, into which we then penetrate deeper and deeper by means of the others. But what I have described to you today does not exhaust the list of senses. It was only an excerpt from the whole, and there is something below and something above the ten mentioned. From the concept sense we can continue upward to a first astral sense, arriving at the senses that penetrate the spiritual world. There we find an eleventh, a twelfth and a thirteenth sense. These three astral senses will lead us deeper into the fundamentals of external objects, deep down where concepts cannot penetrate. The concept halts before the external, just as the sense of smell halts before the inner man. What I have given you is an urgently needed foundation upon which to build cognition of the human being. Through its neglect in the nineteenth century, everything pertaining even to philosophy and the theory of knowledge has been most horribly jumbled. Merely generalizing, people ask what the human being can learn by means of the individual sense, and they cannot even explain the difference between hearing and sight. Scientists talk about light waves in the same way they do about sound waves, without taking into account that sight does not penetrate as deeply as hearing. Through hearing we enter the soul-nature of things, and we shall see that by means of the eleventh, twelfth, and thirteenth senses we penetrate their spirit as well: we enter the spirit of nature. Each sense has a different nature and a different character. For this reason a great number of expositions given today, especially in physics, concerning the nature of sight and its relation to its surroundings may be regarded unhesitatingly as theories that have never reckoned with the true nature of the senses. Countless errors have arisen from this misconception of the nature of the senses. That must be emphasized, because it is quite impossible for popular representations to do justice to what has here been set forth. You read things written by people who can have no possible inkling of the inner nature of the senses. We must understand that science, from its standpoint, cannot do other than take a different attitude. It is inevitable that science should spread errors, because in the course of evolution the real nature of the senses was forgotten. This true nature of the senses is the first chapter of anthroposophy. |
| 296. Education as a Social Problem: The Social Structure in Ancient Greece and Rome
10 Aug 1919, Dornach Translated by Lisa D. Monges, Doris M. Bugbey |
|---|
| If we wish to understand the task of the anthroposophical science of the spirit in the present and immediate future we must consider the character of mankind's evolution since the middle of the fifteenth century. |
| We must, for instance, base education on what we know out of spiritual facts, out of what we learn from anthroposophical spiritual science. Through the stronger, more conscious emphasizing of willing out of the spirit we establish a counter-image to the senseless willing of industrialism. |
| For this reason, I had to say yesterday that if we will to bring about a true form of society in future it must be prepared through people's education. To this end we must not proceed in a small way but on a large scale; for our educational system has gradually taken on a character that leads directly to what I described yesterday as mechanization of the spirit, vegetizing of the soul, and animalization of the body. |
| 296. Education as a Social Problem: The Social Structure in Ancient Greece and Rome
10 Aug 1919, Dornach Translated by Lisa D. Monges, Doris M. Bugbey |
|---|
If we wish to understand the task of the anthroposophical science of the spirit in the present and immediate future we must consider the character of mankind's evolution since the middle of the fifteenth century. Everything that happens now depends on the fact that since that time there lives in mankind the impulse for each single individuality to attain the pinnacle of personality, to become a whole personality. This was not possible, nor was it the task of mankind in earlier epochs of our post-Atlantean evolution. If we want to understand this great change in the middle of which we find ourselves, we must focus our attention still more precisely upon such matters as I characterized yesterday. I said that in our spiritual life we still have a Greek constitution of soul. The way we form our thoughts, the manner in which we are accustomed to think about the world, is an echo of the Greek soul. And the way we are accustomed to look at civic rights and everything connected with them is an echo of the soul-constitution of the Roman. In the State we still see the structure as it existed in the Roman Empire. Only if people will realize that the impulse of the threefold social order must enter our chaotic present will there be clarity in thinking and willing. The soul-nature of the Greek was chiefly determined by the fact that in Greece there existed in the highest degree what were the leading characteristics of historical development right up to the middle of the fifteenth century. Across the Greek territory there were spread a subject population and their conquerors. These latter claimed the land for themselves; but also, through their blood inheritance, they determined the spirituality of ancient Greece. We cannot grasp the soul-nature of the ancient Greeks unless we keep in mind that it was considered justified to think about human relationships in the way that resulted from the blood characteristics of the Aryan conqueror population. Naturally, modern man has outgrown what thus lay at the basis of Greek culture. With the Greeks it was self-evident that there were two kinds of people: those who had to worship Mercury, and those who had to worship Zeus. These two classes were strictly separated. But, people thought about the world and the Gods in the way the conqueror population had to think because of its blood characteristics. Everything resulted from the clash of a conquered and conquering people. One who looks more closely into what lives socially among men of our time will recognize that in our feelings and our subconscious soul-life we no longer have this aristocratic attitude in viewing our world. Yet it still lives in our ideas and concepts, especially if we are educated in the schools of higher learning. These schools, especially the classical schools, shape their instruction in a way that represents a renaissance, and echo of Hellenism. And this is even more the case with our universities, with the exception of the technical and agricultural colleges which have sprung from modern life. Even they imitate in their outer form the structure of universities derived from Hellenism. Through the very fact that we have a high esteem for Hellenism in its time, and for its time, we must also be quite clear about the necessity for our age of a renewal of spiritual life. It will become more and more unbearable for humanity to be led by souls who have acquired the form of their concepts in our classical schools. And today, in almost all leading positions, you find people who did receive the forming of their ideas in the classical schools. It has become necessary today to realize that the time of “settling accounts,” not minor but major accounts, is at hand, and that we must think about such matters factually and stop clinging to old habits of thought. You know that what was formed out of the blood in Hellenism became abstract in Romanism. I have mentioned this here before. The Greek social organism, which cannot be called a State organism, shaped itself out of forces descending through the blood. But this did not pass over to Romanism. What did pass over was the urge to organize as the Greeks had organized, but the cause of this organizing was no longer felt to be in the blood. While it would never have occurred to an ancient Greek to doubt that there are people of a “lower sort,” those in a conquered people, and others being of a “higher sort,” the Aryans, this was not the case with the Romans. Within the Roman Empire there was the strong consciousness that the order of the social organism had been arrived at through power, through might. You need only remind yourselves that the Romans trace their origin to that assembly of robbers in the neighborhood of Rome that had been called together in order, as a robber band, to found Rome; and that the founder of Rome was not suckled with delicate mother's milk but, as you know, was suckled in the forest by an animal, a wolf. These are the influences that were taken up into the Roman nature and led to the formation of the social order in Rome largely out of abstract concepts. What has remained as our heritage in regard to the concepts of rights and the State has thus come from the Roman constitution of soul. In this connection I am always reminded of an old friend of mine. I met him when he was already quite advanced in years. In his youth, at the age of eighteen, he had fallen in love with a girl and they had secretly become engaged. But they were too poor to marry, so they waited and remained faithful to each other. When he finally could consider marriage, he was sixty-four years old, for only then had he acquired enough means to risk taking such a step. So, he went to his home town near Salzburg ready to marry his chosen one of so long ago. But alas, the church and the rectory had burned down, and he could not get his baptismal certificate. There was no record of his baptism anywhere, so there was no proof that he had been born. I remember vividly the day his letter arrived. It stated, “Well, I believe it is quite evident that I was born, for after all I exist. But these people do not believe I was born because there is no baptismal certificate to prove it.” I once had a conversation with a lawyer who said, “In a lawsuit it is not so important whether or not a man is present; all we need is his birth certificate.” Continually one meets such grotesque incidents. The mood living in them shows that our entire public life has been built to a greater or lesser degree on Romanism. We are citizens of the world not through the fact we have become and exist as human beings but because we are recorded and recognized in a certain office. These things all lead back to Romanism. The descent by blood has passed over into registration. Today the situation is such that many men no longer consider their value determined by what they are as human beings but by the rank they have reached in the hierarchy of officialdom. One prefers to be something impersonal, out of Roman rights-concepts, rather than a personality. Since the fifteenth century, however, there exists in mankind the subconscious striving to base everything on the pinnacle of personality. This shows us that in regard to spiritual life and the life of rights the times have changed, and we need a renewal of both, a real renewal. This is connected with many deeper impulses of mankind's evolution. Just consider the fact that since the middle of the fifteenth century the evolution of modern man has been filled with the natural-scientific mode of thought which is based on abstract laws of nature, upon sense perception and the thoughts developed around it. Only what is derived from sense perception is considered valid. Yesterday I drew your attention to the fact that today there are quite a number of people who are convinced, justifiably so, that a view of nature acquired in this way can only lead to a ghost-like image of nature. A picture of the world formed by a student of nature is a specter of the world, not the real world. So, we have to say that humanity finds itself in the position of developing a specter-image of the world in regard to one half of it. For the science of initiation something profound is concealed behind this, and what this is we must now consider. Sense perception as such cannot be altered; whether we consider it to be maya or something else is of no concern to a deeper world view. A red flower is a red flower whether or not we think it maya or reality. It is what it is. Likewise, all sense perception is what it is. Discussion starts only when we begin to form thoughts about it, when we consider it to be this or that, when we interpret it. Only then the difficulty begins. It begins because the concepts we as men have to form since the fifteenth century are different from those of earlier mankind. No attention is paid to this in modern history, which is a fable convenue, as I have often stated. Whoever is able to understand the concepts of mankind prior to the middle of the fifteenth century knows that they were full of imagery, that they actually were imaginations. The present abstraction of concepts exists only since that time. Now why has our human nature so developed that we have these abstract concepts we are so proud of today and that we constantly employ? They have the peculiar character that, although we make use of them in the sense world they are not suited to this sense world. They are worthless there. In my book, Riddles of Philosophy, I have expressed this by saying that the way man forms his concepts regarding the external world constitutes a side-stream of his soul development. Think of a seed in the earth; it is destined by nature to become a plant. But we take many seeds and grind them into flour and eat them as bread. This, however, is not what the seed is meant for; it is a lateral development. If we ask, doesn't the seed contain those chemical elements we need for building up our body? we must say that it does not lie in the nature of the grain of wheat or rye to nourish us but to bring forth new grain. Likewise, it does not lie in our nature to grasp the outer world through the concepts we have acquired since the fifteenth century. We shall reap something different from those concepts if we enter into their nature properly. These modern concepts are the shadow images of what we have experienced in the spiritual world before birth—more exactly, before conception. Our concepts, the forces in them, are the echoes of what we have experienced before birth. We misuse our system of concepts in applying it to the outer sense world. This is the basis of Goethe's concept of nature. He does not want to express the laws of nature by means of concepts; he strives for the primal phenomena. That is to say, he strives for the assembled outer perceptions, because he feels that our conceptual ability cannot be applied to external nature. We have to develop our conceptual ability as pure thinking. If we do so, it points us toward our spiritual existence prior to birth. Our modern thinking has been bestowed upon us so that we may reach with this pure thinking our spiritual nature as it existed before we were clothed with a physical body. If mankind does not comprehend the fact that it possesses thinking in order to apprehend itself as spirit, it does not take hold of the task of the fifth post-Atlantean period. Our natural science was inserted, so to say, into mankind's destiny so that we might remain with pure nature and not speculate about it. We were to employ our concepts to perceive it in the right way, and then develop our concepts in order to behold ourselves as we existed in spirit before we descended into the physical body. Men still believe today that they should only employ their conceptual ability for classifying external sense perceptions, and so on. However, they will only act correctly if they employ the thoughts they have had since the middle of the fifteenth century for perceiving the spiritual world in which they existed before they acquired a physical body. In this way man of the fifth post-Atlantean era is forced toward the spiritual, toward the existence before birth. And still another factor places him in a peculiar situation which he must develop. Parallel to the specter-concepts of natural science runs industrialism, as I mentioned yesterday. Its chief characteristic is the fact that the machine, the bearer of industrialism, is spiritually transparent. Nothing of it remains incomprehensible. As a consequence, the human will directed toward the machine is, in truth, not directed toward a reality. In terms of comprehensive world-reality the machine is a chimera. Industrialism introduces something into our lives which in a higher sense makes man's will meaningless. There will be a significant impact on social life when modern men become convinced that the machine and everything resulting from it, such as industrialism, makes the human will meaningless. We have already reached the pinnacle of machine activity. Today a quarter of all production on earth is not being produced by human will but by machine power.1 This signifies something extraordinary. Human will is no longer meaningful on earth. If you read, for instance, the speeches of Rabindranath Tagore, you ought to sense something in them that remains incomprehensible to the European who employs his ordinary intellect. There is a different tone in what an educated Asiatic has to say today, because in him this adaptation of the European spirit to the machine is completely incomprehensible. To the Oriental the activity of working by means of machines, by means of industrialism, has no meaning. The European may believe it or not, but European politics born in the machine age is also just as senseless to the Oriental. In the educated Oriental's statements there is clearly expressed that this one-fourth of human labor in the present age is felt by him as senseless work—this quarter which is not carried out by the educated Orientals but only by Occidentals and their imitators, the Japanese. The Oriental feels so because, as he still possesses much clairvoyant vision, he knows that labor performed by machines has a definite peculiarity. When a man plows his field with his horse—man and beast straining themselves in labor—this work in which natural forces are involved has a meaning beyond the immediate present; it has cosmic meaning. When a man kindles fire by using a flint, making the sparks ignite the tinder, he is connected with nature. When the wasp builds its house this natural activity too has cosmic meaning. Through modern industrialism we have abandoned cosmic value. In our kindling of electric flames there no longer lives any cosmic significance. It has been driven out. A completely mechanized factory is a hole in the cosmos, it has no meaning for cosmic evolution. If you go into the woods and collect firewood this has cosmic meaning beyond earth evolution; but a modern factory and everything it contains has no significance beyond earth development. The human will is inserted in it without its having any cosmic value. Just consider what this means. It means that since the middle of the fifteenth century we have developed a knowledge that is specter-like and does not touch reality. More and more we employ machines and carry out an industrial activity, and the will inserted into this activity is senseless for world evolution. The great question now confronts us: Is there nevertheless a meaning for mankind's evolution as a whole in the fact that our knowledge is ghost-like, and our will to a great extent senseless? Indeed, there is meaning in it, significant meaning. Mankind thereby is to be urged to penetrate beyond ghost-like thinking to a knowledge of reality that does not stop with the perception of nature but enters into the spiritual behind nature. So long as men received the spirit simultaneously with their concepts they did not need to make efforts to gain the spirit. Since in the modern age men have only retained concepts devoid of spirit, but that also contain the possibility of working one's way up to the spirit as I have stated, there is present in man the impulse to proceed from abstract knowledge and to penetrate into genuine spiritual knowledge. Therefore, since we have industrialism with its senselessness we must seek another meaning for human will. This we can only do if we arouse ourselves to a world view that brings sense into what is senseless—let us call it industrialism—by deriving meaning from the spiritual, saying: We seek tasks that stem from the spirit. Formerly, when willing could derive its impulses from the spirit instinctively, we did not need to arouse ourselves especially in order to will from out the spirit. Today it is necessary that we make a special effort to do this. The senseless industrial willing has to be confronted with a meaningful willing-out-of-the-spirit. Yesterday I gave you an example of the way we ought to educate. We should recognize that up to the seventh year man is an imitator since he develops chiefly his physical body during this period. Imitation, therefore, ought to become the basis for that period of education. We should know that from the seventh to the fourteenth year we have to develop man by the principle of authority. This spiritual knowledge, which we gain by knowing how the etheric body develops during that time, must be made the impulse of education then. We should know also how the astral body develops from the fourteenth to the twenty-first year, and that this knowledge must lie behind education for that, period. Then, only then, do we will out of the spirit. Up to the middle of the fifteenth century man willed instinctively out of the spirit. In external life we tend to immerse ourselves in machines, in mechanism; this is so even in politics, which gradually has turned governments into machines. We must strive for a spirit-ensouled willing. To that end we must accept the idea of a science of the spirit. We must, for instance, base education on what we know out of spiritual facts, out of what we learn from anthroposophical spiritual science. Through the stronger, more conscious emphasizing of willing out of the spirit we establish a counter-image to the senseless willing of industrialism. Thus, industrialism with all its devastation of the human soul, is given us in order that in this devastation we may rouse ourselves to will out of the spirit. Our thinking has to be changed in many ways in our modern age. This requires a careful, intimately developed feeling for truth. We must become conscious that the feeling for truth has to be gradually applied in places where we are not yet accustomed to apply it. I believe many a person will be astonished today if he is told: You are right if you venerate Raphael highly because of his pictures, but if you demand that people paint the way Raphael painted then, you are mistaken. Only he has a right to admire Raphael who knows that whoever paints today the way he painted is a bad painter, because he does not paint as the impulses of our time demand. One does not feel with the times if one does not deeply sense the tasks of a given age. It is necessary that we acquire in our time an intimate feeling for truth in this regard. But here also modern humanity is caught up in what is the very opposite. One gets the impression that the feeling for truth has everywhere sprung a leak and does not function. People are shying away from calling right what is right, and wrong what is wrong; they recoil from designating a lie a lie. We experience today the most abominable things, and people are indifferent to them. The point is that we should have such a feeling for truth that we know, for example, that Raphael's painting no longer fits our present age; that it must be considered as something of the past and admired as such. It is particularly necessary now to pay attention to such things when out of the depths of the soul the impulse for truth comes over us. I am often reminded of a beautiful passage in Herman Grimm's biography of Michelangelo in which he speaks of his Last Judgment. He says that many such Last Judgment pictures were painted at that time and that the people experienced in full reality the truth of what was painted on the walls. They lived in the truth of those pictures. Today we should not look at such a picture as Michelangelo's Last Judgment without being aware that we do not feel as those people did for whom the artist painted it; that we have lost their feeling and at best can say: This is the picture of something we no longer believe in as an immediate reality. Just consider how differently man confronts such a picture with his modern consciousness. He no longer thinks that angels really descend, or that the devils carry on as they do in Michelangelo's picture. If, however, one is aware that what modern man feels when looking at this picture is something gray and abstract, then one is called upon inwardly to experience the whole living movement in these pictures on the wall of the Sistine Chapel. One is stirred to asking how it was possible for the people of Michelangelo's time (although he painted after the decline of the fourth post-Atlantean period his paintings originated in the spirit of that period since he stood at the boundary of the fourth and fifth periods)—how was it possible for people like him and his contemporaries to experience such tremendous imaginations, such mighty pictures? This question confronts us in all its magnitude if one is conscious of how drab and lifeless is what man feels today in front of such a picture by Michelangelo. We must ask: What caused human souls of that time to conceive of the earth's end in such a way? Whence came the structure of these pictures? The reason lies in the following: Since the time when the Mystery of Golgotha entered earth evolution and had given it its meaning, certain things that existed in the ancient manner had to recede into the background and were destined to be regained by mankind later on. One of these was the idea of repeated earth lives. The totality of human life takes its course through earth life, then life in the spiritual world, then earth life again, and so on. This course of the total life of man was the content of the atavistic, instinctive world-view in ancient times. Christianity had to arouse in man concepts different from those of ancient wisdom. By what means, above all, has Christianity accomplished this? It directed human consciousness only to a certain point in time, namely, to the beginning of one's life on earth. It did not consider man as an individuality prior to birth or conception but merely as a thought of the Godhead. Before earth-life man proceeds out of the spiritual world as a thought of the Godhead, only at birth did he begin to be a real human being. Then, after his life on earth, the life after death. In the first period of the development of Christianity the experience of repeated earth lives was, so to say, misplaced. Human experience was limited to looking into the origin of man and the life after death. This, however, supplied the equilibrium out of which the pictures of the Last Judgment were created. Through the fact that Christianity first eradicated from human feeling the teaching of pre-existence, the pictures of the Last Judgment could arise. Today there wells up again out of the deep recesses of the human soul the longing for a recognition of repeated earth lives. Therefore, those pictures fade away which only focus their attention upon the one earth life and a vague spiritual world before and after it. Now there exists the most intense longing to enlarge the Christian world-view of the early ages. The Mystery of Golgotha is not merely effective for those who believe only in one earth life, it is also valid for those who know of repeated earth lives. The present age is in need of this enlargement. Therefore, we should see clearly that we live in a period when we must use the ghost-like nature of ordinary conceptual knowledge, and the senselessness of willing released by industrialism, in order to rise to spiritual knowledge and spirit-permeated willing, as I have described it; and also, in order to enlarge religious consciousness so as to include repeated earth lives. The great and full importance of this enlargement of human consciousness in the present time should be deeply inscribed in the soul of modern men, for upon this depends whether they really understand how to live in the present, and how to prepare the future in the right sense. Everyone, in the situation in which life has placed him, can make use of this enlarged consciousness. Even the external knowledge people gain will cause him to demand something that today plays a large role in the subconscious depths of soul life but that has difficulty in rising and sounding out into full consciousness. Truly, the most striking fact of modern life is that there are so many torn human souls; souls full of problems who do not know what to do with life, who ask again and again, “What precisely is my task? What does life mean to do specifically with me?” They start this or that and yet are never satisfied. The number of these problematic natures increases steadily. What is the reason for it? It comes from a lack in our educational system. Today we educate our children in a way which does not awaken in them the forces that make man strong for life. Man becomes strong through being an imitator up to his seventh year; through following a worthy authority up to the fourteenth year; and through the fact that his capacity for love is developed in the right way up to the twenty-first year. Later on this strength cannot be developed. What a person lacks because the forces were not awakened which should have been awakened in definite periods of his youth—this is what makes him a problem-filled nature. This fact must be made known! For this reason, I had to say yesterday that if we will to bring about a true form of society in future it must be prepared through people's education. To this end we must not proceed in a small way but on a large scale; for our educational system has gradually taken on a character that leads directly to what I described yesterday as mechanization of the spirit, vegetizing of the soul, and animalization of the body. We must not follow this direction. We must strongly develop the forces that can be developed in a child's soul, so that later on he can harvest the fruits of his childhood learning. Today he looks back and feels what his childhood was and cannot gather anything from it because nothing was developed there. Our educational principles must be fundamentally changed if we want to do the right thing for children. Above everything we must listen very carefully to much that at present is highly praised and considered especially wholesome. So, it is necessary that, without undue strain and exertion but through an economy of educational effort, children acquire concentration. This can be achieved, in the way modern man needs it, only by abolishing what is so greatly favored today, namely, the cursed curriculum of the schools; this instrument of murder for the real development of human forces. Just consider what it means: From 7 to 8 A.M. arithmetic, from 8 to 9 grammar, from 9 to 10 geography, from 10 to 11 history. Everything that has moved through the soul from 7 to 8 is extinguished from 8 to 9, and so on. Now here it is necessary to get down to the bottom of things. We must no longer think that subjects exist in order to be taught as subjects. On the contrary, we must have clearly in mind that in children from the seventh to fourteenth year, thinking, feeling, and willing have to be developed in the right way. Geography, arithmetic, everything must be employed so that these faculties can be properly developed. Much is said in modern pedagogy about the need of developing individualities, of paying attention to a child's nature in order to know which faculties should be developed. This is empty talk. These questions take on meaning only when they are discussed from the point of view of spiritual science, otherwise they are mere phrases. In the future it will be necessary to say that for a certain age group we must impart a certain amount of arithmetic. Two or three months are to be devoted to teaching arithmetic in the forenoon. Not a plan of study that contains everything jumbled up but arithmetic for an extended time, then on to another subject. Arrange things as they are indicated by human nature itself for definite points in time. You see the tasks that arise for a pedagogy which works toward the future. Here lie the positive problems for those who seriously think about the social future. As yet there is little understanding for these problems. In Stuttgart, connected with our previous activities, a school is to be built up as far as possible within the present school system. Mr. Molt has decided to found such a school for the children of his employees in the Waldorf-Astoria Cigarette Factory.2 Other children will be able to come, but at first of course only in limited numbers. Naturally, we will have to take into account the educational goals of the State. The children will have to achieve this and that by the end of a year, and we will have to make certain compromises. But we will be able to intermix something with what the State requires, because, according to socialistic ideas, the State is the especially clever idol. So, we shall have to intermix with what it demands that which is required by the real nature of man. This has to be recognized. But who today thinks of the fact that the prevailing plan of study is the murderer of truly human education? There are people whose thoughts in this direction are such that one is inclined to say: The world stands on its head, one has to turn it back on its legs. For many would shorten the lessons and change the subjects every half hour. This today is considered ideal. Just imagine: Religion, arithmetic, geography, drawing, singing, one after the other. In our heads they tumble through each other like the stones of a kaleidoscope. Only the outer world says, “Now that's something like it!”—because there is not the slightest interrelating between these subjects. Few believe it is necessary now to think on a large scale; not to think petty thoughts but to have great, comprehensive views. We experience again and again that people finally have become accustomed to saying, “Indeed, revolution is necessary!” Even a large part of the bourgeoisie believes today in revolution. I do not know if that is the case here, but there are large areas where a majority of the bourgeoisie believes revolution to be necessary. But if we offer them such things as are stated in my book, The Threefold Social Order, they say: “We do not understand this. It is too complicated.” Lichtenberg once said, “If a head and a book strike together and a hollow sound results it is not necessarily the fault of the book.” But people do not believe this, because—it is not self-knowledge that is chiefly produced in men's souls. One can experience that throughout extensive regions the philistines believe in revolution, yet they say, “O no, we cannot enter into such deep questions, such comprehensive thoughts; you must tell us how shoe production can be socialized, how the pharmacies are to be socialized,” and so on. “You must tell us how, in the revolutionized State, I can sell my spices.” One gradually discovers then what these people really mean. They mean that they agree there must be a revolution, but everything should remain as it has been, nothing should be changed by it. Many a person asks, how can we make the world over?—but so that nothing is changed! The most remarkable ones in this respect are the so-called intellectuals. With them one can have the most extraordinary experiences. One heard it repeatedly stated, “Very well, three members—autonomous universities, a spiritual life that governs itself—but then, how shall we live? Who will pay our salaries if the State no longer pays us?” Today we really have to confront these things. It is necessary that we stop turning away from these questions again and again. Precisely in the sphere of the spiritual life a change must be brought about.
|
| 193. The Problems of Our Time: Lecture II
13 Sep 1919, Berlin Translator Unknown |
|---|
| Naturally, the soul's continued existence after death will be assumed in all our future discussions on immortality, but the way in which anthroposophical spiritual science speaks of the continued existence of the soul after death is very far from being accepted by the creeds. |
| I have referred to ancient times of human evolution, known from an anthroposophical standpoint as the first and second post-Atlantean epochs. People in those days were as capable of development right into their old age as only the young are nowadays. |
| He began by uttering some very high-sounding words, then read out the programme of a modern Educational Society. After much stumbling he finally broke down, and, having no more to say, gathered up the threads with "I must therefore claim to have proved that old age no longer understands its own youth," and went out. |
| 193. The Problems of Our Time: Lecture II
13 Sep 1919, Berlin Translator Unknown |
|---|
In the last lecture the endeavour was made to show how necessary it is for men of the present day to turn the eye of the soul towards spiritual science, to those spheres of existence, of reality, in which the rule of the spirit within human evolution is clearly perceptible to anyone who has the faculty of sight in such regions. As I said, the middle of the fifteenth century brought with it a complete change in the relation of civilized man's soul to the three Hierarchies next above man, the Angeloi, Archangeloi and Archai. Hitherto it has been out of their own interests and impulses that they worked in human evolution. In our times, this connection has come to an end. They have for the moment no interest in continuing to work as before on the evolution of man. They will only enter into a new relationship to us when human beings begin to develop an interest in the spiritual worlds, out of free will and of their own accord. If we would not lose all connection with the spiritual worlds, we must occupy ourselves with them in the near future, for the spiritual beings who have been connected with us so far have of themselves no reason to be further interested in us. We can only arouse their interest anew if out of our own souls we again concern ourselves with the spiritual world, fostering thoughts, sentiments, and impulses of will, into which spiritual forces can flow. The question may and must be asked, how can human beings manage so to concern themselves with the spiritual worlds as to maintain their connection with the higher Hierarchies as the Earth evolution proceeds. The answer may deal with things which apparently have little to do with the question; but we shall see that they do provide the foundation on which we can rebuild onwards into the future our, connection with the spiritual world. The first thing which we must examine is the effect of the various confessions, the creeds, existing among civilized people. Hitherto they were necessary, to guide the heart and, mind to spiritual realms, but in future they will help to detach man from the spiritual world, unless they admit something entirely new into their efforts. Fundamentally speaking, the creeds of the present day are based on the egoism of man, as we shall realize if we put before our souls one question of such great importance that it forms, and always must form, a touchstone for their views, the question of the immortality of the human soul. We can see, from the way in which this question is generally handled by the creeds, that they appeal largely to man's egoistic instincts. Of course there are deeper foundations for their speech, but these we are not discussing today: as a rule the creeds speak of the “continued existence of the soul after death"—that is, the continuation of the life of the human soul. To deal with the subject of immortality from this point of view is comparatively easy, for human egotism asserts itself there emphatically. Man simply cannot bear—apart from all truth about the question—the thought of utter extinction at death, so that a certain response is always to be found in man’s soul when "life after death" is mentioned. The treatment generally given today to the idea springs from an egoistic interest in people. They would prefer not to die as souls at physical death. Naturally, the soul's continued existence after death will be assumed in all our future discussions on immortality, but the way in which anthroposophical spiritual science speaks of the continued existence of the soul after death is very far from being accepted by the creeds. But this also is important: that people of our day must hear a very different language about immortality from that to which they are accustomed. One who discusses the question of immortality should not only speak of life after death, but also of that life which is lived here in the physical world between birth and death. For as you know, this life is also a "continuation"; it is a continuation of the life passed between our last death and that birth through which we are now in the physical world. That is the view which men must learn to hold—that the life here is a continuation of the spiritual life before birth. In the growth of a child from day to day, from week to week, from year to year, we must notice forces from the spiritual world arising from its inner being, forces which have come with birth and work so as gradually to form the being of man as time goes by. In a sense we lift the veil of the God in man when we enter into the life of the child to develop it. Social relations must take on something of a religious impulse permeating the whole of life between man and man. For this the important, the essential thing is an attitude which never forgets that physical life is a continuation of a pre-natal life, of spirit and soul. Many things will follow on this. For one thing we shall recognize that our real humanity lies in the depths of our being, gradually emerging. I have referred to ancient times of human evolution, known from an anthroposophical standpoint as the first and second post-Atlantean epochs. People in those days were as capable of development right into their old age as only the young are nowadays. A child goes through a physical evolution about its seventh year with the change of teeth; through another metamorphosis when puberty occurs; but after that what goes on in his evolution is outwardly less noticeable. In olden times this was not so; what man went through in soul and spirit expressed itself into much later stages of life. Nowadays old age sets in at seventeen or eighteen, and we are amazed at its evidences. Here is an example: a short time ago, in Stuttgart, at a meeting of the Cultural Committee where present-day education was discussed from the most varied points of view, a young man got up (let us call him "a young man" though he might equally well be called an "old boy"!) who told us we needed instructing about the true ideals of education! He began by uttering some very high-sounding words, then read out the programme of a modern Educational Society. After much stumbling he finally broke down, and, having no more to say, gathered up the threads with "I must therefore claim to have proved that old age no longer understands its own youth," and went out. I replied that I quite saw we had not understood him, for the simple reason that his speech and behaviour had been those of an old man; he had in fact enunciated as principles, like an ancient grey-beard, the last word in abstractions. Old age, nowadays, means the limit up to which a man can develop. Up to a particular age a person can absorb all sorts of things, and is not ashamed to develop himself. But at about twenty years of age he feels shame at the idea of developing farther. Seldom nowadays do we find people with grey hair and wrinkles welcoming with joy the dawn of each year because each year brings new possibilities of development to the organism and new knowledge, unattainable before, is within reach. At the inconsiderable age of thirty men are ashamed to make themselves capable of development, or to learn anything more. The point is that we should actually retain the possibility, all through life, of rejoicing in the coming year, because each year charms forth the divine-spiritual content of our own inner being in ever new forms. I want to emphasize this point. We should really and truly learn to experience our life as capable of development not only in youth, but through its whole span between birth and death. For this a new education will be necessary. We elders find that to look back at our own schooldays evokes few pleasant thoughts. We must manage to shape schooldays for the children of today so that to remember them will provide an ever new and invigorating source of life. Now this will bring, as you can see, the possibility of opening for mankind real perception of the soul-spiritual within themselves, of experiencing something extending beyond the everyday life which is stirred and stimulated from without. Other knowledge will be recognized as necessary. There is a secret, intimately connected with the present stage of human evolution, which is not known today. In earlier times, before the middle of the fifteenth century, it was not necessary to take much notice of it, but today it must be reckoned with. This mystery of life is that man, constituted as he is today in body, soul and spirit, every night looks, to a certain extent, at the events of the coming day, but without always carrying that vision over into full day-consciousness. It is his "Angel" who has that clear consciousness. But what is experienced at night in community with that being whom we call the Angel is a pre-vision of the coming day. This is no subject for human curiosity, but a matter for practical life. Only when the feeling of this fact fills our inner being can we make right decisions and bring right thoughts into the course of daily life. Let us assume that a man has something definite to do, say at noon. This that he has to do has already been arranged by his Angel and himself during the preceding night, though the fact is not necessarily kept in consciousness and human curiosity has no part in it. People should be filled with the conviction that during the day they should realize in a fruitful way what they have arranged at night in co-operation with this Angel being. Much that has happened of late might draw men's attention with almost shattering force to what I have just said. The last four or five years of agony should have taught men that the consciousness of their association with higher beings through the experiences of the night did not, alas! exist. If the feeling had permeated men that their doings in the day were in harmony with the decisions made with their Angels in the preceding night, how different events would have been! These things must be spoken of now, to point out how man must learn to regard this life between birth and death as a continuation of the life of spirit and soul which was his before birth. It must be made known that man in future should be able to experience throughout his whole life the revelation of the Divine in his own being, and that through all his life in the day this vivid consciousness should persist as: "What I do from morning till evening I have discussed with my Angel, while I slept." Men must turn to feelings which are more concrete with regard to the spiritual world than the modern abstractions of various creeds, which at the same time claim that they appeal to unselfish, not to egoistic human instincts. From such feelings will arise that which will provide the necessary relation to the beings belonging to the Hierarchy of the Angels, who will once more be able to interest themselves on our behalf. Men's attitude to the spiritual world must move in this appointed direction. Yet again we must observe something. The creeds speak much about "God" and "The Divine." What do they really mean? Surely something of which a vague consciousness, at least, exists in the soul of man. After all, it is not, what name is given to a thing that matters, but what it means to a man's soul. Men talk of “God" and of "Christ," but all the time they only mean the "Angel"—the Angel to which they turn because they meet a response in their souls. Whatever the creeds may speak of today, whether of God or Christ or other divine being, the substance of the thought only relates to the Angel Beings who are connected with man, the Angeloi. Higher it cannot rise, since people are disinclined to seek any wider relation to the spiritual world than an egoistic one. The relation to the Archangeloi, the Hierarchy of the Archangels, must indeed be sought in another way. Men's interests today must be considerably widened. I will show you how that extension must take place, so that from making response only to the Angeloi, they may rise in their feelings to the Archangeloi. They must realize that they have passed through terrible experiences all over the civilized world during the last few years. Many have asked about the "causes" of, these events, with mutual imputations of "guilt " and " innocence ": yet we need only look below the mere surface of things and we shall have little interest in all this talk about “causes " and "war-guilt" or " innocence," simply because we can see that what has come up to the surface in these last four or five years is, like waves of the sea, always there, but brought up from the depths to the surface by the forces below. An upheaval of human forces had been going on; one people after another shared in the enormous folly of those years; one could but say: "Some turmoil of elemental forces is surging upwards into view. The sea of human life has become unquiet—What is it?" We shall never get things clear if we do not connect this fact of humanity's unrest with the whole period we call "history." We must convince ourselves that the armed struggle of the last few years is only the beginning of events which will take place in quite other spheres, but which have never before existed among us in this particular form. We are not at the end of a stage of evolution—only superficial observation could lead to that conclusion—we stand at the beginning of the greatest conflicts, the greatest spiritual conflicts of the civilized world, and we must put forth our best efforts to be equal to them. Increasing opposition is threatened in the soul-attitude of East and West in the near future, for East and West have developed in two quite different directions. If we would see into these things, we must set before ourselves certain phenomena in their deepest, most fundamental form as riddles to be solved. For decades we have heard repeated in socialist circles holding the Marxian theory, that everything man experiences as art, religion, custom, law or science is just "Ideology " (I have discussed this at greater length in the first chapter of The Threefold Commonwealth). This means that a view which had been developing amongst the middle classes for the last three or four hundred years, but which they were too timid to admit, has been frankly acknowledged by the socialists of the last half-century. They assert that the genuine reality of social life consists in actual happenings; therefore the real lies only in the economic forces. All conceptions of art, religion, custom, science, law, morality, merely form a kind of vapour rising from true reality, and are mere ideology, with nothing but a semblance of reality. The socialists conclude that it is only necessary to change economic life and all other changes will ensue, since everything else—morality, law, religion and so forth—is only an unreal vapour arising from the events in the economic sphere, which is the "only reality." If, however, the world be considered in no restricted sense but as a great whole, we shall defend this word "ideology " which, but for their timid dislike of facts, the middle classes might have been using for three or four hundred years. They did feel that the economic life was the "only reality" and what displayed itself as science, art or religion was like a vapour; all life was based on this, and it was reserved for their pupils to carry their reasoning to its logical conclusion. Socialists are, after all, only extreme pupils of the middle-class world. This is the view which, forming in the West, reached its climax in the second half of the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. Other impulses have formed the Eastern view of the world, and an Oriental would say: "I look at what is going on in the external world: I see what my senses convey to me, what I use as an instrument for transforming the world around, what shines down on me from the stars, and what I myself am as to my bodily nature—what is it all? It is Maya! What then is reality, and not illusion? Only what is experienced in the human soul—that is reality!" One who does not translate in terms of a dictionary, but according to the inner meaning, knows that the words "Maya" in the East and "Ideology " in the West mean one and the same thing. For thousands of years the Oriental has regarded the outer world which affects the senses—including economics—as Maya. The Westerner, on the other hand, sees his reality in what for the Oriental is "Maya," and what arises in his soul is for him "Ideology." Both views of the world have developed to a certain point. Talk with the leading men in the socialist parties especially in those places where the first Revolution (known here as the "November " Revolution) has not yet taken place, and it is evident that this revolution altered their ideas somewhat, but not their feelings. You hear the same views as obtained right up to the war, that it is not necessary to contribute anything from the will towards transforming, revolutionizing the world, but that all that will happen of itself. Something fatalistic has appeared in the West. People are convinced that they need only wait until the means of production are sufficiently developed, and then by a natural metamorphosis all that is concentrated in private capital will pass over into other forms. Thinking of this sort is as sensible as saying: "This room is full of bad air. I cannot breathe. The window could be opened, but I am not going to open it; I am waiting until the air improves of itself." Fatalism of the West, Fatalism of the East—we know them well. In the East, though not at the very beginning, men fell into complete fatalism, as the philosophy of Maya developed. Every world-philosophy has, in its inner law, the impulse towards fatalism at some time, but we stand today at a point where we must get rid of fatalism. We must pass from mere observation and contemplation to the exertion of will and intention. We must rouse our wills by developing impulses from the truths I have described regarding birth as a continuation of pre-natal life, remaining young notwithstanding white hair and wrinkles, the playing in of the nightly work of the Angel into daily life. Man needs to acquire impulses for his life of will by widening his sphere of interest, by seeing not only what touches his own personal life but what affects the civilized world in manifold forms. Looking at the West, to which we ourselves belong, we see the inner world as ideology, the outer world as reality: in the East, ideology, Maya, in the outer world, reality in the inner world alone. In the interaction of human beings at the present time, we have the task of finding the way of escape from that aspect of these philosophies which has already turned to fatalism. We must look for this way, and we shall only find it if we are in earnest about something which annoys people terribly today. There was a remarkable example of this once, when my hearers were greatly vexed by something I said in a lecture in a South German town, though it was a truth necessary for the present time. The context of my lecture necessitated the remark that the leading classes of the present day have a decadent physical brain. Such statements are unpleasant both to utter and to listen to, but it is necessary that people should realize this fact. The very people to whom the present configuration of our times is due have, in achieving it, acquired a decadent physical brain. It is so, and we are in one sense in the same case as were the people of Europe during the, great migrations and the spreading of Christianity. The Christian impulse came over from the East, by way of Greece and Rome. Naturally the Greek and Roman world was far more highly developed than the. German. The Germans were barbarians. But the brains of the Greeks and Romans were decadent, therefore the surge of Christianity was not absorbed by them in the same way as it was when it reached the Germans. That is a migration of peoples which went horizontally. today it is "vertical." today a wave of spiritual life is coming from the spiritual world. Just as Christianity was at first reflected from the Greeks and Romans, so the spiritual world is reflected from the bourgeoisie today, and that is decadent. The proletariat are not so yet; they are still able to understand what is meant by the spiritual world. But the others will need preparation through anthroposophy, through that part of the brain which is not yet physical that is the etheric brain. We are at present confronted with the fact that the leading classes are not only menaced with a decadent brain, but with entire decadence, if they do not realize that they must grasp the spiritual view of the world by supersensible means. The tragedy of the bourgeois system is that it would grasp everything "physically," whereas our task today is to grasp things with the etheric brain, to take spiritual truths into our being. Modern humanity must steer in this direction, and the West must take the lead. Here we must take into account something very important. Observe the development of language, passing from East to West. Take the German language, today dreadfully misused. If we look back at the language of Goethe, of Lessing, we can see that not so long ago in the very words, through their peculiar quality, it was possible to express what of spiritual life lay within them. today we have dreadfully neglected our language, degraded it into phrases only; but that it can no longer express spirituality is not due to the language alone. The farther West we go as regards language, the more we find in speech, with its tunes and sounds, even with its grammar, a complete rejection of what is really spiritual. From this rejection of the quality of soul and spirit from the Anglo-American idiom follows the mission of the Anglo-American peoples. Their world mission consists in this: in learning, maybe instinctively, yet still learning (as they listen to other men, in course of acquiring world dominion), not only to comprehend the sound, but to interpret the gesture of the language, to hear more than the mere physical sound, to hear something which passes from man to man in speech, going beyond the spoken word. That works from etheric body to etheric body. Here lies the secret of the Western languages, that in them the physical tone loses its significance, while the spiritual gains it. It is part of their task to let the spirit filter into speech, not merely to hear physically, but to hear intuitively more than passes over into the sound. In the West, the spiritual must be sought behind language itself. If we look at the East, we shall notice an ever-increasing urge among the peoples who, as we have seen, sink themselves into their own inner being, not to be bound by the old forms of conception as to "Karma," " Reincarnation," and so forth, but to look out into the world, and in that outer world to perceive something spiritual, even to establish a sort of Philosophy of Nature. These are only trivial instances through which we can widen our interests from our own personality and our nationality to take in the whole of humanity, saying to ourselves "Here in the West is Ideology, though quite another Ideology from the Eastern one," and seeing how elemental forces are stirred up within earthly humanity as a result, of these antitheses. We learn to take our stand within the whole civilized world, and when we develop such knowledge of our position within it at the same time we build in our souls the means of acquiring feelings which lead higher than the sphere of the Angeloi. Our interests will be so much extended that we shall incline to ideas which ascend to the sphere of the Archangeloi, for all that I have been saying about the opposition of Ideology-Maya, etc., works in its primal force in the sphere beyond that of the Angeloi. We can see from this what is really needful for modern humanity. What will the so-called clever people call anyone who speaks of these things—Maya, Ideology and so forth—as having primal forces which function in the sphere of the Archangeloi? Just a fool, quite naturally, since men are so hide-bound by their acquired spiritual outfit that they feel no concern in the wider interests of mankind. That can only be achieved from a spiritual standpoint, by penetrating into everything which works for the great interests of humanity. I have given you an idea of how to work up into the sphere of the Archangeloi. It is possible to rise stilt higher, and present-day humanity must learn that also. Our educated classes have, always been taught to look back to Ancient Greece. Young men (and in recent times young women also) have had to go through a certain schooling to absorb Greek culture, and have thus acquired an impulse which was enough to lead them to feel more and more deeply into the Greek world. This has a great significance for our civilization, that in our most important years of development we have learnt what Greece accomplished for the world. The Greeks did otherwise; it never entered their heads to teach their children the Egyptian tongue: they occupied themselves with immediate reality, for which they possessed a clear, sense. We occupy our young people, not with instruction concerning their environment and the impulses of reality, but with those of an olden time. We have no idea what we are really doing. It is not only that we teach our young children (I suppose I should say our "young ladies " and "young gentlemen ") the Greek language: for in a language, in the configuration of its sounds and its grammar, lies also the character of a whole people. In absorbing the Greek language, as is done today, man acquires the same soul-attitude in the world as was held in Greece. There all cultural life was such that only a small top-stratum shared in the culture; the rest were slaves. In Greece no occupation was worthy of a free man but science, politics and—even then in a supervisory capacity agriculture: everything else was a matter for slaves. This is hidden in the language, and when we take Greek culture and language into our own spiritual education, we unite aristocracy with it at the same time. For the Greek it was quite natural to construct his whole social organism in accordance with his intellectual tendency, for in his case that was connected with his blood. There were the ordinary masses: then those people of a higher type, who possessed the higher life of the mind through their blood. This finds expression even in Greek sculpture. Compare the position of nose and ears in the Hermes-type with that of the Zeus- or Athene-type. The Greeks knew perfectly well what they wanted to express when they set the Hermes-type over against the Aryan Zeus-type. We are permeated with all this more than we think. When we form our views of the world, we really construct ideas still suited to what in the Greeks came through the blood. Our intellectual, our cultural life is saturated with what we absorb from the Greeks. Hellenism intrudes into our times luciferically. Hellenism, in the period which immediately followed it, was metamorphosed into Romanism. Compared with the Greeks the Romans were dull, prosaic people, but they did develop other aspects of life. They lived out in an abstract fashion what came to the Greeks from the blood. Unlike the Greeks they made even man into an abstraction, a "citizen of the State." A man, in the Roman sense, is not really "man"; he is a citizen of the State: an incomprehensible thing to the Greeks. To be born a human being did not make him a man, but being registered in some kind of State archives. This sometimes appears today in grotesque fashion. I once had an old friend, sixty-four years of age; one day he said to me that he had saved such and such a sum—he had always been very poor—and that he wanted to marry the love of his youth. He had become engaged at eighteen, but had no money to marry, and the couple had vowed to wait until they could. He returned to his birthplace, now that the way was open, but found that the marriage could not, take place because his community doubted his existence. Years before, the parsonage, with all the parish registers, had been burned down and there was no one alive who could give evidence as to his identity. My friend assumed that his existence was proved by his presence, but he had no "legal evidence." It is true the marriage did eventually take place, but the difficulties had shown him the much greater importance of a "birth-certificate " than of his own personality. Men then are "citizens." They are what they are in an abstract connection. This view is essentially Roman, as is everything of this sort which we come across in ordinary life. Our education has been taken in hand by the State, which is already abstract, but will become more so under socialist influence. People are not educated today to take their place in the world as free human beings, but to have a professional calling and take their place in that. The State takes young people in hand, not at once, for then they are too “shapeless," so it leaves them for a time to their parents, then, stretching out its talons, it trains them to be useful to it, taking good care that they are so. It gives them an economic life, gives them everything prescribed, and then pensions them off. It means a great deal when a man can assure himself of a pension as well as an income—something substantial, which binds him to the abstract State and affects the rest of his mental attitude. The Roman attitude has passed into men of other times. Say to a man today: "to partake of immortality needs an activity of soul, that thou thyself mayst carry thy soul wide awake through the gates of death"; he will not understand. He has been made wholly unaccustomed to direct his understanding to such a question. Instead of this he is told: "You need only believe in Christ and in what the State does." First he will be looked after by the State, with a pension when he has worked long enough then the Church goes one bit farther; it offers a pension for his soul after death, so that neither in his lifetime need he do anything for his own soul nor when he carries it through the gate of death: A man is "registered " nowadays, and the political essence of Rome, already taken into our own being, will increase. All sorts of dreadful experiences are possible because of this. Helping with the institution of the Waldorf School at Stuttgart, I have had to look at the various School Regulations. Looking back, I must admit that in the 'seventies and 'eighties of last century, the regulations were very small: they included what had to be studied in each class, the aim and the subject matter being given, but in everything else the teacher was left quite free. Nowadays we get an enormous syllabus with "Official," "Ordinance," written on the first page, and specific instructions as to the manner of teaching. So that what should only work on one living personality from out of another, is set down in rules and orders; it has become "official," it is "decreed "! That is the death of mind and spirit, directly traceable from Central Europe to Ancient Rome. This is the second thing we have absorbed—with Romanism, the politicolegal element. In addition to this, however, there is something which could not be transplanted from the old life into the new—the economic life, which can only be modern. It is possible to chew the cud of Greek knowledge, to allow the Roman political ideas to influence us, but we cannot "eat" what the Greeks and Romans have eaten. Economic life must be modern. We have gradually woven into our economic life the Greek life of intellect and the Roman life of rights, and our task is to disentangle them again. To understand that these three strata brought out of different epochs have, as it were, been joined together and must be separated means to extend one's interest in time (as, in the East and West in space) down to the present; that means to make ourselves capable of feelings which can raise us to the Archai! How few develop an interest for these things, an impartial interest in how the Zeitgeist (Time-Spirit) acts by thrusting one period into another. I spoke at Stuttgart on the artificial nature of our classical education. It may have been mere coincidence that a few days after there appeared in the papers great announcements signed by all kinds of Zöpfen—professors—(I beg their pardon!) to the effect that a classical education should not be undervalued, seeing that it had contributed to the greatness of the German people, so gloriously displayed in the latter days. This, literally, was to be read as the alleged opinion of educationists in April, 1919—after what happened in October, 1918! And to think that this and other things should be possible in our times! Unless we reach a stage at which we can see things so as to absorb the impulses which work into our physical world out of the spiritual—unless we realize that man, just as he is connected through his bodily organization with the animal, plant, and mineral kingdoms, is also connected in his spiritual organization with the Angeloi, Archangeloi and Archai (Angeloi as the guardians of personal development, Nation Spirits as guardians of development of peoples in space, Spirits of Time as guardians of development throughout the ages)—unless we can understand these things from their spiritual foundations, we can advance no farther. Everything depends on man having courage and force today to look into the spiritual world. We are at the beginning of a hard struggle, in which will be stirred up all the instincts springing from the one half-truth that economic reality is the only reality, that everything belonging to soul and spirit is Ideology; and from the other half-truth that the only reality is the psychic spiritual, all outside it is Ideology, Maya. These contradictions will let loose in human nature such instincts that the spiritual conflict will blaze for long periods in forms of which people at present have no idea. We must grasp this; and, further, learn how we are to raise ourselves, in harmony with our time, to a view of the spiritual world as we conceive it. It is this which the times themselves ordain and demand; to this we must turn our attention. |
| 133. Earthly and Cosmic Man: Form-Creating Forces
20 Jun 1912, Berlin Translated by Dorothy S. Osmond |
|---|
| Not for personal reasons, not for national reasons, nor for any “human” reasons whatever, but for purely theosophical reasons it makes one's heart bleed that in England today the President of the Theosophical Society should be making speeches which really cannot be described as “theosophical” but are eminently political. |
| The reference here is to certain prejudiced and faulty views contained in the teachings emanating from the Theosophical Society.2. Man in the Light of Occultism, Theosophy and Philosophy3. For those who have only lately become acquainted with the Anthroposophical conception of the world, let it here be mentioned that these words were spoken at the time when Mrs. |
| 133. Earthly and Cosmic Man: Form-Creating Forces
20 Jun 1912, Berlin Translated by Dorothy S. Osmond |
|---|
In the preceding lecture we studied the principles and powers in the being of man belonging specifically to Earth-existence. Certain forces operating in human nature are, in reality, “heritages” from the earlier embodiments of the Earth: from the Old Saturn period, the Old Sun period and the Old Moon period. These heritages from primeval epochs of evolution are contained in the physical body, the ether-body and the astral body of the earthly human being; but it is the Earth, the forces deriving actually from the Earth, that have made the physical body into the instrument of man's present form of consciousness. The ether-body has received, specifically from the Earth, the qualities whereby it becomes the bearer of the memory, the instrument of remembrance. The astral body itself developed during the Old Moon period of evolution—the planetary predecessor of the Earth—and the Earth adds the forces which provide for the operation of human karma. But something else exists as an activity, an expression of the human personality, something specifically connected with the “ I ” in man which has been acquired only during Earth-evolution. Waking consciousness, memory and remembrance, the operation of karma—these were the active principles added to the physical-, ether- and astral-bodies in that man was endowed with the “ I.” We said that the forces of the “ I ” are sent outwards, towards the outer spiritual world, and that these forces, unlike those inhering in karma, or in memory, do not remain inexorably bound up with the human being. A man's memories and remembrances remain part of him; his consciousness, obviously, has significance only for him, for other beings have quite different forms of consciousness; and karma is bound up with the human being in so far as it has to operate during the earthly incarnations to adjust and make compensation for his deeds. But “forms” or “forces” begotten of thoughts or feelings—these detach themselves from the real “ I ” of man, and in a certain respect acquire independent existence, independent reality. Unlike the other forces, they do not remain connected with him. Now in respect of the forms or forces deriving from the “ I ” of man, a sharp distinction must be made. The human “ I ” or Ego can unfold either selfishness or selflessness in the inner life. According to whether selfishness, or selfless love and compassion are unfolded, these “forces” or “forms” operate quite differently. The forces of selfish thoughts become forces of disturbance, even of destruction; they pass into the spiritual world actually as destructive forces. On the other hand, all forces of selfless thoughts enter into the spiritual life of Earth-evolution, not as destructive but as upbuilding, constructive forces. In that these forces of selfless thought detach themselves as it were from the “ I ” of man, they leave behind certain traces in him. Especially is it true of forces begotten of selfless thoughts and feelings, that as they go forth from the “ I,” they leave traces behind in the human being—traces which are quite perceptible. The more the “ I ” sends out forces born of selfless thoughts and feelings, the more does a man develop individuality of form, of gesture, facial expression, and so on—in short, the power inherent in his own being. The forces of selfish, self-seeking thoughts and feelings, however, operate in him in such a way that he has little power to give expression to his own individuality. We must therefore ask: What is the principle underlying the distinction to be made among the individual forms of men in the course of the evolution of humanity? Everything that is “form” on the Earth derives from the Spirits of Form. The name “Spirits of Form” is actually given to these Beings of the Higher Hierarchies because everything that has form, shape, life—everything that takes on shape inwardly and evolves an outer form, has received the essential impetus for this form from the “Spirits of Form.” Now all these Beings of the Higher Hierarchies are involved in a constant process of evolution. Not only man, but in a certain sense all the Beings of the different Hierarchies are involved in a constant process of evolution. In our present age, the Spirits of Form are moving to the higher rank of “Spirits of Movement”; the “Spirits of Personality” to that of “Spirits of Form; the “Archangeloi” to that of “Spirits of Personality” or “Archai.” As the Spirits of Form move upwards in rank they no longer function, in the primary sense, as “Spirits of Form,” but the succeeding Spirits of Personality do not, at once, assume the functions of Spirits of Form. This will help you to understand that something quite definite will come about during the second half of the period of Earth-evolution into which we have now passed. At the beginning of Earth-evolution, the Spirits of Form stamped the principle of form into man; this comes to expression in the different human forms. Just as the various races have developed their characteristic qualities, and individual human beings take on the traits of the several races, so have the various groups of humanity as a whole all over the Earth received their stamp from the Spirits of Form. What the Spirits of Form stamped into human beings has long since passed into the processes of heredity; it has long since become a heritage, handed down from generation to generation. In a sense, the Spirits of Form leave man greater freedom as they themselves move into a higher category and withdraw from the form-creating function devolving upon them at the beginning of Earth-evolution. So far as the Beings of the Hierarchies are concerned, man is drawing nearer and nearer to his “coming of age.” But of this we must be clear—The Spiritual Beings, moving up as they do to higher ranks, have themselves to evolve, and prepare for the next planetary condition of the Earth, in order that during the Jupiter-existence they may endow the beings who once belonged to the Earth with forms which will then be appropriate. Towards the end of a planetary age it is always the case that the being of central importance—and on the Earth this is man—is left free, so that the qualities with which he was originally endowed may pass more freely into his own hands. In the course of Earth-evolution in the future, therefore, the forces of form, the forms begotten by thoughts and feelings, will assume greater and greater importance. And in so far as they are selfless, in so far as they are the offspring of selfless wisdom, selfless love, these forces will work formatively upon man. For the design or pattern of the evolutionary process may be indicated in the following way. The further we go back into the past, the more do we find that the outer form of the child resembles that of its forefathers; but the further we go into the future, the more will the human being, in his outward appearance, become an expression of the individuality who passes on from one incarnation to another. This means that in one and the same family (even now it is very frequently the case and nobody with an eye for such things will deny it) there will be less and less likeness between the faces of the children and between the faces of the children and between the other parts of the human figure, for the reason that the forms will no longer be the expression of family or race, but more and more the expression of the individuality. Anyone with a knowledge of Spiritual Science, if he really observes human beings living all over the Earth, can perceive, even today, side by side with the inherited characteristics of race or family, more and more strongly individual lineaments of face, head, and other bodily forms; he can perceive the striking differences in form and figure among members of one and the same family. In this respect, of course, we are in a period of transition; but the Sixth Post-Atlantean epoch is in preparation, together with its paramount characteristic, namely, that unlike the conditions obtaining in earlier periods of culture, outer marks of race will be much less of a criterion. In the Sixth epoch the criterion all over the Earth will be the extent to which the individuality has impressed upon his countenance and upon the whole of his being, the forces left behind by the forms begotten of selfless thoughts and feelings—especially those deriving from wisdom. It is contrary to every principle of true Spiritual Science to say that just as there was one leading race in each of the culture-epochs in the past, so in the future, too, there will be another such race, distinguished by physical attributes. The ancient Indian culture was borne and sustained by a leading race; so, too, was the culture of ancient Persia, of the Egypto-Chaldean and Graeco-Latin epochs. But already today it is apparent that culture, instead of being borne by one specific leading race, spreads over all races. And it is by Spiritual Science that culture—a spiritual culture—must be carried over the whole Earth, without distinction of race or blood. It is already apparent that our epoch will be succeeded by another of quite a different character, an epoch when, all over the Earth, the extent to which a man expresses his innermost being in his outer form, will be made manifest. It would be sheer contradiction of every principle of Spiritual Science to speak today of continental limits, or the limits of any particular territory, in connection with human beings belonging to the Sixth epoch of culture—for they, in the future, will be spread over the whole Earth. Only one whose vantage-point is not that of Spiritual Science, who has some queer bee in his bonnet that a kind of wheel revolving in spiritual evolution causes everything to repeat itself just as spring, summer, autumn and winter repeat themselves when a year has run its course—only such a one could make the statement that what was necessary for the creation of races in earlier times will simply be repeated for the Sixth epoch. Such a statement would be entirely at variance with true Spiritual Science, and would cut across all knowledge of the actual and real progress of humanity. The inner power of the soul becomes more and more manifest as evolution goes forward. The old is not repeated merely in slightly different form, but actual progress takes place in the evolution of humanity. If Theosophy is to keep faith with its good old principles—the first of which is to promote culture without distinction of race, colour, and so forth, it will not cherish groundless hopes of a future culture emanating from one particular race. The deeper connection of Theosophy with the actual course of evolution consists precisely in this:—that the processes operating in world-evolution are understood, that thinking and feeling are brought into harmony with theosophical knowledge, and the necessary impulses of will made effective in the world. In order to understand how the power of the soul will more and more be made manifest in humanity, it is only necessary to bring out one point clearly, and then we shall realise how the human being evolves as an individual. (The point that has been developed today has been dealt with repeatedly, for many years.1). At the beginning of Earth-evolution, the human being was part of a group-soul—as expressed in race, blood, family and so on—to a far greater extent than was the case later on. As evolution continues he becomes more and more of an individual, develops his individuality. We have heard what an important part certain forces play in the development of the individuality during Earth-evolution: consciousness that is dependent on the physical body; memory and remembrance which are dependent upon the ether-body; and karma, whereby a man can make real progress, in that his imperfections and faults do not remain but can be overcome by him as he passes through one incarnation after another. But the “forms” or “forces” created by thoughts and feelings, although they detach themselves from the human being and lead an independent existence, are nevertheless closely united with him, in that they leave vestiges behind; these vestiges, as they are sent out by the “ I ”, contribute to the definition of the individuality and man gradually divests himself of the qualities belonging to the group-soul. The trend which will become more and more general over the globe and will form the essential, fundamental character of the Sixth epoch of culture, is no kind of approach to a new group-soul, but far rather the laying aside of the attributes of the group-soul. Intimately connected with this is the fact that the spiritual guidance of human beings will become more and more a matter individual to each one; they will have greater inner freedom in this respect. Anyone who has understood the trend of the little book The Spiritual Guidance of Man and of Mankind will realise that a movement in this direction is in very truth taking place in the human race. It is a fact that in ancient times men lived under external leaders and teachers, but even in those days, leadership was gradually becoming an inner concern. Just as the outer form becomes an expression of the Individuality, so does the path to the spiritual worlds taken by human beings become more and more their individual concern. It is the duty of those who have insight into the signs of the times to insist that human beings have not remained stationary at an earlier stage of development, that the forces once employed, cannot be repeated in the same form, simply because men have gone forward in their evolution. In the age that is coming, the souls of men will become more and more mature, able to discern and perceive those things of which Spiritual Science teaches today. The “Mystery of Golgotha,” as the essential Christ Event, was an outer happening, striking into the physical world; a future Christ Event will be an inner concern, inasmuch as the soul of man has been so quickened by the first Christ Event that in days to come, the way to Christ will be found in the Spirit, out of the life of soul. Wherever you look in Spiritual Science as it is presented here, you will always find—even in the case of very specialised details—that it is consistent with your own powers of reason and free judgment, provided only that you make a real effort to apply this free power of judgment. In that the individual human being is all the time becoming more accessible to influences from the spiritual world, the authority of external leadership will gradually lose its weight. It is very important to realise that the ancient wisdom exists and must be understood, that understanding of it can constantly increase if men's souls are open to the spiritual worlds and if they strive to grasp this wisdom with their powers of reason. This is the very essence of progressive evolution. However specialised the subjects may be, appeal to individual reason and judgment must never be excluded. It is a very different thing to bring forward some young man and announce that he has this and that incarnation behind him! If I were to tell you such things I should beg you at the outset not to believe them simply on my word—but I should never dream of making such assertions authoritatively, for the simple reason that you could not possibly convince yourselves objectively of their truth. When, however, it is said that the same Individuality was present in Elijah, John the Baptist, Raphael and Novalis—all long since dead—you can yourselves discover by studying their lives, whether there are reasonable and sound grounds for such a statement. And no other kind of appeal must ever be made: the respect due to each individual soul demands that such a test should be within the realm of possibility. There are, of course, lazy-minded people who say: “We have to “believe” you when you speak of the same Individuality having lived in Elijah, John the Baptist, Raphael and Novalis.” ... No! they are not obliged to believe it ... but they can try, at least, to find evidence in the different lives of what, admittedly, can only be actually discovered by occult research. This evidence can be found, and it is pure laziness when people say that if someone speaks of the incarnations of human beings long since dead, this must be taken on authority just as is the case when the incarnations of some young person living today are announced. That is a very different matter! In this respect a deep appeal must be made to Theosophists to put everything to the test of reason and not to rest content with the cheap excuse that things cannot be proved. They can be proved, if there is willingness to do so. This must be constantly emphasised. A kind of counterbalancing process operates in the world and while, on the one hand, the development of the individuality is progressing, on the other, something else will become more and more universal, namely, the objective knowledge which must be acquired by man. Objectivity of knowledge, uniformity of knowledge does not gainsay the principle of individuality. Mathematics in itself is an illustration of this fact. And so it is the task of occultism—if one may speak of occultism having such a task at the present time—to provide objective wisdom and knowledge of the universe. Even although, in the nature of things, the ideal is not immediately in sight because not every individual has sufficient time and opportunity to put specific details to the test, it is true, nevertheless, that although things can actually be discovered only through occult research, they can be examined and endorsed by every individual; it is not necessary to take them on faith. All that is required is to reflect about things, with reason and sound judgment. Let us take a definite case, remembering that what will be said about it is applicable everywhere. Suppose someone says: “Mankind has evolved. Progress is a reality in evolution. This progress reveals itself in the fact that man is becoming more strongly individual in his nature and being. It follows that whereas in olden times, leadership was vested more in persons, in times to come this kind of leadership will be superseded by objective wisdom, objective knowledge; personal leadership will recede and become merely an instrument and means for bringing objective wisdom to the human being. The ideal vantage-point is that the occult teacher is no different from a teacher of mathematics, who quite obviously has his function. But mathematics are not accepted merely on the authority of the teacher of mathematics; every individual accepts mathematics because he gradually acquires knowledge and understanding of the fundamentals. Hence the element of wisdom and of knowledge will more and more supersede the element of personality” ... Suppose that such a statement were confronted by another, to the effect that “the world rolls onwards like a wheel; in olden days there were great Teachers of humanity, and new ones are about to come ...” When faced with a statement like that, it is not possible to adopt the easy-going principle that either the one or the other may be believed; it is a matter, then, for deciding: which of the two is acceptable to reason? There is the choice between deciding whether no progress is to be ascribed to humanity and everything thought of as eternal repetition, or whether humanity does really progress and that evolution has meaning and purpose. Those who refuse to recognise any meaning in evolution can speak, if they like, of the eternal repetition of epochs of time; but those who see meaning and purpose in Earth-existence as brought to light by occult research, will not speak of eternal repetition of the same things—which does not, in fact, take place. It is all-important to realise that the faculties of man have developed and that in this development—to take one example—the following is involved. In the ancient Mysteries each human being was obliged to submit to certain enactments and procedures directed to his own person; thereby he became an “Initiate.” He passed through the “different grades of Initiation.” In and through the Mystery of Golgotha these grades of Initiation became a world-historical Event, made manifest for all humanity. What had in olden times been an affair of one or another particular centre of Initiation, became a world-historical event, passed into the common estate of humanity, and was thereafter accessible to every advancing individuality. In my book Christianity as Mystical Fact, therefore, the Mystery of Golgotha is described as the culmination and, in a sense, the close of the ancient Mysteries, because it brought all the ancient religions into one great unity. Occultism reveals still more clearly how the several streams of culture are gradually converging into one; but as they converge, they must be recognised and identified. The very operations of occult research reveal how the fruits of this research harmonise with what everyone can accept for himself, from his own observation of happenings on the physical plane. Let us take a very far-reaching example, of which you may well say, to begin with: “There he is telling us something that really cannot be put to the test of reason, nor even approached by reason.” You may well say this, when it is first put before you. My book An Outline of Occult Science describes how, at one time, Sun, Moon and Earth were united in a single planetary existence; the Sun then separated off and, at a later stage, Mercury and Venus; still later, Mars separated off from the Sun. The further we go back in time, the more does such a process become a spiritual process and the question it is essential to understand is really this:—Who were the Beings who thus separated? Of primary importance as regards the Earth, was the Christ Being, the great Sun Being Who through the Mystery of Golgotha subsequently united again with the Earth. Thereby all the antecedents of Christianity were brought to a kind of climax and culmination in Christianity itself. With the Mystery of Golgotha, a mighty Cosmic Power streamed into Earth-evolution. It might conceivably be argued that if the Christ came once and once only, this would imply injustice to the souls who lived before His coming. If a materialist were to bring forward such an argument, it might be understandable, but it would certainly not be understandable if it came from a Theosophist. For he knows that the souls living today also lived in earlier times, before the Mystery of Golgotha; the coming of Christ, therefore, is of equal significance for the souls of the pre-Christian ages, because they all incarnate again in the times following the Mystery of Golgotha. There is, however, this point to be made and it must be understood by Theosophists, namely, that in a certain sense the Buddha forms an exception. We must reach the vantage-point of the true Buddhist who says that the Individuality in the Buddha was that of a “Bodhisattva” who was born as the son of King Suddhodana, rose in his twenty-ninth year to the rank of Buddha, thereby attaining a height whence he need no longer return to a body of flesh. That, therefore, was the final incarnation of the Bodhisattva Individuality who does not reincarnate in the era following the founding of Christianity. The lectures in Christiania2 drew attention to the fact that a very special mission in the universe devolves upon an Individuality as sublime as the Buddha. The Individuality who became the Buddha had been sent from the hosts of Christ on the Sun to the “Venus men” before they came to the Earth (see also the description in Occult Science); the Individuality of the Buddha, therefore, had been sent forth by Christ from the Sun to Venus, as His emissary. This Individuality came to the Earth with the “Venus men” and had thus reached such an advanced stage of development that through the Atlantean, on into the Post-Atlantean era, he was able to attain to the rank of Buddhahood before the coming of Christ. He was in very truth a “Christian” before the time of Christ. We know, too, that later on he revealed himself in the astral body of the Jesus-Child of St. Luke's Gospel—since he need no longer return in a body of flesh. United as he is with the Christ Stream, a different task devolves upon him for the times to come. (This task was described in greater detail in the Christiania lectures.) The Buddha need not incarnate again in a body of flesh. It fell to him to fulfil a certain Deed on Mars—a Deed not identical with the Mystery of Golgotha but to be thought of as a parallel—namely, the Redemption of the people of Mars. There is, of course, no question here of a Crucifixion as in the Mystery of Golgotha, for as may be read in Occult Science, the people of Mars are quite differently constituted from human beings on Earth. These things, of course, are the results of occult observation and can only be discovered through clairvoyant investigation. Now let us think of this fact—that the Buddha was an emissary of the Christ and had lived on Venus. Then think of the uniqueness of the Buddha-life, of its fundamental character, and proceed as I did myself. First, there came to me the occult knowledge: Buddha goes from Venus to Mars in order there to accomplish a Deed of Redemption for the beings of Mars. And now take the life of Buddha, and observe how strikingly it differs from the lives of all the other founders of religion in that period. The teachings of all the others tend in the direction of concealing the doctrine of reincarnation; Buddha teaches reincarnation and founds a community based essentially upon piety, upon a kind of remoteness from the world. Ask yourselves whether there are beings for whom this quality would be of fundamental significance—beings whose redemption could be wrought by all that the Buddha had lived through and made his own? If it were possible, now, to say more about the constitution of the Mars beings, you would see that the Buddha-life was a kind of preparation for a higher mission; that it occurred in Earth-existence as a kind of culmination and can have no direct continuation. You may compare much in the Buddha-life with the indications given by occultism and then you will be able to form some real judgment of matters with such far-reaching cosmic connections. To discover them—that will still be beyond you; but you will be able to examine and study them with the help of all the material at your disposal, and you will find agreement and conformity among the indications given. That Buddha is connected with Venus was known, also, to H. P. Blavatsky. In her Secret Doctrine, she writes: “Buddha=Mercury”—“Mercury,” because in earlier times the names for Venus and Mercury were confused and reversed. “Buddha = Venus” would be the proper form. A knowledge possessed by occultists today is already hinted at in H. P. Blavatsky's Secret Doctrine—but it must be understood correctly. These things are connected with the whole process of advancing evolution. The evolution of man must be studied in connection with the whole universe; man must be thought of as a microcosm within the macrocosm. The fact that Beings do actually mediate between the several planets is entirely in line with these concatenations of cosmic existence, so that a being like the Buddha can actually be regarded as a mediator between planets. A good principle on which judgment of all these things may be based, is recognition of human progress as a reality, recognition of “evolution,” not as a catchword, but as a truth. How can we fail to realise that evolution is a reality? Goethe has shown with such beauty that in each plant, green leaf, petal, calyx, stamen and pistil are a unity and yet progress is clearly to be observed—from the green leaf to the petal and the fruit. Progress in the spiritual life is still more clearly perceptible. It would be pure abstraction to say that the path of the Mystic has everywhere been the same, among all peoples and in all ages. If one were content with cheap persuasion it would be quite easy to tell people that the mystical experience of a Yogi has never differed from that of a Christian Saint. But such a statement would not be based upon knowledge of the facts—not even of the external facts. The experiences of a Yogi and those of a Christian Mystic like St. Theresa, for example, differ fundamentally and essentially! Is it not casting all sense of truth to the winds to compare the experience of an Indian Yogi with experiences that are permeated through and through with the Christ Principle—or with the Jesus Principle in the case of St. Theresa? As true as there is a difference between the red petal of the rose and the green leaf on its stalk, so is it true that there is a difference between experiences arising in the practice of Yoga and those of a later age. There is a fundamental difference and a progression as well. Even if many lapses occur, it can be perceived, nevertheless, and the progress outruns and overcomes the lapses. It is possible for everyone to put these principles to the test of reason—and that is essential. For Theosophy must be given under the assumption that it speaks to the innermost soul, the innermost heart, but is also grasped and assimilated. It would imply that human beings could never come of age, if in the future they were obliged to wait, in the same way as was necessary in olden times, for the coming of World-Teachers—and this quite apart from the fact that no true occultism will ever speak of such an abstract principle of repetition, because it is a direct contradiction of what actually happens. As world-evolution progresses, the factor of independent judgment and examination will assume greater and greater importance. That is one of the reasons why it is so difficult in the present age to speak truly of an Individuality who is so misunderstood, even among occultists—I mean the Individuality known as Christian Rosenkreutz. Those who have a real link with him will never disobey the principle here described. But recognition of the principle of evolution—which reveals itself most clearly in the intrinsic worth of a human being—is difficult and gradual. Christian Rosenkreutz whom we recognise as the one by whom the true occult movement will be led on into the future and who will assuredly never add weight to his authority by means of any outer cult, will be misunderstood—he more than all. Those who have any knowledge of this Individuality know, too, that Christian Rosenkreutz will be the greatest of martyrs among men—apart from the Christ Who suffered as a God. The martyrdom of Christian Rosenkreutz will be caused by the fact that so few make the resolve to look into their own souls, in order there to seek for the evolving individuality, or to submit to the uncomfortable fact that truth will not be presented ready-made but has to be acquired by intense struggle and effort; requirements of a different character will never be brought forward in the name of the Individuality known as Christian Rosenkreutz. These requirements are in line with the character of the present age and with what is felt by men of the present age, even if in many respects they misinterpret it. The present age feels quite distinctly that the principle of individuality will assume greater and greater prominence. Even if here and there this truth is expressed grotesquely and sometimes far too radically, the very fact that it is expressed is indication of a sound instinct in humanity. Many a time one is amazed that in spite of the materialism and the many absurdities current in modern civilisation, an absolutely true instinct, although it is often pushed to extremes and caricatured, prevails in regard to many things. An example occurs in a book recently published: Zur Kritik der Zeit, by Walter Rathenau. It contains a passage to the effect that the time for the founding of sects, for belief in authority, has gone forever as a possible ideal for mankind ... As, however it is a fact that every sound development in our time calls forth its opposite, belief in authority and mania for dogma are rampant in certain circles. And yet: anyone who knows the world today will realise that nothing can so deeply undermine peace and harmony among men as non-recognition of the principle here outlined. The ideal of man must be to fathom and recognise objective truth, to be led through objective truth itself into the spiritual worlds. Hindrances would be laid in his path by attempts to base some truth upon narrow, personal authority—a mode of procedure that is, furthermore, quite impermissible so far as the future is concerned. This must be clearly understood. Many years of work in the field of Spiritual Science have shown how very difficult things are. Not only here, but wherever theosophical work is possible, it is always difficult to make this principle of theosophical striving the root-nerve of theosophical activity. The reason of the difficulty is that there are always people who will not bestir themselves to grasp what must be the fundamental impulse of our age. Objections that may crop up here and there would die a natural death if people would only give a little thought to the fundamental requirements of the times and realise that humanity is ever and everywhere going forward. To lay hold of the whole essence and spirit of Theosophy—that is what matters! But it would run counter to the very essence of Theosophy if a certain teaching that is being broadcast today were to find any widespread acceptance, namely, that culture which should be the common property of all mankind without distinction of race and colour, is conditioned by some particular continental factor. Is it really possible to take back with one sentence what has been proclaimed in another? Is it difficult to see the contradiction when it is said on the one hand that universal wisdom must be spread as a possession of all men without distinction of race and other differences, while on the other it is said that the civilisation of the future rests with a race localised within geographical boundaries? It is high time to reflect on these things and get to the root of them. Is it possible to speak of the progress of humanity when it is constantly reiterated that the same need—in this case, the authority of a personal teacher—exists in the world as of yore? Is it possible to say that man's own spiritual forces must grow stronger, that he must by his own efforts find the way to the spiritual world, if this is made dependent upon the authority of a single individual on the physical Earth? It is extremely easy to say that all opinions have equal weight in the Theosophical Movement. This remains a catchword when it is not taken really in earnest. Above all it remains a catchword when the opinions of others are misrepresented. Once before I have been obliged to say that “equal right of opinion” is no more than a phrase if our work here—which has nothing whatever to do with any specific territory or race on the Earth—is presented by the other side as though it were suitable only for the German mind. It is an affair of humanity, like mathematics—not the affair of any particular nation. To speak of our work here as being an affair of one particular nation, of a strictly limited territory, is an untruth. To quote a catchword does not justify the spreading of untruths in the world. In such circumstances, moreover, the other side may well become the victim of injustice. A semblance of intolerance may easily be created, simply because a stand has to be taken for the truth. The hour shows signs of becoming very serious in this connection. What I am saying here will be understood only by those who take Theosophy in real earnest and will not countenance things that run counter to the fundamental principles of theosophical work. Suppose one were obliged to ward off certain untruths from those who cannot put everything to the test for themselves, can the other person say: “That is intolerance”? He can, of course, say so if, under the guise of truth, he is merely seeking domination and authority! In the future, spiritual truth will work by reason of its own inherent strength, its own power, independently of physical circumstances. And it will be a great and splendid achievement if Theosophy can promote unity of culture over the whole Earth. Not for personal reasons, not for national reasons, nor for any “human” reasons whatever, but for purely theosophical reasons it makes one's heart bleed that in England today the President of the Theosophical Society should be making speeches which really cannot be described as “theosophical” but are eminently political. Thinking of the good old traditions of Theosophy, the heart bleeds to hear it said in a theosophical address that the day will come for proclaiming: “England together with India, at the centre; America and Germany, right and left. One World Policy under the banner of Theosophy!” ... And then we are accused of “intolerance” when it is necessary to protest against the introduction of the personal element into the leadership—where it should never be. It makes an occultist's heart ache that the label “theosophical” should be tacked on to this kind of statement. Once again I repeat: the heartache is not caused by personal or human considerations but for purely theosophical and occult reasons. It is grievous that the root-principle of theosophical teaching should be tainted—either consciously or unconsciously—with national and imperialistic aspirations! It is grievous to me not because I have anything whatever against any country or any aspirations on the Earth, but because the placing of such aspirations in the foreground shows at the very outset that the most intensely personal element is insinuating itself into the true ideal of Theosophy. Many times I have spoken earnest words of the tasks and aims of Theosophy. The occultist does not speak without reflection. He knows very well when he must use such words! What I have said to you is entirely remote from any emotion, any desire, any sympathy or antipathy; it is demanded by something you may perhaps yourselves realise, namely, the seriousness of the hour—I mean, for Theosophy, for Occultism. As I have so often said, Theosophy must draw from the well-springs of human wisdom the message that is needful for mankind in the present age. If Theosophy is to move towards this ideal, it must stand on its own feet, set up its own rules of conduct—not only for what it has to say, but for how it has to confront the world—in order that standards prevailing in the outside world shall not play into our theosophical Movement. For there they become an evil, a great evil. As often as certain usages current in the outside world are introduced into the theosophical Movement, just so often is the Movement handed over to the forces of destruction. To outside eyes, these usages, when introduced into Theosophy, sometimes assume so grotesque a form that the world will certainly take good care not to copy things that may grow from the rich and fertile soil of occultism. Every kind of league exists in the world today—for the promotion of Peace, Vegetarianism, Anti-Alcoholism and what not—all of which are perfectly justifiable goals. But when the basic principles of a society are stretched in order to include the foundation of Unions or even Orders connected with the coming of figure-heads, founders of religion, future World-Saviours3 ... then the outside world will certainly not follow suit! I cannot imagine that a Statesman would found a league to await the coming of a new Statesman, or a General to await the coming of a great General in the future! These things are so simple that only a little reflection is necessary. For to found an Order to await the coming of a World-Saviour is just as grotesque as it would be to found a league to await the coming of a new Statesman or a great General. A certain person who is striving today to found a branch of such an Order, used the following argument to me: “Yes, but after all, in the year 1848 a league was founded for the purpose of uniting the German States—and then there was Bismarck too ... he certainly helped to bring the German Reich to birth.” I could only reply: “Really I am not aware that a league was ever founded to await the coming of a “Bismarck”! Do you think I am saying this jokingly? I say it because occultism has also this side to it, that if it is not cultivated in the right way, it can actually undermine instead of developing the powers of judgment, and I say it because I am in deep earnest about these things. Many occult teachings have been gathered together here; in fifty years, possibly, one point or another may have been investigated still more closely, may have to be differently expressed. But even if no fragment remains of the knowledge that has brought forward—I do desire that one thing shall have survived, namely, this: that here there was inaugurated and sustained a theosophical-occult movement taking its stand solely and entirely upon integrity and truth. Even if in fifty years it is already said; Everything must be corrected; but at least they were out to be true, to let nothing happen except what is true ... even then my ideal would have been attained. That integrity and truth can prevail in an occult movement, whatever storms may rise up against us in the world—I am not so arrogant as to say that this has been “achieved,” but rather that this is the goal towards which we have striven.
|
| 181. A Sound Outlook for Today and a Genuine Hope for the Future: Problems of the Time II
06 Aug 1918, Berlin Translator Unknown |
|---|
| On one hand there is the extreme theological teaching which only and always speaks of “the simple man of Nazareth”, the man of physical nature, not of that Man who has in himself the seed for the future. Further, there is the Society founded to combat the Christ, and with that came to set up a false picture of Jesus: the Jesuit Society, which virtually aims at testing out the Christ-concept from the Christ-Jesus concept, and to install Jesus alone as an absolute ruler of developing humanity. |
| I have often referred to the significant conversation between Goethe and Schiller when both were in Jena for a conference of a natural history society, at which Batsch the botanist had lectured on plants. As they left, Schiller said to Goethe, “The botanist's outlook dismembers everything; it ignores the connecting links”. |
| For all these reasons it will certainly be very hard part in a few weeks from this room, which was fitted up so devotedly with the help of our anthroposophical friends; but we must look upon such a parting in the right way, as a symbol. People will be obliged to part from much in the course of the next few decades. |
| 181. A Sound Outlook for Today and a Genuine Hope for the Future: Problems of the Time II
06 Aug 1918, Berlin Translator Unknown |
|---|
You will have seen in the last lecture that efforts were directed towards presenting certain conceptions (which we can make our own out of Spiritual Science), in such a way that they can be of service to us in grasping what surrounds us, daily and hourly, in present-day civilisation. If We want to add yet another to these considerations, as a final one, it can be summed up only thus: significant characteristics of our present time have been selected and brought into connection in various ways with what has sounded forth as the keynote of these studies. If we determine to keep in mind what seems to stand out particularly in our time, we shall find that of all the limiting and hindering factors to-day, the worst is that the mode of thought and comprehension evolved during the recent centuries leads men to have little foresight of coming events. This is shown by the fact that most events come as a surprise, in the most curious way, and it is quite impossible to gain credence for anything that is foreseen. It is considered inevitable that remarkable events should take people by surprise. Speak of what is to come, and people are astonished , or they make ironical remarks about the apparent longing for some sort of prophecy. Suppose that anyone wished to call attention to conclusions such as may result from hypotheses like those we have lately brought forward here—for instance, what now looms over the world from the Far East—he would at present encounter little understanding or belief, although the fact already throws its shadow all too clearly before it. Far too little need is felt for a clear view into things. Connected with this is man's disinclination to admit the truths which, within the only circles open to them, point to future events. Of course there is no question here of any kind of “soothsaying”; or of any sort of prophecy in the bad sense, but always an earnest, scientific method of thought and conviction derived from Spiritual Science. If we wish to ruminate upon the causes of this trend of the present day characteristic just mentioned, we may perhaps have to go far afield for them. Man as a rule is absolutely unconscious how far the causes of the thing lie from what appears as its effects . He generally looks for the causes much too near at hand. If we are to look for causes of what has just been described, they must be sought in a tendency deeply ingrained in the human soul at the present time—a tendency towards dead conceptions and ideas devoid of life and vigor. It should be comprehensible that to think of the future, the imminent, with the same ideas as on the past, the determined, is impossible; but at the present time, value is attached only to what, in the current phrase can be “proved” and this question of proof is tied down to the special kind of proof which is popular today. Anyone who rightly understands this kind of proof knows that it applies only to truths connected with things in the universe which are in the process of dying. Therefore the only science or knowledge desired in the present age is concerned with what is dying and perishing—especially so in the case of those who claim to be the most enlightened. They welcome only a will bent in that direction. If we are not conscious of this, we are really preferring—in the widest sense of the words—to deal only with what is passing away. We lack the courage to think in terms of growing, becoming, for what is growing refuses to be grasped with the narrow, limited conceptions capable of being “proved”, which are suitable for what is passing away. So people protect themselves against the reproaches which are really implicit in what I have just pointed out. To speak against these things, as one must do, involves the danger of incurring the reproach of frightful fantasy, dilettantism, or perhaps even worse. Conceptions are sought which protect people from the obligation of thinking about anything fruitful, or endowed with seeds of life for the future. One idea, according to this view, must be received by those who hold themselves to be among the really intelligent leaders of thought: the idea of “the conservation of matter and energy” as understood at the present time. Quite comprehensibly, everyone is adjudged to be a duffer who does not admit this indestructibility of force and matter to be a truth underlying the whole of science. Yet it is a fact that if we sound the depths of a real view of the universe, what we call matter and force are perishable and transitory; and all science, all knowledge attainable on the subject, our investigations into the transitory. Because it is insisted that science has to be concerned with that, and that only, it is dogmatically asserted that something solid, something permanent and there must be: either matter—In spite of its being transitory—or energy. This law of the permanence of matter and energy plays a great part even for those who are not concerned to analyze it scientifically; such a part that is clothes everything with mystery. Our scientific education is such that the dregs of opinion on the subject of the conservation of matter and energy penetrate our popular literature and are treated by the ordinary reader as something obvious. Now we know, through a cold science, of the Saturn, Sun, Moon and Earth-developments. Nothing of what is now called matter and energy will pass beyond the Venus evolution. Hence the most lasting kind of matter, that which reaches Venus, will then come to an end. We have just passed the middle of our world-evolution, as we view it, and are in the fifth period of the earth-evolution, beyond the middle of that; and we are already living in the setting.: that is, in the time of devolution, in which the vanishing of matter and energy comes to pass. The right you take as we studied physics and chemistry would be this—that the knowledge acquired through these sciences bears only upon the transitory, which at latest will disappear from the universe with the Venus-stage. In the whole purview the present-day science there is nothing which deals with the permanent; because by means of the ideas and concepts that can be “proved” in a manner favored today, it is impossible to discover only what in this sense is transitory. Man moves only in the transitory. An essential reform is necessary in our ideas concerning this most essential sphere, and those who consider themselves particularly scientific have the most to learn before they can replace their current notions with correct ones.—Now why am I saying this, seeing that the matter in its general bearing may not perhaps seem particularly important? It really is important, because according to the concepts which men assimilate in the way I have described, other concepts are formed in conformity with which they will; they direct their will-power. From the mode of thought thus acquired are begotten social and political concepts. These latter shape themselves in accordance with the characteristic use made of such forces—a use consisting in this, that only the transitory is dealt with in such conceptions, and this habit spreads into ideas concerned with the living. This crops up in a particularly striking way as we look at the main points of the programms put forth by many who confidently regard themselves as the very last word in advanced thought. For instance, the schemes of many Socialists, very much in the public eye nowadays, all more or less adopt the theory of Karl Marx as a starting-point. This theory is the calamity of Russia two-day, because—for reasons I explained last time—what happens there according to historical premises can ensue elsewhere from Marxism. This way of looking at things is an extreme form of the determination to deal only with transitory. Anyone who familiarizes himself with the ideas of this school knows that the fanatical adherents of Marxism imagine themselves to be possessed of the ideas of the future, whereas they have only such as are directed to the transitory. This stands out naïvely in the so-called socialist view of life, for throughout it refuses admittance to ideas with a fruitful bearing on the future. It preaches the blessing of having none! The formula is repeated in many different ways:—Get rid of everything at present existing; then, of itself, without any reflection on the matter, something will result from the welter. This is unequivocally stated. But although it comes from the looks of those who have been brought up in Church doctrines for centuries and who do nothing but trace the events of the last centuries according to the Church, they must nevertheless say the following.—In truth this view refuses to entertain ideas with any germ of life in them: the only ones it admits are concerned with what is passing away; and the only effect of these ideas is to complete the process of destruction. Men believe they possess productive thoughts; that is all to no purpose unless the concepts are rooted in reality. These ideas are useless for establishing anything new; all they can accomplish is to turn destruction into an institution. This Socialism seems to me like a lady (a bygone person to-day) who cannot endure a crinoline. She hates the wide skirt and wants to alter it. But what does she do? She pads it out; so that it looks just as before, but is a stuffed out with wadding inside. Just so these Socialists: they never think of fertilizing what history has achieved with new concepts; they leave it alone—and themselves take the place of the former administrators. They hang on to the crinoline, but stuff it out. Look even at extremist views—they are simply a longing to administer what is perishing and dying out! To what is this due? It is due to the fact that with the concepts of present-day science, concerned merely with things of the senses, based on the intellect, taking account only of material perception, all that one can encounter is the transitory, not the living. Only what is already dying can be grasped; nothing that is seed-bearing, growing. For the germinating, growing element must be grasped at least through Imagination, the first stage of higher knowledge; as described, for instance, in the book, “Knowledge of Higher Worlds.” And to attain to still higher knowledge of the “becoming”—Inspiration and Intuition must be applied. Those who approach such things with the outfit of ideas held hitherto may talk as much as they wish—they are only talking of laws which apply to what is on the way to destruction, unless they let themselves admit what super-sensible knowledge alone can reveal as the “becoming”. Things too-they are on a razor's edge. It is impossible to know anything on certain subjects, and civilization must fall into chaos if we are satisfied to live in it without admitting any vision of the spiritual. What we need, and what is striven for through Spiritual Science, is a sort of revival of the Mysteries, in a form adapted to the modern mind. Unless we understand the meaning of the ancient mysteries, we shall not fathom the meaning of the epoch which is intermediate between them and what must come as the new form of the Mysteries. Comprehension of all this is necessary. The most startling experience for the pupils of the old Mysteries was to be shown clearly how the old atavistic, clairvoyant, hidden knowledge was doomed to extinction. This could not be grasped by observation, it had to be revealed in the Mysteries, where people were shown that something different from the old clairvoyant vision into the Spiritual World's was destined to become man's possession. There it was disclosed to the pupils of the Mysteries that this old capacity of the human soul, this vision of cosmic expanses in Imaginations, was dedicated to death. This was made them somewhat in the following way.—What can be perceived by physical senses on earth is not the content of the genuine Mysteries of the earth-existence; this is revealed only when the human soul ascends in the clairvoyant contemplation to Mysteries of the cosmos, of the super-earthly, and the cosmic events beyond the sphere of earth, unfold before it.—The ancient seers grasped all that, but not what happened on earth. The pupils of the tapestries were shown depth knowledge of that type, ascending into the Cosmos, would no longer be possible; and still more was disclosed to those who were to penetrate into the Christ-Mystery. Something like this conception came to them: “Although the old seers did not speak of ‘the Christ,’ their inspirations came from the world in which Christ always was, for He is a Cosmic Being. He dwells in everything Cosmic and universal, in the whole content of man's old atavistic clairvoyant vision; but from the time when the Mystery of Golgotha is due to be enacted, all this will be no longer accessible to mankind in the old way.” What happened? The Christ descended from the world of the cosmos to the earth. Because the cosmos was no longer accessible to men as in ancient times, because Christ was no longer to be found in the old way, because the kind of knowledge and state of soul with which men had formerly looked at the world was dying out, but Christ had to come down to them. He came to the earth. Everything, therefore, which enlightened spirits had ever known of the spiritual world in ancient times through the pagan tapestries and through pagan Mystery-knowledge, was summed up in the Christ, and could be beheld in Him. The one all-important thing was to recognize the Cosmic Being, Who in Christ descended to the earth from the cosmos. That was one point. The other was this. Remember that through the intellect and of the senses only the transitory can be observed in all the array of systems, whether of nature, of social structures or of civilizations, and that transitory knowledge will endure no farther than the Venus-existence. But learned men, believing that their ideas point to the future, are very often immersed in what is passing away. And what the senses perceive and the intellect grasps there is no seed of the future; all of it is doomed to perish. If the only knowledge were concerned with that, there would be nothing but knowledge of death; because the actuality which surrounds us is itself doomed to death. Where shall we find the “enduring”? Where is the imperishable which shall outlast this existence, apparently permanent but doomed to die? While Adamson forces, to which materialistic superstition attributes permanence, betray their impermanence and fall to ruin, where is the imperishable to be found? In man alone! Amongst all the beings, animals, plants, minerals, air, water, and everything that perishes, there is but one thing which will outlast the Earth-evolution and the evolution to follow it—that which lives in man himself. Man alone on earth bears within him an enduring element. One cannot speak of the permanence of atoms, matter, force, but only of the permanence of something in Man. This, however, can be seen only through Imagination, Inspiration and Intuition. All else, perceived by our vision, is fleeting. The material, the physical, is entirely transient; the super-sensible, which outlives it, can be perceived only by super-sensible vision. In man, as he treads the earth, lies all that will be saved out of the entire Earth-existence. If we asked: “Where is the germ of something which will continue to grow on after the Earth, Jupiter, and Venus developments—from the present civilization into the future?” The answer must be: “In nothing external on earth; only in man”. In the part of his being accessible only to super-sensible knowledge, man is the cradle of the seed for the future. Only someone who is willing to include the super-sensible in his view is able to speak correctly of the future; otherwise he must err. Thus the Christ, dissenting from worlds becoming more and more inaccessible to human knowledge, had to unite Himself with Mankind—to take up His abode in Jesus of Nazareth and become Christ-Jesus, so that in a human body there might dwell that which bears within it the future of the Earth-development. So we have in Christ the Cosmic Being, that Cosmic Being whom ancient knowledge alone could grasp directly; and in the Jesus to whom the Christ came, we have what henceforth bears within it, in human will alone, the seed for the future. He cannot be comprehended purely as “Christ”, nor as “Jesus”. To speak of the “Christ” only, is not to comprehend Him; for the “Christ” of—for example—the old Docetics (a certain sect of Gnostics) belongs to the old atavistic clairvoyance and can no longer be laid hold of. And “Jesus” cannot be understood without taking into account the Christ Who drew into him. Unless we give due weight to this fact of the Christ in Jesus, we cannot grasp that only through the human seed on earth can the cosmic be saved for the future. To understand how far Christ-Jesus is this double Being is a great task; but at the same time many have taken pains to create obstacles to such an understanding. In modern times it has been a question of inducing forgetfulness of indwelling of Christ in Jesus by all sorts of means. On one hand there is the extreme theological teaching which only and always speaks of “the simple man of Nazareth”, the man of physical nature, not of that Man who has in himself the seed for the future. Further, there is the Society founded to combat the Christ, and with that came to set up a false picture of Jesus: the Jesuit Society, which virtually aims at testing out the Christ-concept from the Christ-Jesus concept, and to install Jesus alone as an absolute ruler of developing humanity. We must see the connection of all this, for the different impulses here pointed out work and present-day life more than is supposed, and very intensely. Without open eyes and a longing to understand the concrete events around one, it is impossible not to be taken by surprise by what happens; a clearer view of such things as I have mentioned will be lacking. Our own time is in many respects too indolent to wish to achieve clarity; the concepts of Spiritual Science are too hard to compass, and are stigmatized status dilettante, unscientific, fantastic and the like. They are condemned for the reason, I have mentioned, because of the determination to take no account of what is really significant for the future. Thus we see around us to-day this dreary waste in the midst of the chaos into which the old religious creeds and currents of thought have led. Within this chaos, which people with curious supposed to call “war” (a work which has ceased to be applicable for a long time now), we see an array of lifeless, barren thoughts and ideas, because fertile ones can come only from comprehension of the super-sensible, the spiritual. Man two-day has to choose between cultivating the vanishing, the dying, ending by becoming a pupil of Lenin—it's taking into account the super-sensible, wherein abides what has to come in the future. I am not referring simply to the London works his mischief now in Eastern Europe—I taken more as a symbol, for we have many such Lenins around us and the whole environment of our daily life, in one domain or another. Yet the world refuses to take in hand anything except what is dying. Remember something I once pointed out here, ‘the plant lives,’ I said; it can be described as a living being. But what does ordinary science describe as the plant? Not what lives in it, for that of super-sensible; but the dead, literal part of it, which “fills out” the living element. We find nothing else described by modern science but the mineral filling of the living being, which brings death to it. Genuinely fruitful concepts regarding nature are consequently unattainable to-day. The concepts of present-day botany have no life. All that they describe as something filled out with a stony mineral substance, which circulates inside. That can be described equally well in the animal and in man. All three kingdoms become entirely different as soon as one gets away from this circulating mineral substance. For instance, a certain Herr Uexküll has written an article on “The Controversy about the Animal Soul”. He is possessed by masochistic savagery as regards all knowledge of the soul, or anything that suggests it. I said “masochistic savagery” because in this article he writes: “It is impossible to decide whether a soul exists or not: all that can be decided is that science can settle nothing on the subject”—an ordinary savage kills; but anyone who is masochistically savage, like this Herr von Uexküll, only “probes” the dead and makes sneering remarks. That is thoroughly typical of modern science; but it is not noticed, because nobody wants to admit it. People refuse to breakthrough the dividing wall between themselves and their environment; hence they cannot reach the ideas they really need in order to learn once more how to understand their environment. We know from spiritual science that the essential being of man, the kernel of his life, descends from the spiritual worlds, and unites itself with what surrounds him as a bodily-material chief between birth and death, or rather between conception and death. The problems of conception, of birth, of embryology, are investigated to-day; but they cannot be truly investigated, because the research is directed only to the dead part of man, which is embedded in the living. This path will never lead to a grasp of what alone can make the human being understandable. When Man the Suns in this way from the spiritual world, he is “received” by father and mother, and goes through all the stages of his embryonic development. Science two-day assumes that the parents give the child existence; and since father and mother are the center of the family, and the family is the foundation of the community, therefore the communities, which are extended families, consider men as their own property. Thus a galling idea is brought into modern life—but it is not really true. What, then, does the act of conception bestow upon man? What does he gain? A Spiritual Science shows, what he receives is the possibility of becoming a mortal being—of dying. You will see, if you think of what is to be found in my various books, that it is the necessary consequence. With conception there is implanted in man what makes his death possible here on earth. The whole of life from birth is a development towards death, and the seed of death is implanted at conception. What man is as “man”, as a living being, is not by any means engendered at conception; but the possibility of death is thereby grafted onto what would otherwise be immortal. Parents are called to give death of a child! That is the paradox—they give it a opportunity of bearing a mortal body on earth. What lives in that body comes from the spiritual world. This is what makes the organism—the whole mechanism with which man is clothed and which was received by him with seed of death at conception—capable of life. We must learn to recognize man in his most concrete embodiment as a part of spiritual world-development. Then we shall learn not to stand before the loftiest problems with cowardly fear, past present-day science does, but to grasp them positively. If we shrink back from them, we shall fail to understand even our immediate environment. Round about us to-day, live the most varied peoples. Just think of the incorrect ideas, for example, created by Woodrow Wilson out of his conception of nations and the peoples—a theme with which you are familiar. We must be quite clear that we cannot understand this conception of the people unless we take in the whole of earth-evolution. Whence comes, then, a division of humanity into “peoples”? We know from Spiritual Science of evolution proceeded through a Saturn-embodiment of the Earth, then the Sun-embodiment, with the ancient Moon following that, and then the present Earth-condition; afterwards will come a Jupiter-embodiment, and so forth. The course of evolution, however, was not so straightforward that the old Saturn-body simply changed into Sun, Moon, Earth; at one time a severance of the present Sun from the Earth took place, then a severance of the present Moon, so that we have a continuous evolution, and something which was cut off reunited, and once again severed. A connection with what I have just called “Cosmic Evolution” this severance plates part in the old clairvoyance. And for the old clairvoyance the human seed the future remained “chthonic”, as it was called in the old clairvoyance is, quite unconscious. For what comes from the universe was destined to decay; it was maintained only because it had come under the grip of the Luciferic power. In this way, out of the cosmos reform the many variations in the nations and peoples, but the cosmic forces were impregnated with Luciferic forces. Over against these diverse peoples stand something which was understood in a better time than this—universal humanity. It has a totally different origin. It may be discussed in the abstract, but can be truly spoken of only as one genuinely understands what the seed of the future in humanity is . It has no taint of Nation or peoples; for it is that which did not come down from the Cosmos but which the Christ came to find, and with which He indicted Himself. Christ, unlike the Jehovah-Deity, United Himself with no nation but with universal humanity. He was in the confraternity of those Gods from whom the nations took their rise, but He left that realm when it was ready to pass away; He came to earth and took up His abode in humanity at large. When we say, “Not I but Christ in us”, it is the greatest blasphemy against Christ-Jesus to invoke Him for any need other than that of universal humanity. A grasp of this fact belongs to the most momentous concepts for the future. We must perceive the connection of Christ Jesus with humanity, and also how everything purely national lies outside the realm of Christ-Jesus, for it is the ancient remains of what was right for extinction at the time of the Mystery of Golgotha. Yet, as we see withered fruit in the orchards, so do all things linger on after their right time. So we were bound to get the science which is concerned only with knowledge of what is on the way to extinction, and which—whether it be natural science or social science—deals and ideas that apply only to the transient, in nature or in cultural life. Often in the history of civilization one can see the conflict between the tendency to cling to what is passing away, and to present as important the dead, abstract ideas connected with it, and the wish to grasp that germinal essence of humanity which alone is pregnant of the future. I have often referred to the significant conversation between Goethe and Schiller when both were in Jena for a conference of a natural history society, at which Batsch the botanist had lectured on plants. As they left, Schiller said to Goethe, “The botanist's outlook dismembers everything; it ignores the connecting links”. Goethe, in a few descriptive sentences, put before Schiller his “Metamorphosis” of plants, but the latter said, “That is not an experience more observation—it is an idea.” To which Goethe answered “Then I see my ideas with my very eyes.” What he had been describing was visible to him, as real as a thing perceptible by physical senses. They confronted one another—Schiller, representative of the mind unable to look up to the spiritual, bemused by dead, abstract ideas; and Goethe, who wished to derive from knowledge of nature what is imperishable, vital for the future, the imperishable in humanity, of which all that is transient is merely an image. He wanted to unite the transient with its archetype, the real. He was not understood, for he looked on the super-sensible, the imperishable, as though it were perceptible to the senses. Thus the urgent need of our time is that Goethe's teaching should be more widely developed and further elaborated in its own sphere. Then things will become clearer, and we shall see that the particular creeds, whether Jewish, or more particularly the Catholic, are only the presuppositions of what is old and outworn, standing out in evolution as parched remnants, supported only from outside; and that side-by-side with these, interpenetrating them, stands Americanism, which wishes to carry the transient into the future. Therein lies the kinship between Americanism and Jesuitism, of which I spoke last time. Standing in opposition to all this is Goetheanism. By this I do not mean anything dogmatically fixed, for we have to use names for things which far transcend them. By “Goetheanism” I do not mean what Goethe brought up to 1832, but what will perhaps be thought in the next millennium in the spirit of Goethe; which may develop out of Goethe's views, concepts and sentiments. It may be concluded, therefore, that in everything connected with Goetheanism, outworn beliefs sees its particular any. The most extreme paradoxes are to be found in this sphere. It really is a paradox to find that the cleverest book about Goethe whatever may be said to the contrary—has been written by Jesuit, Father Baumgarten. No details concerning him is neglected. The usual distinguishing mark of Jesuit work on the subject is hostility to Goethe: but this is a highly intelligent, painstaking book, not superficially written. Yet it has happened to Goethe to be portrayed as an ordinary citizen of the 18th century, born in 1749 at Frankfort-on-the-Main, who studied at Leipzig, was given a post in Weimar, traveled in Italy, live to be old, was incorrectly called it on both came good to “Johann Wolfgang Goethe;” this was how he was described in the work of a distinguished English Gentleman, Lewes—which was much admired. A book headed “Johann Wolfgang Goethe,” describing him as an ordinary 18th-century citizen, is no real book. A cultural paradox lies in the Jesuit's book on Goethe for the trend of opposing forces in modern times can be seen in it, and where the real ones are to be found. A small way it shows itself amongst us. So long as we were reckoned a “hidden sect”, Anthroposophy was seldom attacked; but when it began to spread a little, virulent attacks began, especially from the Jesuits; and the Journal, “Voices from Maria Leach”, now called “Voices of the Time”, is not content with one article, but contains a whole series about what I've called Anthroposophy. I must warn you, again and again, attacks come from this side, not to believe that from the point of view of these writers, it is for our good when they say that we “speak of the Christ”, or that we “promote understanding of Christ”. They forbid that everything; it is exactly what must not be done; outside the doctrines of the Church, there must be no assertion about the Christ! No-one in our circles need be so naïve as to believe that by being a good Christian, he can propitiate the Church. Just because he is a good Christian, and does all in his power to advance Christianity, he arrays Catholicism against him as a supreme enemy. It becomes more and more necessary to take care that naïveté in these contemporary matters should disappear from amongst us. We must more and more firmly determined to realize what is active in the forces around us, whether they be in the ascendant or are declining. We must get beyond the longing, present among us in so many forms, simply to penetrate a little way into an imaginative world. I have often said that we must above all be able to place our Spiritual Science alongside modern concepts, and bring keen observation to bear on life as it is in the present age; because to gain true insight into this is possible only from the standpoint of Spiritual Science. How many people come to me and say, “I have seen this or that”. Well they may well have done so. Imaginations are not so very distant. “Was that the Guardian of the Threshold?” many then ask. A simple yes and no does not answer questions on such matters, because the answers involve the whole of human development. But the answers are given. I am now correcting my Occult Science, for a new edition. I see that in it may be found everything necessary for the answering of such questions. Every precaution, every limitation to be observed is exactly described; the feelings to be developed, the experiences to be undergone, are all set forth. To elaborate the whole content of Spiritual Science would have required 30 volumes. This one must be read carefully, drawing the necessary conclusions—and it can be done. I do not like writing thick books. But read attentively and it will be found that this book indicates clearly that he endeavors to enter the super-sensible world strides towards meeting the Guardian of the Threshold; but the meeting is not so simple a matter as to have a dreamlike imagination. The latter, of course, is the easiest method of entering that world. The meeting with the Guardian of the Threshold is fraught with tragedy; it is a vital conflict as regards all intellectual concepts and laws, all man's connections with this virtual world and with Ahriman and Lucifer. This life-and-death struggle must be endured by him who would meet the Guardian of the Threshold. Should this experience come to a man merely as a dreamlike imagination, it means that, he wants to slip through comfortably, so as to have a dream out of the Guardian of the Threshold as a substitute—nowadays people are fond of substitutes the commission!—for the real thing. We must think healthily on the subjects; and it will then become evident that healthy thinking can alone provide the basis of a remedy against all superstition, and against all the charges made by superficial opponents of Spiritual Science. Moreover, in this kind of thinking, in this raising oneself to experience on the spiritual, lie all the necessary seeds for finding the real way out of the present world-catastrophe. The layout must be grasped—not in the realm of the earth and senses, not in institutions which are mismanaged and sucking the life out of what exists. The thing to be grasped does not exist! We must be stirred with burning zeal for the top attention of what does not yet exist! This non-existent thing can be grasped only according to the pattern given by super-sensible knowledge. It cannot be grasped by looking into the past. Such men as Kautsky prefer to look back into the past, finding and “Anthropology” the ground-plan of mankind. They tried to study conditions at a time when man was hardly yet created in order to understand the social connections of to-day. These two sons of a misconceived Catholicism, such as Kautsky, want to have it so. But one cannot look back to the past, because in the past, those things which have extended into the very latest present, were created by means of atavistic forces, instinctively. In the future, nothing more will be achieved “instinctively”, and if man holds only to the products of ages of instinct, he will never attain to what bears the future within it, and can lead out of this catastrophe. An active, earnest understanding of the present depends entirely upon a right attitude to the spiritual world. I should have to say much if, continuing in this strain, I were to speak to you about many things closely related to this present time. Yet if, in the weeks while we are separated, you will bring rightly be for your souls what has been said in these lectures, and which should culminate in realizing the necessity for knowledge of the twofold figure of Christ Jesus, you will go far this summer in meditative comprehension of the cosmic Christ and the earthly Jesus; remembering that the cosmic Christ descended from the spiritual worlds because these worlds were henceforth to be closed to man's view, and that man must apprehend what lies within him as the seed of the future. In the cosmic Christ and the earthly human Jesus and their union, lies much of the solution of the riddle of the world—at least of the riddle of humanity. In man lies the seed of future; but it must be fructified by Jesus. If it is not so fructified, it will assume an Ahrimanic form, and the earth will end in chaos. In short, in connection with the Mystery of Christ-Jesus we can find a solution of many, many questions to-day; that we must endeavor so to seek these solutions as not to be lightly contented with what is so often taken for “Theosophy” or “Mysticism”or the like—a “Union with a spiritual”, and “entire absorption in the all”—We must really visualize the true conditions surrounding us, and try to permit them with what we gain from Spiritual Science. We shall then say to ourselves over and over again, with regard to the answers to many questions: truly man today is seeking for something very practical, not merely theoretical; he will find himself in a blind alley in which he can go no further, if he does not go with the spirit. Everything which does not go forward with the spirit will wither away. This is a weighty question for the future of mankind. Has man the will to journey with the spirit? I would fain impress this on your hearts today as the feeling which can arise from the reflections we have pursued. Probably we are meeting to-day for the last time in this room, which we used so gladly for years as a place for our studies. It was one of the first to be arranged in keeping with our own taste, and one can only work according to the opportunities that exist. We fitted it up as we did because we were always convinced that endeavors on behalf of spiritual Science ought not to be mere theory but should be expressed in everything wherein we meet as human beings. The room is now to be taken from us and we must look for another. Obviously, under present conditions, we shall not be able to fit it up as we did this room, but we must be content with it. This room has become dear to us, for we have come to regard it as impossible to speak elsewhere of our relations with the spiritual as we can in this place, where in many ways we have tried to do the same things that are being attempted in Dornach on a larger scale. In times gone by we had to try all sorts of arrangements. Perhaps there are still a few here who were present when we had to speak in a beer-shop; I stood there, facing the audience, while behind me the landlord or landlady filled beer-mugs. Another time we were in a room like a stable: we had booked another, but that was all they gave us. In other towns I have lectured in places with no boards on the floor, and that too had to be put up with; it is not exactly what could be wished for as an outcome of our movement, and it would be a misunderstanding if it were said that we would just as soon speak of spiritual things in any surroundings. The spirit's task is to penetrate into matter, and to permeate it completely. That is the sense in which I have been speaking of social and scientific life to-day. For all these reasons it will certainly be very hard part in a few weeks from this room, which was fitted up so devotedly with the help of our anthroposophical friends; but we must look upon such a parting in the right way, as a symbol. People will be obliged to part from much in the course of the next few decades. They will be taken by surprise, although they do not believe it. One thing will be deeply rooted in those who have grasped the deepest impulse of Spiritual Science. Whatever may be spoken, this cannot be shaken, and that is what we have grasped in the spirit, and what we have determined to do and accomplish in the spirit. No matter how chaotic everything looks, that will show itself to be the right thing. So many leaving this place is symbol for us. We must move into another, but we carried away with us something of which we know that it is not simply our own deepest inner being, at the deepest inner being of the world, of which man must build if he would build a right. He who stands within Virtual Science is convinced that no one can take away, either from us or from humanity, what we have accomplished through it, and that it must lead to human affairs to a healthy condition ; this he knows, to this he clings. We may not as yet be able to say how we shall accomplish many things; but we may be sure that we shall accomplish them rightfully if we steep ourselves in the knowledge of what Goetheanism signifies for Spiritual Science, and if on the other hand we accept what has recently been mentioned here—that's the world stigmatizes and defames all that is connected with Mid-European civilization of the 18th and early 19th centuries, and that we, bringing all this before our souls, can nevertheless take our stand on our sure convictions: whatever happens, this Mid-European culture will be fruitful for the future of mankind, which indeed depends upon it. To save their own faces, because they have no wish for this feature of mankind, the opponents of this particular culture defame it; but let us grasp it in the spirit, recognize its inner spiritual content, knowing that we can build upon it. Then we shall be sure that though all devilish powers vow its destruction, yet it will not be destroyed! But only that can escape destruction which is united with the genuine spirit! |
| 96. The Lord's Prayer: An Esoteric Study
28 Jan 1907, Berlin Translated by Floyd McKnight |
|---|
| It is a small but important aspect of the occult scientific basis of religions that I wish to discuss. Even the simplest people in contemporary society recognize this hidden background of religions as a spiritual fact involving the deepest truths. |
| All formulas for meditation in the world's great religious societies throughout history have had their origins in spiritual science. Analyze every true prayer that exists—word for word—and you will find it to be no arbitrary stringing together of words. |
| 1. For a full discussion of these anthroposophical terms, see Steiner's Theosophy: An Introduction to the Supersensible Knowledge of the World and the Destination of Man. |
| 96. The Lord's Prayer: An Esoteric Study
28 Jan 1907, Berlin Translated by Floyd McKnight |
|---|
Today I should like to indicate the extent to which religious systems reveal, in specific instances, their hidden spiritual-scientific foundations. It is a small but important aspect of the occult scientific basis of religions that I wish to discuss. Even the simplest people in contemporary society recognize this hidden background of religions as a spiritual fact involving the deepest truths. Seeking these truths brings to light how wisdom-filled and fraught with mystery are the ties binding together the spiritual life of mankind. Think of Christian prayer. You all know what it is. It has often been spoken of, and anthroposophists have often reflected upon its relation to the spiritual-scientific world view. This spiritual-scientific world conception has brought to members of the anthroposophic movement another method of elevating the human being—the human soul—to contact with the divine, spiritual, cosmic forces. This method is meditation, by which a person experiences the spiritual content within himself, and receives something of what is given by the great guiding spirits of humanity or by the spiritual content of great civilizations in which the human being immerses himself and so identifies himself with the divine spiritual currents in the world. Meditating in even the simplest way upon one of the formulas pronounced by the spiritual leaders of mankind, admitting to the mind a formula that embodies a great thought—not every thought is suitable, as you know, but only one handed down for this purpose by the guiding spirits of humanity—and letting such a formula really live in the heart and experience, brings a person to union with the higher spirituality. A higher power, in which he lives, streams through him, and patient perseverance to the point of letting this flow of power strengthen him enough morally and intellectually, brings him to the moment when the content of his meditation can awaken the deeper forces latent in the human soul. This kind of meditation may reach any of a number of stages, from the smallest gain in moral strength to the highest attainments of clairvoyance. But time, patience and energy are needed to bring most people to the higher degrees of clairvoyance by this means. Meditation is usually thought of as an oriental approach to the divine. In the Occident, especially in Christian communities, prayer has taken its place. It is by prayer that the Christian customarily approaches the Divine, and through it he seeks entry to the higher worlds. It should be noted by the way that what passes for prayer today would by no means have been considered such in early Christian times, least of all by the Founder of Christianity, Christ Jesus Himself. For if it were to happen that someone were really to gain the gratification of his personal wishes by prayer or entreaty, he would soon entirely disregard the all-embracing effect that the granting of the prayer should bring. He would assume that the Deity granted his wishes rather than those of others. One peasant might pray for sunshine for a particular crop; another for rain for another crop. What would Divine Providence then do? Or suppose two opposing armies are facing each other, with each side praying for victory and supposing its cause alone to be just. Such an instance makes immediately obvious how little universality and sense of brotherhood attach to prayers arising out of personal wishes, and the granting of such prayers by God can satisfy only one group of supplicants. People so praying disregard the prayer in which Christ Jesus set forth the fundamental attitude of mind that should prevail in all prayer: “Father, let this cup pass from me; nevertheless, not my will, but thine, be done.” This is the Christian attitude of prayer. Whatever the object of the prayer, this fundamental temper of mind must echo readily as an undertone in the soul of the petitioner for his prayer to be given in a Christian manner. When this is the character of his plea, the form of his prayer will be but a means of rising to higher spiritual realms to experience the Divinity within the soul. It will be such, moreover, as to expel every selfish wish and will-impulse. Its spirit will be that of the words, “Not my will, but thine, be done.” The result will be a rising to the divine world and absorption in it. Attainment of this soul mood in Christian prayer renders it similar to meditation, though more colored by feeling. Originally, Christian prayer was not essentially different from meditation. Meditation is more imbued with thought, however. Through it, the thoughts of the great leaders of mankind draw the meditant onward toward harmony with the divine currents streaming through the world. Through feeling, prayer accomplishes the same result. The goal of both prayer and meditation is thus clearly the soul's union with the divine currents in the world. This union, on the highest plane, is the so-called unio mystica, or mystical union, with the Godhead. Never could the human being attain to this union with God, never could he gain a relationship with higher spiritual beings, were he himself not an emanation of the divine-spiritual. Man's nature is twofold, as we know. In him are the four oft-mentioned human principles—physical body, etheric or life-body, astral body and ego. Then, within the ego, he has the possibility of unfolding for the future the three higher principles—manas, buddhi and atma, known in our western languages as spirit self, life spirit and spirit man.1 To understand rightly this twofold human nature, let us consider the period of man's origin. From previous lectures, you will remember that man now represents the blending of these two natures—the blending of the three higher potentials (spirit self, life spirit and spirit man) with the four existing lower principles (physical body, etheric body, astral body and ego) developed in a far-distant past, which we term the Lemurian epoch of the earth. Tracing man backward from the present epoch through the Greco-Latin, Egypto-Chaldean, Persian and Indian periods of mankind to the great Atlantean flood recorded in the deluge-myths of all nations, we reach those ancestors of ours who lived on the land-mass we call Atlantis, between present-day Europe and America. Still further back, we come to a primeval land-mass, which we call Lemuria, lying between Australia and India. It was in the middle of that Lemurian period that the higher triad of spirit self, life spirit and spirit man united with the four lower human principles—physical body, etheric body, astral body and ego. Correctly speaking, at that period in the Lemurian epoch, the highest being on earth was not yet a physical human being in our sense of the word. Only a kind of envelope existed, made up of the highest animal nature—a being, or collection of beings, made up of the four lower principles of human nature. But until then the higher human being, which is the internal part of human nature, destined to evolve further and further in the future through the three principles of spirit self, life spirit and spirit man, rested in the bosom of the Godhead. To picture the scene at that time by a trivial modern comparison, it was as though all the people living on earth had been building bodies capable of receiving a human soul as a sponge absorbs water. Picture a vessel of water. It is impossible to tell where one drop of water ends and another begins. But picture also a number of little sponges immersed in the water, each soaking up a part of it. What had been a uniform mass of water is now distributed among the many little sponges. So it was with human souls in that remote age. Previously, they had been at rest, without individuality, in the bosom of the Divine First Cause, but at that particular moment they were absorbed by human bodies and so individualized, like the water by the sponges. What was then absorbed by the separate bodies, or four lower principles, continued to evolve further, and will so continue into the future. In spiritual science it has always been called the higher triad, and the triangle and the square were made symbols, especially in the Pythagorean school, of the human being as he came into existence at the middle of the Lemurian epoch. The diagram on the next page thus represents the constituent elements of the human being, But the higher, eternal portion, which passes through all incarnations, has a double character, as you can see, From one side it may be regarded as the primordial, eternal element of humanity and, from the other, as a drop of the Divine Essence given up by the Godhead and poured into the fourfold human vessel. As a result, a drop of the independently individualized Divinity is to be found in each of us human beings. The three higher members of the human being—the eternal portion—may thus be looked upon as the three highest principles in man, but equally as three principles in the Godhead Itself. Actually, the three highest principles of human nature are at the same time the three lowest principles of the Divinity nearest to man. An enumeration of man's principles must start with the physical body, continue with the etheric body, astral body and ego, thence from spirit self to spirit man. But a corresponding enumeration of the principles of those Divine Beings who gave a drop of their own soul nature to man at the time of which we are speaking in the far-off past, must begin with spirit self, continue with life spirit and spirit man, and thence proceed to principles above spirit man, of which contemporary man can only conceive when he is a pupil of Initiates. 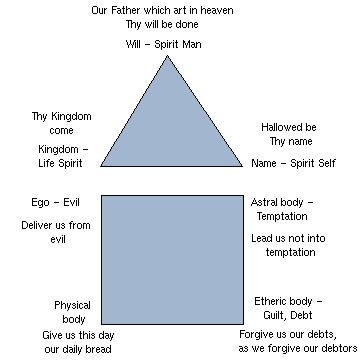 You see that the three principles of higher human nature may be looked upon as three divine principles, and today we shall so regard them, not as human, but as divine principles, describing them accordingly. The highest principle in us, which we shall only develop at the end of our earth incarnations, or, we may say, at the end of our present planetary course, is called spirit man in terms of spiritual or occult science. The original essence of this human principle is faintly comparable to the will element in present-day human nature. This comparison is not exact, but only a faint indication. Yet the fundamental character of this highest of the divine principles in us is of the nature of will—a kind of willing. This will element in us, today only feebly developed in our inner being, will become in the course of our ever ascending development the predominating principle in us. Man is today essentially a consciousness, or understanding being, whereas in many ways his will is limited. He understands the surrounding world as a totality—that is, to a certain degree—but has no real control over all that he penetrates with his knowledge. This control by his will is a development of the future, and it will become ever stronger until he attains that central goal of existence known to spiritual science as “the great sacrifice,” signifying the power of will to sacrifice oneself completely, not merely in driblets of human sacrifice of the kind of which man is capable today with his puny present feelings and will power. In future time he will have developed the strength to sacrifice his whole being by letting it flow directly into material substance. One may picture this “great sacrifice,” the highest expression of will in divine nature, by imagining oneself before a mirror in which one's image is reflected. This image is, of course, an illusion, a semblance. Now carry over this image to the point of imagining yourself dying, sacrificing your existence, your feeling and thought, your very being, to inject life into that image. Spiritual science in all ages has called this phenomenon the “outpouring,” “the emanation.” If you could really make this sacrifice, it would be clear that you would no longer be here because you would have given up your whole being to this reflected image to imbue it with life and consciousness. When the will has become capable of making the “great sacrifice,” it actually creates a universe, great or small, whose mission is bestowed upon it by its creator. Such is the creative will in the Divine Being. The second principle in the Godhead, life spirit, insofar as it has flowed into humanity, has already been indicated in the comparison that has been made with the mirror. This second principle is the reflected image itself. Now imagine the inner being of a Divinity that has in this way created a universe, with itself as the center. If, for example, you imagine yourself as the central point in this room, surrounded not by these six surfaces of walls, ceiling and floor, but by a hollow globe that reflects its content, you will see yourself, as the central point, reflected on all sides, everywhere. In like manner you can picture a Divinity as a central will, reflected on all sides, and the mirror is both image of Divinity and the universe. For what is a universe? Nothing but a mirror of the essential nature of Divinity. The universe lives and moves because the Divinity is poured into it—the “outpouring”—when Divinity makes the “great sacrifice” and is reflected in the universe. The pouring of life and being into a reflected image is an exact picture of this divine creative process. The divine will expresses itself in infinite diversity, animating thereby the entire universe. In spiritual science, this process of Divinity repeating itself in infinite differentiation, in multiplicity, is known as “the kingdom,” distinguished from the will itself. The will is the central point; its reflection, the kingdom. The will is in this sense comparable with spirit man; the kingdom, or will's reflected image, with life spirit. The kingdom, in turn, reproduces the being of the Divine in infinite variety. Observe it fully, at least to the extent to which it is our kingdom, our multiplicity, or universe. Observe its visible manifestations in minerals, plants, animals and human beings. The kingdom is manifested in each separate being of all these, a fact that even our language expresses in the terms “mineral kingdom,” “vegetable kingdom,” “animal kingdom” and all the great divisions of our universe. The kingdom is all these; each of these in turn, is a kingdom, and if we observe the mass of details involved, we find the nature of all to be divine. In all of them the divine being is reflected, just as the central being is reflected in a hollow globe. So an observer, looking at the world in the sense of spiritual research, sees God reflected in every human being as an expression and image of the Divine. In a graded series of beings, in infinite diversity, the Godhead appears in the kingdom, and the separate entities are distinguished from one another in the sense of spiritual science by their names. An observer at a stage of existence sufficiently lofty to look upon all these separate entities as “emanations,” or “outpourings,” of the Divine is able to give these entities their names, to give each manifestation of the Divine its name. Of all beings in the universe, only man thinks the name of each of the separate members of the great multiplicity of the kingdom, distinguishing each from all the others. The will, as we have noted is comparable with spirit man; the kingdom, or reflected image into which the will has been “outpoured,” is comparable with life spirit. The third of the three highest human principles that emanate from the Divine, by which the separate members of the great multiplicity of the kingdom are distinguished from one another and separately named, is comparable with spirit self. The occult science of the different religions has thus simply taught what it was that emanated from the Godhead and flowed into a person to become his eternal image or archetype. Thus, if you could see yourselves in that condition to which you should finally rise—the condition of spirit man—you would recognize its will-like nature. If you would rise in thought to a comprehension of the vehicle of will (spirit man)—in other words, to life spirit—you would see that it is the kingdom that represents it in the divine sphere. If you would rise to penetrate what the names, or conceptions or ideas of things really signify in spirit, you would see that it is the name that represents this wisdom in the divine sphere. So does ancient teaching reveal that the emanation of Divinity, which has flowed into human nature to form its eternal part, consists of name, of kingdom, of will. Thus what is called the higher triad in man is recognizable as part of the Divine. To complete this picture, think of the four lower principles of perishable human nature. The three higher principles may be thought of, we know, as principles of the Godhead. Similarly, the four lower principles may be considered as of the perishable world, as human principles. Think of the physical body, composed as it is of the same substances and Forces as is the seemingly lifeless world around it. The physical body could not go on existing without the inflow into it of matter and force from the surrounding world. The physical body, in a strict sense, is a continual thoroughfare for all that is in it. Into it and out of it again the substances continuously flow that are at one time of the outer world and at another time within us. In the course of seven years, as we have mentioned in other connections, the entire material composition of the human body is renewed. In none of you are the substances that were in you ten years ago. We are perpetually renewing the substances of our physical body. What was formerly in us is now somewhere else, distributed outside us in nature; something else has replaced it inside of us. The body's life depends upon this continual inflow and outflow of matter. Just as we have considered the three higher human principles as parts of Divinity, we may observe the four principles of our lower nature as parts of Divine Nature. The physical body may be seen as part of the physical substance of our planet. Its substance is taken from the material planet, then is returned to it. The etheric body likewise may be considered a part of the environment surrounding us here, and so also the astral body. Think of the etheric body and the astral body together. The astral body, as you know, is the vehicle of all that lives in man as impulse, desire and passion, all that surges up and down in the soul as joy and sorrow, pleasure and pain. The etheric body, on the contrary, is the vehicle that represents and bears within it the more lasting qualities of soul. Often I have compared the development of the etheric body and astral body with the hour-hand and the minute-hand of a clock. A great difference is observable between what you knew and experienced as an eight-year-old child and what you now know and have experienced, as I have also reminded you on other occasions. You have learned so much, gained so many concepts, in the intervening period. Much that your soul has taken in of joy and sorrow has left it again, actually has passed through it. How different are these relatively ephemeral experiences from such human elements as temperament, character and tendencies that are persisting and continuing. You will find, for instance, that if you were passionately inclined as a child, you are probably still so in later years. Most people keep throughout their lives such basic elements in their natures. It is to overcome this relatively stationary quality of the etheric organism that spiritual training and development are instituted; for, as has often been emphasized, such training is no matter of mere theoretical knowledge. The student has accomplished a great deal, indeed, if he has changed one quality of temperament to which he is predisposed, so speeding up the hour-hand of the clock even a little. Whatever evolves slowly in this way—a human being's lasting tendencies, enduring qualities of temperament, habits that persist—is rooted in the etheric body; whatever changes quickly by contrast, minute- hand-wise, has its roots in the astral body. Applying these facts practically to the human being in his environment, to life in the external world, the observer notices a person's connections with the epoch in which he lives, with a nation, with a family, all of which are revealed in his habits, temperament and enduring inclinations. These relatively fixed and abiding qualities tend to be observable, not only in the person himself, but in all with whom he is in any way connected—his family, his nation, etc. A nation's separate individuals are recognizable through their common habits and temperament. An individual who is to achieve a higher spiritual development, to unfold his higher nature, must change his disposition and basic habits. Such a man is called “homeless” in the terminology of spiritual science, because he is obliged to change his etheric body, through which he has been, except for this higher development, connected with his nation. Life in one's native community reveals, too, that the qualities linking one to a family or nation, stirring one to feel relationships with individual people of the nation, are similar also to qualities widely discernible in one's era. If an ancient Greek should walk into your life, you would have little in common with him. His etheric body would be so unlike yours. Human beings understand one another through common qualities in their etheric bodies. In the astral body, however, is rooted a man's ability to lift himself more readily out of certain qualities binding him to a common life with others, and to establish himself as a separate individual in his family, in his folk, so that he is not a mere Frenchman nor a mere German nor a member of a family, but stands out as a special individuality within the folk, the family, etc. Thus he can outgrow the totality of characteristics of his nation. Those qualities that he transcends are rooted in the astral body. The astral body is their bearer. The astral body is thus seen to bear more of what is individual and personal in man. So it is that faults committed through the etheric body render a man more a sinner toward his fellow men through neglect of those obligations and conditions making social life possible among them, between one man and the next. On the other hand, faults of a more individual nature, a man's wrong-doings as a separate personality, result from qualities in the astral body. Spiritual science has always termed as “guilt” (German, “Schuld”) those sins that are against the community, and that originate in a faulty etheric body. The more common English word “debts” (“Schulden”) has in German an origin similar to the word “guilt,” with its more moral connotation in English, signifying what one man owes another in a moral sense. Debt, or guilt, derives from defective qualities in the etheric body, whereas a defective element in the astral body leads to what spiritual science associates with the word “temptation.” The man yielding to temptation takes upon himself a personal fault, or failure. The ego, or true personality, too, can commit faults. The Paradise story indicates the kind of fault through which an ego may fall. The human being's higher soul became an ego when it descended from the bosom of the Godhead and entered an earthly body for the first time. It was taken up by the earthly body like a drop of water by a sponge. The higher soul, or individuality, can commit faults within the ego. These ego-failures, which are different from those stemming from faulty qualities of the etheric and astral bodies, occur through the very fact of a man's attaining independence. To rise gradually, in full consciousness, to freedom and independence, man had to pass through selfishness and egotism. As a soul, he is descended from the Godhead, which is incapable of egotism. A member of an organism never imagines itself independent; if a finger were to imagine itself independent, it would fall away from the rest of the hand and wither. The self-dependence that is so necessary to human development, and that will attain its full meaning when its fundamental nature is unselfishness, could originate only from selfishness. It was when this selfishness entered the human body that man became a self-seeking, egotistic being. The ego naturally follows the body's inclinations. Man devours his fellow man, follows selfish impulses and desires, is completely entangled in his earthly receptacle as the drop of water in the sponge. The Paradise story shows the individual placed in a position to sin just by having become an individual, a really independent being. Whereas formerly he drew in what he needed from the universe, as a single drop in a mass of water derives its force from the mass, his impulses as a fully independent individuality derive wholly from himself. The eating of the apple in Paradise signifies this kind of error stemming from independence. It is significant, too, that the Latin malum means both “evil” and “apple.” All real meanings of words, of course, provided they have any spiritual scientific background, are deeply connected in an inner sense. Spiritual science never uses the word “evil” for any transgression that does not stem from the ego. Evil is thus the fault proceeding from the ego. Trespass, or guilt, is the fault proceeding from the etheric body of a man in social relationships with his fellow men. Temptation may assail the astral body in any respect in which it is individually and personally at fault.
Consider the relation of the four lower principles of human nature to their environment, that is, the planetary conditions surrounding them. The physical body continually takes in physical substance as nourishment; so it maintains its existence. The etheric body's life in a finite condition is possible only by maintenance of fellowship with people into whose community one has grown. The astral body is maintained by overcoming temptation. The ego is maintained, and undergoes development in the right way, by not succumbing when “evil” threatens. Now bring before your mind's eye the whole human being—the lower quaternary and the higher triad—so that you can say: In individual man there lives a drop of Divinity; he is evolving to the Divine through the expression of his deepest, innermost nature. In once expressing outwardly that deepest, innermost nature, he reveals that he has by gradual development transmuted his own being into what Christianity calls the “Father.” What lies hidden in the human soul and hovers before humanity as its great goal is called the Father in Heaven. One wishing to attain that degree of development must be capable of bringing his higher triad and lower quaternary to the point at which they can maintain the physical body adequately. The etheric body must live socially so that an adjustment is effected with whatever exists of “trespass” within it. The astral body must not perish in “temptation,” nor the body of the ego fall in “evil.” Man must strive upward to the Father in Heaven through the three higher principles—the Name, the Kingdom, the Will. The Name must be felt in such a way that it becomes hallowed. Look around you. All things in their diversity express the Godhead. In calling each thing by its name, you make it a member of the divine order of the world. By beholding in every single thing or being that you name in your environment some element that reveals in it a principle of Divine Being, you help make each part of your environment sacred. You hallow each part. You grow into the Kingdom—which is the outpouring of Divinity—and develop yourself up to the Will, which is spirit man but at the same time a principle of the Godhead. Think, now, of a meditant who concentrates wholly upon this meaning of human development, and who wishes to gather this meaning—the seven principles of man's spiritual evolution—into seven petitions in prayer. How will he pray? To express the aim of the prayer, he will have to begin, before he utters the seven petitions: In this form of salutation, man concerns himself with the deepest foundation of the human soul, the inmost element of the human being, which Christian esoteric teaching characterizes as of the kingdom of spirit. The link of the first three petitions, which follow this exalted salutation, is with the three higher principles of human nature, with the divine substance within man: Now the prayer moves from the spiritual to the earthly kingdom: Thy will be done on earth, as it is in Heaven.The four last petitions are linked with the four lower principles of human nature. What appeal is the supplicant to make with reference to the physical body that it be sustained within the planetary life? Give us this day our daily bread.What is he to say with reference to sustaining the etheric body? Forgive us our debts, as we forgive our debtors.The adjustment of what takes place through the transgressions of the etheric body is what he asks for here. What is he now to ask with regard to the astral body? Lead us not into temptation.And with regard to the ego? Deliver us from evil.The seven petitions of the Lord's Prayer are thus seen to express the fact that the human soul, when it aspires rightly, implores the Divine Will for a development of the seven elements in human nature that will enable a man to find his right course of life in the universe, a development of all these seven elements in the right way. Through the Lord's Prayer, the petitioner, at the time when he uses it, may rise to understand the full meaning of the development of his seven-principled human nature. It follows that even when the users of these seven petitions are the simplest people, who do not necessarily at all understand them, these petitions express for them, too, the spiritual-scientific view of human nature. All formulas for meditation in the world's great religious societies throughout history have had their origins in spiritual science. Analyze every true prayer that exists—word for word—and you will find it to be no arbitrary stringing together of words. Never has a mere blind impulse been followed to string together so many beautiful words. Not at all; rather, the great wise men have adopted these prayer forms from the wisdom teaching that is now called spiritual science. Every true form of prayer was born of this great knowledge; and the great Initiate Who founded Christianity—Christ Jesus—had in mind the seven principles of human nature when he taught His prayer, expressing in it the seven-principled nature of man. So are all prayers arranged. If it were not so, their power could not have continued to be exercised for thousands of years. Only this manner of arrangement is effective, even among simple people who do not in the least understand the deep meaning of the words. A comparison of human life with occurrences in nature will make this appeal of true prayer to the simplest of people more understandable. Observe a plant. It delights you, though you may know nothing at all of the great universal laws according to which it has come into existence. It is there, and may have interest for you, but it would never have been created if primal, eternal laws had not existed according to which the necessary creative forces flowed into it. There is no need for simple natures to know these laws at all, but if a plant is to be created it must be produced in accordance with them. Similarly, no prayer that has not issued from the fountainhead of wisdom has real meaning for either the learned or the simple. It is in this present age that those who have so long observed the plant and received its blessing can be led to the wisdom in these great universal laws. For two thousand years the Christian has been praying as the unscientific man observes a plant. The time is coming when he will discern the power that prayer possesses from the deep source of wisdom out of which it has flowed into being. Every prayer, especially the prayer that is central to Christian life, the Lord's Prayer, expresses this primeval wisdom. As light is manifested in the world in seven colors, and the Fundamental sound in seven tones, so does the seven-membered human being, aspiring upward to its God, attain expression in the seven different feelings of aspiration that refer to the seven-principled human nature and are expressed in the seven petitions of the Lord's Prayer. Thus, in the soul of the anthroposophist, this prayer expresses seven-principled man.
|
| 253. Community Life, Inner Development, Sexuality and the Spiritual Teacher: Methods and Rational of Freudian Psychoanalysis
13 Sep 1915, Dornach Translated by Catherine E. Creeger |
|---|
| If, as I believe, this larger context turns out to be what is most important for our anthroposophical movement, we will find ourselves obliged to study this case for our own edification and for the sake of spiritual science itself. |
| 17 Notwithstanding all the contributions Nietzsche's genius made to the world, it was necessary to point out that Nietzsche would be misunderstood if the psychopathological factor in him were not taken into account. It is important for our Society that psychopathological elements not gain the upper hand, that they be eradicated from our minds and seen in the right light so that psychopaths are not looked upon as some kind of higher beings. |
| This shows us that we must study such cases; they should be of great interest to us precisely because our Society represents a spiritual movement. I could speak at much greater length on this subject, but I must stop for today because you need to get on with your deliberations. |
| 253. Community Life, Inner Development, Sexuality and the Spiritual Teacher: Methods and Rational of Freudian Psychoanalysis
13 Sep 1915, Dornach Translated by Catherine E. Creeger |
|---|
Considering the kind of deliberations you are engaged in at the moment, my friends, I must assume that your minds would be less than ready to take in a continuation of yesterday's lecture. For those of you who want to hear it, that lecture will be given tomorrow, but today I would like to speak about something that will relate in some way to things you all must necessarily have in mind at the moment. First of all, and from a very specific point of view, I would like to address the question of what is really confronting us in the Goesch-Sprengel case. In recent lectures I have often said that it is important to arrive at the appropriate perspective from which to try to resolve any given issue. How, then, can we arrive at the right perspective on this particular matter through objective study of the case? In order to deal with a case like this objectively, we must first of all remove it from its personal context and insert it into a larger one. If, as I believe, this larger context turns out to be what is most important for our anthroposophical movement, we will find ourselves obliged to study this case for our own edification and for the sake of spiritual science itself. And in fact there is a larger context to the case, as will become apparent if we look at Mr. Goesch's letter of August 19 with an eye for his main motives and arguments. Since you have important deliberations ahead of you, I will not detain you too long, but will only select a few essential points for your consideration. The first is Goesch's claim that promises have not been kept. If you listened to the letter carefully, you will have noticed that the emphasis in his reproach is not on the alleged making and not keeping of promises. His primary accusation is that I looked for and systematically applied a means of making promises to members and not keeping them, and that once the members noticed that these promises were not being kept, they were put into a state of mind that forced them into a particular relationship to the one who had made and not kept the promises. As a result, forces accumulated in their souls that eventually made them lose their sound judgment. So the first hypothesis Goesch presents is that systematic attempts were made to stifle the members' good sense, that deliberately making and breaking promises was a means of dulling their normal state of consciousness, resulting in a kind of stupefaction that turned them into zombies. That is the first point his letter addresses. His second point has to do with one of the means of carrying this out. To put it briefly, through handshakes and friendly conversations and the like, I am supposed to have initiated a kind of contact with members that was suited, because of its very nature and the influence it allowed me to exert, to bringing about the above-mentioned effect on their souls. A third thing we must keep in mind as a red thread running through Goesch's whole letter is the nature of his relationship to Miss Sprengel. We could add to these three points, but let us deal with them first. To begin with, how does Goesch manage to construct such a systematic theory, based on his first two points, about how steps were taken to undermine the members' state of consciousness? We need to go into this thoroughly and try to find out where it comes from. In Goesch's case, we are led to his long involvement with Dr. Freud's so-called theory of psychoanalysis.1 If you study this theory, you will begin to see that it is intimately related to how the pathological picture presented in the letter develops. Certain connections can be drawn between this pathological picture, as it relates to Goesch's first two points, and his involvement with the Freudian psychoanalytic point of view. Of course, I am not in a position to give you a comprehensive picture of Freudian psychoanalytic theory in brief—my intent is only to present a few points that will help clarify the Goesch-Sprengel case. However, in a certain sense I do feel qualified to talk about psychoanalysis, because in my earlier years I was friends with one of the medical experts involved in its very beginnings.2 This person eventually abandoned the theory of psychoanalysis after it degenerated later on in Freud's life. In any case, please do not take what I am going to say now as a comprehensive characterization of Freudian theory; I only want to highlight a few points. Freudian psychoanalysts start from the assumption that an unconscious inner life exists alongside our conscious soul-activity—that is, in addition to the soul-activity we are conscious of, there is also an unconscious inner life we are usually not aware of. An important component of psychoanalysis is the doctrine that certain experiences people have in the course of their life can make impressions on them, but these impressions disappear from their conscious awareness and work on in their subconscious. According to the psychoanalysts, we do not necessarily become fully conscious of these experiences before they sink down into the unconscious—for example, something can make an impression on a person during childhood without ever coming to full consciousness, and still have such an effect on that person's psyche that it sinks down into the unconscious and goes on working there. Its effects are lasting, and in some cases lead to psychological disturbances later on. I am skipping a lot of links in the chain of reasoning and jumping right to the outcome of the whole process. In other words, we are to imagine in the soul's subconscious depths a kind of island of childhood and youthful experiences gone rampant. Through questioning during psychoanalysis, these subconscious proliferating islands in the soul can be lifted up into consciousness and incorporated into the structure of conscious awareness. In the process, the person in question can be cured of psychological defects in that particular area. During the early years of the psychoanalytic movement, it was the practice of Dr. Breuer in particular to carry out this questioning with the patient under hypnosis.3 Later on, this practice was discontinued, and now the Freudian school conducts this analysis with the patient in a normal waking state of consciousness. In any case, the underlying assumption is that there are unhealthy, proliferating islands present in the psyche below the level of consciousness. This psychoanalytic outlook has gradually spread to incorporate and try to explain all kinds of phenomena of ordinary life, particularly with regard to how they appear in people's dreams. As I already explained once in a lecture to our friends in another city, it is at this point that the Freudian school really goes out on a limb in saying that unfulfilled desires play a primary role in dreams.4 Freudians say that it is typical for people to experience unfulfilled desires in their dreams, desires that cannot be satisfied in real life. It can sometimes happen—and from the point of view of psychoanalytic theorists, it is significant when it does—that one of these desires present on an unconscious island in the psyche is lifted up in a dream and reveals in disguised form an impulse that had an effect on the person in question during his or her childhood. Please note the peculiarity of this train of thought. It is assumed that as young boys or girls, people have experiences that sink down into subconsciousness and work on as fantasy experiences, clouding their consciousness. The pattern, then, is this: experiences of waking life are repressed and continue to work on the subconscious, leading to a weakened state of consciousness. This is exactly the same pattern Goesch constructs with regard to promises being given and broken and working on in the subconscious—all with the intention to create the same effect in the subconscious as the “islands” in Freudian psychoanalytic theory. According to Goesch, this was done cunningly and deliberately and resulted in a state of stupefaction analogous to what occurs when experiences of waking life have sunk into subconsciousness and are brought up again in a dream. Psychoanalytic theory is a very tricky business, and if you dwell on it long enough, it gives rise to certain forms of thought that spread and affect all your thinking. As you can see, this has something to do with why Goesch came up with such a crazy idea. In addition, as I have said before, the concept of physical contact plays an important part. I am now going to read certain passages from one of Dr. Freud's books, a collection of essays from the Freudian magazine Imago, and I ask you to pay close attention to them.5 But I must precede that with something else concerning the Goesch-Sprengel case. Those of you who have known Miss Sprengel for some time will recall that she was always very concerned about protecting herself from other people's influence on her aura—she lived in horror of having to shake hands and things like that. Even before Goesch arrived on the scene, she had already gotten the idea that shaking hands is a criminal act in our esoteric circles. The following incident is absolutely typical: I had business to do in Dr. Schmiedel's laboratory and happened to meet Miss Sprengel there.6 I extended my hand to her, which gave her grounds for saying, “That's how he always does it—he does whatever he wants to you and then shakes hands, and then you forget all about it.” There you have the origin of that theory about handshaking. Yesterday you all heard what this theory became in Miss Sprengel's confused mind with the help of Goesch. He contributed his understanding of Freud's theories and combined things systematically with Freudian ideas. The following passage is from page 29 of the above-mentioned book by Freud:
This is followed by a long discussion of the role fear of physical contact plays in cases of neurosis:
Considering the obsessions involved in fear of physical contact, you can well imagine how it would have been if Miss Sprengel, as a person suffering from this fear, had ever been seen by a psychoanalyst who, in line with usual psychoanalytic practice, would have questioned her about her fear of contact and tried to discover what caused it. A third factor I want to emphasize is the relationship of Miss Sprengel to Mr. Goesch. According to psychoanalytic theory, this relationship would of course be characterized by the presence of repressed erotic thoughts. I mean that quite objectively...9 At this point, my friends, we must look a bit more closely at the whole system of psychoanalysis. As I have just outlined for you, psychoanalysis lifts up into consciousness certain “islands” in the unconscious psyche, and it assumes that the majority of these islands are sexual in nature. The psychoanalyst's task, then, is to reach down to the level of these early experiences that have sunk into subconsciousness and lift them up again for purposes of healing. According to Freudian theory, healing is brought about by lifting hidden sexual complexes up from the depths of the subconscious and making the person aware of them again. Whether this method is very successful is a matter of much discussion in books on the subject. As you can see, psychoanalysts' thinking is often colored by an underlying pervasive sexuality, and this is taken to extremes when psychoanalysis is applied to any and all possible phenomena of human life. For example, Freud and his disciples go so far as to interpret myths and legends psychoanalytically, tracing them to repressed sexuality. Consider, for example, how they interpret the story of Oedipus.10 In brief, the content of this legend is that Oedipus is led to kill his father and marry his mother. When psychoanalysts ask what this story is based on, they conclude that such things always rest on unconscious, repressed sexual complexes usually involving sexual experiences in earliest childhood. The Freudians are firmly convinced that a child's relationship to his or her father and mother is a sexual one right from birth, so if the child is a boy, he must be unconsciously in love with his mother and thus unconsciously or subconsciously jealous of his father. At this point, my friends, we might be tempted to say that these psychoanalysts, if they actually believe in their own theory, should apply it to themselves first and foremost, and admit that their own destiny and outlook stem from an excess of repressed sexual processes experienced in childhood. Freud and his disciples should apply this theory to themselves first. They derive the Oedipus legend, for instance, from their assumption that most little boys have an illicit emotional relationship to their mother right from birth, and are thus jealous of their father. Thus, the boys' father becomes their enemy and works on as such in their troubled imagination. Later, however, they realize rationally that this relationship to their mother is not permissible, and so it is repressed and becomes subconscious. The boys then live out their lives without becoming aware of their forbidden relationship to their mother and their adversarial relationship to their father, whom they experience as a rival. According to psychoanalytic theory, then, what we need to do in cases of defective psyches is to look for psychological complexes, and we will find that if these are lifted up into consciousness, a cure can be effected. It's too bad that I can't present these things in greater detail, but I will try to give you as exact an outline of them as possible. On page 16 of the above-mentioned book, for instance, you can read the following:
This essay explains why primitive peoples so strictly enforce the ban on marrying one's mother or sister and why relationships of this type are punished. “Incest” is love for a blood-relative, and one of the first essays in this book is entitled “The Horror of Incest.” This fear is explained by assuming the existence of a tendency to incest on the part of each male individual in the form of a forbidden relationship to his mother.
Thus, according to psychoanalytic theory, the central complex involved in neurosis is a boy's forbidden sexual attraction for his mother and sister.
From this point of departure, an atmosphere of sexuality spreads until it pervades the psychoanalysts' whole field of activity. Their whole life is spent working with ideas about sexuality. That is why psychoanalysis has been the biggest contributing factor in making an unbelievable mockery of something quite natural in human life. This has crept into our life gradually, without people noticing it. I can sympathize deeply with an old gentleman by the name of Moritz Benedikt (who spent his life trying to bring morality into medicine) when he says that if you look around, you'll find that the physicians of thirty years ago knew less about certain sexual abnormalities than eighteen-year-old girls in boarding school do today.13 This is the truth, and you can really empathize with this man. I mention it in particular because it is really extremely important to regard certain processes in children's lives as simply natural, without having to see them in terms of sexuality right away. Nowadays, these complicated psychoanalytic theories lead us to label a lot of what children do as sexually deviant, although most of it is totally innocent. In most cases, it would be enough to regard these things as nothing more than childish mischievousness that could be quite adequately treated with a couple of smacks on a certain part of the anatomy. The worst possible way of dealing with it, however, is to talk a lot about these things, especially with the children themselves, and to put all kinds of theoretical ideas in their heads. It is hard enough to talk about these things with grownups with any degree of clarity. Unfortunately for people who are often called upon to provide counseling, parents frequently come with all kinds of complaints, including some really dumb ones, about how their children suffer from sexual deviance. Their only basis for these complaints is that the children scratch themselves. Now, there is no more sexuality involved in scratching yourself anywhere else than there is in scratching your arm. Dr. Freud, however, upholds the idea that any scratching or touching, or even a baby's sucking a pacifier, is a sexual activity. He spreads a mantle of sexuality over all aspects of human life. It would be good for us to look more closely at Freudian psychoanalysis in order to become aware of the excesses of materialistic science; specifically, of those of psychoanalysis in seeing everything in terms of sexuality. In a book introduced by Dr. Freud, the Hungarian psychoanalyst Ferenczi writes about the case of a five-year-old boy named Arpad.14 There is no doubt in his mind as to the sources of Arpad's interest in the goings-on in the chicken run:
We could wish for a return of the days when it was possible to hear children say things like this without immediately having to resort to such awkward sexual explanations. I can only touch on this subject today, but I will discuss it at greater length sometime in the near future in order to reassure all you fathers and mothers.16 But of course, Freud's theory, which is spreading widely without people noticing it, is only a symptom of a worldwide tendency. And when parents come with the complaint that their four- or five-year-old sons or daughters are suffering from sexual deviance, in most cases the appropriate response is, “The only deviant thing in this case is your way of thinking about it!” In most instances, that is really what's wrong. My intention in telling you all this has been to point out the kind of atmosphere Freudian psychoanalysis is swimming in. I am well aware that the Freudians would take issue with this brief characterization. But we are fully justified in saying that psychoanalysis as a whole is positively dripping with this psychosexual stuff, as its professional literature reveals. Suppose the assumption that psychosexual islands exist in the human subconscious actually proves to be true in the case of a certain individual. A Freudian theorist might subject that person to questioning and be able to add a new case history to the annals of Freudian psychoanalytic theory. In the case concerning us, Goesch might have undertaken this line of questioning and made some discoveries among those psychosexual islands that would have served to verify Freud's theories. But to do that, Goesch would have needed to be stronger in his own soul. As it was, however, he succumbed to a certain type of relationship to his new lady friend. The material in our possession supplies ample evidence of this relationship and will allow anyone who applies it in the right way to describe their relationship with clinical, objective precision. Since what can be learned from a specific case is often of greater significance than the actual case itself, let me point out that this case can lead us to the same conclusions I presented in my essay, published in the Vienna Clinical Review in 1900, entitled “The Philosophy of Friedrich Nietzsche as a Psychopathological Problem.” 17 Notwithstanding all the contributions Nietzsche's genius made to the world, it was necessary to point out that Nietzsche would be misunderstood if the psychopathological factor in him were not taken into account. It is important for our Society that psychopathological elements not gain the upper hand, that they be eradicated from our minds and seen in the right light so that psychopaths are not looked upon as some kind of higher beings. That is why it is also important to see the current case in the right light and assess what is actually involved from the right standpoint. It is already too late for me to describe now at length how the storm developed. When I was in Vienna in May of this year, one of our members wrote me a letter I had to tear up on returning here, since taking letters across the border is no longer allowed. This letter contained accusations very similar to those raised by Goesch under the influence of Miss Sprengel and showing a similar involvement in Freudian psychoanalysis. They came from the same quarter; the same wind was blowing in both sets of accusations. In fact, if I could have read you some sentences from that letter, they would have sounded remarkably like what Miss Sprengel inspired in Goesch. What, then, was actually going on in the Goesch-Sprengel case? Goesch could not really function as a psychoanalyst, because to do that his relationship to Miss Sprengel would have had to be an objective one like that of a doctor to a patient. Her influence on him was too overwhelming, however, and thus his involvement in the examination was not fully conscious and objective. In Freudian terms, everything at work in the psyche of his friend, the “keeper of the seal,” came out, but since it sank down into Goesch's unconscious, it was masked by the whole theory that came to light in his letter. The Goesch-Sprengel case grew out of one of the greatest mistakes and worst materialistic theories of our time, and we can only deal with it by realizing that both people involved threw a mantle of secrecy over their human, all-too-human relationships. In essence, this consisted of shrouding their relationship in Freudian psychoanalytic theories, as the documents very clearly reveal. When we attempt to help people who come to us in such a confused psychological state, they are often fawning, enthusiastic supporters to begin with, but later on their adulation changes into enmity. That, too, can be explained in psychoanalytic terms. However, our most urgent concern at the moment is our relationship to the rest of the world. Just as we are now experiencing hostility coming from the direction of psychoanalysis, steeped as it is in sexuality, we can expect to encounter at any moment new opposition from all kinds of aberrations resulting from other all-too-human impulses. This shows us that we must study such cases; they should be of great interest to us precisely because our Society represents a spiritual movement. I could speak at much greater length on this subject, but I must stop for today because you need to get on with your deliberations. I simply wanted to point out the first tentative steps we must take in seeing where the dangers for our movement lie and how urgent it is that we all do as much as we can to help the world out there learn that we are not chicken-livered. We know how to stand up for ourselves. When things come up in disguise as they did in this letter, we must rip off the mask and expose where they come from. Their origins lie much deeper than we usually think; they originate in the materialistic outlook of our times, which has not only become the dominant view in science but has contaminated our life as a whole. Combating it is our movement's very reason for existence, but we must keep our eyes wide open and see what is going on in the world. We must recognize what the people coming to us have learned out in the world and what they bring with them when they come to us.
|
| 198. Roman Catholicism: Lecture III
06 Jun 1920, Dornach Translator Unknown |
|---|
| So that you may not take the matter too lightly. For in our anthroposophical spiritual science it is verily not a question of the sort of things which go on, for instance in the Theosophical Society. That the Theosophical Society is not to be taken seriously is clearly to be seen from the fact that one day it came to accept by a majority the whole farce of Krishnamurti as the reborn Jesus Christ of Nazareth. |
| 198. Roman Catholicism: Lecture III
06 Jun 1920, Dornach Translator Unknown |
|---|
You will have noticed that all my lectures for years past have stressed the importance, both for the spiritual and social evolution of humanity, of the spread of what we spiritual scientists call the results of initiation research. You know also that by the word initiation, to use an ancient term, we understand a seeing into a spiritual world separated from our physical-sensible world by a kind of veil; a veil which may very easily lead to illusions. What is first given to man is the physical-sensible world, and he makes use of this either for the concerns of ordinary life or in pursuit of what today is called science. He combines his perceptions in the physical world with all kinds of concepts, ideas and so on; but all that does not lead him beyond the world of the senses; and we may say that the only means through which in ordinary life the human being can to a certain extent look beyond and above the sensible is in dreaming. The dream, as we experience it today in ordinary life, is only a poor imitation of what may be called experience in the super-sensible world. The super-sensible world has to be perceived not only with the same degree of consciousness that one has in ordinary life, a degree of consciousness which is not there in the dream condition, but with a consciousness of even higher degree. In order to experience the super-sensible world, one must enhance one’s consciousness, to come to a state which bears a similar relation to that of ordinary life, of ordinary consciousness, as that of ordinary consciousness bears to sleep consciousness, or at any rate to dream consciousness. Thus a kind of awakening out of the ordinary consciousness has to take place. Hence the dream is, of course, only a poor imitation of what is experienced in that other condition. But really the dream differs far less from ordinary thinking than is believed to be the case. When you become aware of the picture world of an ordinary dream, it is actually in its content essentially the same as what underlies one’s thoughts, only that in thinking the human being enters into the outer world through his senses; and therefore what is arranged in the dream by mere analogy, is in thinking ordered in accordance with quite external relationships, is ordered by the perception of the outer sense world, in accordance with what this world says to us. You can have a kind of proof of this if you sit down and shut your eyes, or let us say if you are lazy and just allow your thoughts to wander, and then notice how they have wandered, notice that as you recall them in your mind you can hardly find between them any more connection than one finds in the events of a dream. The ordinary uncontrolled flow of man’s ideas is in a certain sense subject to the same law as that of the dream. It is only through our senses that we are torn out of our dreams. And as soon as we silence our senses, then we really begin to dream. This dream activity has to be intensified. It has to be so organized that it becomes permeated by a higher consciousness than that which our ordinary senses confer. Then imaginative consciousness arises, and then by degrees comes inspired consciousness, of which I told you yesterday in my public lecture, that it is recognized by Thomism as a justified source of cognition. In our initiation science, then, we have the results of such an intensified condition of consciousness. The difficulty in the present evolution of humanity and in that of the near future is that humanity will most certainly need this science of initiation, and will not be able to get on without it, for if only the materialistic knowledge that has been developed in the last three to four centuries should continue to permeate human evolution, conditions such as we are now experiencing in the present social chaos of the civilized world will repeatedly recur, broken only by short intervals. What science has been able to give to humanity since the middle of the Fifteenth Century has certainly been sufficient for the making of technical discoveries; has been sufficient to spread over the earth a network of commerce and business intercourse, but it does not suffice for the creation of social arrangements really adapted to the consciousness of present-day humanity. That is something which has gradually to be realized. As long as the science of our universities, our recognized public education, rejects the science of initiation, as long as an external, material science is alone recognized, so long will humanity be perpetually in the grip of chaotic social conditions, such as we are now having. The science of initiation will alone be able to save humanity of the future from such chaotic social conditions. Above all, the science of initiation will be able to give those human beings who can approach it a consciousness of the fact that the life here on earth, which we enter through the gate of birth, is the continuation of a spiritual life which we have spent in the super-sensible world between the last death and this present birth. Now you know that this spiritual life which precedes our birth or conception is not spoken of in the churches of our modern civilized world. It is never spoken of, and for a quite definite reason. Because at a certain point of time, which coincides with that of the Greek evolution between Plato and Aristotle, all consciousness of a pre-natal spiritual life was lost. Plato speaks clearly of that life, but Aristotle vehemently defended the theory that every time a human being is born on the earth, a quite new soul unites with his physical body. The Aristotelian doctrine is that for each physically-born human being a new soul is created. Now if one holds such a view, one cannot say otherwise than that the life which begins with death, which a man begins by throwing off his physical body—and of this Aristotle also speaks—continues to exist and does not again descend to earth. For, of course, unless one can speak of a prenatal existence, one has no justification for believing otherwise than that after his death man remains forever in a spiritual world. That had already led Aristotle to draw some very weighty conclusions. For instance, he argued that if anyone between birth and death here on earth has led a life which burdens his soul with evil, that human being is for all eternity forced to look back on that evil, which can never again be blotted out or overcome. So that according to Aristotle’s view, when the man dies, he has to look back eternally on the one earth life for which he has to pay. This doctrine of Aristotle was taken over in its entirety by the Catholic Church, and when in the Middle Ages the Church sought for a philosophy which could carry its theology, it took over, as regards the life of the soul, this Aristotelian doctrine, and one can still today recognize its echo in the idea of eternal punishment in hell. Now, after having for thousands of years had this doctrine of the origin of the soul with the body impressed upon them, how is it conceivable that people can free themselves from it again and arrive at the truth? They can only do so by receiving a new spiritual science. Without this renewal of spiritual science mankind will not be able to accept a life before birth as a justified belief or, rather, before conception. Just think what it signifies for the whole evolution of humanity not to speak of a prenatal life. When in the churches of today we are told only of a life after death, that simply arouses instincts connected with man’s egotistical desire not to be extinguished at death. My dear friends, an essay, a thorough-going study is needed—“On the Cultivation of Human Egotism by the Churches”—In such a study one would have to explore the real motives which are worked upon in the sermons and doctrines of all the usual religious denominations, and one would everywhere find that appeal is made to the egotistical instincts of man, especially to the instinct for immortality after death. One could extend this study to cover more than a thousand years, and one would see that these religious denominations, by eliminating the life before birth under Aristotelian influence, have fostered in the highest degree the egotism in human nature. Churches, as cultivators of the deepest egotistical instincts, is a subject well worthy of study. By far the largest part of the religious life of the modern civilized world today panders to human egotism. This egotism can be felt in pronouncements which I could quote by the dozen. Again and again it is written, especially in pastoral letters, “that spiritual science busies itself with all kinds of knowledge about super-sensible worlds, but man does not need that. He only needs to have the childlike consciousness of his connection with Christ Jesus.” That is said both by pastors and by the faithful; this childlike connection with Christ Jesus is always emphasized. It is brought forward with immense pride against what is, of course, far less easy to attain—penetration into the concrete details of the spiritual world. It is preached over and over again. Again and again man is led to believe that he can be most Christian when he least exercises his soul forces, when he least strives to think something clear with what he calls his Christ consciousness. This Christ consciousness must be something which man attains by absolute childlikeness—so say these easy-going ones. And best of all they like to be told that Christ has taken all the sins of mankind on Himself, and has redeemed mankind through His sacrificial death, without men having to do anything themselves. All this points to the belief that through the sacrificial death of Christ, immortality is guaranteed after death; but that merely tends to nourish in humanity the most extreme egotism. By this cultivation of egotism on the part of the churches, we have finally brought about what is dawning today over all the civilized world. Because this egotism has been so widely cultivated, mankind has become what it is today. Just think if the human being, not merely theoretically with ideas and concepts, but with the whole inner life of his soul were to grasp the truth that this earthly life as he enters it through birth lays upon him the obligation of fulfilling a mission which he has brought with him from a life before birth! Just think how egotism would vanish if that thought were to fill our whole souls, if this earthly life were regarded as a task which must be fulfilled because it is linked to an over-earthly life through which we have previously passed! Egotism is combated by the feeling that stirs in us when we look upon life on earth as a continuation of an over-earthly life, just as it is fostered by the religious denominations which speak only of life after death. That is what is important for man’s social well being, to restore the fact of his pre-existence to the consciousness of mankind of the present and of the future, and of course the idea of reincarnation is inseparable from that of the pre-existence of the human soul. Thus we can say that the Catholic Church itself accepted the Aristotelian doctrine and made it into a dogma of her own; but this dogma must now be replaced by the higher knowledge of repeated earth lives, of pre-existence, which Aristotle was clearly the first to leave out of account. You see, if you can estimate what importance it has for mankind to absorb certain elements into its inmost life of soul, then you will recognize what it means for man’s life of feeling in its widest sense. It means that the human being gets quite another consciousness of himself. Now, my dear friends, let us add to what has just been said, the words of St. Paul, that this ordinary consciousness must become permeated more and more by the consciousness, “Not I, but Christ in me.” When we look upon ourselves as something different, Christ will also become different within us. If we look upon ourselves as something which, even as regards the soul-spiritual, has only originated at birth, then of course the Christ can only be in what has come into existence with this present birth, and will only have the task of carrying our souls through the gate of death and further through all eternity. But if we know that we have had a prenatal life, we can know also that it is the Christ Himself Who has laid on us a mission for this life on earth, that we have to develop our own forces, that we have to find Him in our forces, that we have to seek Him as the best we can have in us, the best in our spirit and soul. The Catholic Church, by doing away with the spirit in the Eighth Ecumenical Council in Constantinople in the year 869 has always taken care that those belonging to it should never think about the real psycho-spiritual nature of man. The Church laid down in that Council that man consists only of body and soul, though the soul has a few spiritual attributes; but that to regard man as consisting of body, soul and spirit is heretical, and when the Jesuit Zimmerman brought forward certain reproaches against spiritual science, he reckoned as its deepest sin that it seeks to re-establish the validity of trichotomy, by declaring that man consists of body, soul and spirit. For thereby the true nature of man and also his real relationship to the Christ must inevitably come to light. But what the Church worked for more and more was that man should not come to a true understanding of his real relationship to Christ. We may say, my dear friends, that the development of the western churches consists really in drawing an ever denser and denser veil over the real secret of Christ. You see, fundamentally, all institutions are built on external abstractions. When a state is young it has but few laws and people are relatively unfettered by them. The longer a state exists, and especially the longer the various parties in the state apply their clever arguments, the more laws are made until finally no one knows where he is, for there is no longer only one law, but everything is entangled in the meshes of intertwining laws from which one has the greatest difficulty in freeing oneself. That is the case also with the churches; when a church begins to make its way through the world, it has relatively few dogmas; but men must have something to do, and just as the statesman is always making laws, so do Churchmen create more and more dogmas, until finally everything becomes dogma, dogma becomes consolidated. It is only since the time when Scholasticism was at its height that this consolidation of dogma has been especially noticeable in modern civilization. Anyone who really studies thoughtfully the Scholasticism of Albertus Magnus and Thomas Aquinas will find that in their time everything to do with dogma was still fluid, still a matter for discussion, that discussion was still taken as a matter of course. True, in the Scholastic period there was already a certain opposition within the western church. There was the opposition between the Dominicans and the Franciscans. The Dominican Order, of which Scholasticism was the flower, developed its knowledge through strictly logical ideas. The Franciscan Order declined to do that; the Franciscans wanted to achieve everything through a childlike feeling. I will not now enter into the relation between Dominican and Franciscan teaching, but I should like you to imagine what it would be like if people fought as vigorously today about the content of Dominican and Franciscan doctrine as they did in the Middle Ages, when they discussed dogma so freely. Of course, the Roman bishop even at that time declared people to be heretics; and he could have gone on doing so for a long while, had not the secular governments come to his assistance and burnt the people whom he merely wanted to condemn. In this matter one has to admit that greater blame falls on the secular rulers. All this did not prevent there being free discussion in the Catholic Church at that time. This free discussion has gradually been completely eliminated. Free discussion was something which the Catholic Church, as time went on, could not stand. And why not? Because a quite new consciousness was arising in humanity. This was the transformation of consciousness in man, which took place, as I have often explained to you, in the middle of the Fifteenth Century. The human being wants ever more and more to form his own judgment from the depths of his own soul. In the Middle Ages that was not so. Man then had a kind of communal consciousness, and only a few learned people, the real scholars, could get beyond that. They were able to evolve out of this common uniform folk consciousness because they had been trained in Scholasticism. This also applies to a certain number who were trained in the Rabbinical teaching. In general, however, man’s consciousness was uniform. It was a community consciousness, a family consciousness. But the individual consciousness was developing more and more. Now, one thing that the Catholic Church had always had, because it had attracted highly educated people, was historical foresight. The Catholic Church knows quite well what I am now saying, that the principle of modern development is to foster the individual consciousness of man—but the Catholic Church is unwilling to let this individual consciousness arise. She wants to maintain that dull communal consciousness, from which only those will stand out who have received a scholastic education. Now, my dear friends, there is a very good way of maintaining this dull communal consciousness—it is always a dull one. And this is to damp down the ordinary consciousness which a person has whenever he makes use of his sense organs, to subdue it thoroughly. Just as the dream damps down the ordinary consciousness, similarly the consciousness is subdued for the purpose of making of it a dull communal consciousness. Now one of the many characteristics of the dream is that in many respects it is a liar. Or would you deny that the dream is a liar, that it represents things which are not true? It is, however, not due to the dream but to the subdued consciousness that when we dream we cannot test what is true and what is untrue. Hence it is one of the properties of this subdued consciousness that it takes away from human beings the possibility of distinguishing truth from untruth. Now if one is versed in these matters, what does one do? One relates to people under authority things which are not true, and one does this systematically. Thereby one subdues their consciousness to the dim state of the dream consciousness. Thereby one succeeds in undermining what since the middle of the Fifteenth Century has been seeking to emerge as individual consciousness in the souls of men. It is a fine undertaking so to work under authority as to write articles such as are now appearing in the “Katholischen Sonntagsblatt”; for thereby one succeeds in preventing men from developing in the way they should since the middle of the Fifteenth Century! Although the individual may not know it, the whole hierarchy is behind what happens in this respect, and has organized things extremely well. If one believes that these things happen out of mere naivety or purely from rancor, one is making a great mistake. Naturally, we must fight lying and untruth with all the means at our disposal, but we must not believe that these lies proceed out of simplicity or even out of the belief that what is said is the truth; for if these people spoke the truth, they would not attain what is their purpose to attain, which is to subdue consciousness by deliberately telling men lies, and that is a mighty and diabolical undertaking. Now, my dear friends, this, too, must be said quite frankly. The simplicity is entirely on the other side. Simplicity today is not on the side of the Catholic Church but on the side of their opponents. They do not believe that the Catholic Church is great in the direction I have described; they do not believe that the Catholic Church long ago foresaw that the social condition which has now come over Europe would some day come about, and that the Catholic Church took her own measures to make her influence felt in those social conditions. What the Catholic Church intends is to create a bridge between the most radical socialism, Communism, and its own domination. You see, this magnificent foresight is something one has to recognize in everything which has a real spiritual basis, a spiritual foundation that is rooted in a real spiritual life, and not in mere abstraction. You see, with all this modern enlightenment one arrives at nothing which can have a far-reaching significance in the course of human evolution. But the ceremonies practiced in the Catholic Mass are of far greater significance than all the sermons from evangelical pulpits, because they are deeds accomplished in the sensible world, and in their form they are at the same time something which enchants the spiritual world into the sensible world. For that reason the Catholic Church has never been willing to deprive herself of magical means of working on human beings. These magical means do exist. And we must not believe that anything other than re-entry into the spiritual world in all true inner sincerity and uprightness can be effective against these things. And as what one might call an external sign that the Catholic Church has always had a connection with the spiritual world, you can take something which I have already told a few of you. In the first decade of the Twentieth Century a Papal Encyclical was issued which declared various things to be heretical. Papal Encyclicals speak in such a way that they always adduce the doctrine in question and then say: “Whoever believes that is anathema.” Thus it quotes some doctrine taken from one of the books of Haeckel or someone, and then says: “Whoever believes that is anathema.” It does not state what is true, but says: “Whoever believes that is anathema.” Now, you see, the science of initiation makes it always possible to investigate such things, and I set myself the task of making certain investigations concerning this Encyclical. I am bound to say that here, as in so many other things, what was promulgated by the Pope “ex cathedra” at that time was really drawn from out of the spiritual world. I mean that what has flowed into that Encyclical did come down from the spiritual world. But in an extraordinary way it was completely reversed! Everywhere where there should have been a ‘yes’ there was a ‘no’, and vice-versa. That is something—and I could give other instances—which shows that the Roman Church has today some sort of real connection with the spiritual world but one that is extraordinarily harmful for mankind. Therefore, we need not be surprised that it sees in the rise of modern spiritual science something which it wishes at all costs to get rid of, for, my dear friends, what is the effect of this new spiritual science? It brings about a consciousness of a prenatal life, of pre-existence. That may not be! Under no circumstances shall that happen! So spiritual science must be condemned; for spiritual science calls man’s attention to his own being, makes him aware that he consists of body, soul, and spirit. Under no circumstances may that be; therefore spiritual science must be condemned. People would see, for example, that the dogma of eternal damnation in hell is an Aristotelian consequence of the creation of the soul at physical birth. Suppose a Catholic theologian today studies the connection between Aristotle and Scholasticism, and perceives that the Scholastics derived their proof of the origin of the soul together with the physical body from the philosophy of Aristotle! He would see behind the scenes of the origin of dogma. What is done to prevent this? The theologian is made to take the oath against Modernism. He is made to swear that it is part of his creed that he can never come to a historical conclusion contrary to dogmas which are given out from Rome. The fact that he has taken this oath works so strongly on his feelings that he is confused in his sober research and can never come to see that dogma is bound up with the historical evolution of humanity. Now things cannot remain in this state if the science of initiation arises, and therefore this science of initiation must under all circumstances be condemned. Why am I telling you these things, my dear friends? So that you may not take the matter too lightly. For in our anthroposophical spiritual science it is verily not a question of the sort of things which go on, for instance in the Theosophical Society. That the Theosophical Society is not to be taken seriously is clearly to be seen from the fact that one day it came to accept by a majority the whole farce of Krishnamurti as the reborn Jesus Christ of Nazareth. Such a comedy is only based on hypocrisy, even though this hypocrisy be taken seriously by many. But what should grow on the soil of Anthroposophy, of spiritual science, should be a search for truth, sincere through and through. It is therefore something which, as the Catholic Church is well aware, penetrates behind the scenes, to what must not be discovered if that church is to maintain the dominion in the world to which she lays claim. All that I am now saying is simply to show you that these things may not be taken lightly. For it must be recognized that the Catholic Church has shown great foresight. Though the individual sheep follows the lead and merely obeys orders, though he may be ignorant of what this systematic lying means for the whole evolution of mankind—though the individual knows nothing and does as he is told, the whole system is thoroughly well established, for the lying will be believed by large numbers. On the other side there is the naïve belief that all the external fabrication of natural laws which today forms the subject of our university education can be of significance for the further development of humanity, that all that nonsense about the conservation of matter and energy can be of significance for the further development of mankind! Today people cannot even look with an unprejudiced eye upon the snow which is spread before them every winter (if they are living in the temperate zone), yet through the covering of the forces of growth by the snow crust one part of the earth goes through a complete transformation; and folk consciousness which speaks of the purity of the snow knows far more than our modern science which talks of the conservation of matter and energy. Of course I can only say what I am now saying because I have spent many weeks in showing you how ill-founded are the modern laws of the conservation of matter and energy, how in fact in every human being matter and energy are destroyed, as they work up towards the head, and new matter and new energy arise. All these things are bound to be fiercely contested in some quarters, and the only thing which can help is for as many people as possible to become conscious of the present task of mankind—to be aware that the individual consciousness must lay hold of the world. It will do so, but it can either lay hold of the wisdom of the world or of the blind instincts. If it seizes hold of the blind instincts there will come about a completely antisocial condition, such as is now being prepared in Russia. That, my dear friends, will gradually evoke an antisocial condition against which the English or North American governments, not to speak of the French or any other, will be absolutely defenseless. It would be childish to believe that the English Parliament will be able to deal with what will then lay hold of humanity if the individual consciousness works merely by instinct. But there is one power which will be ready to deal with it, and that is the power of Rome. It is only a question of how it will be done. Rome can establish a dominion; it has the necessary means for this. Thus the only real question is not whether Bolshevism or the Anglo-Saxon bourgeoisie will get the upper hand; the question is whether there will be antisocial chaos, Roman domination, or the resolve on the part of mankind to fill itself with that spirit which in 869 at the Council of Constantinople the western Church declared it heretical to recognize. There is no other alternative than that mankind determine not to go on living in the way which is natural when there are only materialistic thoughts about the world. How does mankind live in a materialistic world? People earn their living in accordance with the fluctuations of the market; there is no other measurement for the social order. After that they may perhaps have a philosophy of life, as a sort of luxury, but only as a luxury. Those supposed to be still more profound say that one must raise oneself into the spiritual world and leave the evil material world behind; a really profound nature can have nothing to do with the material world; he must understand nothing about the material world, but become a mystic and live in the higher world! But even these profound natures as well as the less profound have children and have the notion that these children must “earn,” that it would be very, very wrong if the children were not sent to schools where they would be trained in present-day methods of earning a living. Thereby they have already come to terms with the existing state of things; thereby they hand on this materialism to the next generation. Now when someone talks like this he is an inconvenient person, and it is best simply to revile him, for to hear what I have just been telling you is for most people as if they were being irritated by vermin. Now people do not like being irritated in this way by psychic vermin and so they cover themselves with a thick skin which makes them impervious to what spiritual science has to say about our present culture. It is on this side then that the naivety lies; and when the Catholic Church saw that people were becoming so one-sided, they took care to have people specially trained, and in this they really were indirectly guided by spiritual impulses. And the foundation of the Jesuit Order by Ignatius Loyola as a result of fundamental influences from the spiritual world is one of the most significant events of metahistory, and in it one has to do with a strong spiritual efficacy. Now, my dear friends, we must, of course, among ourselves be able to speak frankly; hence I have been obliged to speak of the grand but questionable training of the Jesuits. I also dealt with this theme in the cycle From Jesus to Christ, which some misguided member has now delivered into the hands of a mudslinger and fabricator of nonsense. You know that in the Karlsruhe cycle I discussed the fundamental basis of Jesuit training. What, may I ask, is the use of stating in each cycle that it is printed as a manuscript for members only, when mudslingers have the cycle at their disposal and can use it for the preparation of all sorts of lies? This incident bears out in a remarkable way what I have already often said, that the time would come when one could no longer count on these cycles being restricted to a small circle, for mankind is not at present fit to be entrusted with anything. Of course, everything written in that quarter is rubbish and untrue, but it is written not on the basis of my public writings, but of private cycles which have been passed on, and I have good reason to believe that one of the first cycles given into the hands of the Catholic clergy was that very Karlsruhe cycle on the Jesuits. For they on their part are not inclined to let the truth about Jesuit training be known. The world must know nothing of how Jesuits are trained; the world must know nothing of their powerful discipline. Modern mankind in its simplicity is merely retarding its own consciousness. On the subject of the Jesuits there are absolutely no true ideas. There are numerous men within that Order of such spiritual capacity that if they were scattered about the world and did not spend their time in the way they do but were working at external science or painting or poetry, they would be honored as individual geniuses; they would be recognized as the great minds of mankind. Within the Jesuit Order there are countless men who would be great lights if they were to appear as individuals and were busy with something different—with, for instance, materialistic science. But these men suppress their very names; they submerge themselves in their Order, and one of the conditions of their strength is that the world should know nothing of the way in which many a head, clothed in black cassock and Jesuit cap, has been trained. These things are intended to show you how fundamentally different the whole form of consciousness is in different categories of human beings. But our modern simpletons, who consider themselves enlightened, will not take these things seriously. That must be emphasized again and again, and that, my dear friends, is what I had to speak to you about today. Now for the next two weeks while I am away we can have no more lectures here. In conclusion to what I have said, partly in public, partly in these private lectures, I had to add all that I have said here today in order that you should not ignore the importance of this misuse of our lecture cycles by our own members. Of course, when the cycles were given, I thought I had to do with people who would respect the undertaking which in a certain sense they had been given. But I was mistaken, and it is quite clear from the rubbish that appears in articles today who has all the cycles at his disposal! |
| 213. Human Questions and World Answers: Twelfth Lecture
21 Jul 1922, Dornach |
|---|
| When he entered the monastery, he realized that it is impossible to live in today's society if you want to become a human being. This has increased to such an extent that now, when he has become his own judge, he condemns himself to death. |
| And if one is purely intellectual, one can, in the way it happened after our anthroposophical congress in Vienna at a meeting, one can, from the standpoint of today's monism, quite intellectually lead the fight against the spirit. |
| I have pointed out how one could get into all kinds of branches in the Theosophical Society, and there were great schemes, races and rounds, whole world systems and all kinds of things were built up in wonderfully intellectual forms - all intellectual! |
| 213. Human Questions and World Answers: Twelfth Lecture
21 Jul 1922, Dornach |
|---|
The last lectures here were essentially devoted to an examination of the way in which we have to think about the present time consciousness. I then tried for the last time to reach back into earlier periods and to draw attention to the fact that what now lives in the souls has actually been preparing itself within Western civilization for a very long time. Today I would like to highlight some episodes from the immediate present that may draw your attention to how a spiritual life must necessarily arise out of the general consciousness of the times, simply out of the necessity inherent in the development of humanity. We can say: Wherever we observe man, whether in the West of present civilization, in the Middle or in the East, everywhere, on closer examination of the times, it can become clear to us how, without the onset of a spiritual impulse, things simply can no longer go on. Today, we want to take a look at the last fifty years of Central European spiritual development, so as to prepare for tomorrow and the day after tomorrow, by considering the characteristics of the beginning and the end. I will do this symptomatically. I will characterize some things at the beginning and at the end of these last fifty years. If we go back to the beginning of the 1870s, we find a wide range of spiritual phenomena that indicate the state of the human soul at the time. I will highlight a few of these spiritual phenomena. In 1872 and 1873, for example, there was a sensational novel that was closely related to the trends of the time. These things are actually forgotten for the younger people in our time, but the novel I mean is one that did indeed capture the imagination in an extraordinarily incisive way fifty years ago. I am talking about Paul Heyse's “Children of the World”. Paul Heyse, who was a famous writer of novellas at the time, wanted to use this novel to depict a number of personalities in their lives, all of whom were already imbued with a certain vague religiosity, but who had at the same time fallen away from some religious denomination or other. So, the children of God, whom, I might say, Paul Heyse saw in the traditional terminology of belonging to some denomination, he wanted to contrast with the children of the world, who belonged to no denomination, who, as they were said at the time, were without religious affiliation, but who nevertheless had a certain tendency towards embracing a religious belief. Now I do not want to talk too much about this novel itself, but I would like to draw attention to how such a work, which thus portrays people who are undenominational, made an impression in those days. I have often mentioned my old friend and teacher Karl Julius Schröer before. He had the peculiarity of following intellectual phenomena as they made their impact in broader social life. Karl Julius Schröer characterized the effect of Paul Heyse's “Children of the World” by saying that it was extraordinarily strange how this novel was passed around fifty years ago, how it interested everyone, interested in how this novel actually gave people the idea that they had never thought about before: that they had no connection to any positive religious belief and that their religious search did not stop at any particular religious belief. And Schröer made the extraordinarily interesting comment at the time that people who had previously taken part in the religious practices of their church, who had thus gone along with their old religious practices, the customs of their church, out of habit, that such people said that this work actually expresses their innermost convictions. And then Schröer concludes with a sentence that is actually interesting: that in the face of such an apparition, religious disputes appear as an anachronism, as something that no longer fits into the present – he is referring to the present at the beginning of the 1970s – because people have already moved beyond them in their thinking. But as I said, although all this is true, we must still say: the people who are described there have lost all connection with any of the existing faiths, but there is a certain trait in them that allows them to find some kind of religiosity. They just can't find it. They go through the world without any religious affiliation, unable to find a connection to a spiritual world through religious feeling. If we now look from such a phenomenon, which took place more within the literary-belletristic life, into the lecture halls, we find that it is roughly the same time in which the conviction of an extraordinary number of people within science was expressed by Du Bois-Reymond with the “Limits of Natural Knowledge”, which I have already mentioned frequently. In this famous lecture, which Du Bois-Reymond gave in 1872, it is stated that certain knowledge is only possible if one follows and penetrates the external phenomena of nature through experiment and observation, to a kind of mathematical-mechanical thinking about the structure of the world, to a kind of mechanism, an atomistic mechanism of the world. Science does not go beyond such a comprehension of the world, everything else must be left to faith. But if one had asked the people who spoke in this way at the beginning of the 1970s, such as Du Bois-Reymond in his “Grenzen des Naturerkennens” (The Limits of Natural Knowledge), how people should now seek their way into spiritual worlds in a religious way, no answer would have been forthcoming. There would only have been a comment, very similar to the comments made by the people in Paul Heyse's “Children of the World” who are described as having no religious affiliation. Now it must be said that all those people who took part in the life that one calls educated, who absorbed something of scientific thought, who adopted something from other schools of thought, who lived in that time, were actually all more or less in a certain frame of mind. Whether they continued to practice their old religions or not depended essentially on old habits, on all kinds of prejudices and the like, and not on a strict and rigorous assertion of what the Zeitbewußtsein would have given to souls. In the last fifty years, people have actually lived in an indefinite, fickle relationship to the spiritual world. But we can also find something similar in other areas. A few years before the publication of Heyses “Children of the World” and Du Bois-Reymonds “Limits of Natural Knowledge”, the famous art writer Herman Grimm published “The Invincible Powers”, which is also a novel. In it, the prejudices and differences between social classes that dominate people in Western civilization are presented as invincible powers. And in an interesting way, this novel contrasts the differences in class and rank within Western civilization with what developed from certain, I would say unhistorical, habits in America as a new life, as a life that did not have to struggle in the same way with class differences and class prejudices. And it is interesting how Herman Grimm, at the end of the 1860s, that is, also about half a century ago, describes how, despite everything, European man, despite all his liberalism, despite all his humanism, does not have the strength to truly overcome class differences. These are insurmountable forces for him. If you want to go deeper and ask yourself: Why are such things insurmountable forces for the European man? then one cannot get any other answer than this: because thinking, which in the case of the European has assumed a certain passive character, the thinking that I have characterized when, for example, I spoke about Richard Wahle, that thinking extends only to “events” and does not want to go into the primal factors, that therefore does not want to grasp forces but only wants to grasp appearances, because this thinking has dominated precisely the decisive people in the last fifty years. With such thinking, which has no power in itself, which is actually only a thinking, one might say, in powerless thought images, with such thinking one simply cannot overcome what has arisen in reality as class differences and class prejudices. What was needed was a thinking imbued with reality, a thinking permeated by reality. And this thinking permeated by reality, which once created the differences in social standing, which once created everything socially real, this dynamic thinking, in contrast to mere descriptive thinking, has actually been completely lost to people within European civilization over the last fifty years. It was absent from their science, which was therefore based only on observation and experiment; but it was also absent from their lives, so they continued to reproduce what had arisen from old habits based on old class prejudices. They did not think about it any further. Because if they had wanted to think about it, they would have needed active thinking. And when the proletarian class began to consider class differences, then this weak thinking, which contains no dynamism, was completely abandoned. It was said: these class differences do not come from forces that would have been within human thinking, but only from economic, physical forces. A conclusion was simply drawn. There you have the situation at the starting point of our modern intellectual life fifty years ago. And now I want to present to you a work that was published recently and that is characteristic of our time, namely Werfel's “Mirror Man”. There you have something that has been born out of certain forces of our time, just as the “Children of the World” or the “Invincible Powers” were born out of the time of fifty years ago. So what is the situation for people like Werfel today? In recent decades, this weak and anemic thinking has been at work. People have somehow sought something of a religious context, of a connection with a spiritual world, but nothing has emerged. But human nature cannot remain one-sided in the long run. It can do so in the development of world history for about fifty years, but then a reaction of human nature begins again. In a certain way, it wants to strive for something more powerful – if we stick with the last fifty years – than the powerless and insipid thinking was. Now, quite a few contemporary works already bear witness to this striving for a more powerful grasp of reality, but Werfel's 'Spiegelmensch' is particularly illustrative of this. Werfel's “Mirror Man” compels us to speak about the present in this way: for long enough, people have sought their way in an indefinite, weak and impotent manner to something that makes man a full human being in the first place. Now an indefinite inner feeling asserts itself on the paths that have been taken in the last fifty years and which are actually not paths at all, but slippery passageways on which one continually slips. Nothing can really be achieved on these slippery passageways; one must get some iron into one's blood again. From such a striving for the times, something like this “mirror man” has emerged. Let us sketch with just a few lines what is depicted in this “mirror man”. It is not my intention to sin against the artistic by characterizing what is in this mirror man. But that is not the point at all; rather, we will see immediately afterwards that what I am about to say also touches on the artistic. We see here a half-grown human being who has grown tired of the outer life as it can be led today. He takes leave of this outer life and now actually wants to become human. For he admits to himself that within the ordinary life, as we live it today, both in Asian and European and American civilization, one cannot really become human. You get up in the morning, have breakfast and do something to maintain yourself within the social order, you eat lunch or receive your guests and say things that perhaps need not be said, that ultimately do not aim to achieve much more than to make the lips move, that are not idle; you take your guests for a walk or whatever else you do today. You can't become a person in such company – I'm not quoting verbatim, I'm just characterizing. It is necessary to try a different path if you want to become a person. And so this “hero” – to use the old aesthetic style – tries to become a person by seeking admission to a monastery. But he is told that this is something extraordinarily difficult. I do not want to characterize the details, but only point out what is important to me today. He is therefore informed that it is something extraordinarily difficult and that, above all, he must be clear about the fact that he has to go through three stages of knowledge. In the first stage of knowledge, he would have to become clear about the human being's position in the world, insofar as this position is contained in the human ego itself. So this life in the ego and this striving to overcome the ego as the first level of knowledge. The second view of the world would consist in the fact that, after one begins to shed the ego in a certain sense, one no longer sees the world from one's prejudiced point of view, as one used to do before, when one had not even begun to shed the ego. And the third vision would be where man would truly penetrate into the world and its reality, not as seen by man living in his ego. He is told this. And he is admonished in the appropriate way not to want such an incarnation too urgently. He is made aware of the difficulties. But he does not back down. So he is initiated in the appropriate way. The initiation takes place – I will mention only the essentials – by being led into solitude for the night, into a room where only a monk watches over him. And there, after he has initially abandoned himself to his thoughts, he falls into a brief sleep, from which he very soon believes he will wake up. And now he finds himself in the room whose one wall has a mirror on it. In this mirror he sees himself, and he is amazed at what is meant. It is meant that when one, after a collection of thoughts and after such a strong decision as this person has made, steps in front of his own reflection, one sees oneself in a different way. So it is actually pointed out that the person is only now beginning to see himself. The mirror image looks so similar to him, but yet again somewhat different. And by doing what must follow from such a surprising experience: by striking the mirror, believing that he has wounded himself, the mirror man steps out of the mirror towards him, that is, that of him which, in a certain respect, is himself and yet again not himself. Now the person has arrived at the first step of knowledge. He must get used to not only going through the world as a person without ego consciousness, but also to having that which is himself and yet not completely himself, his mirror-person, accompany him. In the company of this mirror-man, who now tempts him to do all kinds of things in the outer world, lies a new encounter with world phenomena, with his own deeds, in that he finds himself precisely in the presence of his own ego. Now, I do not want to go into the details. The person in question is actually lying in bed, but he goes through what he can go through according to his previous experiences of external world experiences and external actions. These are not always very nice. But how someone describes something like that depends on their own taste. You can see from the way the author describes things how he feels about such a case. People also experience the world according to their tastes. So we are led through the experiences of the world. Just as Mephisto in Faust has something of the driving force, this mirror man is now always the driving force, and he is led from event to event, being made to do many wrongs. Everything appears to him in a new light, because he has looked into the mirror and seen himself. He now sees one thing after another in the world. He sometimes sees things as they appear to him because he is an ego-person, and sometimes as they appear to him after he is already able to see his reflection. He becomes more and more familiar with the phenomena of the world. In the process, he comes out of his ego more and more. The mirror-man, who is rather slight at first, becomes fatter and fatter. This is a polar-parallel phenomenon, which is not uninteresting. And so this person now lives through the world by experiencing in a different way what he could have experienced earlier, now that he has seen his own self. And in the end he has become so entangled in the experiences of the world that he has to become his own judge, condemning himself to death, which is again very characteristic. He finds that he cannot really live in the world. When he entered the monastery, he realized that it is impossible to live in today's society if you want to become a human being. This has increased to such an extent that now, when he has become his own judge, he condemns himself to death. And now he awakens. In a sense, he awakens from the execution of his own death sentence. He is again in the same room where he was. Now he looks at the mirror again. But by looking now, he notices, for example, that the mirror does not reflect a procession of monks passing by. Earlier, when he looked into the mirror, he saw himself and everything in front of the mirror. But now a procession of monks is passing by and is not reflected. He realizes from this that he is not standing in front of a mirror now, but that the mirror has become a window. He looks through it and sees out into the wide world, sees the landscape. He has attained the third vision. Now he sees the world, whereas at the beginning he saw only what the mirror gave. Because he had the mirror man at his side, he saw what he had seen before in a different way. But now, as it were, he sees through the surface of things - that is how it is presented - out into the free reality. It is, of course, implied that he now also sees out into the spiritual reality. So we have a trilogy before us: the first is the mirror, the third is, let us say, the window. The mirror has become the window. So there we have the two polar opposite views of the world. At first, everyone sees in the other 'their own reflection', sees only what they already have within themselves in the other, where they are caught up in their own ego, and thus sees only their own reflection everywhere in their neighbor or in anything they see in nature. Finally, after breaking through the mirror, they no longer see the mirror, but through the surface of things into the spiritual. And in between where the two merge into one another:
Now, I would like to point out two characteristic features of this drama. The first is this: we see that there is a desire to depict a person in the process of rising to a certain religious connection with another world. That the first part, the mirror, is short, one can forgive, because it is very interesting to see how the person lives into an insight into his own ego, so that this ego becomes so concrete to him that it now accompanies him through his experiences in the world. The middle part is quite detailed, and a great many experiences are described. In order to find these appealing at all, one must have a taste, one could even say sometimes, distaste, for them. But as I said, everyone has to do it according to their own taste. In any case, this part, where one looks into the experiences of the world, is very long. But the third part is quite short, and what is seen out there is actually only hinted at, I would say symbolically, by looking through the window; nothing real comes into view. It is quite short, this third part. That is the one peculiarity I would like to emphasize. But the other peculiarity is this: one must recognize that here is the most beautiful expression of the striving to pour strength and energy into thinking. But one also sees that the modern man, of the kind that Werfel is, cannot do that at first. Why? Yes, it is very peculiar. When I had finished reading this drama – and I read with the greatest interest, I must say, because it is extremely significant for our present spiritual life as represented by individual personalities – I had to say the following to myself: the process is as follows: 1. Der Spiegel; 2. Eins ins andere; 3. Das Fenster. But one could also read the whole thing backwards from front to back. Of course, it would have to be rewritten, but one could also read the whole thing backwards from front to back. Because why? It is entirely possible to understand the matter in such a way that one says to oneself: the way a person initially relates to the world is how things appear to him. He is no different from the things. He has not awakened to his sense of self. He stands before the window, looks out into the world. Now we could say that the old monk, to whom he has now come and to whom he says that he can no longer bear it, that everything is always only inside, what he sees through the window, that he wants to find himself – that the old man now says to him: Yes, there are three views to go through. The first view shows us the world without our finding our ego in it. We lose ourselves to the world. The second view allows us to gain something of the ego, and then, gradually, a multitude of beings comes towards us from the world. The world is brought to life, spiritualized. We used to see it as spiritless, now the world is spiritualized. Everywhere, from every being, from plants, animals, clouds and so on, something spiritual comes towards us. Many spiritual beings come towards us in this second part. In the third part, we wake up. We step in front of the window, we look out. But we see everything anew, because now we see the real world for the first time. The window has been transformed into a mirror, the human being has come to himself. He unites all these mirror beings that have come to meet him in the world of plants, animals, clouds; they are in his only self, which has become cosmic to him. And now, by recognizing himself, he actually sees the cosmos for the first time. You could easily describe the whole thing backwards, the last part of the trilogy first, then the middle part, then the part with which it started. That is extremely interesting, because it is precisely this that makes this drama particularly characteristic of the present. What is the peculiarity of intellectualism? Yes, the peculiarity of intellectualism is this: you can start with the idea anywhere and stop anywhere, and you can assert one thing and you can assert another – I have emphasized this many times. In terms of thought, you can prove anything, in terms of thought you can refute anything. Intellectualism, which is nothing more than a system of vapid and feeble thoughts, allows you to start anywhere and go somewhere, but you will stop at a certain point. But you can also start at this latter point and go the other way. Today, one can be a very clever person and a gross materialist, because materialism can be quite well proven in an intellectual way. And if one is purely intellectual, one can, in the way it happened after our anthroposophical congress in Vienna at a meeting, one can, from the standpoint of today's monism, quite intellectually lead the fight against the spirit. One can prove very well that materialism is right. But one can also want to be a spiritualist and prove this just as well. All these things, as long as one lives only in the intellectual, can be proved quite well, and they have the appearance of tremendous cogency, these intellectualistic discussions. And so it is in our time. People do not suspect, as they become entangled in spiritualism, materialism, realism, idealism, that they are becoming entangled in the intellectual spirit. They rightly feel: this can be firmly proven. They are the creatures of intellectualism. Because it is indeed true that things can be proved, that is why it is so dismal when one is obliged today to seriously discuss something based on reality, and then 'free discussion' is set up. One person says this, another says that, a third says something else. Basically, if you are just a little bright, you can say: they are all right. Of course, they are all equally wrong. The whole point of the talk is, after all, that one or the other sees what a tremendous swindle of one's own self it is to live in intellectualism, because with intellectualism, everything can be easily proven. The only thing that matters is that one has immersed oneself long enough in some direction or current, in some sect or party or something else, then one can quite rightly say: Yes, that's all clear; the other one who claims the opposite is an idiot. - Certainly, but the other one can just as easily prove that the first one is an idiot and his own claim is correct. Today, with the configuration that intellectual life has attained, this is perfectly possible and is taken for granted. And so it is a matter of course that one can write such a piece today without arriving at a real spiritual insight. The fact that Werfel is not approached proves that nothing significant is seen through the window; the spiritual insight would only begin if something significant were seen through the window. But if you merely describe three steps, and then, after describing how he woke up and looked out, you do not describe what he sees, if you make so many concessions to the general consciousness that you can write such a “Mirror Man” and still say something reasonable in response to something like “Occult Science in Outline” or “How to Attain Knowledge of Higher Worlds” or the like: If one has to say that one would not be in one's right mind if one accepted it, and if one can only say: Yes, the person in question has arrived at the window, but I am wary of seeing what one sees when looking out through the window, then one is simply not yet ready to immerse oneself in the real spiritual life, then one is simply completely stuck in intellectualism. That is why I was allowed to speak in this way. Of course, one would not have the right to give a philosophical critique of a work of art. But I did not give a philosophical critique at all; what I said is just as much an artistic view. Because it happens to you, you read a trilogy, read it with the utmost interest. Afterwards, when you're done, you suddenly feel upside down! It's an uncomfortable feeling, and to get back on your feet again, you would have to rewrite the whole story from back to front. It would take a very long time before you could finally work your way back to your feet, to your footing. Yes, it is quite true that one is also artistically cheated by becoming aware: in there is the spinning wheel of intellectualism, while the work of art must indeed make a beautiful impression. You cannot reverse that. Try to turn Goethe's “Faust” around, to start writing from the back to the front. You cannot! A work of art cannot be turned around. Here in this work you can, because the intellectualism predominates, because it has not penetrated to the real looking. Intellectualism has indeed received the vague, unconscious feeling that there must be juice and strength in the thoughts, but in reality neither juice nor strength has entered, there is nothing in it. There is only a pattern of a more real inner experience in it. And so we see just from something that is really full of spirit, which is extremely significant in terms of what our time can bring forth, where the path must go. For fifty years it has been the case that people actually feel: they must go in the direction of something spiritual, but they would avoid the real path. So they take something out of all kinds of old traditions, like the three-part path and the like. But it is characteristic that today they take up this three-part path; you can find it in all kinds of books that describe some old atavistic clairvoyant paths. As long as one refrains from accepting what one sees when looking through the window, this story of “mirror” and “one into the other” and “through the window” can very easily still be part of our spiritual life. It is easy to describe if one only has such general ideas about it. But as long as you stop at that, you still can't get out of intellectualism, which holds the people of the present day captive with a tremendous magic. I have pointed out this intellectual element in our time in the most diverse forms. I have pointed out how one could get into all kinds of branches in the Theosophical Society, and there were great schemes, races and rounds, whole world systems and all kinds of things were built up in wonderfully intellectual forms - all intellectual! On the other hand, when it was a matter of characterizing the structure of the human being, there was a scheme: physical man: dense physical matter; etheric body: finer matter; astral body: even finer; kama manas: even finer; manas: even finer, ever finer and finer. Yes, but only from the intellectual point of view! This thinning out did not stop at all! But it is just purely intellectual. Just as you can always turn a wheel, you can, if you just stick to the intellectual, let matter become thinner and thinner. And so we had an intellectualized theosophy, and so we have here an intellectualized poetry that even borders on mysticism and that will certainly be admired by a great many of our contemporaries, and rightly so, because one can see from such poetry how the striving of our time is again turning towards something spiritual. But my judgment is not an unartistic one. When I look at this mirror man who accompanies the hero throughout his entire evolutionary life, this mirror man is something completely different than Mephisto in relation to Faust. There is life in Faust. You know, I once showed how Mephisto is ultimately only the other side of Faust, like Wagner. “You resemble the spirit you comprehend, not me.” You resemble Wagner, you resemble Mephisto, and so on. But there is life in it. But it is not yet life when the self jumps out of the mirror, is initially frail and then becomes fatter and fatter as the person himself grows more and more out of life. In short, what dominates from beginning to end is the inanimate, the abstract. The abstract can always be turned around. And because nowhere in the artistic work can one feel a full-blooded, intense contemplation, but everywhere one sees only thought-patterns blown up into images, one feels an unartistic quality. And it is strange that in the present day, this is often defended by saying: Anthroposophy, yes, that is only the pursuit of ideas, and that is not artistic. But in Anthroposophy, the aim is to gain insight, only one must really be prepared for this insight. One must look through a window and see something. But here, the actual artistic is called something that has not quite hatched, that is just about to hatch from the egg, but is content to remain in the egg. You know what I mean, that the chicken does not really hatch from the egg to live in the world. It is as if man wants to begin a journey of knowledge, but still avoids the spiritual world in all its concreteness and certainty. I don't want to say how the egg feels when the chicken just can't get out! But isn't it true that it is just the same with such intellectual products that don't really get out. This is not to say anything against the value of such things. In the sense of the present I actually see something of the very first order in this mirror-man. But from a higher point of view it must be characterized and placed in the spiritual life, in the whole cultural life of the present, as I have tried to sketch it. |
| 302. Education for Adolescents: Lecture Six
17 Jun 1921, Stuttgart Translated by Carl Hoffmann |
|---|
| We try to teach them skills and facts that allow them to participate in the technological life, so that their work can be meaningful and valuable for society, so that they themselves may find their place in life, their connection to the social life, to other people. |
| When we today—permeated even a little with anthroposophical consciousness—take a walk in the streets, we no longer see human people; rather we see moles that move about in the smallest of circles, circles into which they were placed, moles whose thinking is limited to these narrow circles, cannot reach beyond them, moles who take no interest in what is happening outside these circles. |
| We have a culture, an education, that at best prepares us to be able to function outwardly, mechanically, to maintain the status quo in society. For this we are prepared. As human beings we get nothing. Our education does not reach our limbs but remains stuck in the intellect. |
| 302. Education for Adolescents: Lecture Six
17 Jun 1921, Stuttgart Translated by Carl Hoffmann |
|---|
As we consider the education of the older children, it will be especially necessary to address ourselves to the deeper aspects of human life and the cosmos. Without such a deeper understanding of life, we cannot really in good conscience accept the tasks connected with the high school. We must understand that life is actually a totality, a oneness, and that by removing any one part of it, we do harm to it. As children, we grow into this life as we find it. We are placed into it by, in a way, sleeping into it. Just think of the absolutely unconscious way children confront the world during their first years. They then gradually increase their consciousness. But what does this mean? It means that the children learn to adapt their inner life to the world outside, to connect the outer world to the inner, the inner to the outer. They also learn to be conscious of the outer objects and to differentiate themselves from those objects. This dichotomy between inner and outer grows ever stronger. The children look up, beyond the horizon, at the sky, they perceive the cosmos, they may even sense the existence of cosmic laws; but as a rule, the children grow into the totality of the world, into which they are received, without in any way getting close to the mystery of the connection between the human being and the cosmos. The children continue to grow, they are cared for by the people around them, they are educated and instructed. The children develop in such a way that the necessity of participating in world events in some form or other rises from their whole individuality. We prepare the children for world events by letting them play during the early years, thus awakening their activity. We make every effort to do things with them that meet and satisfy their needs, to educate them healthfully, hygienically—body, soul, and spirit. We try to do something else. We try to adapt them to the demands of the social and technological life. The attempt is made to educate the children in a way that allows them, later in life, to work, to participate in events, to interact with other people. We try to teach them skills and facts that allow them to participate in the technological life, so that their work can be meaningful and valuable for society, so that they themselves may find their place in life, their connection to the social life, to other people. We do all of this. And in order that we do this in the right way, so that we, on the one hand, really meet the needs of human nature, so that we do not place human beings into the world with spiritually, psychologically (soul), and physically sick or stunted organisms, we must, on the other hand, admit to ourselves that human beings must grow into the social life in such a way that they can do something by which they may advance both themselves and the world. We must see to meeting both these demands. And yet we have to tell ourselves that it is not easy today to accomplish this, to give the children what they need in these two areas. And if we take an unbiased look at our situation as teachers, it even causes us a certain skepticism, a certain doubt. We can easily understand today’s concerns and the many discussions on the subject. How should our children be educated? What should we do? All these questions and problems that arise in our culture with such vehemence did not exist in older civilizations. You only need to study these old cultures without bias. Of course, there were a lot of things in those cultures that are incomprehensible to us today. We quite justifiably reject the slave and helot system of ancient Greece. But when we study the Greeks’ views on education, we shall soon see that such discussions as we have today—discussions in which so many diverse and opposing opinions are thrown about—would have been unthinkable then. Beyond the effort we put into teaching, we need educational methods, and we need to develop teaching skills. But when we watch the heated discussions and see the impossibility of agreement—some emphasize the physical, some the mental-academic aspects, some these, some those methods—we arrive at the conclusion not only that teaching has become difficult but that in regard to our position as teachers and educators we cannot break away from being ignoramuses. We should really have this feeling of helplessness; and it will, I believe, be even more pronounced if we take a wider view of the situation. You will get this wider view when you study how the current outpouring of educational principles and ideas has its roots in central European culture. I suggest that you make yourselves familiar with everything that was said about spiritual, psychological, and physical education by individuals steeped in central European cultural life. Read the books by Dittes and Diesterweg; read about their views on education. I recommend to you the interesting essay in Karl Julius Schroer’s book Aspects of Education [Unterrichtsfragen], in which—quite correctly, I believe—he speaks of the place of physical education in the curriculum and offers a detailed program for this subject. During your perusal, I would like for you to consider the mode of thinking and the attitudes from which the thoughts arise. Consider how despite the real understanding of physical human nature and of the need to prepare the children for becoming practical and efficient adults, there is nonetheless also a strong consciousness of the reality of the soul and of the necessity to consider the human soul in all aspects of education. Then compare—not the outward features; as anthroposophists you ought to be above doing that—compare what lies embedded in the depths of the soul, compare the basic attitudes contained in any of the numerous treatises on education in the Anglo-American literature. Everywhere in this literature you will find chapters on intellectual, aesthetic, and physical education. Think of the deeply held conviction from which they are written. You will get the feeling that the word “education” no longer applies. Everywhere in this culture—even when spiritual or intellectual education is mentioned—the human being is thought of as a kind of mechanism; it is thought that if the physical/corporeal organism, or mechanism, is properly developed, all the moral and intellectual development will follow as though by itself. We have with this view a much stronger inclination to the physical/corporeal in the human being. I would like to suggest that the central European writers assume that it is possible to include soul and spirit in education and that by doing this the correct treatment of the physical will follow. The Anglo-Saxon idea emphasizes physical education. One then ignores a kind of tiny room inside the human being; one “educates” around the physical, along the periphery, and assumes that there is a tiny room in which the intellect and the moral and religious life are locked up, a kind of instinctive and logical religious and moral life. Once the physical body has been sufficiently educated, its forces will spread to within and dissolve the walls of this room, and the intellectual, moral, and religious life will by itself rush out. We must learn to read between the lines when we study these books and thus discover the underlying reasons and attitudes. It is necessary to pay attention to these differentiations across the world today. It is much more important than merely observing superficially, in the modern fashion, when one considers these symptoms. Try to understand these symptoms of our transitional culture by following the extraordinarily important debates that have taken place in England during recent weeks. The debates have been triggered by the worsening social conditions and by the general industrial actions (strikes) that have threatened the whole social life. The press was reporting these discussions in full. And then, suddenly, a complete change of interest. Why? A season of ball games has begun, and interest in sport overshadows the interest in the most important social matters. Those involved in the discussions try to get away from the debating rooms as quickly as possible, rushing to the tennis courts, the football fields, and so on, with the feeling: “I want to move in a way that my muscles can grow as strongly as possible; I am interested in such important things.” I am probably describing the feeling in an amateurish way, but I cannot be bothered about detailed facts in this cultural phenomenon: “I am interested in such important matters as watching how somebody throws a ball-like object and how somebody else can catch it correctly with his big toe or another part of his body.” The picture we get from studying these differentiations is indeed a peculiar one. Reading the papers is of little use. What the journalists are writing is of little significance. It is far more important to discover their reasons for writing about a subject. To enter a discussion with people, to listen to their opinions, is quite useless today. It is far more profitable to discover what is living deep down in their souls, to discover what induces them to act in a certain way, to have this or that opinion. It is this that matters today. What the French and German ministers are saying to each other, if one agrees with either the one or the other, is of no importance whatsoever. It cannot be the concern of someone who wishes to participate in the progress of our civilization. What matters is to discover the differing nature of the untruths expressed by these individuals. We must keep in mind the intentions behind the lies of both speakers. We must know that we are living at a time when the words people are speaking have no longer any meaning; the forces behind and between the words are significant. A teacher wishing to educate modern youths must understand this, must become part of his or her age in this way, must do so in an ever deeper sense. But the teacher must not share the current basic characteristic attitudes and mode of thinking. When we today—permeated even a little with anthroposophical consciousness—take a walk in the streets, we no longer see human people; rather we see moles that move about in the smallest of circles, circles into which they were placed, moles whose thinking is limited to these narrow circles, cannot reach beyond them, moles who take no interest in what is happening outside these circles. If we do not succeed in growing beyond this molelike existence, if we cannot do more than reproduce the judgments and opinions—from various points of view—to which we have been conditioned through the events at the end of the nineteenth century and the beginning of the twentieth century, then we cannot positively participate in what ought to be done, in order to overcome this unhappy situation. If there is anyone who ought to be gripped by what I have just outlined, it is the teacher in charge of the young, who wishes especially to help the students to come to terms with their more mature age in the ninth and tenth grade classes. The whole school must be so structured that such ideas can be included. To do this, it is necessary to understand them even better, so that all of us, not only those directly involved in the higher classes, but all the teachers, can say to ourselves that what matters is that we have an elementary feeling for the whole of education and its practical application, that we experience the whole weight and force of our task—to place human beings into the world. Without this experience of our task, our Waldorf School will be no more than a phrase. We shall say all sorts of beautiful things about it, until the holes have become so large that we shall lose the ground under our feet. We must make it inwardly true, and we can do this only by getting ourselves to the stage at which we can have a thorough understanding of the teaching profession. As we do this, the question will surely arise: As human beings at the present time, what are we really? We were placed into our age through the way we were brought up, conditioned by the events during the last third of the nineteenth century and the beginning of the twentieth century. And what are you today, my dear friends? Some of you have studied philosophy or history in the way these subjects were taught in the high schools and universities at the beginning of this century. Some of you have studied mathematics or other practical subjects. Some of you have become teachers of singing or physical education. Various methods were used in teaching these subjects. There are those among you who, according to the predilection of the staff, accepted the model of the gentleman or lady, but with a physical/corporeal understanding. There are those of you who have preferred what could be called a more inward path, but a path made inward through intellectualism. We are the sum total, the result of the ways we were conditioned—as far as into our fingertips and toes. We must be quite clear about our task today—namely, to take full charge of what has been implanted in us through our education. This is possible only through a timely exploration of conscience that extends beyond the individual aspects. Without such exploration we cannot grow beyond what our time can provide us with. And we must grow beyond what our time can give us. We must not become puppets of the trends developed at the end of the nineteenth century and the beginning of the twentieth century. Above all, we must admit to the limitations of what is given us by today’s culture; through a comprehensive exploration of conscience, we must attain the correct knowledge, knowledge that will allow us to find our place in life. At this point we ask: Has not everything that has made us the way we are been infected by the materialistic attitudes of our time? Certainly, there is no shortage of goodwill. But even this goodwill has been infected by the views that are the result of the natural-scientific world conception. And our knowledge of physical education has emerged from such views. Humankind has really always wanted to hide from, to avoid, the necessity of exploring its conscience. Humankind has wanted to avoid the exploration that would thoroughly stir up its inner life by asking: How do we older people confront the young? When we look at the girls and boys reaching the age of sexual maturity, when we see them coming to us after having attained this maturity—if we wish to be honest with ourselves, we can only have one answer to the question: We don’t know what we should do for them, unless we educate and teach on the basis of fundamentally new concepts. Otherwise, we produce nothing but a wide gap between the young and ourselves. This great question has practical dimensions. Take a good look at the youth movements as they have developed today. They are nothing else but documentation that our various experimentations have resulted in the loss of our leadership in education. Just look at what has happened. At the age we are now discussing, the young feel inwardly urged to withdraw from the leadership of the old, to take their guidance into their own hands; this happened with tremendous rapidity. We cannot fault the young for this. Discussion of this phenomenon is of great spiritual-scientific interest but not initially of pedagogical interest. Our pedagogical interest must be limited to the fact that the old have been responsible for their loss of leadership and understanding of the young. Since the old no longer have anything of substance to give to the young, the teenagers and adolescents have formed themselves into groups [Wandervögel] that traverse the countryside with singing and conversing, searching in a vague way for what the older generation has failed to provide. Thoughts and words have become hollow; the older generation having nothing to give to the young, the young then roam the woods, searching among themselves for what they cannot receive from the words and models of their elders. It is one of the most significant phenomena of the present time. The young find themselves confronted by the great question that used to be answered in the past by the older generation but that now can no longer be answered by them, because their language is no longer comprehensible. Remember your own youth? You had, perhaps, more courage than the members of such groups, took less interest in traipsing through the countryside. You managed to survive somehow. You pretended to listen to the older generation and adhered to the status quo. But the Wandervögel do not pretend. They have withdrawn from the older generation and have taken to the woods. We have seen this happen, and we have also witnessed the results of this youth movement. Not so long ago, they felt the need to make contact among themselves, wishing to discover for themselves what they could not get from their teachers, wishing to escape them and take refuge in nature. They mean to find their answers in some vague, undefined sphere. They make contact among themselves, forming small cliques. It really is a strange phenomenon that is immensely instructive. The old have lost their leadership, have become philistines. They cannot accept the fact that this deep longing has awakened in the young, in the members of such groups. And how have the old reacted to this, those among them who are at least a little affected by modern times? They do not say to themselves: “We must advance to a deep exploration of conscience; we must from our mature stage of development find a way to the young.” No, they react differently: “Since the young,” they say, “do no longer wish to learn from us, we shall learn from them.” And you can see this happening in all our educational institutions—the old adapting to the will and demands of the young. When you look at this new phenomenon without prejudice, you will see that the old wish to be led by the young, that they have placed the leadership into their hands—representatives of the student body are now counselors and members of boards and trusts in educational institutions. We must consider the deeper implications of this phase. What has it done to the young? They have passed from their need for contact, from their wish to find themselves in cliques, to searching for their inner (soul) life in a hermit existence. The final stage of this development is a kind of fear of contact, everyone feeling the necessity of relying only on himself or herself. The former certainty of finding answers in the world outside has given way to a kind of atomizing longing, a brooding: “What is the reason for my inability to do justice to the human being in me?” You can see this feeling spreading everywhere; you only need to be awake enough to see it. You can see this growing uncertainty in the fragmentation of soul forces. You can perceive a special fear, a horror vacui, that makes the young shudder and feel scared in view of their future. They are fearful of the life ahead of them. There is basically only one answer, one remedy—the deep exploration of conscience. And this cannot limit itself to externalities but must lead to the question: How has it come to pass that we, when we wish to lead and guide the young, no longer understand them with the forces of the old? Let us, by contrast, take a look at a distant age, such as that of the ancient Greeks. The older Greeks, as we know from history, still had a certain understanding for the young. If you try to understand Greek culture, you will find a peculiar and very definite relation between the period from the thirteenth or fourteenth to the twentieth or twenty-first year and the period from the twenty-eighth to the thirty-fifth year. This is characteristic of both the Greek and Roman cultures—that people in their late thirties had a fine understanding for children between seven and fourteen and that people in their early thirties felt a special affinity for, an understanding for the needs of, teenagers and adolescents. There was this relation according to different age groups—a relation of those in the third seven-year period with those in the fifth and a relation of those in the second seven-year period with those in the sixth. It really is not easy to see behind the mysteries of human evolution. But we can indeed clearly feel that for the Greeks when the girls and boys arrived at sexual maturity they looked up to the twenty-eight- and twenty-nine-year-olds, choosing the ones they liked best, the ones they wished to emulate in freedom. They could no longer obey an authority as such, only one of their choosing in this specific age group. As humanity evolved through the Middle Ages to our time, this relation became ever weaker until it disappeared altogether. People were thrown together in a helter-skelter way; a spiritually given structure gave way to chaos. This very real situation has, then, prompted a social problem in our world; in education, it has prompted a pedagogical/didactic problem. Without keeping in mind the whole of evolution, we cannot make any progress. I would like to show you the cause for this phenomenon by pointing to a concrete fact. All you have then to do is to generalize this concrete fact in order to discover the causes for this lack of understanding between the old and the young. You see, during our current preparation for life, during our education, we are, for example, taught that there are some one hundred elements. We learn this, and when we become teachers we are, as a rule, aware of these chemical elements—that they exist, even though this theory has recently come under attack. But we have absorbed this knowledge, carry it within us, the knowledge that there are these one hundred or so elements, that through their synthesis and analysis everything in the world comes about. We even develop a world conception on this basis. And this is the farce, that during the last third of the nineteenth century a world conception was constructed on the basis of the then seventy chemical elements. This prompted the question: How could the planets, everything that solidified, arise through chemical and physical changes? How did abiogenesis come about through an especially complicated chemical synthesis? It was the wish to comprehend the whole world with thoughts that had their roots in such elements. The Greeks would have thought of this one-sided intellectual (head) approach to the world as nonsense, as inhuman. If they had been told to imagine the world as the result of the synthesis and analysis of these one hundred elements, they would have felt, deep down, as though the human being would disintegrate into dust during the process. The Greeks would not have been able to comprehend it. What indeed would a human being do with such a world that consists of these elements that synthesize and analyze? What does it mean? What would happen? The world could well be there, be a gigantic cosmic test tube, but the human being, how would the human being exist in it? Is is as though we were to put a large test tube in a room, allow all sorts of elements to boil in it, and then open a door and push a human being through an opening into the tube, into this mixture of salts and acids. This the Greeks would have imagined if they had been asked to think of the world as structured by these elements. They would not have accepted this idea, their feelings would have resisted it. The picture I have just characterized would have arisen instinctively in their minds. But we are not merely heads. It was only at fairgrounds that living, talking heads used to be shown as exhibits. No, we don’t exist as head only but as complete human beings. And if we wish to develop such ideas with only the head, if our life of feeling, of will, and of the whole physical organism were to be so constituted that we could believe in a world made up of such stuff, we would have to feel very differently, would have something different in our fingertips than what the Greeks had, the Greeks who would have dismissed such a notion as pure nonsense. One feels differently about, places oneself differently into, a world if one believes that the world is something that is fit for a test tube but not for the universe. The same point applies with regard to the social life in ancient Greece. We must consider these things. We don’t just think that the world consists of one hundred elements. We carry this feeling into everything we do during the day—even when we wash and dry our hands. The fact that it is possible for our head to have such an inhuman world conception while we wash ourselves—thinking in this way impresses a definite quality into our feelings. And then—when we can think and feel in this way, when there is no room for the human being in such a world conception—when we then confront the fifteen-year-old girls and boys with this thinking and feeling, it should come as no surprise that we cannot reach them, that we don’t know what to do with our feeling and thinking. With this world conception we can lecture in universities and colleges, teaching what we believe to be right, but we cannot live with it. The graduates of our universities then become teachers who have no idea of their connection with the young. This is the terrible abyss that has opened up before us. But as far as human beings are concerned, there is something in us at the age of fifty or fifty-five that bears a certain resemblance to today’s teaching of chemistry and physics. We then have become sclerosed to the extent that our inner organism faintly resembles the world outside. The cosmic powers are gradually doing something with us during the course of our lives on earth. We, too, harden in our physical organism in older age. At about fifty, we become dissociated; we, as it were, disintegrate inwardly into dust. But this dissolution is a gradual, slow process, not as cruel as what would be happening to us in a test tube. Neither does it go that far—although it has the same tendency; it is a more humane process. But at the age when we approach death something does begin to be active in us that is synonymous with the teaching of modern science. Our world conception is such that only the very old may comprehend it. Nature is kind. It compensates the old by making them childish. Talking about such things in this way may make it seem as though one wishes to poke fun at the world. No, it is not a matter of humor; it is a matter of the deepest tragedy. It is true. We are describing the world today as processes that are synonymous with those in human corpses, no more. After our death something similar takes place. In older age, we have a presentiment of the processes in our physical body after death. And we describe nothing else in our modern sciences. Our cultural institutions are full with such knowledge that applies to the physical human being after death. But such knowledge does not live in our limbs. Such are the feelings we absorb from the thoughts given us today. And the traditional theological beliefs have become mere words, because they have no place in the teaching of natural science about the human corpse. As long as we limit this teaching to a theory of knowledge, it is more or less harmless. If, however, we consider the human being as a totality and ask what happens to the human being when he or she is influenced by such a life, the question is one of life and death. And this we must not ignore, must not evade. The forces active in the children in our classrooms are quite different from those we learned about. We no longer know anything of what is active in them; we are separated from them by a gulf. Yes, the Greeks would have considered our talk about the elements nonsensical. What did they say? They believed not that the structure of the world consists of some one hundred elements but that four elements—earth, air, fire, and water—are interacting in it. Our academics, our professors, the leaders of our culture and education will tell us: “This is a childish world conception. We left it behind and no longer bother with it.” Someone who has begun to think a little will tell us: “Oh well, we too are working with these things. Today we call them aggregate conditions—solid, gaseous, liquid. We see warmth differently from the naive way the Greeks did. Yes, we have them all, but we have developed them correctly. Of course, we admire the Greeks for their knowledge.” This is a benevolent, patronizing, condescending attitude: “We are fortunate in having progressed so far, in having discovered all these elements, whereas the ancients used to practice all sorts of animism and talked of earth, air, fire, and water.” But these leaders are wrong. There is a deeper meaning to the conception of the Greeks. When the Greeks spoke of earth, air, fire, and water, they did not look at them as we do today. If you had asked one of those people who lived within the Greek world conception—and there were still a good number of them in the fifteenth century, the later ones having read about it in books; our modern people sometimes take a look at it without understanding it—if you had asked one of them: “What is your idea of fire, of warmth?” the Greek would have answered: “I think of fire as being warm and dry.” “What about air?” “I see air as warm and damp.” The Greek did not think of the physical properties in fire and air but rather formed an idea. This idea contained the sub-ideas: warm and dry, warm and damp. The Greeks did not limit themselves to the physical appearance but imagined the elements as inner qualities. One had to raise oneself to something that could not be seen by physical eyes, that had to be grasped by thinking, in order to get to a knowledge of the elements, of what one then called the elements. What did they achieve by this? They arrived at an understanding that corresponded to the etheric in the human being—the etheric body in its effectiveness. This understanding of the elements as inner qualities allowed them to experience the etheric body. Their experience was not that of being in the etheric body but rather in how the etheric body worked in the physical. It is not possible to achieve this understanding merely by studying the interactions of oxygen and carbon intellectually. It is impossible to arrive at an understanding of the way the etheric body is working in the physical if one only studies the interactions of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and sulfur. Such studies take one away from the activities of the etheric, keep one within the physical. This means that one remains in the sphere in which the processes in the human being take place after death. The life processes, in which the etheric body is working in the physical, can only be understood by imagining warm and dry, cold and damp, warm and damp—by inwardly grasping the qualities with which the etheric body takes hold of the physical, by having this living comprehension of nature in the four elements. This is not a childish idea that regards only the physical but one that regards the working of the etheric. And this idea was lost in later times. But this has an effect on the whole of the human being. Think about it. People are growing up, are told that the world consists of one hundred or so elements—iodine, sulfur, selenium, tellurium, and so forth—all whirling into each other. This affects our feelings, to the extent that we, as human beings, are removed from the process. The elements are there, and we are not part of any of them. One could have the justified idea of being a part of the other way of looking at the world, of looking at the four elements—earth, air, fire, and water—in the ancient Greek way: earth as cold and dry, air as warm and damp, fire as warm and dry, water as cold and damp. When one imagines these qualities and makes them live in oneself, they grip one—qualitatively. One becomes permeated by them, they take hold of the limbs; they take hold of us. Such ideas that reach as far as into the limbs make us into beings different from beings for whom the ideas affect the limbs only after death. The corpses in the graves may well feel in line with the one hundred or so elements that combine according to chemical laws. But such a concept does not do anything for the life of human beings. By contrast, in having this idea of the four elements, we perceive ourselves in our etheric bodies. You see from such reflections that education has really become quite unnecessary today for us human beings. We have a culture, an education, that at best prepares us to be able to function outwardly, mechanically, to maintain the status quo in society. For this we are prepared. As human beings we get nothing. Our education does not reach our limbs but remains stuck in the intellect. It does not affect our feelings and will. If we wish to have any effect at all, we must resort to sermons and the like. We must approach people from without. But we do not give them anything that affects their inner life. The way we deal with the young today involves a terrible untruth. We tell them to be good without providing the means whereby they can be good. All they can do is to obey us as their authority. If we can manage to cow people throughout their lives in one way or another, some order can be maintained. The police will deal with the recalcitrants. Head knowledge has no meaning for the inner life. This is the reason for our impotence in relating to the young at the important time in their lives when they are supposed to connect the spirit and soul to the physical/corporeal, to bring them into a reciprocal relationship. What indeed are today’s adults to do with the young who wish to relate spirit and soul to the physical, to the life around them? This is the situation we shall take as our starting point in tomorrow’s talk, when we shall further acquaint ourselves with this problem. My intention today has been to evoke in you the feeling that as soon as we are supposed to find a way to the hearts of children at a definite and important time in their lives, we are dealing with the important issue of a world conception. |

