| 306. The Child's Changing Consciousness and Waldorf Education: Lecture II
16 Apr 1923, Dornach Translated by Roland Everett Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Knowledge of the human being made possible through anthroposophical research—as outlined briefly yesterday—fundamentally differs from the findings of modern science and other research. |
| What is gained through this approach then forms the background for the attitude from which judgments are made regarding the living, healthy human being. The anthroposophical approach begins by looking at the human being as an entity, an organization of body, soul, and spirit. |
| It incorporates statics and dynamics into its entire being. Anthroposophical research shows us that what most accomplished experts in the field of statics and dynamics manage to think out for the external world is child's play compared with the way the child incorporates these complicated forces while learning to walk. |
| 306. The Child's Changing Consciousness and Waldorf Education: Lecture II
16 Apr 1923, Dornach Translated by Roland Everett Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
To begin with we will try to understand more fully the nature of the growing human being, bearing in mind the later stages in life, in order to draw conclusions about education from our findings. Knowledge of the human being made possible through anthroposophical research—as outlined briefly yesterday—fundamentally differs from the findings of modern science and other research. The knowledge of the human being produced by our contemporary civilization is based mainly on what remains when the human spirit and part of the human soul are ignored. Such knowledge rests on what can be found, both anatomically and physiologically, when one looks at a corpse. Furthermore, it is supported by investigations into pathological changes, due to illness or other causes, from which conclusions are drawn with regard to the healthy human being. What is gained through this approach then forms the background for the attitude from which judgments are made regarding the living, healthy human being. The anthroposophical approach begins by looking at the human being as an entity, an organization of body, soul, and spirit. It attempts to comprehend the human being not in an abstract and dead way, but through a living mode of observation that can recognize and comprehend with living concepts the human totality of spirit, soul, and body. This approach enables us to perceive accurately the various metamorphoses that take place during a lifetime. Children are different beings depending on whether they are going through the development between birth and change of teeth, or between the second dentition and puberty—the latter period being the time when they are in the care of the class teacher—or during the stage following puberty. Human beings are completely different creatures depending on which of these three stages they are going through. But the differences are so deeply hidden that they escape a more external form of observation. This external method of observation does not lead to a clear perception and judgment of how body, soul, and spirit are permeated by spirit in entirely different ways during each of the first three periods of life. It would surely not be proper for teachers to first acquire theoretical knowledge and then to think: What I have learned in theory I will now apply in my teaching in one way or another. With this attitude they would only distance themselves from the child's true being. Teachers need to transform their knowledge of the human being into a kind of higher instinct whereby they can respond properly to whatever comes from each individual child. This is another way that anthroposophical knowledge of the human being differs from the usual kind, and can lead to a routine approach to education at best, but not to a firmly founded pedagogical sense and teaching practice. To achieve this, one's knowledge of human nature must be capable of becoming pedagogical instinct the moment one has to deal with a child, so that in response to all that comes from the child one knows instantly and exactly what must be done in every single case. If I may use a comparison, there are all kinds of theories about what we should eat or drink, but in ordinary life we do not usually follow such theoretical directions. We drink when thirsty and eat when hungry, according to the constitution of the human organism. Eating and drinking follow a certain rhythmical pattern for good reasons, but usually one eats and drinks when hungry or thirsty; life itself sees to that. Now, knowledge of the human being, which forms the basis of a sound and practical way of teaching, must create in the teachers, every time they face a child, something like the relationship between hunger and eating. The teachers' response to a given pedagogical situation has to become as natural as satisfying a sensation of hunger by eating. This is only possible if knowledge of the human being has permeated flesh and blood as well as soul and spirit, so that you intuitively know what needs to be done every time you face a child. Only if your knowledge of human beings has such inner fullness that it can become instinctive can it lead to the proper kind of practical teaching. It will not happen on the basis of psychological experiments leading to theories about pupils' powers of memory, concentration, and so on. In that case, intellectual ideas are inserted between theory and practice. This presents an unreal situation that externalizes all educational methods and practice. The first thing to be aimed for is a living comprehension of the child in all its pulsing life. Let's look now at young children as they grow into earthly life. Let our observations be straightforward and simple, and we shall find that there are three things with which they have to come to terms, three activities that become a decisive factor for the entire life to come. These are what are simply called walking, speaking, and thinking. The German poet Jean Paul—this is the name he gave himself—once said: “The human being learns more for the whole of life during the first three years than he does during his three years at university.”1 This is entirely true; it is a fact. For even if academic studies nowadays extend over longer periods of time, their gain for life amounts to less than what is acquired for the whole of life during the time when children are learning how to walk, speak, and think. What does it actually mean when we say the child is learning to walk, speak, and think? The capacity to walk comprises far more than is generally realized. It is by no means simply a case of the young child—after the stage of crawling—managing to stand up and take the first steps in order to develop what will eventually become an individual and characteristic way of walking. An inner adjustment underlies learning to walk; there is an inner orientation of the young child. The equilibrium of the organism, with all its possibilities for movement, becomes related to the equilibrium and all the possibilities for movement of the whole universe, because the child stands within it. While learning to walk, children are seeking to relate their own equilibrium to that of the entire cosmos. They are also seeking the specifically human relationship between the activities of arms and hands and those of the lower limbs. The movements of arms and hands have a special affinity to the life of the soul, while those of the legs lag behind, serving more the physical body. This is of immense importance for the whole of later life. The differentiation between the activities of legs and feet and those of arms and hands represents the human quest for balance of soul that is lifelong. When raising themselves up, young children are first of all seeking physical balance. But when freely moving arms and hands, they are also seeking balance of soul. There is infinitely more than meets the eye hidden behind what is commonly called “learning to walk,” as everyone can find out. The expression “learning to walk” signifies only the most obvious and outwardly important aspect perceptible to our senses. A deeper look at this phenomenon would make one wish to characterize it in the following way. To learn to walk is to learn to experience the principles of statics and dynamics2 in one's own inner being and to relate these to the entire universe. Better still, to learn to walk is to meet the forces of statics and dynamics both in body and soul and to relate these experiences to the whole cosmos. This is what learning to walk is all about. But through the fact that the movements of arms and hands have become emancipated from those of the legs and feet, something else has happened. A basis has been created for attaining a purely human development. Thus, the child who is learning to walk adapts itself outwardly to the external, visible world with its own rhythms and beat, as well as inwardly with its entire inner being. So you see that something very noteworthy is woven into the development of the human being. The activities of the legs, in a certain way, have the effect of producing in the physical and soul life a stronger connection with what is of the nature of beat, of what cuts into life. In the characteristic attunement of the movements of right and left leg, we learn to relate ourselves to what lies below our feet. And then, through the emancipation of the movements of our arms from those of our legs, a new musical and melodious element is introduced into the beat and rhythm provided by the activities of our legs. The content of our lives—or one might say, the themes of our lives—comes to the fore in the movements of our arms. Their activity, in turn, forms the basis for what is being developed when the child is learning to speak. Outwardly, this is already shown through the fact that with most people, the stronger activity of the right arm corresponds to the formation of the left speech organ. From the relationship between the activities of legs and arms, as you can observe them in a freely moving human being, yet another relationship comes into being. It is the relationship that the child gains to the surrounding world through learning to speak. When you look at how all this is interconnected and belongs together, when you see how in the process of sentence formation the legs are working upwards into speech, and how the content, the meaning of words, enters into the process of sound production—that is, into the inner experience of the structure of the sentences—you have an impression of how the beat-like, rhythmical element of the moving legs works upon the more musical-thematic and inward element of the moving arms and hands. Consequently, if a child walks with firm and even steps, if its walk does not tend to be slovenly, you have the physical basis—which, naturally, is a manifestation of the spirit, as we shall see later—for a good feeling for the structure of both spoken and written sentences. Through the movement of the legs, the child learns to form correct sentences. You will also find that if a child has a slouching gait, it will have difficulties finding the right intervals3 between sentences, and that the contours of its sentences become blurred. Likewise, if a child does not learn to move its arms harmoniously, its speech will become rasping and unmelodious. In addition, if you cannot help a child to become sensitive in its fingertips, it will not develop the right sense for modulation in speech. All this refers to the time when the child learns to walk and talk. But something else can also be detected. You may have noticed that in life the proper timing of certain processes is sometimes disturbed, that certain phases of development make their appearance later than one would expect according to the natural course of development. But in this context you can also see that the proper sequence of events can be safeguarded if children are encouraged to learn to walk first, that is, if one can possibly avoid having children learn to speak before they can walk. Speech has to be developed on the basis of the right kind of walking and of the free movement of the arms. Otherwise, children's speech will not be anchored in their whole being. Instead, they will only babble indistinctly. You may have come across some people whose speech sounded not unlike bleating. In such a case, not enough attention was paid to what I have just tried to characterize. The third faculty the child must learn on the basis of walking and speaking is thinking, which should gradually become more and more conscious. But this faculty ought to be developed last, for it lies in the child's nature to learn to think only through speaking. In its early stages, speaking is an imitation of the sounds that the child hears. As the sounds are perceived by the child in whom the characteristic relationship between the movements of the legs and arms is deeply rooted, it learns intuitively to make sense of the sounds that it imitates, though without linking any thought to what it has heard. At first, the child only links feelings to the sounds coming toward it. Thinking, which arises later, can develop only out of speech. Therefore, the correct sequence we need to encourage in the growing child is learning to walk, learning to speak, and finally, learning to think. We must now enter a bit more deeply into these three important processes of development. Thinking, which is—or ought to be—the last faculty developed, always has the quality of mirroring, or reflecting, outer nature and its processes. Moral impulses do not originate in the sphere of thinking, as we all know. They arise in that part of the human being we call the conscience, about which we shall have more to say later on. In any case, human conscience arises in the depths of the soul before penetrating the sphere of thinking. The faculty of thinking, on the other hand, that we acquire in childhood, is attuned only to perceiving the essence of outer nature and its processes. Thus all of the child's first thinking is aimed at creating images of outer nature and its processes. However, when we turn to learning to speak, we come across quite a different situation. With regard to the development of this faculty, present-day science has been able to make only tentative observations. Orthodox science has achieved quite wonderful results, for instance in its investigations into the animal world. And when it compares its findings with what happens in a human being, it has made many discoveries that deserve our full recognition. But with regard to the comprehension of the processes taking place when a child is learning to speak, contemporary science has remained rather in the dark. The same applies to animal communication through sound. And here a key question needs to be answered first. In order to speak, the human being uses the larynx and other speech organs. The higher animals also possess these organs, even if in a more primitive form. If we disregard certain animals capable of producing sounds that in some species have developed into a kind of singing, but think instead of animals that emit only very primitive sounds, an obvious question comes to mind (and I raise this question not only from a causal, but also from quite a utilitarian point of view). Why should such animals have a larynx with its neighboring organs, since these are used for speech only by the human being? Though the animal is not capable of using them for speaking, they are there nevertheless, and this even very markedly. Comparative anatomy shows that even in relatively dumb animals—dumb in comparison with the human being—organs of this kind exist. It is a fact that these organs, at least to a certain extent, have possibilities destined to be realized only by the human being. Though incapable of making use of these organs for speech, the animal nevertheless possesses them. What is the meaning of this? A more advanced physiology will come to discover that the animal forms of the various species depend, in each case, upon the animal's larynx and its neighboring organs. If, for instance, a certain animal grows into a lion, the underlying causes have to be looked for in its upper chest organs. From there, forces are radiating out that create the form of a lion. If an animal grows into a cow, the cause of this particular form is to be found in what becomes the speech organ in the human being. From these organs, the forces creating the animal forms radiate. One day this will have to be studied in detail in order to learn how to approach morphology more realistically. Then one will find out how to correctly study animal forms, how to grasp the nature of the upper chest organs and the way these pass over into the organs of the mouth. For it is from this region that forces radiate creating the entire animal form. Human beings form these organs into speech organs on the basis of their upright walk and freely moving arms. They take in what works through sound and speech from their surroundings—if we are dealing with present times. And what is it they absorb in this way? Think of how the potential to give form to the entire human organism lies in these organs. This means that if, for instance, a child hears an angry or passionate voice, if it is surrounded by loud and ill-tempered shouting, it will absorb something the animal keeps out. The animal lets itself be shaped only by the larynx and its neighboring organs, but members of the human species allow vehement or passionate voices to enter their inner being. These sounds flow into the human form, right into the structure of the most delicate tissues. If children hear only gentle speech in their surroundings, this too flows right into the structure of their finest tissues. It flows into their very formation, and especially so into the more refined parts of their organization. The coarser parts are able to withstand these influences, as in the case of the animal. But whatever is taken in through speech flows into the finer parts of the child's organization. This is how the differing organizations of the various nations come about. They all flow out of the language spoken. The human being is an imprint of language. You will therefore be able to appreciate what it means that in the course of human evolution so many people have learned to speak several languages. It has had the effect of making such people more universal. These things are of immense importance for the development of humankind. <And so we see how during the early period of childhood the human being is inwardly predisposed, right down to the blood circulation, by what comes from the environment. These influences become instrumental for the orientation of a person's thought life. What happens in a human being through learning to speak is something I ask you to consider most seriously. This human faculty might best be understood in its essence by comparing it with animal development. If an animal could express what lives in its forming and shaping, emanating from its upper chest organs, it would have to say, My form conforms with what streams from my upper chest and mouth organs, and I do not allow anything to enter my being that would modify this form. So would the animal speak if it were able to express this relationship. The human being, on the other hand, would say, I adapt the upper organs of my chest and mouth to the world processes that work through language, and I adjust the structure of my innermost organization accordingly. The human being adapts the most inward physical organization to what comes from the surroundings through language, but not the outer organization, which develops in a way similar to that of animals. This is of immense importance for an understanding of the entire human being. For out of language, the general orientation of thought is developed, and because of this the human being during the first three years of life is given over entirely to what comes from the outer world, whereas the animal is rigidly enclosed within itself. For this reason, the way that we find our relationship during these three years to statics and dynamics, then to speech, and finally to thinking, is of such profound importance. It is essential that this process develops in the right way. No doubt you are all aware that this can happen in the most varied ways in each individual human being. On what does it depend that these processes take their prper course? It depends on many things. But the most fundamental factor during the first stage of childhood is the right relationship between the child's times of sleeping and waking. This means that we have to acquire an instinctive knowledge of how much sleep a child needs and how long it should be awake. For example, suppose that a child sleeps too much, relatively speaking. In this case it will develop a tendency to hold back in the activity of its legs. If a child gets too much sleep, inwardly it will lose the will to walk. It will become lethargic in its walking, and, because of this, it will also become lazy in its speech. Such a child will not develop a proper flow in its speech and it will speak more slowly than it should according to its natural disposition. When we meet such a person in later life—unless this imbalance has been put right during the subsequent school years—we sometimes despair because he or she gives us the opportunity, one might say, to go for a little walk between every two words spoken. There are such people who have difficulties in finding their way from one word to the next. And if we come across them and look at their childhood, we will find that when they were learning to walk, they were allowed to sleep too much. Now let us take the case of a child whose parents or those in charge did not ensure that it had the relatively long hours of sleep appropriate to its age. The inner being of such a child is incapable of gaining the necessary control over its leg movements. Instead of walking normally, the child will have a floppy gait. In its speech, instead of controlling the sequential flow of words with the forces of the soul, it will let the words fall out of its mouth. The words of the sentences will not cohere. This is quite different from the case of a child who has difficulties in finding the right words. Here an overabundance of speech energy prevents it from getting from one word on to the next. Thus, in the instance mentioned previously, I was referring to the opposite, namely to a lack of the necessary energy. The words, as they follow each other, are not carried along by the flow of the soul; instead, the child waits for the right moment to “click in” the next word. If this reaches extreme proportions, the result is stammering. If one finds a tendency toward stammering in people, especially in their twenties and thirties, one can be sure that as young children they were not given enough sleep. From this you can see how knowledge of the human being can give us the fundamentals of what needs to be done. Now let us consider the entire human organism and see how during the first three years it adapts itself to earthly conditions of life, how it allows the principles of statics and dynamics, underlying the faculty of autonomous movement, to flow into what is produced through shaping the air in speech. In this process there is much more involved that is of consequence for the development of thinking. Compare this situation with that of an adult, and you will see that in the child there is a much stronger working together of these inner dynamics—of walking, fidgeting, movements of arms, and creating mental images. In the child all this flows together into a unity far more than in the adult. The child remains a far more homogeneous being than a grown-up in other respects as well. If, for instance, we as adults suck a sweet (which we really shouldn't do), this merely amounts to a titillation of the tongue, for the sweet taste does not go much further than that. But the child is in a different position. There the taste continues to spread. Children don't tell us this and we don't notice it; nevertheless, the taste continues to have an effect upon the child. Many among you will surely have observed how, according to their individual makeup, certain children are strongly permeated by soul and spiritual forces and how this quality comes to outer expression in them. It is far more interesting to watch the arms and legs of such a lively child than its mouth, when it is standing some distance away from a table where there is a bowl full of sugar. What the mouth says is more or less obvious, but the way such a child develops desire right down to its toes, or in the arms, as it steers toward the sugar bowl: you can clearly see it is not just a matter of the tongue anticipating sweetness, but changes are taking place throughout the entire being of the child. Here, tasting flows throughout the whole human being. If you enter into these things without preconceptions, you will come to realize that the young child, in a certain sense, is really just one great sense organ. Mainly this is so during the very first years (and more generally so between birth and the change of teeth) and is, naturally, less so in later years. What has become localized in the sense organs on the periphery of the human body in the adult, permeates the child's entire organism. Of course, you must understand these things with a certain discernment, but fundamentally they are real. Their existence is so real that orthodox physiology will one day be able to prove them with regard to the most conspicuous of all our sense organs, namely the human eye. People come to me quite frequently and ask, Considering the present state of science, what would you recommend as a suitable theme for a thesis? (Theses, too, belong to the chapter on “school misery.”) If such a question is asked by students of physiology, I refer them to a topical problem. I tell them to observe the developmental phases of the human eye as seen in the embryo, and then to compare these with the corresponding phases of the entire embryo from its germinal stage onward. This will lead them to a kind of inverted parallel between the eye and the whole embryo as its development progresses. They will discover that, in a certain way, the eye begins its development later, it omits the first stages. In contrast, the embryo as an entity never reaches its final stage—as the eye does—but stops short beforehand. This points to something of great significance for embryology. If one looks at the whole development of the embryo, one will come to recognize that in these beginning stages we may observe ideal stages that exist only as an indication. The eye continues to develop into a perfected sense organ, whereas the embryo remains behind in its development only to continue its further growth later on. But the situation in the young child is still one where, in its entire soul and spiritual development, the child's senses are poured out, as it were, over all of its corporeality. In a certain way the child is entirely a sense organ and it confronts the world as such. This has to be borne in mind, not only with regard to educational matters, but concerning everything that is happening in the child's environment before the change of teeth. We shall go into questions relating to more practical methods of teaching at a later stage. But it is only if one can see the fundamentals in the right light that one will be able to find the correct answers to particular human questions. One of these has been handed to me, which is of extraordinary importance for anyone who does not merely look at human evolution from external and well-known aspects of history. As you know, in the past, as you know, there was far more discussion of sin and original sin than is customary today. Now I do not wish to go into this question in detail, I only want to outline what this expression implied to those who studied such questions as we study general scientific subjects today (not in its present popular sense where such matters have undergone a certain coarsening). To those inquiring minds, original sin stood for all inherited characteristics.4 This means that what a person had inherited from his or her forebears was considered to represent original sin. Such was the actual concept of this expression; only later on was it changed to what we associate it with today. In earlier times, it was definitely felt that physical features inherited from one's ancestors gave rise to sinfulness. And what do we say today? We not only believe in studying inherited characteristics most carefully, but we even encourage their cultivation! If an earlier form of science had been asked to judge the modern attitude, it would have responded, With all your progress you have managed to come up with a most extraordinary principle—you have actually taught society to cultivate what is of sinful origin in the human being! Because we know of historical events only from what is rather superficially recorded in history books, we do not notice such subtle changes of interpretation. However, if you look into what I have told you today—namely how the child, through its relationship to dynamics and statics, through learning to speak and to think, adapts itself to the environment—then you will be able to distinguish between the part played by purely physical heredity and that of the environmental influences, which are far stronger than is generally realized. Often we hear it said that someone has inherited a particular trait from either the father or the mother, whereas in reality it is simply the result of imitating a certain way of walking, or a characteristic gesture of hands, or a specific manner of speaking, from those close to the person in his or her early childhood. The child's total surrender to the influences of the environment is what is of preeminent importance during the first years and not heredity as such. In their proper place, theories of heredity have their justification, but these also need to be seen within the context of what I said yesterday, when speaking about soft ground into which footmarks were imprinted.  If now some hypothetical Martian were to appear on the Earth, a being unacquainted with the human race, it might explain the origin of these footprints in the following way: Certain forces have pushed up the Earth, more in some places and less in others, which has caused the configuration of these footmarks. This is how some people would explain the nature of the human soul on the basis of heredity and as a result of the working of the brain. Just as the footprints have been pressed into the Earth from outside, so have environmental influences, experienced during the childhood stage of imitation, through learning to walk, speak, and think, been imprinted in the body, and particularly so in the brain and the nervous system. What orthodox physical psychology maintains is perfectly correct. The brain is a clear imprint of what the human individual is as a being of soul. One only has to know that the brain is not the cause, the creator of the soul element, but the ground on which the soul develops. Just as I cannot walk without the ground under my feet, neither can I, as a physical being, think without a brain. This is obvious. But the brain is no more than the ground into which the activities of thinking and speaking imprint what is received from the surrounding world. It is not a matter of heredity. Perhaps now you can see that people tend to have only unclear notions about what is happening in the child during these first three “nonacademic” years. During that time, to a large extent, the foundations are being laid for a person's whole inner life and configuration. I have already spoken of how thinking, which develops later, turns toward the outer world. It forms images of the natural world and its processes. But the faculty of speaking, which is developed earlier, absorbs—at least in nuances and in modified form—what lives spiritually in language. And language, coming from the child's environment, works upon the child's soul. Through language we take in from our surroundings what we make our own in the realm of the soul. The entire soul atmosphere of our surroundings permeates us through the medium of language. And we know that the child is one great sense organ; we know that inner processes are inaugurated through these soul impressions. So that, for example, if a child, is frequently exposed to the outbursts of an over-choleric father who utters his words as if in constant anger, it will inwardly experience its father's entire soul background through the way he forms his words. And this has an effect not only on the child's soul, but, through the atmosphere of anger surrounding it, causes the activity of fine glandular secretions to increase as well. Eventually, the glands of such a child become accustomed to an enhanced activity of secretion, and this can affect the whole life of such a child. Unless these harmful influences are balanced through the right kind of education later on, a tendency will develop toward nervous anxieties in any angry atmosphere. Here you have an example of how a certain soul condition directly enters and affects the physical organization. The attempt is often made to comprehend the relationship between the human soul and body, but a fact such as this, where during the first period of life a physical condition directly manifests itself as a symptom in the realm of the soul, simply goes unnoticed. And now, while the child enters into the realm of statics and dynamics working through its surroundings, it does something unconsciously that is of great importance. Think for a moment of how much trouble it means for many an older pupil to learn the laws of statics and dynamics and to apply them, even if only in the field of mechanics. The young child does this unconsciously. It incorporates statics and dynamics into its entire being. Anthroposophical research shows us that what most accomplished experts in the field of statics and dynamics manage to think out for the external world is child's play compared with the way the child incorporates these complicated forces while learning to walk. It does so through imitation. Here is an opportunity to observe the strange outer effects of imitation in just this situation. You can find many examples in life. I will give you one. There once were two girls of roughly the same age, who could be seen walking side by side. This case happened many years ago, in a town in central Germany. When they walked next to each other, they both limped with one leg. While both were performing the same limb movements, they displayed a marked difference between the movements of their more mobile right arms and right fingers and a somewhat paralyzed way they carried their left arms and left fingers. Both children were exact copies of each other. The slightly younger one was a true copy of the older one. And yet, only the older sister had a damaged left leg. Both legs of the younger one were perfectly normal. It was only by sheer imitation that she copied the movements of her handicapped sister. You can find similar cases everywhere, though many of them, being less conspicuous, may easily escape your notice. When a child learns to walk, when it makes the principles of statics and dynamics its own, it takes in the spirit in its environment. One could formulate it in this way: In learning to walk, we take hold of the soul element of our milieu. And in what the child ought to learn first after entering earthly life, it takes hold of the spirit in its surroundings. Spirit, soul, and body—spirit, soul, and nature—this is the right order in which the surrounding world approaches the human being. But as we take hold of the soul element in our surroundings, we also lay the foundations for our future sympathies and antipathies in life. These flow into us quite unnoticed. The way we learn to speak is, at the same time, also the way we acquire certain fundamental sympathies and antipathies. And the most curious aspect of it all is that whoever is able to develop an eye for such matters (an eye of the soul, of course) will find in the way a child walks—whether it does so more with the heel or with the toes, whether it has a firm footstep or whether it creeps along—a preparation for the moral character the child will develop in later life. Thus, we may say that together with the spiritual element the child absorbs while learning to walk, there also flows into it a moral element emanating from the environment. And it is a good thing if one can learn to perceive how the characteristic way a child moves its legs portends its moral character, whether it will develop into a morally good or bad person. For the most naturalistic quality belongs to what we take in through our thinking during childhood. What we absorb through language is already permeated by an element of soul. What we make our own through statics and dynamics is pervaded by moral and spiritual powers. But here statics and dynamics are not of the kind we learn about in school; here they are born directly out of the spirit. It is most important to look at these matters in the right way, so that one does not arrive at the kind of psychology that is based primarily on physical aspects. In this kind of psychology one reads in fair detail what the author has managed to establish in the first thirty pages of print, only to find that relevant aspects of the soul are stuck on artificially. One must no longer speak today of the human spirit, since an Ecumenical Council abolished it, declaring that the human being does not consist of body, soul and spirit, but only of body and soul, the latter having certain spiritual properties.5 The trichotomy of the human being was dogmatically forbidden during the Middle Ages, and today, our contemporary “unbiased” science begins its psychology with the declaration that the human being consists of body and soul only. Blissfully unaware of how little “unbiased” its findings are, it is still adhering to medieval dogmatism. The most erudite university professors follow this ancient dogma without having the slightest notion of it. In order to arrive at an accurate picture of the human being, it is essential to recognize all three constituent parts: body, soul, and spirit. Materialistic minds can grasp only human thinking—and this is their tragedy. Materialism has the least understanding of matter because it cannot see the spirit working through matter. It can only dogmatize—there is only matter and its effects. But it does not know that everywhere matter is permeated with spirit. If one wants to describe materialism, one has to resort to a paradoxical definition. Materialism is the one view of the world that has no understanding of what matter is. What is important is to know exactly where the borderlines are between the phenomena of body, soul, and spirit, and how one leads over into the other. This is of special importance with regard to the child's development during the first period of life.
|
| 183. Mysteries of the Sun and of the Threefold Man: Lecture II
25 Aug 1918, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| You know how I have hinted emphatically that I like a little warmth even in the treatment of anthroposophical truths.) The other people have not troubled themselves about this head-breaking but have left those alone who have looked at the world from what is really a very narrow point of view, those who have only seen the world from the aspect of the factory, from the inside of factories, from the inside of printing works, and so on. |
| This has been allowed to arise through men adopting the principle of only troubling themselves about things aesthetically. When the Theosophical Society was first formed it had as its basis principle the mutual love of all mankind. How this was breached: But I have said enough on that point; its easiness equals its fruitlessness. |
| It is important that we do not merely pursue half-asleep what should be the will of the Anthroposophical Movement. We must pursue it as indeed is necessary with our consciousness full of life and force. |
| 183. Mysteries of the Sun and of the Threefold Man: Lecture II
25 Aug 1918, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Yesterday I showed you threefold man diagrammatically. It is indeed true that in our present life of spirit very little feeling exists for the understanding of man's being as it must be grasped from the standpoint of spiritual science. Nevertheless, we must bestir ourselves to get a clearer understanding of man's being. For it is out of the understanding bound up with threefold man that we are able to master also the most significant conceptions that must be gained concerning the whole of human life, including man's development between death and a new birth. Today let me just consider in detail this threefold man. Yesterday indeed we saw how first of all we have to point to man's head. In a certain sense this human head is really a kind of independent form of being. You can picture to yourselves the human skeleton and how easily the head can be detached; it can be lifted off like a ball. It is true that in reality the separation between the three members of man's nature is not so simple that we can describe what can thus easily be lifted off like a ball as the head part. Things are not so definitely separated. We have gradually to work ourselves away from the purely diagrammatic away too, from what nature herself suggests, to a living feeling, a living experience And, as you saw, I had yesterday to draw not indeed three circles lying next each other, but one circle for the head, a second circle that overlapped the head, and a third circle that overlapped both the others. So that if we would draw threefold man diagrammatically in accordance with his physical nature, we should have to show him thus: Head part (see circle A in diagram 1; body (oval); and the limb-system; really three balls even if these balls have to be drawn out longwise. With the head part, with what is here shown as the red circle A, is connected the spiritual which is, as you saw yesterday, a young formation (see small yellow circle) This spiritual part of the head is a young spiritual formation whereas the head itself is an old physical formation, a physical form-being. For the head, what is applied to man in general is pre-eminently right; it is not right when applied thus in general but for the head it is right. What with regard to the head, I have shown here as white, spiritual, is outside the head when you are asleep. When you are awake it is united with the head and then for the most part inside the physical head. It is therefore separated most easily from the physical head, going out and coming back inside again.  That is certainly not so as soon as we come to the middle man, the breast man, shall we call him? What is enclosed by the thorax, by the breast cavity, enclosed by the ribs and the backbone, is bound up with the spiritual, and when you sleep the spiritual is not so pronouncedly outside; for this breast man during sleep it remains in close connection with the physical. And for the third man of the limb-system, to which sex man belongs, there is practically no real separation between the sleeping and waking conditions. One definitely cannot say that the soul-spiritual actually disconnects itself in sleep; it remains more or less united. So that one can well draw this other diagram of waking man saying: when physical man is awake (see a in diagram 1) then the spiritual man would be thus (yellow with circle a) And this would be sleeping man (see b diagram 1); the spiritual remains you see more or less connected with the body, and only this goes outside. From a certain standpoint this would be the actual drawing for the contrast between waking and sleeping man. Now if you are to understand the important things now to be described, you will only do so by crossing this membering of threefold man with another membering of man that is linked with what I was describing here recently. And if once more we go over head, breast man, man of the limb system, we can say that in the truest sense man is only breast-man. He it is into whom the Elohim breathed the breath of life. He is the breathing man. The division here is not so simple as in the skeleton; the breathing process through nose and mouth belongs to the breast man. Thus the partition in reality is not so easy, to show diagrammatically as one would wish. However these are the difficulties to be expected in understanding a matter of this kind. Thus the actual man, man on earth, is in a sense breast-man. And head-man, as physical form, is something that is not man through and through. It cannot be said that it is man all through. It even has in it much that is ahrimanic. In effect, it is organized as it is because certain formative principles are particularly present in it that have remained there since the old Sun—the second stage of earth-evolution. Our head, in all its complicated formation, would not be as it is had it not received its first form in those primeval days of the old Sun-evolution. Thus they are actually old, primeval formative principles today projected into the earth-sphere, and for this reason we must call them ahrimanic. Survivals of old principles are always to be looked upon according to the point of view as either ahrimanic or luciferic. The middle-man, the breast-man is what makes man of the earth, and where the principles of becoming earthly are mainly in play. Neither is the man of the limb-system wholly man, but is permeated by the luciferic; its formative principles are not yet complete in their development, and will not be so until the earth has reached its Venus stage, or till the Jupiter age is passing over into the Venus age. By the time the Venus age has come these formative principles will be working at their full intensity, in their correct form. (He might say that today they are still developing mere shadows of the real being of this third part of man's nature, the extremities-man.) Thus we presuppose what will only be in existence at the time of Venus, and make an incomplete picture of it in seed form, not letting it go beyond the seed form. This is how the matter stands when considered cosmically. To look cosmically at our formation, in our heats-forces we are repeating the old Sun-period, in our breast we carry the earth evolution, and in so far as we are extremity man we bear in us the seed of the Venus evolution. This is regarded from the cosmic point of view. Considered humanly—it is rather different. There we must look upon the human individuality as it progresses from incarnation to incarnation. Then we have to say: what in this incarnation we carry as our head, shows itself to be connected with our previous incarnation; what we now bear in us as breast-man is really only related to our present incarnation; what we have in us as as extremity man will become head in our next incarnation, is already related to our next incarnation. I have said previously: there is something revealing in the head especially in its negative. If you were to take an impression of the physiognomy of your head and consider it, you would recognise in this negative much of what had its origin in your previous incarnation.1 It is just the other way round with the extremities man. You cannot here take an impression but must proceed differently. Think away in man the head and the breast-system. But imagine all that your hands and legs do now—make a picture of what they do. Here you have to make a kind of map. You see, every time you do anything with your hands this is done at another place. They go around outside, they come into relation with other beings. If you would paint all that your hands and legs do, if you would draw a picture of what your hands and feet, arms and legs do in the course of your life—and this would be a very animated picture!—in this drawing you would discover a complicated map, where you would find revealed what is stored up in you karmically for your next incarnation. In this map you would be able to read a great deal of the karma of your next incarnation. This is of profound significance. As the negative impression of the physiognomy when at rest, reveals in the firm outlines of the drawing, what in the previous incarnation has already happened, so what one can jot down of the movements of arms, hands, legs and feet are extraordinarily instructive about what the man will do in his next incarnation. This is particularly instructive about what he will carry out, where he will go, where his legs will take him. If you simply follow in his track to all the places where his legs will carry him, you could make a map of it. You would get remarkable patterns on which men's secret inclinations are not without their influence. Much of man's secret inclinations are not without their influence. Much of man's secret inclination is expressed in these patterns. These traces that are there are most revealing for what his next incarnation will bring to a man. Now we have been considering this from the human point of view, whereas the other was a cosmic view. This membering of man that has the present in view signifies, however, a connection with the secrets of the old Mysteries, in which the matter was recognized in a more atavistic way, but where the secrets I have just been disclosing to you were already known. There is a beautiful saga concerning King Solomon about the certainty with which man sets his foot on the place where he is destined to meet his death. The meaning of the saga is that a definite place exists on earth where man will die, and thither man directs his footsteps.2 This is connected with the old Mystery-Knowledge. Now when man is living his ordinary life he has actually only his ordinary consciousness; but as we have seen this man is a highly complicated being. When he is awake, when he has his head, his most recent spiritual member, in his physical head, he knows nothing of this head. You will be right in saying: Thank God we do not know anything of our head for knowing of our head means to have a headache. Men only know about their head when it aches; then they are conscious of having a head, otherwise they are unconscious of it—unconscious to a most remarkable degree, far more so than in the case of any other member of the human physical body. Man may count himself lucky when in normal consciousness he knows nothing of his head. But beneath this consciousness of the head that ordinarily takes notice only of the outer world, that only gets as far as knowing what is around it—beneath this consciousness lies another, a kind of dream consciousness, dream-knowing. Your head, my dear friends, is always dreaming. And while you are conscious of the outer world in the way familiar to you, under the threshold of consciousness, in the subconscious, you are actually perpetually dreaming. And what you are dreaming, if you were able to bring this head dreaming into your consciousness and fully grasp it, would give you a picture, a correct comprehensive picture, of your previous incarnation. For in your head unconsciously, you are dreaming of your former incarnation. That is indeed so. There is always a slight consciousness of your previous incarnation going on, a dreaming consciousness, only it is overpowered by the strong light of of ordinary consciousness. By the year 747 before the Mystery of Golgotha, the external consciousness had become so strong that gradually this subconsciousness of the previous incarnation was completely extinguished. Before that year, however, man knew a great deal about this dream consciousness of the head. For this reason you find everywhere at the basis of the ancient cultures repeated lives on earth treated as a fact. This is due simply to the sub-consciousness of the head not then having receded so completely into the background as it did in the course of the fourth, but principally the fifth post-Atlantean age. Even in ordinary consciousness very little is known of what is connected in a soul-spiritual way with the thorax and the middleman. It is in itself of a dream nature. This middle, thorax consciousness sometimes pushes up into man's dream consciousness, but only very chaotically and irregularly. If a man is able to breathe regularly, when his heart beat even is when in fact all the functions of man's thorax, his middle part, are in order, the consciousness of this part is not so clear as that of the head; it too in ordinary life runs its course dream fashion. We dream in our feeling, as I have stated here during past years, in feeling we dream of this middle man. But when we bring to light through consciousness, that becomes more clairvoyant, what lies in the feeling, what man experiences only in his feeling, or to put it differently, when man learns to look at what is going on in his thorax, as otherwise he can only look at what is in his head consciousness, then the consciousness of the thorax, the middle-body splits definitely into two parts. One part dreams itself back into the whole time between the previous death and the most recent birth or conception. Therefore while in your head consciousness in a dream way, in deep dreaming, you have unconsciously what was in your previous incarnation, in the dreams of your thorax you have what has meantime been passing since that incarnation up to your present birth. And in the dreams that belong more to the lower part of the thorax you have a definite consciousness of what there will be between your coming death and next earth life. Thus the consciousness concentrated in the breast, which, however, for modern man remains more or less subconscious, is in reality a dream consciousness of both the time before this birth and the time after the next death. For this subconsciousness in the middle man the riddle is solved of what lies between our last earthly death and the following earthly conception, with the exception of or even including what we are now experiencing between birth and death. Out of the third man, out of the subconsciousness of the extremities man, the tableau of the next incarnation on earth can be developed in what during the whole of life remains strictly subconscious. This can only be brought to the surface when a man is able to draw it up through ceaseless activity in the study and exercises of spiritual science, so that certain moments of sleep-life that otherwise would pass in unconscious sleep, are lifted to the surface and the man then becomes conscious during sleep. What today man has as waking consciousness is really a kind of collateral impulse of his which rays into the head from outside. Behind this consciousness, however, lies another that stretches itself over the former incarnation, over the life of that incarnation to this one, over the life of this incarnation to the next, and then over the next again. But man sleeps away this consciousness. In the head it is the consciousness of the previous incarnation. In all the organs that principally serve the out-breathing there works a strong consciousness of the life between the previous incarnation and this one. In all the principle functions that serve the in-breathing works a consciousness of the present incarnation up to the next incarnation on earth. And in the limb-system, in all its most secret processes, works a consciousness of the next human incarnation, which remains pre-eminently subconscious. These states of consciousness have become more less veiled since the beginning of the fourth post-Atlantean period, 747 years before the Mystery of Golgotha. And the cry of our age is for the definite consciousness of the concrete events of cosmic and human evolution to be brought back out of the general chaos of human consciousness. We must meet all that I have just been developing with another aspect of what is part of the being of man. You see it is really necessary that we should enter into these difficult details, otherwise we cannot arrive at an exact understanding. I should very much welcome it if such knotty points were met not only by a certain passive acceptance, but—and this is so necessary for present day man—that even for these difficult matters a little enthusiasm were aroused, a little keen participation, which is exactly what is so hard in any society today.  Now, you turn your senses outward. There by means of your senses you find the external world spread out as something perceptible. I will draw diagrammatically what lies around us outside as something spread out for the senses. Allow this (see blue in diagram 2) to be what is lying outside. When you direct your eyes, your ears, your sense of smell, or whichever sense you like, to the external world, the inner side of this outside turns towards you, turns towards your senses Thus this is the inner side of the outside (see left of diagram). Suppose you turn your senses here to what I have drawn (see arrows). These are the senses directed towards the outer world and you see what here inside inclines within. Now follows the difficult conception to which, however, I have to come. Everything you look at there presents itself to you from inside. Imagine it must also have an outside. So I will call it up diagrammatically before your souls saying: When you look out thus you see the permanent as the limit of your vision; that is approximately so, only I have drawn it small. But now imagine you could quickly fly out there, fly beyond there and take a peep through from the other side and from the other side see your sense impressions. You could look out thus (see upper arrows in diagram). No, naturally you do not see this but, could you thus look at it, it would be the other aspect. You would have to go outside yourself, you would have to look from the other side at your whole perceptible world. You would see the reverse side of what meets you as color, what meets you as sound, and so on. You would see the reverse of what comes to you as smell, you would receive the smell in your nose from behind. Thus, imagine your view of the world from the other side; imagine the perceptible things spread out like a carpet, and now the carpet viewed from the other side. You see only a little bit of this reverse side, a very little bit indeed. I can only represent this little bit by doing it like this. Imagine now that I am drawing in red what you would see from the other side, so that I can say, one sees the perceptible diagrammatically thus. To one's ordinary view it appears blue; seen from the other side it appears red (but naturally one does not see it.) In what you would see red, is hidden first that is experienced between death and a new birth; secondly, everything described in Occult Science as the evolutions of Saturn, Sun, Moon, Earth and so forth. Everything hidden from sense perception lies there stored up. There it is, on the other side of the sphere, but you see only a little bit. I can indicate this best by saying: take this small bit of red; this goes over (see below in diagram) and crosses the blue, so that the blue instead of being, as now, in front, is behind. (were I to draw in accordance with reality, I should have to do so in four dimensions, so I can only keep to what is quite diagrammatic.) Thus the senses here are now turned to the blue (left); there they do not turn to the blue but to the red which moreover you do not see. Behind the red, however, there crosses what otherwise would be seen and that is now underneath. And this little bit that crosses the other there, you see continually with your ordinary consciousness. It is indeed your stored up memories. What arises as memory does not arise in accordance with the laws of the outer world of the senses but according to laws suitable to this world that is behind. What is within as your memories is what is suited to the other side (right). As you look within on all your memories you are actually looking at a bit of the world on the other side; the other projects inwards a little and then you see the world from the other side. And if now you could slip through your memories thus received (I spoke of this a week ago,)3 if you could get underneath and see below your memories, look at them from the other aide from down there (see right in diagram), you would see them as your aura, There you would see man as a being with a soul-spiritual aura just as ordinarily you look at the external world of sense perceptions. But as I showed you a week ago this would be hardly pleasant because man on this other side is not yet beautiful. Thus these are the interesting features of what must work across the other knowledge we have of threefold man. This crossing takes place here in the middle man, the breast-man. You remember the drawing I made a week ago where I had the lemniscates with one loop reversed, turned inside out; I must draw those here I must draw here the breast man with the leminscates described. (see below on left of diagram.) That would coincide with the sphere of memory. So that in his middle part the threefold man has this turnabout where the inner becomes outer and the outer inner. Here you now have in your own small microcosmic memory a tableau, what otherwise you would see as the cosmic tableau—as the great cosmic memory. In your ordinary consciousness you see what you have been collecting since about your third year until now; this is an inner record, a little bit of what is of the same kind as the other record for the whole world-evolution and lies on the other side. 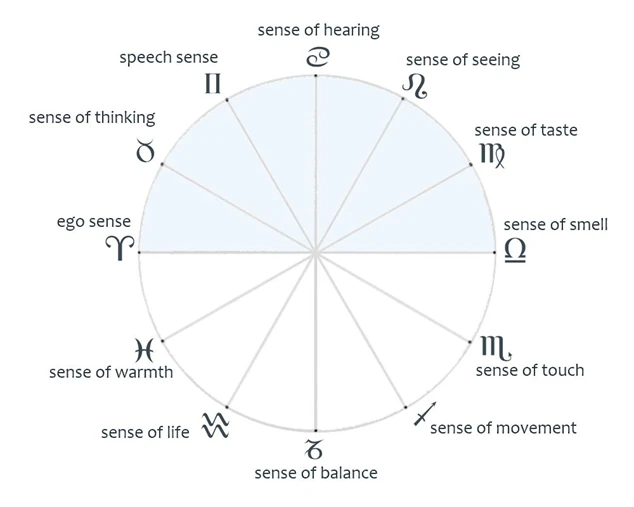 It was not without reason that I once told you that man actually has twelve senses. Most of you know this quite well and I have mentioned it also in the notes at the end of my last book Riddles of the Soul. We must think of the senses in this way: that a number of them are turned towards what is sense-perceptible, whereas others are directed backwards. Below they are directed towards what is turned back. Those directed towards what is perceptible to the senses are: the ego sense, and the senses of thinking, speech, hearing, seeing, taste and smell; they go towards what is sense perceptible. The other senses do not come into man's consciousness because they are first of all directed toward what is within him and then to what in the world is reversed. These are the senses of warmth, life, balance, movement and touch. We can therefore say that for the ordinary consciousness seven senses lie in the light (above in diagram 3) and five in the dark (below). And the five senses lying in the dark are turned to the other side of the cosmos, turned also to the reverse side in man (see diagram 2). You therefore have a complete parallel between the senses and something else of which we are going to speak. (see diagram 3) Let us suppose we have to note down as senses: hearing, speaking, thinking, the ego-sense, and the senses of warmth, balance, movement, touch, smell, taste, sight; then you will have essentially all of them from ego-sense to sense of smell lying in the light, in what is accessible to the ordinary consciousness (see shading in diagram 3). And all that is turned away from ordinary consciousness, as night turns away from day, belongs to the other senses. Naturally the boundary is also diagrammatic, there is an overlapping—reality is not always accommodating. But this membering of man according to his senses is so that, even in the diagram, you only need draw in place of the senses the signs of the Zodiac, and you have Ram, Bull, Twins, Cancer, Lion, Virgin, Scales, seven signs for the light side and five for the dark: Scorpion, Archer, Goat, Waterman, Fishes; day, night: night,day, Here you have a perfect parallel between microcosmic man—what is turned towards his senses and what is turned away but really turned towards the senses—and what in the cosmos signifies the change from day to night. In a way the same thing happens to man, as in the cosmic edifice. In the cosmic edifice there is an interchange between day and night, in man there is also the interchange of day and night in his waking and sleeping, even though both may have emancipated themselves from each other for the present cycle of man's consciousness. During the day man is turned towards his day-senses, or we might say to Ram, Bull, Twins, Cancer, Lion, Virgin, Scales, as we might say ego-sense, sense of thinking, speech and so on. Every ego can see that of another man, you can understand the thoughts of another man, you can hear, see, taste, smell—those are day-senses. In the night it is the same with man as when the earth is turned towards the other side; man is turned in the night to his other senses, only these are not yet fully developed. Not until the Venus age will they be so fully developed that they can perceive what is on the other side. They are not yet sufficiently developed to perceive what is towards the other side. This is shrouded by night just as the earth is shrouded when passing by night through the other heavenly bodies, the other pictures of the zodiac. The passage of man through his senses is a perfect parallel with the course—whether you say the course of the sun round the earth or the earth round the sun is immaterial for our purpose; but those things are connected. And with these connections, the wise men of the Old Mysteries were very well acquainted. In the fourth post-Atlantean period this gradually vanished from consciousness but it must be brought back in spite of the resistance put up against this; it must be reinstated in the cultural life of mankind. For in these concepts that man makes his own there lies what lets us see quite clearly all that is happening now in the social, historical life. So long as you separate the life of nature from that of the spirit, as modern man loves to do, you do not arrive at concepts that can play a part in historical evolution; you are overpowered by the concepts that are working in historical life. Overpowered: There are indeed many instances of this. Now you will agree that men believe that, shall we say, for two hundred years they have been thinking a tremendous deal. We can gather up what they have been thinking for two hundred years, what they have developed as ideals, what they have talked of still talk of, as great ideals. We can do this from the time of the ideals of the age of enlightenment to that of the great would-be Caesar, Woodrow Wilson. All that is talked of about the various ideals, men have been thinking during these centuries, these last two centuries; this has formed men's thoughts. World history, however, is very little affected by these thoughts, world history has been affected by something quite different, by the thoughts that have been working and weaving in things. And in reality never were the thoughts filling men's heads farther removed from the great cosmic thoughts living in things than at the present time. What for the last hundred and fifty years, shall we say, has prompted man to work for a definite fashioning of the world is not thoughts of freedom, equality, brotherhood, justice, and so on and so forth, it is the thoughts interwoven with the coming of the machine loom. That the machine loom arose in modern development in the second half of the eighteenth century; that this significant invention took the place in mankind's evolution of the old hand-weaving; that from the machine loom came the whole machine civilisation of modern times; in all this there weave the objective thoughts the real thoughts, that have given the world its present form, out of which has arisen the present chaotic catastrophe. Should we wish to write a history of this catastrophe, we have not to turn to the thoughts teeming in human consciousness; we must turn to the objective thoughts of the founding, the invention, of the machine loom up to the development of big industry with its shadow, socialism. for even if these two things, big industry and socialism, appear as opposites they are polaric opposites belonging to one another, and as such inseparable. We must put our questions to these objective thoughts and observe history in its becoming. Then we find that during the eighteenth century, all through the nineteenth, and especially so far as we have gone in this our twentieth century, men have given themselves up to many illusions. They are given over to illusion in their thoughts; but the objective, historic-cosmic thoughts have completely overwhelmed them. These are weaving in things. And an interest—though terribly one-sided—for these objectively weaving thoughts has really been gradually developed only by those who have built up socialism as a world-conception. That is something tremendously characteristic. If you follow the course of the nineteenth century you will see that the bourgeoisie increasingly loses interest in the great questions of world outlook. These great questions are indeed becoming most distasteful to the bourgeoisie; where possible they relegate them to aesthetics. A perfectly average bourgeois will listen in the theatre to all kinds of discussions about whether there are spiritual beings or not, when there is no need to believe in them, and when it is not a question of the truth of anything. Then the most varied matters can be put forward by Björnsen and people of that ilk. And what concerns the conception of the world is today for the bourgeoisie transferred into the realm of aesthetics, into all manner of dabbling with so-called art. In recent years people have been breaking each others heads over questions concerning conceptions of the world in the sphere of socialism. (I don't look on this as an ideal in a physical sense but in a spiritual sense in a certain way it is so. You know how I have hinted emphatically that I like a little warmth even in the treatment of anthroposophical truths.) The other people have not troubled themselves about this head-breaking but have left those alone who have looked at the world from what is really a very narrow point of view, those who have only seen the world from the aspect of the factory, from the inside of factories, from the inside of printing works, and so on. And it is extremely interesting what kind of world outlook has been produced out of the point of view of the factory—for that is socialism, my dear friends. It is the factory aspect, the aspect of men who know nothing beyond the inside of their factories. And in all that has developed in this sphere, little interest has been really shown by the bourgeoisie with their abstract ideas; the bourgeoisie who even concern themselves with aesthetics in an abstract way to avoid the breaking of heads. Thus in a curious way the bourgeoisie have found themselves between the old completely moribund world-conception bereft of the spiritual that would prefer to relegate all great questions to the realm of aesthetics, and what has newly arisen as socialism. This socialism has so far no concepts at all; it is a system founded entirely on words. This is because as yet it has no view of the world whatever and can only see the factory, and even so only the most external part of the mechanism. Just imagine what it really means when a man has no inner knowledge of the kingdoms of the minerals, the plants, the animals, and only knows of the way in which a certain cock is moved mechanically up or down in a machine, this or that filed or planed, and things of that kind: Socialism is a world-outlook founded on the perception of a purely mechanical world. It is the bit of the world cut out by the socialist—the bit that is mechanical, and on this he builds his concepts. This has been allowed to arise through men adopting the principle of only troubling themselves about things aesthetically. When the Theosophical Society was first formed it had as its basis principle the mutual love of all mankind. How this was breached: But I have said enough on that point; its easiness equals its fruitlessness. But this also arises from the desire whenever possible to push what has actual content into the realm of what has none. So there could be no genuine interest in the real course of things. Individual people however have found pleasure in the peculiar—we should say conventional—way of considering history. Now let us take an example of this; let me take whatever example you like from the time of the Caesars; try to learn about this time from the text books, or any books written by the great historical authorities. I fancy you will gain very little knowledge in this way about a certain personality who in the reign of Nero played an important political part (so even under Nero you could have political aspirations!) This personality aroused quite special notice and gained considerable influence on Roman politics under Vespasian and Titus, so much so that it may be said that he was the soul of the Government under these two emperors. Then this personality went over to the other side in the reign of Domitian considering him as a disaster for the Roman Empire. He turned to the other side and a lawsuit was brought against him, a lawsuit that made a great deal of stir in Rome and was of much interest. During this case Domitian changed suddenly from the tyrant into one who did not know how to proceed in the lawsuit and was therefore unable to pass sentence on the man. Then again, as Nero succeeded Domitian, we see this personality actively connected with the Emperor, the Caesar. We watch him creating out of the whole world-conception of that day what was great in politics, and at the same time see how he once more sought to implant for the last time during the Roman Empire into the political events really vast concepts brought down from the cosmos. Strangely enough in no current history book do you find any accurate account of this personality, not even in Seutonius or Tacitus, only in Philostratus. And Philostratus describes him in such a way that one does not know whether he is giving a picture of any Roman or of a real man—he paints the life of Apollonius of Tyana. For it is Apollonius of Tyana of whom I have been speaking as having had so great an influence on politics from the time of Nero to that of Nerva, and especially under Vespasian and Titus; and Philostratus describes him. Bauer the theologian and historian of Tübingen was absolutely astounded that one should thus find nothing about such a personality as Apollonius who played a part of the utmost importance in what is historically represented. Naturally Bauer did not see into the real reason for this; for it is a question of our having in Apollonius a historical personality wielding indeed this great influence but drawing down his principles straight from the cosmos above. That was in the highest degree fatal for the Christianity then arising in Rome. And now I shall ask you to take notice that everything in history is there by grace of the Church. There is nothing in history except what the Church has allowed man to have. Not without justification has an old and by no means foolish man maintained that there was never a Plato nor a Sophocles, but that monks in the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries wrote their plays—for there is no proof, no strict proof of their existence. Even though the assertion is untenable, is indeed nonsense, nevertheless, as we have often emphasised, all that is conventional history is most uncertain. And we should be quite clear about it. We must indeed bring the present into connection with the past, for we are now coming to a great and pregnant question. We have once more this time from the modern point of view, referred to threefold man, his connection with cosmic truths and the necessity for all this again to be disclosed. Now, my dear friends, in what has consisted the main activity of the Church, especially since the eighth Ecumenical Council in Constantinople in 869? What has been its chief activity? Its chief activity has been to wipe out, to blot out from man's consciousness, what in those ancient times even Christianity still understood as the connection of man with the cosmos, with the great spiritual world. Everything betraying this connection has been suppressed in real alarm. And only because not everything can be suppressed, because Karma is working against this suppression, have such works remained as those of Philostratus. Therefore you can understand when now you bring the present into connection with the past that certain churchman are made terribly uneasy by the growing tendency to foster the connection between what makes roan a cosmic being, this man himself, and his task. It is important that we do not merely pursue half-asleep what should be the will of the Anthroposophical Movement. We must pursue it as indeed is necessary with our consciousness full of life and force. With this I have indicated what is to be continued and enlarged upon tomorrow.
|
| 189. The Social Question as a Question of Consciousness: Lecture I
15 Feb 1919, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Thus, in a particular way, because it is not called forth arbitrarily but by observation of the forces of the times, the spiritual knowledge of Anthroposophy becomes in the anthroposophical members the needed healing power in the highest sense. It is not indeed the programme of one individual or of several individuals, but the result of observing what the spiritual leadership of the world dictates as necessary for mankind's present progress. |
| We have reason to be thankful that in the midst of our society personalities have been found with understanding, active understanding, at what is aimed at here, so that they will also actually do something. |
| What has to come must be created spiritually, and the bearer of this will be the Anthroposophical Movement. This is what I wanted to tell you on this eventful evening of our Lecture Cycle, as something that has proceeded out of the inner being of our movement. |
| 189. The Social Question as a Question of Consciousness: Lecture I
15 Feb 1919, Dornach Translator Unknown Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
In some of the lectures I have recently held here I have dealt from several aspects with the now urgent, burning social question. Everyone who does not sleep through the events that weave themselves into his life, can be aware that this so-called social question has long been, and continues to be, an urgent and burning one for all mankind. From lectures I have held here and also from extracts of some given publicly by me in different parts of Switzerland, it can be seen how far in man's modern necessities of life, and in his most recent development, this social question has taken a definite form, a most incisive form, for life. In our Anthroposophical Movement, therefore, it behooves us to arrive, from our point of view, at a judgment about human destiny especially in regard to the social question, a judgment which in a way possible to us could be put into actual effect. For a considerable time certain of our members have endeavoured to make their powers of use in our difficult times. Many things have been considered and put under review. Naturally for each of us it is possible to intervene in affairs only in the way his fate, his karma, and his position in life allow. As a result of the various aspirations among us, the following has now evolved. Three well-known members, who set themselves the special task of working in Stuttgart to meet the demands of modern life, Herr Mott, Dr. Bock, and Herr Kühn, came to me early in February and decided to put into practice, as far and as suitably as possible, what we have been able to learn from our world-outlook and conception of life. When we are dealing with a matter not of mere consideration but of practical application, the question can only be what at a definite point of time is suitable, what answers the purpose, what in a certain relation is the fitting thing with which to begin. If one does not make a suitable beginning one will rush in where angels fear to tread and, as a rule, accomplish nothing. For us at the present moment it is a matter of doing something in accordance with what has gone before, something the hard-pressed German people will find justified. In the events of the present day, above all appears one thing that is most significant—the existence of a deep gulf between the classes of men. On one side of this gulf stand the circles that have hitherto more or less led men's destiny; on the other side, the proletariat pressing forward with the reality of their social claims. The proletariat, it is true, appears to the observant in two forms, the workers themselves, and their leaders. I have often shown here how all the thoughts, aspirations and impulses in the heads of the leaders, by the help of which they gain their influence over the workers, are fundamentally a legacy from the middle-class thinking of the previous century. We have spoken of this here from various points of view, and sought to confirm it. Now one of the most significant phenomena is this deep gulf between the two human groups. In recent days this has been clearly visible to those who follow the history of the times; on the one side Paris, where the standpoint of the formerly leading circles of mankind prevails, where man's destiny and that of the present time are dealt with; on the other side, Berne with its Conference in which lives everything that is divided from the other by the deep gulf. Whoever has carefully followed what has issued from Paris and what on the other hand has been attempted in Berne, at the socialist Congress, could not but confess that the essential thing, the significant and lasting thing, that will make itself felt in human evolution, is not the result of what is thought and hoped for in Paris or Berne, but the fact that in these two places two such very different social languages have been spoken. To be really honest one has to confess that here we have two totally different languages, languages up to now mutually incomprehensible. On due consideration this significant phenomenon may strike everyone as justifying what I have so often said here, namely, that if we are to understand these things and share in the working out of possible solutions, many root causes must be looked for that are deeper than those sought today by either side. Time and again we have the opportunity of seeing what I referred to two days ago in a public lecture at Basle—that the social question, the social movement, is already an actual question, a question of present events for a great part of civilised mankind, in as deeply decisive a way as anything in the history of mankind. It presents itself in this way to all those of insight. And how often have I pointed out here that the deeper causes are to be found only through those considerations of reality that result from the Movement here for Spiritual Science, Anthroposophy—the deeper causes also for the social study of life and of things. At the beginning of the year [ Note 1 ] I pointed out something I believe to be significant, namely, that today it is possible for mankind to be thoroughly pessimistic not just from emotional reasons but on actual social grounds. At the time, I read to you an excellent article by a man [ Note 2 ] who in this way is really able to estimate social matters. I have told you that it is profitable to think pessimistically only when one is not conscious of the other side of the fact—that help can be found by turning to the spirit. For that, a consciousness must be cultivated more and more that there is only ground for belief in destructive forces, which can produce terrible results in the coming decades, if men refuse to turn to the consideration of the realities arising from Spiritual Science. Naturally we do not mean by this the dogma of some spiritual movement or other, what we mean is an appeal to any forces of the spirit that alone can heal and help at this critical juncture in human evolution. Thus, in a particular way, because it is not called forth arbitrarily but by observation of the forces of the times, the spiritual knowledge of Anthroposophy becomes in the anthroposophical members the needed healing power in the highest sense. It is not indeed the programme of one individual or of several individuals, but the result of observing what the spiritual leadership of the world dictates as necessary for mankind's present progress. It is on that account only that we can speak of Spiritual Science, of Anthroposophy, otherwise it would obviously be presumptuous. But what springs from true modesty need not be deterred when making itself felt, by the reproach of the presumptuous. What has come from Paris can be said to be in keeping with an attitude towards life that in the last four-and-a-half years has led ad absurdum. From Berne has streamed what seems salvation to many, but has originated in an insufficiently deep source. From Paris there flows what occasions fear in almost all mankind; from Berne was meant to stream what in a great number of men can arouse hope and belief. And these two things speak quite different languages; there is no possibility of mutual understanding across the abyss. That will come only from the soul's inner appeal to Spiritual Science. From such impulses arose the thought first at least to speak to the understanding of part of mankind. For it is a question of understanding. I have continually emphasised that in our social chaos we shall make no headway until we succeed in our appeal to the understanding of a sufficiently large number of men before instincts become too uncontrolled. This is what inspired my lectures in Zurich, Berne and Basle. Recently, various people with whom I have talked have given frequent opportunity for discussing how to approach the understanding and whether it be possible to discover the way before there is complete disaster? Now the latter question is one that cannot be raised by anyone who thinks in realities. For anyone thinking in realities does not speak with hypotheses about what is possible or not possible, but seizes on what he considers necessary to be done. When one one sets out on some road, a first step has to be taken; and we should not think, when the first step seems incompatible with the desired goal, that this step is useless. On a long road the first step can only take us a very short way. When going towards a specified goal it is first simply a question of not going in the wrong direction, either to right or left of the goal. Secondly, having once started on, the path, it is a question of having the will to keep to it and not to stumble against anything either left or right. If we would take our stand on realistic ground, we must also be in touch with what is happening at the time, what is already there, and not build castles in the air. Our though must be linked with something showing that from a certain direction a real stream is flowing. The first step may often seem most unfortunate, and only after a time perhaps turn out to be otherwise. Now the three men previously named—Herr Mott, Dr. Boos, Herr Kühn, have discussed this matter with me. Since a spiritual appeal is to be made to the understanding of mankind, it must first be asked where anything of the sort has been seen to have an effect on men's thinking. You may remember an appeal made to the so-called world of culture, issued by ninety-nine German personalities, for the most part professors, or so I believe. Judged from the point of view of reality and not of emotion, this appeal can only be considered very clumsy. Yet for the most part they were professors: The appeal made an impression, however, and influenced thought in an unfortunate way. And it still haunts us. Being in a certain sense a reality it was a reality that had a worse effect than many others for it set waves in motion. This makes one wonder how it might be in the present urgency to send out an appeal in contrast to this untimely set of antiquated notions, an appeal to man's understanding, arising out of the real conditions of modern human life. First, arising out of the facts themselves, an appeal to the German people, who have experienced the fate of seeing swept away the whole framework of a State in which they had hoped to realise their appointed task. They should be appealed to in a way to make them see that facts are speaking to them and not just a collection of words or some particular opinion or idea. Whereas perhaps the greater part of mankind would be loath to listen as long as old forms still remain, it can be assumed that the Germans would be more likely to listen, because no longer able to remain on the old ground they must perforce seek out a new basis for their life's task. For men are like that; so long as anything of the old remains—when it is not just a matter of clothes—they will unquestioningly hold firmly to it, unconscious of any sign that this is no longer possible. No one believes what a part love of comfort plays in the inner life of man. Out of these thoughts I have composed a sort of Manifesto, and imagine it may be listened to by those souls who, where our own particular cultural questions are concerned, can be brought to an understanding based on reality. Above all I hope it may be understood by those Germans who are intelligent; to these it is addressed. But I mean it to be read by the enemies of Germany also, as something that has been considered and found fit by the people of Germany to be translated into reality. I thought of the ninety-nine signatures; if another ninety-nine of the Germans of the old Germany and of the old Austria can be found, and if the ninety-nine could perhaps be increased by a few personalities having an understanding of the present necessities of life—people in neutral countries, in Switzerland for example,—then something positive might be done in contrast to the former negative undertaking of the ninety-nine. I beg you to understand me aright. This is first and foremost an appeal to the German people. But it is thought that what will be discussed in this form among the Germans themselves should be heard by the whole cultural world. I shall read this appeal here. The ideas will be known and familiar to you, since we have often discussed them. It is not meant to give advice, but it should show people that there is a way and how this way may be found. Certainly the presentation can be criticised as too short. But it is not a question of a textbook, it is an indication that there is something within mankind that can be of help. The Appeal is addressed: “TO THE GERMAN PEOPLE AND TO THE CULTURAL WORLD” The German people believed the structure of their empire, set up half a century before, to be secure for an unlimited time. At the outbreak of this catastrophic war, in August 1914, they saw this structure firmly established and imagined it would prove invincible. Today they see only its ruins. After such an experience must come reflection, heart-searching. For this experience has shown that the thoughts prevailing for half a century and more, especially those holding good over the war years, to have been tragically misleading. The question necessarily, arising in the souls of the German people is: where lie the reasons for this tragic error? This question must promote inner reflection in souls, and on their power for such reflection depends the very survival of the German people. Their future depends upon how far they are able to consider the question in all seriousness: How did I fall into this error? If today they face this question, the knowledge will dawn on than that, half a century earlier they founded a realm but omitted to set it the tasks arising from the essential nature of the German people. The realm was set up. In its early years all efforts went to the adjustment, as far as life allowed, of demands remaining over from the old tradition and yearly arising from new needs. Later men went on to confirm and increase their outer predominance in material strength. With this they combined measures concerned with the social claims born of the times, measures that certainly took into account the needs of the day but lacked the larger aims which should come from knowledge of the evolutionary forces to which modern man must turn. Thus the realm was established in a world-connection that lacked a real goal to justify its survival. The course the catastrophe of the war took has revealed this in a tragic way. Until the very outbreak of hostilities the world outside Germany could not see in the conduct of the realm anything to suggest that its rulers were fulfilling a world mission of historic import, not to be lightly swept aside. The failure of the rulers to find such a mission has necessarily given rise in the non-German world to the opinions that to those of insight have been the deeper grounds for the German downfall. For the German people infinitely much now depends upon their impartial judgment of this state of affairs. In misfortune there must arise the insight which, in the last fifty years, has not been willing to show itself. Instead of the feeble thinking about day-to-day demands, a greater impulse must arise towards an outlook on life that with vigorous thought strives to understand the forces at work in evolution, and devotes itself to these with courageous will. There must be an end to the petty desire to sweep aside as unpractical idealists all those who pay heed to evolutionary forces. So too must cease the pride and presumption of those who imagine themselves to be practical people, who through their narrow vision in the guise of the practical have brought about disaster. Heed must be paid to what the truly practical men—decried as idealists—have to say about the present requirements of evolution. The ‘practical’ men in all directions have for a long time seen that quite new human demands are being made, but they have tried to fit them within the frame of ordinary traditional thinking end organisation. The economic life of the day has produced demands that private initiative seems incapable of satisfying. One class of men consider it necessary that private enterprise should in individual spheres be transferred to companies; and this would be carried out wherever it appeared profitable according to the outlook on life of this particular class. The drastic transference of all individual work to associations became the aim of another class who, through the development of modern economic life, have no interest in retaining the handed-down aims of private persons. In all the endeavours in connection with the modern demands of mankind up till now, there is something in common. They press for the socialisation of private undertakings, and count on the latter being taken over by the community (State, Commune) that has sprung from conditions having nothing to do with modern demands. Or men think in terms of newer associations, such as companies, that are nevertheless not formed in complete accordance with these new demands but copy old forms,out of traditional habits of thought. The truth is that no associations formed in the sense of these old habits of thought can take up what one would like to see accepted. Prevalent forces press towards recognition of a social structure of mankind having something quite different in view from what is customary. Until now the social communities have for the most part been formed out of man's social instincts; the task of our time is to penetrate the forces of these instincts with full consciousness. The social organism is membered in the same way as the natural organism. And as the natural organism must manage its thinking through the head and not through the lungs, so in the social organism the membering into systems must be such that no system can take over the task of another; all must work together but maintain its own independence. The economic life can thrive only in developing as an independent member of the social organism in accordance with its own laws and its own forces, and avoids creating confusion in its structure by allowing itself to be absorbed by another member, the political member, of the social organism. The member that works politically must have a completely independent existence alongside the economic life, just as in the human organism the breathing system exists alongside that of the head. Their mutual work cannot be carried on beneficially if the two systems are under a single set of laws and administration; each must have its own, working, however, in a living way with the other. For the political system must destroy the economic life if it wants to take it over, and the economic system loses its forces of life when it becomes political. To these two members of the social organism must be added a third, completely independent and formed out of the possibilities of its own life. This member is all that is produced spiritually, in which the spiritual part of the two other spheres also have a share. The spiritual part must be given over to them by the third member that is provided with its own laws and administration, but this spiritual part cannot be governed nor influenced by the other spheres more than member organs of a whole organism are influenced by one another. Already today what has been said here to be necessary for the social organism can be quite scientifically substantiated and developed. Here there can only be given the guiding principles for all those who would follow up what is necessary. The establishment of the German Empire happened at a time when these necessities were first appearing to modern humanity. Its Government did not understand how to give the Empire a task through insight into these necessities. This insight would alone have given it the right inner structure, it would also have given its foreign policy a competent direction, and enabled the Germans to live in common understanding with other peoples. Insight must now ripen out of misfortune. We must develop the will for a social organism that is possible. It is not a Germany that no longer exists that should have to face the world outside, but a spiritual, political and economic system in its representatives must have the will to negotiate as independent delegations with those who have cast down that Germany which has been made into an impossible social form through the confusion of the three systems. One fancies one can hear the ‘practical men’ becoming eloquent over the complexity of what has been said and finding it troublesome even to think about the working together of three corporate members. This is because they have no wish to know of the real demands of life, preferring to fashion everything according to the easier demands of their own thinking. They must come to see that they must accommodate themselves in their thought to the claims of reality or they will have learnt nothing from misfortune and in what arises further, will go on repeating the past ad infinitum. While I was lecturing in Zurich, Basle and Berne, Herr Mott, Dr. Boos and. Herr Kühn were busy in Germany obtaining signatures for the Appeal. And in Austria others were similarly employed. So far, although it is only a short time since we began, we can be well satisfied with our progress. For we have an Appeal as well supported as the former unfortunate one. And in the lectures recently given in Zurich—held there because Switzerland is the pivot for the connections of the civilised world—my object was to show that here and there people were to be found whose understanding was ripening. Thus, naturally it was important to learn the results before the last Zurich lecture. By 11th February I could make the happy announcement that about a hundred names had been collected, exclusive of those in Switzerland and Vienna. The news came from Germany where our fiends had been working everywhere, in a suitable way, to make this thing a reality. At the same time I received the following telegram from Vienna: “By midday 11th, 73 signatures, more certain tomorrow”. And on the following day: “Total 93 signatures”. That could be announced from Vienna, and more signatures were reported later. Results so far have been satisfactory. What we need next will be to find among them a number of signatures of well-known personalities capable of making the Appeal public, so that it is seen by those it concerns. For in a case of this kind much depends upon this. It actually concerns everyone today. And it may indeed be said that in the subconscious of man's soul something is calling upon him to understand such an affair as this. As I have told you in the course of these lectures, the idea appearing in this form is no new one to me. At the time when this catastrophic war was taking a decisive turn, I tried to help, on this necessary impulse towards reality wherever it came to my notice. I have described to you how this took place. I told those who had to do with the matter that this is not just a programme, not just an ideal, but that it should be considered as something having evolutionary force for modern mankind, something that certainly will be made a reality in the next ten, twenty or thirty years. It is not a question whether it is realised but solely how it is realised. I said to many of these people: You now have the choice either of having recourse to reason and of bringing about something through that, or of undergoing cataclysms and revolutions. It did not take long for people to be convinced that this was no false prophecy. It is hard, however, for the easy-going man of today to find the way from a certain understanding to that courage in life which, in accordance with his situation, is necessary for him to carry on the matter into the realm of reality. Here in Switzerland, too, several signatures have already been obtained. We have always to consider here that in the first part of this Appeal something is said of the necessity for the German people to reflect about themselves and the errors in which they have been implicated. Thus, it has been said that it is impossible for the Swiss to give instructions across the frontier to the Germans. I do not believe that today we should still think like that. Before 1914 such things might have had a certain significance as old mummified thought, but now they have lost that significance. In these times the narrow-mindedness that comes from judging on national grounds must cease. The misfortunes of the last four-and-a-half years should have taught men this. Today even in Switzerland one should be able to think differently from the way one did four-and-a-half years ago. For here, too, something should have been learnt if thinking is to correspond to the picture we get by following the last four-and-a-half years with a little insight. They really appear like centuries which have been poured over mankind. And it seems most remarkable that people today have been willing to set up a new world-order, a new map of Europe, out of old national prejudices of a former age, or out of mummified thought, which really by 1914 should have come to an end. This map-building in Europe will be very quickly upset by other forces, the only ones with power at the present time and the only determining forces for what is called politics, that is, the social factors. For today all the rest is a mask. That, however, is the reality. The Europeans will very greatly deceive themselves if they form their judgments and criticisms out of ancient mummified, thinking. Of course the objection can be made—I myself could easily give you a whole catalogue of objections—that with this impulses are given to all the States; that this can only come to pass when all States make a beginning. No! One single so-called State can make a beginning; it is indeed so, one single State can begin. And the beginning once made, the State will have done something for all mankind. It is indeed a misfortune for the German people that its Empire should have been set up at the start of more modern history, when at the time of its foundation the necessity already existed for the Empire to be given this as its task. And because the Empire did not accept this task it has never been understood why it should have any place in the world. Had it undertaken the task everything would have happened differently, for then men would have had before their very eyes the conditions of their existence and seen this existence justified. Today people make their decisions out of mummified thoughts. There are many in Europe who cannot free themselves from mummified thinking and today regard the world-famous personality, Wilson, as a savior—perhaps out of some fear, it is difficult to express it. Nevertheless, if people should think without condemning Wilson, and put their question on a basis of fact, they must ask themselves why he has become such an influential man in his own country. This is because he is against all other Parties, and out of sound American instinct has carried out a policy utterly opposed to that of a great part of Europe. A great part of Europe wants to steer towards a community, the politics of a social community, in which the individual forces of liberty will go under. Wilson owes his election and his influence entirely to the circumstance that as an American democrat he has contributed to the release of the individual forces in economic life. Let us suppose that Europe realised the ideal of Bolshevism, the ideal of the Berne social democracy, which means the social democracy of the Socialist Congress. What would be the consequence should these people achieve what they are dreaming of? Europe would take on a form so that despite every national prejudice all free forces would of necessity flood over into free America, where Wilson has become great by means of his opposite policy. Between Europe and America terrible competition would have to arise, making it impossible for anything to happen but pauperism in Europe and wealth in America—not from any injustice but out of the foolishness of European social politics. That would be the shape of things if Europeans do not, in accordance with their task, interpret and bring to realisation the social forces so that they meet the demands of a healthy social organism. In this Appeal we have not to do with something merely thought out, but we are indicating forces everywhere present in what is reality, forces that must be brought to realisation, without which the fate not only of Germany and Austria but of all Europe can be simply a fall into poverty, suffering and alienation. from the spirit. We are living in serious times from which we cannot escape by trivial thinking. In men there lives something that attracts them to what is said in this Appeal, something that can already be observed. Because this is so, because one can hope to find the way to the hearts and souls of men, we are seeking now to reorganise what, as I said, was a necessary form to be sought during the catastrophe of the war, into the form necessary for present-day conditions. I only hope no one thinks that this kind of Appeal has a significance that is absolute. I spoke of this to someone—concerned with it later—in January, 1918, as it was then drafted, and ended by saying: This can of course take on many different forms according to the different conditions prevailing at the time. It has nothing to do with a theory, nor a programme, nor an ideal, but with what has been thought out of reality. I said further that because the thought comes out of reality, for me it is nothing Utopian. Utopians who set up their programmes imagine everything to be bad that is not carried out according to their plan. It does not strike me at all in this way. It may happen, for example, that such a matter touches men's souls, and because they consider it practical they begin to put it into practice. And today it can be said quite clearly that a beginning has been made to put it into a practical form, suitable for life everywhere. I can quite well imagine that nothing may remain of all I have said here and in the lectures in Zurich, Berne and Basle, but that everything will take on a different form. For anyone who thinks in realities it is not a matter of his forms and phrases being put into practice, but that they should somewhere be laid hold of by reality. Then it will soon be seen what becomes of it. Perhaps it will go another way, there is always that possibility, but it is certain that the result must be in conformity with the conditions. For it is not any abstract ideal, any programme striven for, but simply a seizing hold of the forces of reality. What we are concerned with here should be as far removed as possible from all fantasy, from all dogmatising. Therefore I was much astonished when a well-known personality, whose signature one of the three friends mentioned above had undertaken to procure, let it be known that he would have thought, in making the appeal, I should have addressed it more to men's spirit, and went on to say that mankind's salvation could only come by their finding the way back to the Spirit. Thus people want one always to be repeating spirit, spirit, spirit! But that is not what is of importance; what matters is that the Spirit should be shown and proved able really to give form to the facts. They are fundamentally dangerous who keep on speaking of the spirit without giving any indication of its reality; for they refer to it simply in the sense of an ideology. We have reason to be thankful that in the midst of our society personalities have been found with understanding, active understanding, at what is aimed at here, so that they will also actually do something. One hears constant echoes of this. Our friend, Dr. Boos, after in my last lecture in Zurich I had referred to the results of our Appeal, issued an appeal on his own account that, from among the audience, people willing to take a practical part in this matter should come forward and give their addresses. The result of that evening, too, was extraordinarily satisfying. There were of course objections but I could well understand them. They were, however, of a nature to make one see that men today do not take their stand upon reality, they are carried away by enthusiasm. And this applies precisely to those considered the most practical. Hence, at Zurich, in a lecture when speaking of enthusiasts, I gave General Ludendorf as a good modern example. That is the type, the representative, of an enthusiast, a man who may be good or bad, but to my thinking bad at understanding strategy, and in regard to everything else remote from life and all reality, having no idea of the conditions of the reality in which he should have been active. He was an abstract idealist in a way that only a socialistic utopian can be. One should pay good heed to this insane concept of the ‘practical man’ which has done such harm to mankind. This being practical, up to now in such favour, is nothing but enthusiasm carried into actual fact through brutality, an unrealistic way of thinking, and it is above all this that must vanish. What has to come must be created spiritually, and the bearer of this will be the Anthroposophical Movement. This is what I wanted to tell you on this eventful evening of our Lecture Cycle, as something that has proceeded out of the inner being of our movement. Notes: 1. Lecture of December 31, 1981 not translated |
| 296. Education as a Social Problem: The Inexpressible Name, Spirits of Space and Time, Conquering Egotism
17 Aug 1919, Dornach Translated by Lisa D. Monges, Doris M. Bugbey Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| We could tell this repeatedly to Europeans, yet they will not believe that in English-American countries there really exist societies in which the attempt is made to find out through questions cleverly put to mediums what the great goals of mankind are. |
| We must feel ourselves influenced by the working together of our anthroposophical and our social movement. I should like you to comprehend more and more why it is that the anthroposophically oriented science of the spirit must flow into the souls of men if anything is to be achieved in the social field. |
| Saying to oneself, “It is true nevertheless,”—saying it so earnestly that it fills one's whole soul, this needs the inner courage we must have. May it permeate us as anthroposophical substance. Then we shall do what we have to do, everyone at the place where he is. This I wanted to say to you today. |
| 296. Education as a Social Problem: The Inexpressible Name, Spirits of Space and Time, Conquering Egotism
17 Aug 1919, Dornach Translated by Lisa D. Monges, Doris M. Bugbey Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
What I said yesterday about the path of the human intellect toward the future, rests upon definite facts that can be brought to light through spiritual-scientific knowledge. Today we shall deal with some of these facts. You must be conscious in a practical way, I might say, of the following. When a man confronts you, he is that being we speak about in spiritual science. That is to say, above everything we must always be aware that he is a four-membered being, as you know from my book Theosophy. We have before us the ego, the astral body, ether body, and physical body. The fact that every time a person stands before us we are confronted by these four members of the human entity, brings it about that ordinary human perception does not know what it faces in man. Ordinarily one thinks: “What I see before me, filling space, is the physical body.” But what is physical in it we would not see as we usually see it if it were to confront us merely as physical body. We see it as it usually is today only because it is permeated by the ether body, the astral body, and ego. Strange as it may sound, that which is the physical body proper is a corpse, even during our lifetime. When we are confronted by a human corpse we are actually confronted by the physical body. In the corpse we have physical man not permeated by ether and astral body and ego. It is forsaken by them and shows its true nature. You do not visualize yourself properly if you believe you carry what you consider to be the physical body of man with you through space. A more correct view would be if you thought of yourself as a corpse with your ego, astral and etheric bodies carrying this corpse through space. A consciousness of the true nature of man's being becomes more and more important for our age. For the conditions existing in the present cycle of mankind's evolution were not the same in earlier periods. What I am now relating cannot be ascertained by outer physical science, but spiritual-scientific cognition does observe these facts. As you know, the fourth post Atlantean age begins in the eighth century B.C.; further back we come to the Egypto-Chaldean period. At that time human bodies had a constitution different from that of today. Those you find now in the museum as mummies had a much more delicate constitution than present-day human bodies. They were much more permeated by the plant element; they were not so completely corpse as is the modern human body. As physical bodies they were akin to plant nature, whereas the present-day physical body, since the Greco-Latin age, is akin to the mineral world. If through some cosmic miracle the bodies of that ancient population were to be bestowed upon us, we would all be ill. We would carry proliferating growths in our body. Many a disease consists in the fact that the human body atavistically returns to conditions that were the normal ones in the Egypto-Chaldean age. Today we find tumorous formations in the body which are caused by the fact that a part of this or that person's body develops the tendency to become what the whole body was for the ancient Egypto-Chaldean population. This is closely connected with human evolution. We as modern men carry a corpse in our body. The ancient Egyptian carried as his body something of a plant-like nature. The result was that his knowledge was different from ours, his intelligence acted differently. What do we know through our science that we are so proud of? Only that which is dead. Science shows that life cannot be grasped with ordinary intelligence. To be sure, certain research scientists believe that if they continue with their chemical experiments the moment will come when they will be able, through complicated combinations of atoms, molecules, and their interactions, to know the processes of life. This moment will never come. On the chemico-physical path one will only be able to grasp the minerally dead; that is to say, one will only grasp that aspect of the living which is a corpse. Yet, what in man is intelligent and gains knowledge is nevertheless this physical body, this corpse. What then does this corpse do as we carry it about? It achieves most in a knowledge of mathematics and geometry. Everything is transparent there. The further we move from the mathematical-geometrical the more un-transparent do matters become. The reason for this is that the human corpse is the real knower today; the dead can only recognize the dead. Today what the ether body is, the astral body, the ego, does not think in man; it remains in obscurity. If the ether body would be able to know in the same way that the physical body knows the dead, it would know the life of the plant world. This was the peculiar thing with the Egyptian, that with his plant-like, living body he had knowledge of the plant world in a way quite different from ours. Much instinctive knowledge of the plant world can be traced back to what was embodied in Egyptian culture through their instinctively knowing consciousness. Even what is known today in botany about substances for medicinal use comes often from traditions originating in ancient Egyptian wisdom. You know how a number of so-called lodges, not founded on genuine fundamentals, call themselves Egyptian lodges. That is because they refer back to Egypt if they want to impart certain knowledge—which, however, is no longer very valuable. In these circles there still live certain traditions stemming from the wisdom which could be had through the Egyptian body. One can say, as humanity gradually progresses into the Greco-Latin period the living, human plant-body gradually died out. We carry an extremely dead body in us; especially is this true for the head. The science of the initiates perceives the human head as a corpse, as something continually dying. More and more will humanity become conscious of the fact that its vehicle for knowledge is a corpse; that it therefore knows only what is dead. For this reason, the further we go into the future the more intensively will we feel a longing to know what is living. But the living will not be known through ordinary intelligence bound to the corpse. Much will be needed to make it possible for man again to penetrate the world in a living way. We must know today what it is that man has lost. When he passed over from the Atlantean to the post Atlantean age there was much he could not do that he can do today. Since a certain time in your childhood you are able to say “I” in referring to yourself. You may say it without any great respect. But in former ages of mankind's evolution this “I” was not referred to with so little respect. There were times, prior to the Egyptian age, when a name for “I” was used which, when pronounced, stupefied a person. Pronouncing it, therefore, was avoided. If people right after the Atlantean epoch had experienced the pronouncing of the name for “I”—at that time it was only known to the initiates—the whole congregation would have fainted, so powerful was the effect of uttering this name for “I.” An echo of this fact lingered with the ancient Hebrews who spoke of the unutterable name of the Deity in the soul; a word which only the initiates were permitted to speak, or that was expressed before the congregation in a kind of eurythmy. The ineffable name of God had its origin in what I have just told you. Gradually this fact was lost, and the deep effect of such practices diminished. In the first post-Atlantean epoch a deep effect in the ego; in the second epoch a deep effect in the astral body; in the third epoch a deep effect in the ether body, but the effect was bearable—an effect which, as I stated yesterday, brought men into connection with the cosmos. Today we can say “I”—we can say anything—without its having a deep effect upon us, because we grasp the world with our corpse. That is to say, we grasp what is dead, what is mineral in the world. But we must arouse ourselves to rise again to those regions in which we can take hold of the living. Whereas the Greco-Latin period created more and more dead knowledge for the corpse, in our time intelligence follows the path I mentioned yesterday. We must, therefore, resist mere intelligence; we must add something to it. It is in the nature of our time that we have to retrace the path of development, so that in the fifth post-Atlantean period we learn to know the plant, in the sixth period the animal, and in the seventh the truly human. Thus, it will be our present task to pass beyond a knowledge of the mineral and learn to know the plant element. Now after realizing this, ask yourself who is the person who exemplifies this search for plant knowledge. It is Goethe. Contrary to the preoccupation of all outer science with what is dead, he occupied himself with the life, the growth, the metamorphosis of plants. Thus, he was the man of the fifth post-Atlantean period in its elementary beginnings. In his small treatise of the year 1790, An Attempt to Explain the Metamorphosis of Plants, you will see how Goethe tries to comprehend the plant from leaf to leaf as something developing, unfolding, not as something completed, dead. That is the beginning of the knowledge that should be sought in the fifth post-Atlantean epoch. In Goetheanism we have the keynote for this. Science will have to wake up in the Goethean sense, will have to pass from the dead to the living. This is what is meant when I say again and again that we must acquire the ability to leave behind the dead, abstract concepts and arrive at those that are living and concrete. What I said two days ago and yesterday is basically the way to these living, concrete concepts. It will not be possible to enter into these concepts and ideas if we are not ready to develop our general world view and concept of life as a unity. Through the special con-figuration of our culture we are forced to let the various currents of our world view run side by side in a disorganized fashion. Just think how man's religious view of the world and his scientific view often run parallel, completely disconnected. He builds no bridge between the two; in-deed, he is afraid of doing so. We must make it clear that this state of affairs cannot continue. I have drawn your attention to the egotistical way man forms his world view at the present time. I have described how men today are chiefly interested in the life of the soul after death. This interest springs from pure egotism. I have said we must pass on to interest in the life of the soul from birth onward, seeing it as a continuation of the life prior to birth. If we were to observe the child's growth into the world as a continuation of his pre-natal existence, with the same concern we feel for his soul after death, our thinking about the world would be much less egotistical than it is today. But this egotism in our world view is connected with many other things. Here I come to a point where men today must become ever more clear about underlying facts. In the period of time culminating in our age the egotistic element was chiefly developed. The ego has permeated man's viewing of the world; it has also permeated his will. We must not deceive ourselves about that. The religious denominations in particular have become egotistical. This you can see even in externalities. Just consider how modern preachers have to reckon with people's egotism. The more they make promises concerning the life of the soul after death the more they reach their goal. People today have little interest in other spiritual questions; in, for instance, that creative flow of life which shows itself so wonderfully after birth in the soul that previously was in the spiritual world. A result of this lack of interest is the way man thinks about the Divine in the various religious denominations. The fact that we visualize a God as The Highest has no special meaning. Here it is essential that we free ourselves from deception. What do most people mean today if they say “God?“ What kind of being do people refer to when they speak of God? It is an Angel; nothing else but their own Angel whom they call God. People have just a bare intimation that a protective spirit guides their life; they look up to him and call him their God. This is the egotism of the churches, that they do not pass beyond the Angel with their concept of God. A narrowing of interests is caused by egotism; and this narrowing of interests is to be clearly seen in public life. Do people today ask about the general destiny of man-kind? Oh! it is often very sad if one wants to speak to people about human destiny. No one has any idea of the degree of change that has taken place in this respect in a comparatively short time. Today we may say to people: The military conflict that has spread over the earth during the last four or five years will be followed by the mightiest spiritual battle, which will cover the earth in a form never experienced before. Its origin lies in the fact of the Occident naming as illusion or ideology what the Orient calls reality, and the Orient feeling as reality what the Occident calls ideology. We may draw people's attention to this weighty matter and it does not even dawn on them that if something similar had been said only a hundred years ago it would have so taken hold of people's souls that they would never have gotten over it. This change in humanity, this growing indifference to the great questions of destiny, is the most striking phenomenon. Everything bounces off mankind, so to say. The most comprehensive, incisive facts are accepted like a sensation. People are not deeply shaken by them. The reason for this is the clever, ever increasing egotism that constricts men's interests. We may have whatever fine democracies where men meet in parliaments, but concern for the fate of man-kind does not permeate them, because the people who are elected to these parliaments do not feel the urgency to know mankind's destiny. Egotistical interests hold sway. Every-one has his own egotistical interest. Similarities in outer interests such as often arise from one's profession, lead people to form groups. When the groups are large enough, majorities arise. In this way a concern not for human destinies but only for egotism, multiplied by the number of persons involved, becomes active in parliaments and men's proposals. Because of the way egotism lives in people now, even their religious professions are under its influence. They will have their necessary renewal if people's interests broaden; that is, if men will again look beyond their personal destiny to the destiny of mankind; if they will be deeply moved when one tells them that in the West a culture develops that is different from that of the East, and that the culture of the Middle is again different from that of both East and West. Or if one tells them that in the West the great goals of mankind are sought, when they are sought, through the use of mediums who are put into a trance and are thereby consciously brought into a sub-earthly relationship to the spiritual worlds, out of which they speak of great historical aims. We could tell this repeatedly to Europeans, yet they will not believe that in English-American countries there really exist societies in which the attempt is made to find out through questions cleverly put to mediums what the great goals of mankind are. People likewise do not believe that the Oriental obtains knowledge about the destiny of mankind not through mediums but on the mystical path. In the beautiful speeches of Rabindranath Tagore, easily available today, you can read what the Oriental thinks on a grand scale about the goals of mankind. These speeches are read as one reads the feature articles of any hack journalist; because today people distinguish little between a journalistic hack and persons of great spirituality like Rabindranath Tagore. They are not aware, I might say, that different racial substances can live side by side. What is valid for Middle Europe I have put forward in public lectures for many years. It was not received as it should have been. With this I only wish to point out that one may become aware of something that reaches beyond the egotistical fate of a man and is connected with the destiny of groups of men, so that we can make specific differentiations across the face of the earth. If one lifts his view toward comprehending human destiny in mankind as a whole, if one concerns himself intensely with what thus passes beyond personal destiny, then one tunes his soul to comprehending a higher reality than the Angel; actually, that of the Archangel. Thoughts concerning the significance of an Archangel do not arise in one's soul if one remains in the regions concerned with egotistical man. Preachers may talk ever so much about the Divine; if they only preach within the confines of egotistical man they speak merely of the Angel. Calling it by a different name is just an untruth; it does not put the matter straight. Only if one begins to be interested in man's destiny as a unity over the whole earth does his soul begin to elevate itself to the Archangel. Now let us pass on to something else. Let us feel what I have indicated in these lectures about the successive impulses of mankind's evolution. You will find that most of our leading citizens were educated in the classical schools—Gymnasium—during the years when the soul is pliable and flexible. These classical schools were not born out of the culture of our age but of the Greco-Latin age. If those Greeks and Romans had done what we did, they would have established Egypto-Chaldean classical schools. They didn't do that; they took the subjects for their teaching from immediate life. We take them from the previous period and educate people accordingly. This is very significant, but we haven't recognized it. Had we done so a note would have sounded within the feminist movement that did not resound, and that is: Men, if their intelligence is to be specially trained, are sent into antiquated schools. There their brains become hardened. Women have the good fortune of not being admitted into the classical schools. We want to develop our intelligence in an original way; we want to show what can be developed in the present age if we are not made dull in our youth by Greco-Latin classical education. These words did not resound, but in their place: Men have crept into and hidden under the Greco-Latin classical education, let us women do the same. Let us also become students of the classical schools. So little has understanding spread for what is necessary! We must realize that in our present time we are not educated for our age but for the Greco-Latin culture. This is inserted into our lives. We must sense it. We must sense what, as Greco-Latin culture, acts in the leading people of today, in the so-called intellectuals. This is one aspect of what we carry within us in our spiritual education. We read no newspaper that does not contain Greco-Latin education; because, although writing in our national idiom, we actually write in the Greco-Latin form. And in regard to our concept of rights we live in Romanism, again something antiquated. To be sure, the old national rights battle at times against Roman law, but they do not prevail. We must feel how a time that has passed lives in what man calls right and wrong in public life. Only in economic life do we live in the present. This is a significant statement. Perhaps I may say in passing that many women use the concepts of the present in their cooking, in managing their households. In doing so they actually are the people of the present age; everything else that is carried into the present is antiquated. I do not present this matter of their cooking as something particularly desirable, but the other aspect is much less desirable, namely, that the souls of women also want to go back from the present to antiquated cultures. In looking upon our cultural surroundings we have not only what acts in space but also the effects of bygone eras. If we acquire a feeling for this, not only the past affects us but the future as well. It is our task to let the future work into us. Because, if there did not live in every person, however slightly aware of it, a kind of rebellion against the Hellenism of education and the Romanism of rights, if the future were not to ray in upon us, we would be pathetic creatures, really very pathetic creatures. Besides space we must also consider time in our culture; that is to say, what as history reaches over into our present from the past and from the future. We, as people of the present, must realize that past and future play into our souls. Just as America, England, Asia, China, India—the East and the West as two opposites—have their effect upon us as Europeans, so do we carry Greece, Rome, and the future in us. If we are willing to focus our attention on the future by becoming aware of how what is past and what is coming into being live in our souls, then another attitude arises in us concerning human destiny, an attitude that transcends egotism and is different from what is aroused by a merely spatial consideration. Only if we develop this soul attitude is it possible for us to form concepts about the sphere of the Time Spirits, the Archai. That is to say, we come to the third rank of divine beings in the order of the Hierarchies. It is good if man by such means places before himself these three Hierarchies in concepts and ideas, because the Spirits of Form who come next are much harder to comprehend. But it suffices for modern man if he attempts to penetrate beyond egotism into the sphere of the unegotistic, doing this repeatedly, and occupying himself with what I have just explained. I must emphasize again, that especially the training of teachers should make use of these facts. A teacher should not be permitted to instruct and educate without having acquired an idea of the egotism that strives toward the closest God, the Angel; without also having acquired a concept of the unegotistic, destiny-determining powers who are side by side in space above the earth, the Archangel beings; and without having acquired a concept of how past and future reach over into our culture, the Roman life of rights, the Greek spiritual substance, and the undefined rebel of the future, which saves us. Mankind at present has little inclination to enter into these matters. Some time ago I repeatedly emphasized that it is one of our social tasks to derive from the present our educational subjects to be used during the time spent today in classical schools. To do as the Greeks themselves did, namely, take the subjects for education from present-day life. Shortly after the time, and in the same place where I had spoken about the social importance of this problem (I do not wish to imply a causal connection, but the matter has symptomatic meaning) there appeared in all the news-papers in that place a number of advertisements propagandizing the modern classical schools. I had delivered lectures characterizing classical education in the way I have done here. The advertisements declared what the German nation owes to the classical education of its youth, for “strengthening the national consciousness,” “the national power,” and so on. This was a few weeks before the Treaty of Versailles. These advertisements were signed by a variety of local figures from the schools and the department of education. What has to be brought out today as to the factual basis of mankind's evolution, is rejected. People let it bounce off; it does not touch the depths of the soul. For this reason, it is so difficult to be active in the social sphere. One will never be able to take hold of the social question with the superficialities employed today. It is a deeply significant question that cannot be grasped if one will not look deeply into the nature of man and the world. Because this is so it should be evident how important are certain proposals offered by the threefold social order. We must acquire an organ for what is necessary for our age, and it is difficult to acquire this organ in the spiritual sphere. For an education that has gradually been taken over by the State has deprived man of active striving; it has made him into a devoted member of the State structure. How do the majority of people live? Up to the sixth year of age man may live unhindered because the State does not yet consider him sanitary enough. The State would not like to devote itself to the tasks that have to be carried out in the first childhood years. Man is still left to the powers outside the State. But then it lays claim to him and he is trained to fit the pattern of the State; he ceases to be a person and bears the stamp of the State. He strives to fit this pattern because it is instilled in him. He not only gets his keep from the State while he works but beyond the working age up to his death, in the form of a pension. It is the ideal of many people today to have a position that entitles them to a pension. The soul too becomes entitled to a pension, even beyond death, without any effort on its part, because it receives eternal bliss through the activity of the church. The church sees to that. Now it is very uncomfortable to hear that salvation lies in free spiritual striving which must be independent of the State. The State must only serve civil rights, where there will be no claim to a pension. This is reason enough for many to reject it, as we have occasion to notice again and again. Concerning the most intimate spiritual life, the religious life, the world of the future will demand of man that he work for his immortality; that he let his soul be active so that it may receive into itself, through activity, the Divine, the Christ-impulse. In the course of my life I have received many letters from church people who state that anthroposophy is fundamentally a fine thing, but it contradicts the simple Christian faith; that Christ has redeemed the soul, that one can attain salvation in Christ without any effort on one's part. People cannot let go of the “simple belief in the attainment of salvation through Christ.” They believe themselves to be especially pious if they say or write something like that. But they are egotistical, extremely egotistical. They want to be passive in their souls and let it be the concern of the Divine to transport the soul, nicely pensioned, through the portal of death. Matters are not so easy in that world conception in which, in future, the religious element must be created. Here one must understand that the presence of the Divine in the soul must be worked for. One will no longer be able just to surrender passively to the churches, which promise to carry the souls into the beyond. (The involvement of money for such service, a scandal in the past, has now fallen into disuse, but secretly it still plays a role in this process, also in obtaining special blessings.) But the transition to inner activity is what is needed for mankind, something it doesn't yet cherish very much. In order to gain a feeling for what is necessary in this regard we must keep in mind, first, the metamorphosis of humanity since the time of ancient Egypt when the body was more of a plant-like nature. Should there be a relapse into that state in the present age, man would become sick and develop tumors and such things. Secondly, the fact that we carry our body as a corpse which can think, can under-stand. In this way we gain a feeling for what mankind needs, which is, to advance in the solving of social problems in the way this has to be done in the present time. We must no longer allow ourselves to consider such a matter as the social question as being utterly simple. You see, this is what is so difficult at present: That people would like to be enlightened on the most important aspects of life by a few abstract statements. If a book like The Threefold Social Order contains more than a few abstract statements, if it contains the results of an observation of life, then people say they do not understand it. They consider it confusing. But this is the misfortune at present, that people do not wish to enter into what precisely they ought to enter into. For abstract sentences, completely lucid, refer to what is dead; the social element, however, ought to be alive. Here we must employ flexible ideas, flexible sentences, flexible forms. Therefore, it is necessary that we not only reflect upon the transformation of single institutions, but that we really adjust ourselves to a genuine transformation in our thinking and learning, down to their innermost structure. This is what I would like to leave with you today when I have to leave again for a few weeks. We must feel ourselves influenced by the working together of our anthroposophical and our social movement. I should like you to comprehend more and more why it is that the anthroposophically oriented science of the spirit must flow into the souls of men if anything is to be achieved in the social field. And I would bring close to your hearts what I have said repeatedly in various ways: It is of utmost importance to acknowledge that what we can acquire of anthroposophical knowledge is the true guide-line now for all action and striving; that we must have the courage to will to prevail with anthroposophy. The worst thing is that people in these days have so little courage for willing to prevail with what is needed. They permit their best will-forces to break down; though it is so necessary they do not will to carry through. Learn to represent anthroposophy with courage. Receive graciously the people who show an interest in looking at this building which represents our spiritual striving. Rejoice in every single individual who shows even a little understanding. Meet with him. But do not take it to heart if your efforts are fruitless, and people meet our activities with evil intention, or, what is more frequent, with lack of understanding. Just resist it suitably. It is courage that is needed to bring our efforts through to good results. Let us think of ourselves as the handful of people whose destiny it is to know and to communicate to the world what it so sorely needs today. Let the people ridicule us and say that it is presumption to believe all this. It is true nevertheless. Saying to oneself, “It is true nevertheless,”—saying it so earnestly that it fills one's whole soul, this needs the inner courage we must have. May it permeate us as anthroposophical substance. Then we shall do what we have to do, everyone at the place where he is. This I wanted to say to you today. We are longing for the day when our activity through this building brings us closer to the outside world; our activity which in any case is very difficult. This building is the only one that takes into account the great destinies of mankind even in its forms, and it is very gratifying to see that attention is being paid to it. Something else, however, is necessary for favorable progress in social problems, and that is, that this building through its very forms, which are stronger than other modern architectural forms, should aid in the strengthening of humanity's spiritual powers; making men more amenable to what one wishes them to know, so that they may rise not only to the nature of the Angel, but to the Archangel, and to the Spirit of the Time. With these words I take leave of you for a few weeks. I hope to be able then to continue these considerations, and that during this time we shall come into an intensive activity for our building itself. Because, my dear friends, we are justified in emphasizing on every hand that readiness for work, that joy in work is needed for all men. This will not come if people are not moved by great purposes. I believe that if people can be convinced that through the three-folding of the social organism they can attain an existence worthy of man, they will begin to work again. Otherwise they will continue to strike. For in the field of physical labor people need an impulse that takes hold of them in their inmost souls. But we must show that our work has been fruitful in attaining at least one objective, and this radiates into the world. Only then can we give the impulse to mankind to overcome spiritually what is dead in our time. Let us think this over, my dear friends, until the time when we are together again and can speak further about these questions. |
| 265. The History of the Esoteric School 1904–1914, Volume Two: Jakin and Boaz or the Pillars of Hercules
N/A Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| Thus you see how what these symbols, the two columns, mean, is directly related to the ideals and goals of the Rosicrucian student. In some esoteric societies, these two columns are also erected. The esotericist will always associate the meaning that has been attached to them. |
| All the interpretations given in public writings or in certain societies remain only a superficial exoteric interpretation. Nevertheless, such an interpretation will be used here because it sheds light on the significance of the columns in cultural history. |
| In the lecture in Dornach on December 29, 1918, it is pointed out that the columns in today's secret societies can no longer be set up in the right way, nor should they be set up, because the right way to set them up only becomes apparent in a truly inwardly experienced initiation. |
| 265. The History of the Esoteric School 1904–1914, Volume Two: Jakin and Boaz or the Pillars of Hercules
N/A Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
The meaning of the two columns was always explained through the Golden Legend or the Legend of the Wood of the Cross (first mentioned in the lecture Berlin, 29 May 1905). For this reason, the Golden Legend and the explanations given about it are included here. The Golden LegendText from Rudolf Steiner's original manuscript Adam had two sons Cain = the self-seeking human Abel = the revelation-seeking human Abel fell because of Cain's actions. Abel's inheritance went to Seth. Seth reached the entrance to Paradise. There he was not held back by the cherub with the flaming sword. This is the symbol that Seth was the progenitor of the initiated priesthood. The cherub now gave him three seeds (the higher man = atma - budhi - manas). After Adam had died, Seth placed the three seeds in Adam's mouth as instructed by the cherub. The bush that grew from it had within itself the writing in fire. Ehjeh - ascher - Ehjeh (I-am-I) Moses took from it the three-part branch from which he formed his staff. David planted this rod in the ground on Mount Zion. Solomon took the wood from it to make the entrance gate of the temple  Only the pure could pass through there. The Levites, in their folly, immersed these three pieces in the pool of Bethesda. At the time of Christ, the Jews laid the wood as beams across the Kidron Valley. Christ walked across this after his nocturnal arrest on the Mount of Olives. And the cross was also made from this wood. Text from Marie Steiner's original manuscript Adam had two sons: Cain, the representative of humanity that works in self-awareness, and Abel, the representative of that humanity that receives all its gifts as a higher gift and revelation. Self-awareness must pass through guilt. Cain kills Abel. Abel's gifts pass to Seth. When Seth had re-entered paradise after the double fall of man (Eve and Cain), he saw how the tree of knowledge and the tree of life had united. The tree of knowledge means human knowledge. The tree of life means God-revealed wisdom. The cherub with the flaming sword now gave Seth three seeds; in them were all the seeds of the united trees. After Adam's death, Seth placed the three seeds in his mouth; a bush grew from them and in the middle of it was the “name of God”: Ehjeh ascher ehjeh = I am I. Moses formed his staff from the bush. This rod was eternally greening and was later kept in the Ark of the Covenant. David planted the rod in the ground near Zion; Solomon made three columns from its wood. These are: Jakin, Boaz and M. The Levites took the columns and threw them into the pool of Bethesda. At the time of Christ, the columns were removed from the pool and laid in the form of a bridge over the Kedron stream. Jesus crossed this bridge to the Mount of Olives. Then his cross was made out of it. Notes on the Golden Legend Since only a few notes from instruction hours have been handed down, those given during the Munich Congress at Pentecost 1907 on the two columns set up there will be reproduced first. From a lecture in Munich, May 21, 1907. What do the two columns mean to the Rosicrucians? If one wants to explain these two columns, which are standing here before us, one must start from the so-called Golden Legend. This says: When Seth, the son of Adam - who had taken the place of Abel - was ready, he was allowed to gain an insight into Paradise, he was allowed to pass the angel with the sword whirling in the fire, into the place from which man had been expelled. Then Seth saw something very special. He saw how the two trees, the tree of life and the tree of knowledge, entwined each other. From these two entwined trees, Seth got three seeds, took them with him and put them in the mouth of his father Adam when he had died. From the grave of Adam then grew a mighty tree. This tree appeared to some who had psychic senses, as if it were aglow with fire, and this fire coiled itself for him who could see into the letters B, the first letters of two words that I am not authorized to pronounce here, but the meaning of which is: “I am who was there; I am who is there; I am who will be there.” This tree divided into three parts. Seth took wood from it, and it was used in many ways in the evolution of the world. A staff was made from it; the magic wand of Moses, legend says. It was the same wood that was used to form the beams of Solomon's Temple. There they remained as long as men comprehended the ancient secrets. Then the wood was thrown into a pool wherein, at certain seasons, the lame were made whole, and the blind received their sight. After it was taken out again, it formed the bridge over which the Redeemer passed as he made his way to the cross. And at last, so the legend goes, the cross itself, on which the Savior hung, was fashioned out of the wood of this tree, which had grown out of Adam's mouth after the seeds of the entwined trees of life and knowledge had been placed in his mouth. This legend has a deep symbolic meaning. Remember the process, the transformation that the disciple must think of when he goes through the fourth stage of the Rosicrucian training: the production of the Philosopher's Stone. We remember that it has to do with a certain treatment of our red blood. Let us think of the significance of this red blood, not only because Goethe's saying “Blood is a very special juice” points this out to us, but because occultism has taught it at all times. The way this red blood appears is a result of breathing oxygen. We can only briefly point this out. When we are now referred to such an important moment in the legend and in the Bible, to the re-entry of Seth into Paradise, we must remember how man was brought out of Paradise. Man was driven out of Paradise, his ancient state in the bosom of the higher spiritual world, by the following event, which is already hinted at in the Bible as the physical process that goes hand in hand with the descent. Those who want to understand the Bible must learn to take it literally. It says: “God breathed into the man the breath of life, and he became a living soul.” This breathing of the breath was a process that is expressed here in pictorial terms and that extended over millions of years. What does it mean? In the development of mankind, in the formation of the physical body, there were times when there were no lungs in the human body, so that oxygen could not yet be inhaled. There were times when man more or less floated in liquid elements, when he had an organ, a kind of swim bladder, from which the lungs later developed. This swim bladder from the past has been transformed into the lungs, and we can follow the process of transformation. When we do this, it shows itself to be the process that the Bible expresses with the image: “And God breathed into the man the breath of life, and the man became a living soul.” It was only with this breathing in of the breath that the production of red blood became possible. Thus, the descent of man is connected with the production of the red blood tree in his interior. Imagine a man standing before you, and you could only follow the trickling of the red blood: you would have before you a living red tree. Of this the Christian esoteric says: It is the Tree of Knowledge. Man has usurped it, he has enjoyed the red blood tree. The establishment of the red blood tree, which is the true tree of knowledge: that is sin. And God drove man out of the Garden of Eden, lest he should enjoy also of the Tree of Life. We have another tree in us, which you can just as easily imagine as the former. But it has red-blue blood. This blood is a substance of death. The red-blue tree was implanted in man at the same time as the other. When man rested in the bosom of the Godhead, the Deity in him was capable of intertwining what his life and knowledge mean. And in the future lies the point in time when man, through his expanded consciousness, will be able to transform the blue blood into the red; then within himself will be the source for the blue blood tree to be a tree of life. Today it is a tree of death. Thus in this picture there is a looking back and a looking forward! You see that in man a red blood tree and a red-blue blood tree are entwined. The red blood expresses the I, it is the lower part of the knowledge of the I. The blue blood expresses death. As a punishment, the blue blood tree, the tree of death, was added to the red tree of knowledge. In the distant future, this Tree of Death will be transformed into the Tree of Life, just as it was originally a Tree of Life. If you form a mental image of the human being standing before you, you will see that their entire life is based on the interaction of these two trees. 1 The fact that Seth was allowed to enter Paradise again means that he was an initiate and was allowed to look back to the divine-spiritual state where the two trees were entwined. And he put three seeds of the entwined trees into Adam's mouth, from which a tree divided into three arose. This means that the tree that grows out of man, Manas, Budhi, Atma, these three parts that make up the upper part of man, are found in him by nature. The legend thus indicates how the trinity of the divine is already in Adam in his human nature, how it grows out of him and how it is initially seen only by the initiate. Man must go his path of development. All the things that have taken place in the development of mankind and that lead to initiation are further expressed to us in the legend. From the realization that the threefold tree rests within us, the tree of the eternal, which expresses itself in the words: “I am that was – I am that is – I am that will be!” we gain the power that moves us forward and gives us the magic wand. Hence Moses' magic wand; hence the wood of the tree growing out of the seed is taken to the temple of wisdom; hence the cross is hewn out of it, that sign of initiation which signifies the overcoming of the lower limbs in man by the three higher ones. Thus this legend shows how the initiate looks forward to a future state in which the tree of knowledge - the red blood tree - and the tree of life - the blue-red blood tree - will be entwined, where they will intertwine in man himself. Now, he who wishes to develop inscribes in his heart what the two columns - the red column on the one hand, suggesting the red blood column; the blue-red, suggesting the blue blood column - want to tell us. Today, both are separate. Therefore, in the hall, the red column stands on the left and the blue-red column on the right. They want to challenge us to overcome the present state of humanity, to direct our path to the point where, through our expanded consciousness, they will intertwine in a way that is called: J-B. The red column is designated J, the blue-red column B. The sayings on the columns will help you to visualize the connection between the individual columns. The words on the red column are:
Those who meditate on this instill into their red pillar of blood, through the power of their thought, the power that leads to the goal: the pillar of wisdom. The power needed for the pillar of life is implanted by surrendering to the thought that stands on the other, the blue column:
Some words lead to knowledge, others to life. The formative power first “reveals” itself in the sense of the first saying; it only becomes “magical” in the sense of the second saying. The transition from mere power of knowledge to magical working lies in the transition from the power of the saying on the first column to that of the saying on the second. Thus you see how what these symbols, the two columns, mean, is directly related to the ideals and goals of the Rosicrucian student. In some esoteric societies, these two columns are also erected. The esotericist will always associate the meaning that has been attached to them. 2 From a teaching session in Munich, December 12, 1906 The Second Master Legend 3tells us of Seth, the son of Adam, who is initiated into the priestly wisdom, is allowed to enter Paradise again, takes three seeds from there, places them in the mouth of his father Adam when he died, and from which the fresh bush then grows. The rod with which Moses performs his miracles is made from its wood; it is the burning bush in which the Lord appears to Moses. The gate of Solomon's Temple is made from its wood: two columns with the beam above, which was thrown into the pool of Bethesda, generating its healing power. This wood was laid across the Kidron Valley, which Christ crossed after the betrayal on the Mount of Olives. And from this beam, Christ's cross was then made. The red blood and the blue blood mean the Pillar of Wisdom and the Pillar of Strength. Man must be able to stand on these two pillars. The tree of life and the tree of knowledge were entwined in paradise to form one tree. And the tree of life and the tree of knowledge will become one tree again for the wise, for the initiate; it had to be separated into two trees for man. The writing that appeared to Moses in the burning bush: “Ejeh asher ejeh!” is translated as: “I am that I am; I was that I will be!” With birth and death, man has paid for his knowledge. The angel Gabriel is the one who guards the threshold of paradise with a fiery sword as the guardian of paradise. Instruction session for the 2nd Berlin, December 1911 without date Thus the angel appeared to Adam in Paradise under the fig tree. Adam saw this sign as the angel's image and Adam vowed that he would never stray from the power that is documented in J-B. And Adam always found strength and fulfillment when he sought out the place where the apparition was possible.  But in the Lemurian time he had done just that and strayed from the power of J.B. through Lucifer, who brought temptation. And when Adam sought out the place of the angel's appearance again, he now felt terror over his own being there. The pentagram was fallen, open on one side (and thus) turned upside down. It was in this sign that the angel now appeared to Adam, threatening him with the fiery sword, and Adam fled.  Participant records without location or date Adam had two sons, Abel and Cain.  Adam died, and Seth put three seeds in his mouth. From these seeds three branches sprouted from one trunk. This grew. The thorn bush in which Jehovah appeared to Moses had grown from this trunk. The two columns of the temple of Solomon were made from this wood. But it turned out that there was no place for the third trunk to join the two columns, it did not fit anywhere. So they threw it into the pool of Bethesda. When the Lord came, he gave a power to the pond, and the trunk came up again. It was lifted up and laid as a bridge over the Kidron brook. Now over this bridge the Lord went on the way to Golgotha. The cross, which he carried, was also carved out of wood and he broke down under the load. The crossbeam, which is to connect wisdom and strength, is the principle of piety, love, beauty. In pre-Christian times there was no place for it in the world. When Christ Jesus came, as the bearer of Budhi, his power could lift this beam out of the water - the astral plane - in which it rested. A river was bridged with it (the way to the higher worlds). He crossed it on his way of suffering when He offered Himself as a sacrifice for humanity. This could only be done through love, purified, refined love; hence the way over this beam. The cross was also cut from this wood. He had to bear and suffer under His love for humanity. But in Him love and knowledge were united. Therefore his sacrifice was a perfect and eternal one, and the three tribes of wisdom, beauty, and strength were united, for beauty had found its place. In the future, the three tribes, which had flowed apart like three streams, would grow together like three streams that then flow together again, and come to full effect in unity. Seth connects the hostile brothers Abel and Cain. The connection between wisdom and strength is piety or love or beauty. For the meaning of the name of the column, see “Signs, Handles and Words” on pages 272f. An historical aspect of the significance of the two columns was developed in the lecture Berlin, June 20, 1916 (third lecture of the cycle “Weltwesen und Ichheit”, CW 169) as follows: It is truly the case that we move through the whole of life as the sun moves through the twelve constellations. We enter our life with our consciousness for the senses, as it were, rising at one column of the world and setting at the other. We pass between these columns when we enter the starry sky, as it were, from the night side into the day side. These occult or symbolic societies also always sought to point this out by calling the column of birth, which a person passes through when they enter the life of the day side, Jakim. They have to look for this column in the sky in the end. And what is outside during the time between death and a new birth is the perception of the sense of touch spread over the whole world, where we do not touch but are touched, where we feel how spiritual beings touch us everywhere, while we touch the other. During the life between death and a new birth, we live in motion within it, so that we feel this motion as if a blood corpuscle or a muscle here within us were feeling its own motion. In the macrocosm, we feel ourselves moving between death and a new birth, we feel the balance, and in the life of the whole we feel ourselves within it. Here our life is closed in our skin, but there we feel ourselves inside the total, the All-life and in every situation we give ourselves our balance. Here the gravity of the earth and our particular body constitution give us balance, and we actually know nothing about it. At all times we feel the balance in the life between death and a new birth. This is an immediate sensation, the other side of the soul life. Man enters into earthly life through Jakim, and he affirms through Jakim: That which is outside in the macrocosm now lives in you; you are now a microcosm, because the word 'Jakim' means: In you the divine poured out over the world. Boaz, the other column: entering the spiritual world through death. What is summarized in the word Boaz means something like: What I have been seeking in myself so far, the strength, I will find poured out over the whole world, in it I will live. But one can only understand such things by penetrating into them through spiritual knowledge. In the symbolic brotherhoods they are symbolically hinted at. They are hinted at more in our fifth post-Atlantic period for the reason that they may not be lost to humanity altogether, so that later on there may be people who will understand what has been preserved in the Word. But you see, everything that takes place outwardly in our world is also a reflection of what exists outside in the macrocosm. Just as our soul life is a microcosm, in the sense that I have indicated to you, so too is the soul life of humanity, in a sense, formed from the macrocosm. And for our time, it is very significant to have the two images of the two columns that I have spoken of delivered in our history. These columns represent life one-sidedly, because life is only in a state of equilibrium between the two. Neither is Jakim the life, because it is the transition from the spiritual to the body, nor is Boas the life, because it is the transition from the body to the spirit. It is the balance that is important. And that is what people find so difficult to understand. People always look for one side, always the extreme, they do not look for the balance. That is why, in a sense, two pillars really do stand for our time, but if we understand our time correctly, we must go right through the middle of them, not fantasize either the one pillar or the other into being the fundamental force of humanity, but go right through the middle of them! We must really grasp what is present in reality, not brood over it in the thoughtless life in which today's materialism broods. If you look for the Jakim column today, you will find it in our present time. The Jakim column exists in a very important man who is no longer alive, who has already died, but it exists: it is present in Tolstoyism. Consider that in Tolstoy a man appeared who basically wanted to distract all people from the outer life, wanted to refer entirely to the inner life - I spoke about Tolstoy in the early days of our anthroposophical movement - who wanted to refer entirely to what is going on inside the human being. Tolstoy did not see the spirit in outer activity, a one-sidedness that struck me as particularly characteristic when I spoke about Tolstoy back then – it was one of the very first lectures of the very first years that were held here. At the time, Tolstoy could still be shown through a friend of ours. Tolstoy understood the first two-thirds, but not the last third, because it was about reincarnation and karma; he did not understand that. He described the one-sidedness, the complete suppression of the outer life. And how endlessly painful it is to realize that he is describing such one-sidedness! Just imagine the tremendous contrast between the Tolstoyan views, which dominate a large part of Russia's intellectuals, and what is now once again rolling over from there in these days. Oh, it is one of the most terrible contrasts imaginable! That is one-sidedness. The other, the Boaz column, also finds expression in our time in historical terms. It likewise represents a one-sidedness. It is the search for spirituality in the outer world alone. A few decades ago, it appeared in America, where I would say the antipode of Tolstoy emerged in Keely, before whose soul stood the ideal of constructing an engine that is not driven by steam or electricity, but by those waves that a person themselves excites in their tone and in their speech. Imagine an engine that is designed to be set in motion by the vibrations that you create when you speak, or that you can create as a human being with your soul. It was still an ideal, thank God, that it was an ideal back then, because what would this war have become if Keely's ideal had actually been realized back then! If it is ever realized, only then will we see what the attunement of vibrations in external motor power means. That is the other one-sidedness. That is the Boaz column. We must pass between the two. The symbols that have been preserved contain much, much. Our time is called upon to understand these things, to penetrate into them. The contrast that will one day be felt between all that is truly spiritual and that which will arise from the West when the Keely engine becomes a reality will be quite different from the contrast that exists between Tolstoy's views and that which is emerging from the East. Oh, there is no need to talk about that! But it is necessary that we gradually delve a little into the secrets of the development of humanity, that we recognize how, in the wisdom of man, what once becomes reality in different stages is expressed throughout the millennia, either symbolically or in some other way.
|
| 188. Goetheanism as an Impulse for Man's Transformation: Clairvoyant Vision Looks at Mineral, Plant, Animal, Man
05 Jan 1919, Dornach Translated by Violet E. Watkin Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| But he should also consciously grasp the relation between men, life in society, the social life. An uncertain state of affairs hinders him in this. The fatal thing is that man can never have a conception of more than one man. |
| He must rid himself of the immediately personal; for it does not help matters when people carry their narrow personal interests into the Anthroposophical Movement. That is always just the cause of any kind of mischief in the relation taken up towards Spiritual Science. |
| It is very important to keep these connections in mind, for these connections make it terribly difficult today to create an Anthroposophical Movement so that it will prosper. It must be created in a successful way for the sake of mankind's welfare. |
| 188. Goetheanism as an Impulse for Man's Transformation: Clairvoyant Vision Looks at Mineral, Plant, Animal, Man
05 Jan 1919, Dornach Translated by Violet E. Watkin Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
From our considerations of yesterday you will have seen how easily the whole course of human evolution can be misunderstood and how it is particularly misunderstood from many sides today to the detriment of present knowledge as well as of the present social striving of mankind. (see Z-7.) Today we will for once call up before our souls some results of Spiritual Science of such a nature that they can throw light, it may be said, from another side on what becomes so enigmatical if looked at from the points of view holding good at present. Now I have told you that man can come to terms with this present time only if he makes up his mind to find his real bearings by starting on the path to the spirit. He must decide to look for a new relation to external nature since the old means to this end no longer suffice, and also find his way to a new relation to his fellow men, the old relation no longer being suitable, so that he sees what impulses are necessary for the modern social structure of mankind. If we wish to be successful in this, we must earnestly keep before our souls the following—that as man is placed in the world today, in earthly existence between birth and death, he sees but the outer manifestation of his own essential being and enters into actual relationship with merely the outer manifestation of his fellowmen. Life takes on a different form for the different epochs of mankind's evolution, and we exert ourselves really to study these things just in their relation to men of the present time. For the present age is a very critical one for men on earth. Up to the fifteenth century, and, since things do not change in a flash, one might say on into the present time, man is still actually more or less dominated by inherited concepts and impulses of the past. This fifth post-Atlantean epoch is indeed in a certain sense rather out of the ordinary where the evolution of men is concerned. For you certainly know that taking earthly evolution as a whole it divides itself into seven great successive epochs, of which the fourth was the Atlantean epoch and the fifth, our present one, the post-Atlantean. The sixth and the seventh should then follow. In the Atlantean period there was a kind of crisis. For up to that time the whole of the earth's existence was a recapitulation of the earlier existence of Saturn, Sun and Moon. During the Atlantean period there was a kind of crisis but it is true only the beginning of a crisis. There was merely a preparation of things that were actually to be developed in the following evolution of the earth. So that up to Atlantean times man was really only what he had been in his different forms as man on Saturn, Sun and Moon. In Atlantean times, however, he had only intimations of what he was supposed actually to become as man of the earth; then he continues on, and now we are in the fifth post-Atlantean period. In the post-Atlantean period, throughout the old Indian end old Persian development, and so on, ever more definite relations were arising. But the Greco-Latin time, the fourth post-Atlantean period, gives us again even though in another form merely a kind of repetition of what existed on another level of existence in Atlantis. It is only now in the fifth post-Atlantean period, in the time since the fifteenth century, that man stands within his whole evolution in such a way that new impulses arise—impulses which are perceptible in his very being. Previously they were not so noticeable; now they appear in his being noticeably, nevertheless there are still only intimations of their presence. The terrible, catastrophic events of our time, the consequences of which—one can already foresee—will be shattering to mankind, are the expression of how new relations are making their way into mankind's evolution. I have already indicated how from a certain aspect these new relations can be described by pointing to the way in which an on-rolling spiritual wave is clearly perceived, arising from, as it were, a surging up into evolution of the Spirits of Personality. Now we notice it after the manner of Spiritual Science we keep in mind this particular state of soul in which modern man is found here on earth, it is markedly noticeable today, according to the outlook of Spiritual Science, how man when he perceives or is outwardly active in his willing is really surrounded only by manifestations of the being of nature, and the being of his fellow men. He is not surrounded by the real beings into whom he must, as it were, grow in the course of evolution, into whom he will have grown at a later stage of evolution. As you know, man's position in the world is such that—to describe it broadly—he perceives the surrounding world in the mineral kingdom, plant kingdom, animal kingdom and in his own human kingdom. This is what is visible around man. And in the visible human kingdom there is played out what comes from the will and what should find a certain ordering for the social structure. Now people have reflected a great deal about man's attitude to his environment, though insufficient thought has gone into their reflections. But the result of these reflections has been worked into various theories of knowledge. We get very little, however, from these theories of knowledge. And what in schoolmaster fashion is given in these theories today to the young people, who are then supposed to speak to the world as philosophers, is really perfectly inadequate nonsense. For a true insight into what is really revealed in man's surroundings, a real insight, can only be gained when the matter is observed according to the way of Spiritual Science. You see, on one side man can look upon the mineral kingdom and the plant kingdom; on the other side he can look on the animal kingdom and the kingdom of man himself. Both—mineral kingdom and plant kingdom as well as human kingdom and animal kingdom—unveil themselves to him in such a way that if now in a theoretical sense he is honest, in this unveiling, in this revealing, he notices contradictions. He is unable to make anything of the way in which on the one hand the mineral kingdom and plant kingdom, and on the other hand the animal kingdom and human kingdom reveal themselves to him. And when people believe they can succeed in doing so this comes from a certain dullness. Because they take life too easily they are unwilling to go into all the doubts which arise from observing the kingdoms of Nature. But now, when one presses on to knowledge, when one trains oneself in the direction given in Knowledge of the Higher Worlds, then to a certain extent a change takes place in our contemplation of the mineral and plant kingdoms, as well as in our view of the connection with the animal and human kingdoms. Unconsciously men already have, to a high degree today, a feeling for this change, even if it does not enter consciousness. It remains indeed in the unconscious—just as I told you that today in the natural course of evolution man passes by the Guardian of the Threshold unconsciously. It is actually a certain fear of the truth which always unconsciously holds men back from really pressing on so that they come to this change. I am speaking in Imaginations, my dear friends, in Imaginations translated into words. In reality these things cannot be appropriately described in any other way. For when man brings to life within him what can be made living, when he applies himself to what is described in Knowledge of the Higher Worlds, looking at the mineral and plant kingdoms with this transformed power of cognition, he will always experience something like fear. But you should not have to shudder nor get gooseflesh at the description of these conditions. People avoid them because they are afraid. From this you ought to understand that of course when picturing these conditions one can indeed get gooseflesh to a certain degree, and on that account people just get frightened. When such knowledge is acquired, on looking at the mineral and plant kingdoms, one always experiences something like the smell of a corpse; there is a corpse-like smell which characterises as if in a vivid feeling what is living in the mineral and plant kingdoms. On the contrary, When with transformed cognition we look at the animal kingdom and the kingdom of man, there is always a sensation that can be described by saying: actually (you will forgive me, I know, for putting this Imagination into words) actually so long as they are in a physical body men remain—even the most advanced of them—where what in reality is hidden within them is concerned, always children, thorough children. The simple truth is that far more lies hidden in a man between birth and death than he can develop outwardly, can bring to manifestation out of himself. Therefore, because in supersensible knowledge there is always a gradual ascent from semblance to actual reality, you see that when looking at, observing the outer world as it now is, we actually have to do with semblance alone. For the corpse-like smell of which I have spoken and, forgive me, the childishness of men, are veiled. The corpse-like smell finds, if I may say so, too dull a nose in our physical men, the etheric nose not being sufficiently developed. And the childishness of men does not allow us to confess its presence because , as men, we are too conceited to do so. Yet this is how the matter stands. My explaining what I have just been describing one points at the same time to there being far more hidden in in man than can be given practical proof. The question may now be asked: If man does not perceive the reality in minerals nor plants, if he perceives no reality in animals either—not even in his own being as man, where then is his right setting on earth? Strange as it may seem we find him placed among beings who belong neither to the mineral and plant kingdoms, nor to the animal and human kingdoms, but lie between them. He bases his being upon a kind of plant-animal, or animal-plant. were there a being here on earth neither wholly plant nor wholly animal, but having mere plant nature where their inner organisation is concerned, and having the power to go around, to move about at will like the animals—now this is what I meant were there beings who on being examined anatomically would not be found to have muscles and blood within them but whose anatomy would resemble that of the plants, with only their cells and tissue, but if these beings were able to move at will like the animals, or were there wandering round our earth animals that on dying left plantlike corpses, then man in his whole attitude of soul would really belong among these beings. Here in his earthly existence man would really be able to comprehend such beings. But again the remarkable thing is that for their part these beings could not exist on earth, these beings are only to be found in other worlds. They could not flourish in earth existence. Thus, we may say that man really lacks the faculty for knowledge—and this particularly apparent today's—which enables him to penetrate directly into the being of minerals and plants. and also of animals and men. And the beings he would directly perceive in their whole constitution are just these which could not live on the earth. This is the remarkable position of man where his relation to nature around him is concerned. But here on earth man stands also in a strange relation to himself. Man is on the one hand a being who has conceptions. When, however, he puts this faculty for conceiving, for having ideas, into action, in the conception he loses his own identity. And he actually has his identity, that is not able to make an appearance in the conception, only when something—his will—works up out of the unconscious. If the will were not to work up and we were to have no trace of it in us, could we have andy ideas about it. The whole world would seem to us ghostly. We should have a ghostly world before us, which about describes the world of scientific concepts; this would actually constitute our world. Imagine the world looking as it is described by natural scientists or zoologists; just think of it being nothing more than what is found in books on Botany and Mineralogy. Real Botany and Mineralogy contain far more than what we find in books. But imagine you were taken into a world described in books, where there was nothing more than what is described in books; it would indeed be a world of mere apparitions, a proper world of ghosts. The world not being one of ghosts is amply due to the will having something to say. Now look! Were you able to fly—I don't mean with a machine but were you able to fly yourself, if you had no need of earth under your feet and were you able to move freely without the earth—then you would come near to perceiving the world in this ghostly fashion. Even if you could only follow the world with your eyes when awake it would appear very ghostly, not so much so as when described by the natural scientist, but all the same it would appear very ghostly. You have a feeling of the solidity of world existence only because you stand with your feet on the ground. And this pressure of your feet against the ground gives you the feeling, akin to the will, but watered-down will, that you are not in a ghostly world but in one that is solid. Were you not to have this feeling, should you only see, the world would appear to you a very ghostly place. You do not tell yourself what is going on in the subconscious; in the subconscious something is going on that makes man say (in the subconscious he does say it): Yes, the world looks very like a ghost! Were it really what is presented by my eyes I should never be able to stand firm, I should have to sink down; and as I do not sink, the world is not as presented by my eyes. This conclusion is constantly being arrived at in the unconscious. The entirely ordinary, most everyday relation to the world is as complicated as this. It is always an unconscious conclusion that to a certain extent originates with the will. Thus in mere conception we actually lack—to use an erudite expression, a pedantic expression—we lack the subject, it drops out. That we have a subject and feel ourselves bound up with the world comes from the will. Again, when we will, when we develop the will, the object is actually lacking. The object does not come into our consciousness at all as something properly solid. If I want simply to lift this little book from the left side over to the right, and actually do it—the real object of the will does not enter consciousness at all. You can see the passage of the book, the conception which takes its ghostly way into the will, but the actual object of the will does not enter consciousness. So that man when he makes conceptions and also when he wills (this again sounds grotesque because an Imagination is being clothed in words) man as a conceiver as well as a willer is—if you will forgive me—a cripple. He conceives in a ghostly way and wills incompletely. What man is in reality, is actually neither quite within his conception nor his will; once again it is in the centre between the conception and the will. But all this goes on in ordinary life without being able to enter consciousness. In the same way as the plant-animal is unable to enter external nature, what man actually is cannot enter his consciousness. For this reason I have often spoken to you of the fact from another point of view by saying: man perceives the real ego like a hole in life's events. You see we have to be clear that holes can also be perceived. Man knows nothing of sleep, he wakes, sleeps; wakes, sleeps; wakes, sleeps. But reviewing the course of his life he is faced by empty space in his consciousness, the hole in consciousness, and he sees just as if there were a white surface before him with black holes where really nothing is to be seen. Thus he looks at the holes that, during sleep, are there in consciousness. But it is also the same with our ego in waking life. Our ego is not in reality brought into consciousness: in the consciousness there is only a hole for this ego, and perceiving this hole is the only thing that makes us aware that we really have an ego. These things, that appear to the insensitive men of today as sophistry, must gradually become an elementary consciousness in man. For in the future man will not be able to found life on dogmatic conceptions, as has been possible for him in the past owing to the still existing remains and after effects of atavistic clairvoyance. In future we shall have to base life on grounds that are easy to detect. It will have to be part of our everyday conceptions that mineral and plant kingdoms are observed after the manner of Goethe. For Goethe only examined the phenomenon, and did not believe that in the phenomenon there was revealed anything but, at best, the basic phenomena, the archetypal phenomena and that phenomena do not reveal in laws of nature which can be put thoughts. Goethe never looked for laws of nature, for this would have seemed to him very fantastic; he wanted to pursue the phenomena because the external world shows us in the mineral and plant kingdoms nothing but perceptions, appearances. Thus man has to look at the external world to become conscious of himself. In the mineral kingdom, in the plant kingdom I really see only the outer side, and when confronted by the animal and human kingdoms I actually see only something like an embryo of the complete being. That also must be so. For you see, in the mineral and plant kingdoms in reality there exist beings who, when observed by man, reveal only a certain side of themselves because it may be said they cannot reveal themselves in any other way. For in the mineral and plant kingdoms lives something man can only fully recognise if—please understand me, thoroughly he looks back to the world from which he came on entering physical existence through birth. Could you after birth with your thought keep possession of the consciousness that stretches backward before birth, could you, that is, look upon being born as an event in your life like—shall we say—the passing from the fifteenth to the sixteenth year, and were the backward-running thread of consciousness to remain unbroken—the consciousness being quite different before birth, before conception—without more ado you would get a view of mineral and plant kingdoms quite different from the one you get on looking from the standpoint of life between birth and death. For you would then say to yourself the followings I have come from the spiritual world through birth. I have entered this physical realm. Why should I have done this? Why should I not have remained in the spiritual realm? Why have I been enticed down to earth at all? For one may speak here of enticement. Then, if you were able to remember, you might says I have been enticed to earth for the reason that suddenly in the course of my development between death and a new birth, it seemed—I came into a sphere where it seemed—as if certain beings had flown away, as if they really should be there, were missing—and were not there. To put it bluntly, in the time just before birth in the spiritual world one is dogged by the feeling that one misses certain beings which actually belong there and are not there. Everything goes to show that these beings are lacking. And if one comes down through birth, these beings are there in the minerals and in the plants, but as though banished, as if these beings were banished from the world just left, as if they could not really flourish, would half die and thus create the corpse-like smell, would become half dead in the world one has entered. Before birth we long to know certain exiles. We only know there are banished beings, but where are they? Then we go into the physical world and perceive them, but they might be said to be embalmed, mummified. For in the world we have entered it is only possible for them to be embalmed, mummified, dried up. It is perfectly right, on being confronted by the mineral world and the world of the plants, that we should have the feeling we are looking at beings exiled from the spiritual world, from the regions in which we were before having to enter physical life. And when we look at animals and men end see their childishness, then, if we can develop the power to see more deeply into being, we remember that these animals and men, as they actually are here in the world in which we live between birth and death are never finished, never actually bring to completion the whole of their life which is conditioned by their inner being. Anyone looking at animals in the right way, anyone who can look at them with full inward and living force of knowledge, knows well that animals are not immortal, but knows too that animals experience in their group souls the whole tragedy of this not being immortal. The group souls outlast the individual life of the animal but what there is here on earth of the animals is—as I recently sale—in reality sick (see Lecture 1), and this is so on account of its deterioration through belonging to s world from which it is banished. And in his outer physical form man also is an exile in this world. He therefore remains crippled and a mere child. Man remains a child, the animal in his general being, in his physical form, is dried up. For what belongs to animal and man is found when we go through death and enter directly into the spiritual world, which then after death we observe. For actually a circle is described in the life between death and a new birth. What remains hidden here of animal kingdom and plant kingdom, what causes us to perceive that animals and men—as far as men's physical forms are concerned—are exiles from the spiritual world, banished out of the spiritual world, is first perceived by us when we pass into the spiritual world through the gate of death. There we go through an evolution and as we approach ever nearer the cosmic midnight, described in my mystery play, (see The Soul's Awakening, scene 6) we become clear that something is missing, that what is missing has run away from the spiritual world; we pursue it through birth and find it on the physical earth in the mineral and plant kingdoms. On entering this existence through birth we are never really surprised about the mineral and plant kingdoms because they are what we have been expecting. Finding animals on the physical earth, too, and men with an outer form that recalls that of the animal though it is more perfect, is astonishing to us in some measure after being born with our gift of consciousness. We begin ia understand this, however, when we know that a beginning has been made with this outer form of animal and man, which only develops in the world we enter through the gate of death. Now it might be said: For the abstract and completely dried up religious conceptions that still persist (these conceptions were once much more full of life and really gave men something) for these abstract, dried up conceptions still remaining in our age of consciousness, all that men perceive here in the physical world, all that they should conceive as underlying the world experienced by man between death and a new birth, comes upon them too abruptly. What man experiences between death and a new birth remains on this account so problematical for men today, and can so easily be denied by the grossly material mind, because men in arriving at the age of the consciousness soul, which means the age of the intellect, lives as I have explained only in what is reflected into his consciousness. Therefore, he is also only able to live in reflected images when he goes out beyond the perceptions to where, if he stands firmly on his feet, the will plays into him in the way I have previously indicated. If no will plays in however—and in the immortal life after death no will does play in—when there is no interplay of the will and man is restricted to placing before his soul, the reflected images of his conceptions of what the world is between death and a new birth, then this world will have no certainty and will be not only ghostly but without certainty. Indeed we can go as far as to say that if men obstinately cling only to science, if they fix, their attention only upon the ghostly world given them by science, then they are quite right in denying any life at all after going through the gate of death. For what is given by science is only pictures, apparitions. And even this comes to an end when we pass the gate of death. Science is unable to contain anything of what we experience in the realm after death and before birth. For, you see, in books on mineralogy, in books on botany, in everything connected with Physiology, Geology end so forth, in any of the conceptions you can absorb about plants and minerals, you can absorb only about beings who are living in banishment here in this physical world. Again, you can also perceive in the bodies of animals and men only what has been banished here—even with all the help of your books on Zoology and Anthropology, and, if you widen the field of your thought you can really put all knowledge in the same category—you are only able to perceive what is living down here in banishment. But when you reflect that before birth you feel the lack because they really are not there of just these beings experienced here after birth, that in animals and men you then experience what does not exist down here, you will understand that into the conceptual life of science nothing at all of immortal life can enter, and that since it lives in images science in its own domain has a perfect right not to trouble itself about immortal life. It in for this reason that, since the fifteenth century, in the epoch when the conceptions of science are dominating the whole of mankind, man has on the one side the robust, crude nature actually representing for him the whole of reality, and on the other side a realm that he wishes to reach with only the weakened mirrored images of the age of the consciousness soul. This comes before him as though he were saying to himself: Now that I come to see (this happens in the subconscious, for it is there he comes to doubt immortality) when I come to see that what I think are only reflected images, then were I to believe these reflected images would still be there after my death, including the images of my self, I should be just as stupid as if I believed that there were coming towards me out of my mirror here on the wall the men who appear to approach me—that they were not simply reflected but were actually coming towards me. It is simply characteristic of this epoch of the development of the consciousness soul that if man will not advance to a spiritual comprehension of the world, then connection with the world into which he will enter once he has passed through the gate of death will vanish from him more and more. It will also disappear from his thought life, from his conscious life, but he will not cease to long for it. And even the most hardened deniers of immortality have in the depths of their will, where longing is born, the longing to experience something of the world man enters through the gate of death, the world from which he comes on passing through the gate of birth. They have a longing. The present time is sick with this longing. And the many illnesses of the present time are the expression of this longing holding sway in man, and of man's inability to find conscious conceptions for his longing. If anything is living in the sphere of the will which we are unable to master by conception (again one has to develop very fundamental concepts to speaker these things) when man cannot overcome by his conception what is living in the sphere of his will, then he starts to rage. This is the essence of raging, or frenzy, that something is living in the realm of the will that man cannot comprehend with his capacity for conception. And if man refuses to give in and agree to recognise the existence of the spiritual world, so that through the recognition of the spiritual world he comprehends what has already taken shape in the sphere of the will, than this raging will become ever greater and greater in the world; the raging which indeed presents itself today as the next stage for men after the—not forthcoming but always hoped for—conclusion of peace. This is not anything which can be talked about in the way things ere discussed at a bowling club where, according to the usual philistine conceptions, people come to an understanding as to the possibility of getting some kind of relief or redress. No, it is something connected with the deepest reality of human evolution. Man cannot struggle against the development in him of what enters the sphere of his will. He has no power over it. He is able only to make up his mind consciously to penetrate to the sphere of the spirit so that he learns to understand what is permeating the region of his will. By this means an ordered co-operative life for men can be developed in future in place of this raging. You see, men turning to the spiritual world which will be revealed in our time by a special wave of events, is not an affair only affecting mean subjectively; it is an objective necessity for man to turn to the spiritual world in this age of the consciousness soul. For changes have even now entered human evolution. Up to the time in the Mystery of Golgotha took place in earthly life, up to that time, everything man needed for standing here in the world with some measure of security came just through sleep. Before the Mystery of Golgotha man slept in a different way from what he now sleeps, whatever the physiologists may say. Those prophetic natures like the Hebrew prophets to whom such sublime things were revealed in dreams, exist no longer, therefore, in the same form. For today these things are not given to men by God in sleep. This used to happen. This is just the great crossing point in evolution. And pictures of the future were not given only to the prophetic natures but in the time of the Greeks men still had their thoughts given them during sleep. On waking, man brought his thoughts back with him. The structure of the human organism was still such that man could bring back his thoughts. For quite a while this went on working, for the fact is that men actually became headless in the fifteenth century—you will forgive mel To become headless means that the head could no longer he used properly, the head could no longer bring back thoughts out of sleep. One of the results arrived at through Spiritual Science is that we recognise our head as an instrument to have been really of much less use and much more dried up since the fifteenth century than it was before that time. But it is only now that this has become so noticeable; and it will become ever more noticeable if some means is not found to compensate, s0 that the evaporation of the head is made good again by the spiritual world. For up to the present, up to the nineteenth century, the other nature, man's breast nature has always been accustomed to what the head was still getting from sleep during the Greco-Latin period. The breast nature was inured to this, and in their headless condition men were still receiving impulses as an after effect; they were still in the habit—or I might say men still had the gesture of the thought, the shadow of the thought. But this shadow too will pass away and men will have no thoughts at all if they leave their thinking only to their head. And this is really how the matter stands; it is shown by men's reluctance to think. They have less and less will to think. On the one side they want to have thoughts dictated by nature, for what they like best is merely to make experiments and let the experiments say what they themselves should be thinking. But men prefer not to do the thinking themselves. They even have no proper faith in it, for it is their opinion that what they think out lacks true reality. It is true that there is no reality if you take the mere thoughts. We can come to see, however, that thinking, not the thoughts but the thinking, must become active. And when thinking is made active, this means the spiritual world is coming into play. Today when you really begin to think actively, you can do nothing further than let the spiritual world play a part in you. Otherwise you do not think; you think as little as the scientist thinks today who prefers to let his experiments or his investigations dictate everything to him. Or you think so little as the modern students of sociology who, because they have no will to be active, because they do not come to grips with real social impulses which can be grasped only by being active, actually work with what can be discovered in history, what is inherited from the past. Think for once how men, because they themselves no longer have impulses able to create the social structure, have come down to looking back to the time when thoughts were still formed. The matter is then seen from only a false point of view. It was Rousseau who held up to men the natural state, because he had the feeling that in his day nothing could be gained unless men became active in their pursuit of knowledge of the higher worlds. Well, and even modern socialism likes to indulge in a study of mankind's primitive state; it is something that particularly interests the socialists. They study the original conditions of mankind, their primitive conditions, they study the most savage original peoples, primitive peoples, so as to understand how men are meant to live in social co-operation. This is recognised by all who are familiar with these things. Everywhere there is a certain fear of what is making its presence so inevitably felt as the first dawning of connection with the spiritual world, a certain fear of active thinking. This is why there is difficulty in understanding my Philosophy of Spiritual Activity, for example, which makes such demands on active thinking. In it the thoughts are different from the usual thoughts of today. And people often stop short when reading this book for the simple reason that they would like to read it as any other book is read. But the other books particularly popular today—well, I think you will agree, they are read in a comfortable easy chair where one can just let thoughts go by with as little trouble as possible. Many people do any reading they go in for just like that. Don't delude yourselves into believing that these men often read newspapers in a different way (present company, of course, always excluded); it is true that emotions are mixed up with this reading, and worries too. But even the newspapers that are devoured so sensationally are also read by letting the pictures slip by. Ah, but all one has tried to put into The Philosophy of Spiritual Activity cannot be read just like that. There you have continually to give yourself a shake to prevent the thoughts sending you to sleep, my dear friends! For it was not written with the idea that you would simply sit in an easy chair; naturally you can sit, even rest your back, but then, just because you are physically at rest, you have to try with the whole of you to set the inner being of soul and spirit in motion so that the whole thinking begins to move. Otherwise you get nowhere but go to sleep. Many indeed do go to sleep and they are not always the least sincere; the insincere ones are those who read The Philosophy of Spiritual Activity just like any other book and then believe they have really followed the thoughts. They have not followed them, they have on the contrary just jumped over them as if they were the husks of words; they go on reading the words without taking in what actually follows from the words as the spark should be produced by flint and steel. But this is something that must be required of what has to take hold of the evolution of mankind in the present and the immediate future, for through it man will gradually raise himself to the spiritual world in the right way. By active thinking man's inner relations to the spiritual world will be kindled and then he will make ever greater progress. Today he can already get very far by carrying out such things as are described in Knowledge of the Higher Worlds. But there too it is sufficiently indicated how pre-eminently necessary it is to develop coherent, connected thinking where there is no broken thread—when the thread of the thought is carefully followed. In this longing, today more or less lacking in clarity and consciousness, to push oneself upward with unconscious thinking to the sphere of the spirit—and it is possible to do this—there is mingled a desire from the past, a weary desire, to go on thinking incoherently. Just recently I have drawn your attention to how contrary it is to men's sense of comfort to have to progress step by step in conscious thinking. They would much prefer to leave things more to the unconscious, and not in thought go on to the next point and then again to make a further step. Isn't it so? You see, Spiritual Science as we understand it here and as in a sane way it reckons with the unbroken sequence of the thoughts in the way you know—well, it is not that this Spiritual Science cannot be understood if thinking is made active, but men simply want to understand Spiritual Science in a different way from how they must understand it; instead of which they would like the thread to be continually broken. When you go deeply into what Spiritual Science gives you, when you plunge into it with real energy (have patience, in the present epoch only faint indications of this can as yet exist) then, already today, by developing the power of thought, by following in thought Saturn, Sun and Moon, as described in my Occult Science, you can follow this evolution up to where man stands there in the world, and you can press on to your own life, penetrate this life of yours with the thought which is thus made vigorous. Then you come to certain conceptions which, although not as you would like them to appear but entirely in the connection, in the coherence, of the thinking, enlighten you about their being, about their nature, about what they are and their character. By bringing to life what is said about Saturn, Sun, Moon and their corresponding details, and then about the evolution of the earth, applying all this to your individual selves, you would be able to progress to your own being; only you have to go on in your thought to the perception of yourself, not letting the thoughts be broken but keeping them coherent and connected. What in this way man begins rightly today enlightens him up to the stage where he should become clear about his own personal being. In this longing, still present more or less unconsciously in men, however, something else is mingled with the broken thread of thought, something calculated! Man would like to find out something of the kind about his being; what does he do? He takes old antiquated knowledge of which, it goes without saying, the venerable nature is certainly not to be disparaged, which, however, has need of explanation when applied in a new epoch—he calculates, reckons, breaks the thread of thought at any point, calculates constellation of the stars, and after that the thread of thought can break, and quite externally without any sequence in the thought this being of man as he appears on earth is supposed to develop without any thinking. You see, even if the Church, the Roman Catholic Church as I described it to you yesterday, denies what today is most necessary of all, this can be made good just by taking anything like the description of the inner vision of John of the Cross and living today in the sense of the evolution that conforms with Knowledge of the Higher Worlds. What is contained in this book follows on today precisely from what a man such as St. John of the Cross wills; whereas the Catholic Church denies it and wishes even today to see the old way of John of the Cross applied to modern man, as indeed it is to so many people. Because they are too comfort-loving they do not want a life that is active in spirit, a life that has already reached a stage of energetic activity when conceptions are accepted such as those given by Spiritual Science. They would like these to be brought up to date in a more usual form of thought, preferring to remain with what is old and hoping that out of this lack of thought there might spring what should explain present-day mankind. Naturally this is no adverse judgment about what is venerable, but from every point of view it must be indicated that one should not venture to deny what is placed as spiritual necessity into the present evolution of mankind, the evolution beginning with the age of the consciousness soul. The important thing is for man really to understand what today is required of mankind in world-evolution. I believe that out of right feeling for the very things which men find irksome, and do not want, a better attitude towards Spiritual Science will be adopted more and more, and only when this better attitude to Spiritual Science has come about will the social life also be enriched. At this point man will be able to become clear about the life of mankind because he will then have the necessary strength of thought to enlighten himself concerning man's life. For where this enlightenment about man's life is concerned man of today suffers from a very precarious state of affairs. Whether you are a follower of Lenin or Trotsky, whether you are a Marxist or any other kind of thinker about the right form for the social structure of men, in each of these views there lives a state of affairs that is precarious and cannot be understood without the fruitful intervention of Spiritual Science. Doubtless you will admit that man has now entered the epoch of the consciousness soul. He has to develop consciously what arises as social structure. Otherwise nothing will go right. He has to take his place consciously in the world; it is really necessary that man should be conscious. But he should also consciously grasp the relation between men, life in society, the social life. An uncertain state of affairs hinders him in this. The fatal thing is that man can never have a conception of more than one man. And as neither two men (I mean physical men) nor two things (physical things) can be in the same place at the same time—which decides the law of impermeability—two men cannot be in human consciousness at the same time, the actual conception cannot be made of two men! simultaneously. It is very important to take note of this. We cannot live with another man without making a conception of him, neither can we develop any knowledge about the social life in common unless we make conceptions about other men. But today man, because he is able to conceive only of one man, generally prefers to conceive only of himself, to make a conception of himself as man. And social thinking is content to demand a co-operative life in which man's conception is always merely of himself. Man does not get away from the conception of his own self; he often talks of doing so, but in reality today he does not easily get rid of himself. It is only when he makes every effort to fulfil the requirements of Spiritual Science that he gradually finds it possible in some measure to get free of himself. For Spiritual Science sows in the world the seeds of thoughts having a very wide perspective, and this is how man grows into the habit of getting free from himself. As today, if he becomes a spiritualist, man grows more egoistic than he was before, if he would penetrate into the spiritual world on that other path, the path of Spiritual Science, he becomes more selfless. Spiritual Science, therefore, is not simply the handing over of knowledge, but spirit-knowledge is actually something unconditionally necessary for educating modern man in social life. It is for this reason that no cure will be forthcoming if a start is not made in this matter, it men do not really give heed to the necessity for first making a conception. There can be no social reform without schooling to begin with, without men first being instructed. And when this is neglected men miss the possibility of receiving concepts that embrace their longing. And, if I am to get at the root of the matter, men will became more frenzied than ever. This is the inner connection, my dear friends. But it is desirable that this same inner connection should be perceived. One would wish above all things that this inner connection should be felt by everyone entering upon Spiritual Science and wishing to live in it up to some point or other. This is something that everyone will want to ponder who has the wish to take Spiritual Science and the Movement of Spiritual Science in earnest. It cannot well be overlooked, it cannot well remain unnoticed, that when we enter into relation with Spiritual Science this Spiritual Science makes certain demands on the human heart and mind to widen the interests beyond narrow, personal interests. It is really true that in talking of Spiritual Science one simply speaks of things which, if a right relation is to be established with them, makes it necessary for man to free himself from his most narrow interests! He need have no fear of becoming unpractical on that account: he becomes much more practical. It is just this belief that he is practical which has gradually been arrived at through being unspiritual. In reality the practical man of today is terribly unpractical. And these 'practical' men have actually landed us in the present catastrophe. Herein lies something of tremendous importance which man really must always take for granted if he wishes rightly to understand what has to do with Spiritual Science, namely that he must get free from his narrowest interests. He must rid himself of the immediately personal; for it does not help matters when people carry their narrow personal interests into the Anthroposophical Movement. That is always just the cause of any kind of mischief in the relation taken up towards Spiritual Science. It is also naturally the reason for what is still such a difficulty in our Movement, that people although often abstractly in theory, having the good will to come to Spiritual Science with their own thinking, feeling and willing, nevertheless do not bring all the necessary strength really to enter upon selflessness, which indeed must be called upon for understanding rightly what is said from the standpoint of Spiritual Science. Thus a kind of spirit-condition not easily found today in the world, but the opposite of which is prevalent in the modern world, must be demanded for the health of the Anthroposophical Movement, my dear friends! For the difference between the sincere presentation of the knowledge of Spiritual Science and all other knowledge arising at present, lies in this presentation of Spiritual Science being no personal affair, no personal opinion. Were I obliged to hold the view that I should lecture only about merely personal opinions and not concerning what is revealed today and just what is necessary for mankind, I should prefer to remain silent. For to uphold personal opinions and personal aspirations in a Movement that is anthroposophical is something impermissible. That should not be. A Movement such as is striven for here is justified only when there is the will to present merely what one is allowed to observe out of the spiritual world. When you describe the appearance of any town you may, according to circumstance, make the description either interesting or tedious, but what the town looks like does not depend upon you. You describe something objective. What you yourself want, what is your own opinion, should come just as little to expression in Spiritual Science. What must take effect in Spiritual Science according to modern demands is all that is spiritually observed. Those who are able actually to will merely what is personal can for that reason only imperfectly understand what should hold good in a movement for Spiritual Science. They continually confuse what should hold good in a Movement such as is meant here with something else drawn, more than ever from the personal. How many there are who coming to Anthroposophy would like their own opinion to be justified by Spiritual Science. They are not always equipped with the open mind necessary for the acceptance of Spiritual Science. Very often they come to it with something quite different to this open mind. They would like this or that to be true, then in some way, while admitting that the investigator of Spiritual science may know something about the truth, persuade themselves that what one thinks oneself one says. Then they would be happy. But this fine distinction must be noticed; it is a fine distinction although a tremendously far-reaching one; there is a far reaching and important distinction between the one who wants to accept what is imparted by the spiritual world and the one who actually wishes only to have confirmation of what it pleases him to think. Only by the most punctilious self-examination, by conscientious self-examination, will the distinction be discovered. The distinction is often unnoticed by those who come to Spiritual Science; it must, however, be noticed. If it is noticed it will become apparent that through a Movement for Spiritual Science something of a new stream of life must flow which was not there before. It is really not possible for an Anthroposophical Movement to be like a mere soft current of air blowing towards anyone who brings to Spiritual Science the Philistine tendencies of his earlier life and then believes he will find what he is only too willing to acknowledge in Philistinism corroborated by Spiritual Science. When we proceed in this matter earnestly, conscientiously, we shall not want merely to find corroboration of our actual individual opinion; and we shall also come to understand many things which might be said to be obliged to arise as new things in a Movement for Spiritual Science of this kind, things that must do harm if left unnoticed. In a movement in the act of arising like this Movement for Spiritual Science much can work harmfully that cannot cause so much harm in old, dried up Movements, no longer of use or of very little use. We have really to go into these fins points, my dear friends! You see, connected with the endeavour merely to see our own opinions, our own aspirations, justified by what is revealed through Spiritual Science, a remarkable technique of 'touching-up' is developed concerning what comes forth and comes forth perfectly naturally, within a movement such as ours. In this movement for Spiritual Science we must be alive to the fact that phenomena with men cannot be taken as if in a bowling club or something of the kind where men can reveal how verbose they have become in the ordinary world where nothing new is required of them. We must recognise in all earnestness that the aims of investigation into what is spiritual cannot find expression through our own conceptions; we must really prepare ourselves to receive the things. We should picture that something is wishing to flow into the world, something that should more and more widen itself out, so that everything should really be received in full consciousness. Many connections not yet perceived will be perceived later. This willingness to receive everything as in some sense a preparation, will certainly not be present in those who carry their personal aspirations into the impulse of Spiritual Science, for at the first possible moment they will get done with things, giving them the bent of their ordinary opinions. They do not mould their opinions in accordance with Spiritual Science, they mould the knowledge gained through Spiritual Science in accordance with their opinions. And so we often have given out the kind of thing I would like to describe in the following way. Now you know that the Anthroposophist has to judge the world in a certain way, the world of nature as well as the world of human beings. Education in Spiritual Science consists indeed in our learning to judge afresh the surrounding world and our relation to it and in our learning to look more deeply, into the world. People very often remark when, let us say, the relation of three men is in question: The Anthroposophist B. has been criticizing the man A. And, my dear friends, as soon as we overstep the usual Philistine sphere, so largely around us today, two standpoints can be put forward where the formation of judgment between man and man is concerned: one of these standpoints is that of reason, the second being the standpoint of sympathy. Thus B's judgment of A may be in accordance with what arises from an inner necessity at same time to do something or other purely out of his—B's—sympathy for A. Should it now suit C to be antipathetic because he does not reflect sufficiently and does not assume that it may be possible for pure sympathy to come into the matter here, out of necessity, then, basing his judgment simply on reason he will say: whatever can he be doing that for? Or this inner necessity may speak in such a way that it is not sympathy that becomes dominant but, because of certain factors, reason. Yes, and when it suits the other better he lets sympathy have its say and gives as his verdict: what an unsympathetic person! How utterly without feeling the man is and what a prosy rationalist! He judges purely from the standpoint of reason. In this way the crudest misunderstandings arise in the case of just those who bestir themselves to grasp the inner nerve of existence, where they have at one time to do something based on reason, another time something just out of sympathy. And when it suits this other man (C) in accordance with the sympathetic view he condemns what is done from reason, and what is done out of sympathy he condemns from the point of view of reason, and he can always condemn or praise as he likes. By this path we never arrive at what is right, we only arrive at what is right if we begin by saying: I must consider the case, I must look into the causes why sympathy or reason have held sway here. It is things like this out of which the little misunderstandings in life arise which often grow to very destructive proportions in men's life in common. It is just this that our education in Spiritual Science should help us to overcome. For life is such that it expresses itself in a twofold way. And because it expresses itself in a twofold way one can always condemn at pleasure one of the two cases. This is very little taken into account, however, above all not taken into account where the teachings of Spiritual Science itself is concerned. This, too, must be placed in the world with definite intention. In an individual case either one or other of the two standpoints can be chosen according to convenience, if greater attention is not paid to the deeper grounds out of which the spiritual seeker is obliged to act. He may often be misunderstood. And if there is no agreement in what must be done out of inner duty in accordance with the facts, then it is possible to misunderstand everything, since the world has this dual form of expression. You see we can fall into the following error for example. When anyone is eager to have what suits him substantiated, he may just fall into the worst form of belief in authority. Belief in authority can naturally make its influence felt, and this influence is actually frequent and of wide range in the very sphere where Spiritual Science also would be active, which wishes to make man into a perfectly free, self-reliant being. The other pole of the belief in authority, however, is hatred of authority. And fundamentally the man who does not feel himself drawn to Spiritual Science through entering into the facts revealed from the spiritual world, but wishes to have these truths conveyed to him by authority, wanting to believe in authority because it is easier than going into things—this man is terribly apt to spring over from his belief in authority, that always has in it a certain kind of love of authority, to hatred of authority. And all manifestations that have arisen in our particular movement of this leap from blind worship of authority, which sometimes has even appeared with a certain shamelessness in the moment of passing over to hatred, this passing from blind worship of authority to hate—all this is something inwardly present as a danger. It is very important to keep these connections in mind, for these connections make it terribly difficult today to create an Anthroposophical Movement so that it will prosper. It must be created in a successful way for the sake of mankind's welfare. Now, my dear friends, in my life I have found quite a number of people who were spiritual people and were seeking in all sincerity away into Spiritual Science, into some kind of Spiritual Science, who were also in a way advanced in their development. A certain type among them was disillusioned, people who had been disillusioned by one or other of the modern spiritual movements and who then in some place or another came across us—how many are disillusioned today by the Blavatsky Movement, the Besant Movement or some other Movement. There we do not see the characteristic phenomenon that takes such curious forms in the Anthroposophical Movement; but there we have people, for example, who are to a certain extent spiritually advanced; then after some time one again comes across them but now they say: You are completely wrong! And these meetings are not infrequent. Spirituality today is not at all common but there are men indeed who say to one after a time: You are actually wrong, for, you see, the things you give out in Spiritual Science—there's no possible sense in publishing them! But men are not in inclined to accept them; they are certainly not sufficiently mature. All this can only serve one purpose to be developed in oneself and then kept to oneself. I have found many such people who say: It is a definite characteristic of the man who is really advanced spiritually that it no longer enters his head to speak about it to his fellowmen; he keeps the matter to himself. There is indeed no lack of such people in the world. I have never been able to come to an understanding with these people about what out of a certain inner ground I learn from the spiritual world. These men do quite useful work in a spiritual community but they have a hermit tendency, even when at the same time they remain in association with others. For it is possible to become a hermit in spite of wearing elegant shoes and leading an Hotel life. This one sees this double life being led by a number of people; they are indeed the modern Hotel dwellers; for all I care they may be well dressed but they lead this life as an outward mask to hide what is within them; they have their inner life of the spirit with no wish to share it with their fellow men. This seems to one to be doing what is not right, to be sinning against mankind. For one is right in saying that such men have en effect on the spiritual life, what they experience goes into the spiritual stream. Man is not a self-contained being, therefore what he experiences has value and its own significance in the spiritual world, but the question of time always plays its part there. Men like this who live in such a way nowadays, as many do whom I have known, bring about something indeed in the spiritual world which however only comes to maturity after a long time, in the later epochs of mankind. Then, however, can, and quite certainly would, were there always only those who as hermits develop their spiritual being, having no wish to teach what knowledge they have gained from the spiritual world, what they have developed in themselves—then by the time the fruits of these men are ripe, people outside would have so deteriorated that they would no longer be able to receive the knowledge! Earth evolution would be endangered: connection would be missed. We live indeed today at a time when certain spiritual truths such as those of which we have been speaking must unconditionally be imparted to mankind. Things will not be helped by the attitude expressed, for example, by one of my acquaintances who in a certain sense was spiritually advanced. He came to Berlin and I asked him whether he would come to hear a lecture of mine, just to see how the Movement was run (this is some time ago). He answered: No, holding lectures and talking to people serves no possible purpose! To sit together for half-an-hour and have a little talk I find very pleasant—but let us leave spiritual things alone when we can; everyone must settle those for himself! To pay a civil visit and pass the time of day is best for just those people who are seeking the spiritual. And this attitude is a prevalent one. It would be more comfortable, my dear friends, to live in accordance with such an attitude. And the word comfortable certainly does not describe what it is nowadays days to get up in front of people to impart what one feels impelled to impart as a duty. In an Anthroposophical Movement it should be borne in mind that work is done out of inner necessity, and what happens is not a matter of choice but the punctual observance of a duty. I have used these words at the end of our studies today because I have wanted once again to take the opportunity of calling attention to what is necessary if a movement for Spiritual Science is to be taken nowadays as earnestly as it should be taken. For what can be made of an Anthroposophical Movement, if personal aspirations, personal ambition, is brought in, can cause much injury must cause much injury. Besides there is still the shadow side, namely, that whoever thinks to find only what is just personal corroborated through Spiritual Science cannot discern whether the other may not be acting also merely from personal ambition. And a terrible doom is then forthcoming. I wanted to give an indication of these things, my dear friends. We shall be speaking further next Friday. |
| 130. The Mission of Christian Rosenkreutz: The Dawn of Occultism in the Modern Age I
27 Jan 1912, Kassel Translated by Dorothy S. Osmond Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| To me it is objective truth, but you yourselves can put it to the test by gathering together what has been said by anthroposophical Spiritual Science during the last few years, added to what you know of history since the thirteenth century. |
| Moreover the early writings of the Founder of the Theosophical Society, the great H. P. Blavatsky, are explicable only when we recognise the Rosicrucian inspiration underlying them. |
| 130. The Mission of Christian Rosenkreutz: The Dawn of Occultism in the Modern Age I
27 Jan 1912, Kassel Translated by Dorothy S. Osmond Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
The lecture today will be historical in character and the day after tomorrow I shall speak of matters which will give: us deeper insight into the impulses contained in the thinking, the will and the deeds of Rosicrucianism. We can only understand the work of Rosicrucianism today when we realise that it was never a model laid down once and for always but assumes a different form in every century. The reason for this is that Rosicrucianism must always adapt itself to the conditions of the times. It is quite obvious to us that the fundamental impulses of Spiritual Science must find their way into the culture of the present age; but we know, too, that the culture of the West presents difficulties. Spiritual Science cannot make different human beings of us from one day to the next, because through our karma we have been born into Western culture. Our task is not as simple as that of the representatives of communities based upon race or the tenets of a particular religion. For our fundamental principle must be that we are not rooted in the soil of a specific creed but regard the different systems of religion as forms and variations of the one, universal spiritual life. It is the seed of spiritual truth in all religions for which Spiritual Science must seek. As a Westerner, the theosophist may very easily be misunderstood, above all by the different religious confessions and schools of thought in the world. If we rightly understand our task as spiritual scientists we must hold fast to the principle of historical development, realising that Spiritual Science is an integral part of this development. Each one of you here has been incarnated in every epoch of culture—indeed more than once. What is the purpose of these reincarnations? Why must the human being pass through all these different schoolings in the periods of culture and civilisation? It was this question which brought Lessing to avow his belief in the idea of reincarnation. Lessing thought to himself: Human beings have lived through all the earlier periods of culture and they must return again and again in order to learn new things and to be able to connect the old with the new. There must be a purpose in the fact that we pass through different incarnations, and the purpose is that in each of them the human being shall add new experiences to the old. As you have often heard, there are great differences between the successive epochs of culture. Today we shall speak in closer detail of an extremely important period: the thirteenth century. Human beings in incarnation at that time lived through an experience which has not fallen to the lot of others. What I am now about to say is known to all who have reached a certain high level of spiritual life and who are now again in incarnation. In the thirteenth century, spiritual darkness fell for a time upon all human beings, even the most enlightened, and also upon the Initiates. Whatever knowledge of the spiritual worlds existed in the thirteenth century came from tradition or from men who in still earlier times had been Initiates and were able to call up remembrances of what they had then experienced. But for a brief space of time it was impossible even for these men to have direct vision of the spiritual world. Darkness was obliged to fall for this short period in order that preparation might be made for the intellectual culture which was to be characteristic of our modern age. The point of importance is that we have this kind of culture today in the Fifth post-Atlantean epoch. Culture in the Greek epoch was quite different. Instead of the modern, intellectual kind of thinking, direct perception was then the dominant faculty; the human being was one, as it were, with what he saw and heard, even with what he thought. He did not cogitate and reason as he does today, and needs must do, for this is the task of the Fifth post-Atlantean epoch. In the thirteenth century, it was necessary for especially suitable personalities to be chosen out for Initiation, and the Initiation itself could only take place after that brief period of darkness had come to an end. The name of the place in Europe where the happenings of which I am about to speak came to pass cannot yet be communicated, but before very long this too will be possible. We shall, speak today of the dawn of occultism in the modern age. Twelve men were living at the time of the darkness, twelve men of deep spirituality who came together in order to further the progress of humanity. They did not all of them possess the power of direct vision of the spiritual world, but they were able to bring to life within them remembrances of what they had experienced through earlier Initiation. And by the dispensation of the karma of humanity, the heritage left by the ancient culture of Atlantis was embodied in seven of these twelve men. In my book Occult Science it is said that the seven wise Teachers of the ancient, holy Indian civilisation bore within them the surviving wisdom of Atlantis. The seven men were incarnated again in the thirteenth century and formed part of the Twelve; it was they who were able to look back to the seven streams of the ancient Atlantean wisdom and to the continuations of these seven streams. The task assigned to each of these seven individualities was to make one of the seven streams of wisdom fruitful both for the culture of the thirteenth century and of our modern age. These seven individualities were joined by four others; unlike the first seven, these other four were not able to look back to times of the primeval past; they looked back to what mankind had acquired from occult truths during the four epochs of post-Atlantean culture. The first of the four looked back to the period of ancient India, the second to that of ancient Persia, the third to that of Egyptian-Chaldean-Babylonian-Assyrian culture, and the fourth to that of the Graeco-Latin age. These four joined the seven in that “College” of wise men in the thirteenth century; the twelfth had fewer remembrances; he was more intrinsically intellectual than the rest and it was his task to cultivate and foster the external sciences. These twelve individualities did not live only in the sphere of occultism as cultivated in the West, but could also be “incorporated” as it were in men who possessed some genuine knowledge of occultism. Goethe's poem Die Geheimnisse [footnote: The Mysteries by Rudolf Steiner] gives a certain indication of this.—Thus there were twelve outstanding individualities and to them came a Thirteenth who, after the period of darkness had come to an end was to be chosen out for the kind of Initiation demanded by the culture of the West. The circumstances are very mysterious and I can only give you the following information in the form of a narrative. To me it is objective truth, but you yourselves can put it to the test by gathering together what has been said by anthroposophical Spiritual Science during the last few years, added to what you know of history since the thirteenth century. It was known to the College of the twelve wise men that a child was to be born who had lived in Palestine at the time of Christ and had been present when the Mystery of Golgotha had taken place. This Individuality possessed great powers of heart and a quality of deep, inward love which circumstances had since helped to unfold in him. An Individuality of extraordinary spirituality was incarnated in this child. It was necessary, in this case, for a process to be enacted which will never be repeated in the same form. The following does not describe a typical Initiation but is an altogether exceptional happening. It was necessary for this child to be removed from the environment into which he was born and to be placed in the care of the Twelve at a certain place in Europe. But it was not the external measures adopted by the twelve wise men that are of essential importance; what is important is the fact that the child grew up with the Twelve around him, and because of this, their wisdom was able to stream into him. One of the Twelve, for example, possessed the Mars-wisdom and therewith a definite quality of soul—a mood-of-soul tempered by the form of culture standing under the influence of Mars. The forces of the Mars culture endowed this soul with the faculty, among others, of presenting the occult sciences with fiery enthusiasm and ardour. Similar planetary influences were also at work in other faculties distributed among the Twelve. The development of the child's soul proceeded harmoniously under the influences pouring from the twelve wise men. And so the child grew up, under the unceasing care of the Twelve. Then, at a certain time, when the child had grown into a young man of about 20, he was able to give expression to something that was a kind of reflex of the twelve streams of wisdom—but in a form altogether new, new even to the twelve wise men. The metamorphosis was accompanied by violent organic changes. Even physically the child had been quite unlike other human beings; he was often very ill and his body became transparent, as though filled with light. Then there came a time when for some days the soul departed altogether from the body. The young man lay as if dead ... And when the soul returned it was as though the twelve streams of wisdom were born anew. He spoke of new experiences. There had come to him, from the Mystery of Golgotha, an experience similar to that of Paul before Damascus. Thereby it was possible for all the twelve world-conceptions, religious and scientific—and fundamentally there are only twelve—to be gathered together, synthesised in one. The twelve basic world-conceptions were gathered together into one whole which could do justice to them all. Of what was taught we shall speak the day after tomorrow. It remains now to be said that the young man died very soon afterwards. His life on Earth had been brief. His mission had been to create a synthesis of the twelve streams of wisdom in the sphere of thought and to bring forth the new impulse which he could then bequeath to the twelve wise men who were to carry it further. A great and significant impetus had been given. The name of the Individuality from whom this impulse originated was Christian Rosenkreutz. The same Individuality was born again in the fourteenth century and this earthly life lasted for more than a hundred years. In the new earthly life he brought to fruitfulness, in the outer world too, all that he had lived through in that brief space of time. He traveled all over the West and over practically the whole of the then known world in order to receive anew the wisdom which in the previous life had quickened in him the new impulse—the impulse which, as a kind of essence, was to filter into the culture of the times. This new impulse also came to expression in the exoteric world. The inspiration of the being of whom we have spoken, worked, for example, in Lessing. It is not, of course, possible to give external proof of this, but Lessing's whole mode and manner of thinking is such that the Rosicrucian impulse is perceptible to one who is versed in these matters. Again in the nineteenth century—an age so ill-adapted for the ideas of karma, reincarnation and the like—this impulse worked exoterically. It is an interesting fact that towards the end of the 'forties of the nineteenth century a certain scientific body offered a reward for the best philosophical treatise on the subject of the immortality of the soul. Among the treatises submitted was one by Wiedenmann, accepting the principle that the soul has many earthly lives. Naturally, this essay does not speak of reincarnation in the same way as Spiritual Science; but it is interesting that such a writing should have appeared at that time and have been awarded the prize. And other psychologists of the day also acknowledged their belief in repeated earthly lives. The thread of belief in reincarnation and karma was never entirely broken. Moreover the early writings of the Founder of the Theosophical Society, the great H. P. Blavatsky, are explicable only when we recognise the Rosicrucian inspiration underlying them. Now it is of the greatest importance for us to know that whenever the Rosicrucian inspiration is given, in each century, the bearer of the inspiration is never outwardly designated as such. His identity has been known only to the very highest Initiates. Today, for example, it is only permissible to speak of happenings of a hundred years ago; for this is the period of time which must have elapsed before they may be spoken of openly. The temptation to pay fanatical veneration to authority vested in some personality—than which there is no greater evil—would be too great for men. This danger is already too near at hand. Silence is a necessary precaution not only against the wiles of ambition and pride—which it might be possible to resist—but paramountly on account of the occult, astral attacks which would be directed all the time against such an individual. Hence the rule that these things may not be spoken of until a hundred years have elapsed. Such studies must help us to realise that the fulcrum of historical development is contained in Rosicrucianism. By a simple comparison, let me explain to you what is meant by this.—Think of a pair of scales. There must be only one fulcrum, for if there were two, no weighing would be possible. One such fulcrum is also necessary in the process of historical development. Eastern world conceptions do not admit this, nor do they recognise historical evolution in this sense; and the same applies to Schopenhauer. But it is the task of humanity of the West to recognise the flow of history—and it is the mission of Rosicrucianism to promote a kind of thinking which admits the reality of a fulcrum or pivotal point in the flow of history. In regard to what will now be said, the religious confession to which a man may belong is of no consequence. For it can be substantiated from the Akasha Chronicle that the day which represents the pivotal point in the evolution of mankind is the 3rd April in the year 33 A.D. Knowledge of the fact that the pivot of evolution lies at this point is an essential part of Rosicrucianism.—What was it that really happened then? The crisis in the world of the demons! And what does this mean? We know that in earlier times human beings possessed the faculty of primitive clairvoyance. This clairvoyance became progressively feebler, almost to the point of extinction. The fact is that hitherto the human being had been conscious mainly in the astral body and less in the “I.” The crisis came about because of the darkening of the ancient clairvoyance. Man's vision extended only into the lowest regions of the spiritual world. The “I” lived still in the astral world; but the beings and powers which the “I” was able to behold, deteriorated into greater and greater impurity. Man no longer had any vision of the good powers, but as he looked into the astral world he saw only these evil beings. The only means of salvation was the cultivation and development of the “I.” The beginning of this was the enactment of the baptism given by John in the Jordan. What was the experience of one thus baptised? He was first subjected to the physical process of immersion in the water which caused the separation of the astral and etheric bodies from the physical body. This enabled him to perceive that a crisis was at hand in the world of the demons. And those who had been baptised knew: We must change our hearts! The time is at hand when the Spirit is to stream directly into the “I.” Such a man felt that these terrible astral beings were within him, always penetrating into him. A power transcending the astral was about to come into operation—the power of the “I.” Through the “I” it will be possible for communities of human beings to gather together in freedom of soul, communities no longer determined by ties of blood. And now picture to yourselves a man possessed by demons of the most evil kind who know that they are facing a crisis. Picture to yourselves again that to such a man there comes One Whose mission it is to oppose the demons. What must the demons feel under such circumstances? Ill at ease in the very highest degree! And so indeed it was: in the presence of Christ Jesus the demons were ill at ease. Rosicrucianism has within it the impulse by which the demons must be countered. Through this impulse the “I” is to be made supreme—but in this respect little progress has been achieved. Returning to the point at which the lecture began, it is not difficult to realise that it will be harder for us as Anthroposophists to make our voice heard in the world than it will be for any others. The adherents of other views of the world will have less persecution to suffer than Anthroposophists. For nothing makes men more uneasy than to describe to them the true nature of the Christ. But our conviction is based upon the results of genuine occult science and this conviction must be sustained with all the forces of which we are capable. |
| 300b. Faculty Meetings with Rudolf Steiner II: Forty-First Meeting
05 Dec 1922, Stuttgart Translated by Ruth Pusch, Gertrude Teutsch Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| The religious renewal was intended for those outside the Society. You need to be clear that such things have two sides, and that the primary thing is that our anthroposophical friends, both inside the school and outside, need to see that their mission is to straighten out people who are falling into an erroneous path. |
| 300b. Faculty Meetings with Rudolf Steiner II: Forty-First Meeting
05 Dec 1922, Stuttgart Translated by Ruth Pusch, Gertrude Teutsch Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Dr. Steiner: I would like to hear everything about the class schedule. The new class schedule is described. All of the foreign language classes are in the morning. There were no changes in personnel. Once, a language class had to be moved from 12:00 until 1:00. An attempt was made to group the students. A few times Latin and Greek had to be put after eurythmy, but otherwise the language class immediately followed main lesson. Dr. Steiner: You will have to do it that way if nothing else is possible. A teacher: I would prefer having the 4a language class in the afternoon instead of from 12:00 until 1:00. Dr. Steiner: Then we will do it in the afternoon. A teacher: Is that true otherwise? Dr. Steiner: When the respective teachers demand it. It is important that the teachers agree. The religious instruction is described. Voice instruction is always in the morning. Eurythmy, mostly. All the handwork and shop classes are in the afternoon as well as gymnastics, but Wednesday afternoon had to be used also. If Wednesday afternoons are to be held free, then gymnastics and some of the shop classes would have to be in the morning. Dr. Steiner: There is nothing to say against having some things at the end of the morning under certain circumstances. It is, of course, not good when the children move from the practical into the completely theoretical. We should try to keep a Wednesday free. Gymnastics should also not be done before the theoretical periods. It was badly scheduled on Wednesday only because the gymnastics teacher was excluded from the meeting. A teacher: The parents have arranged a number of things under the assumption that Wednesday is free. Dr. Steiner: Surely we can get the parents to choose another day. The teachers need to be able to come to the faculty meetings. That is important. The teachers could meet on Saturday. There is too much to do. Let us try to keep Wednesday afternoon. I think it is best if we do gymnastics in the afternoon. A teacher: We carried out the division between the humanistic and business courses of study. Dr. Steiner: Then this class schedule is possible, and we will see if it is satisfactory. A teacher: I would like to teach foreign languages in my first-grade class. Dr. Steiner: Of course, that is possible. That is how it should have been from the beginning. The fourth-grade teacher would like a fourth period of foreign language. Dr. Steiner: We carefully considered the number of hours, but we should allow you to decide. It needs to be something that is not required. I think, if everyone is satisfied with it, we could actually begin with the class schedule. It would be nice if you could start on Thursday, December 7. Then, on Saturday, when I can look at things again, everything will be under way. They present the individual class schedules. Dr. Steiner: The first grade only has class once in the afternoon. 2a and 2b, as well. 3a is only on Monday afternoon. 3b, only Tuesday afternoon. The same is true of the 4a and 4b classes. 5a has class on three afternoons, two of which are the Catholic religion class. 5b also has handwork and eurythmy on two afternoons. 6a, three afternoon classes. That is not too much. For the time being, only the teachers are carrying too much. Dr. Steiner goes through the list with the teachers, determines how many hours each teaches, and how many hours beyond a reasonable limit each is teaching. He assumes that each teacher should teach sixteen to seventeen hours per week. Thus, for example, N., who teaches twenty hours, is teaching three to four hours too many. Dr. Steiner: Now we have determined that. In normal life, the teachers would demand extra pay for these hours. However, I think we should try to get an additional language teacher. I would also like an additional gymnastics teacher. A teacher asks whether the provisional plan for decreasing the teaching load should be tried. Dr. Steiner: Y. already has too many hours. We could do that only if we could find some trade. If, for example, you, Miss Z., would take over one of the religion classes, then Y. could trade. Make the change with whoever appears most burdened. Mrs. W. has the greatest tendency to give up time. We will wait until Tittmann comes to answer the question of V. V. defends himself. Dr. Steiner: There are also inner reasons. You should be happy we expect more of you. You are more robust. I think you are quite strong. You certainly must admit that you are more robust than Mrs. W. We will see that we get Tittmann here as soon as possible. A teacher: The class teachers have asked if they could teach gymnastics to their own classes. Dr. Steiner: There is nothing to say against that if it does not become a burden. I certainly see no reason why two classes cannot have gymnastics with their teachers in the same room. That would, in fact, be quite good, if it is possible, because we would then achieve a pedagogical goal. We need to remove nervousness from our teaching. If we cannot do that, it would be a sign of nervousness. Actually, we should see it as an ideal that we could teach mathematics in one corner, French in another, astronomy and eurythmy in the others, so that the children have to pay more attention to their own work. A teacher: That is also relevant for eurythmy? Dr. Steiner: I would be happy if you could do it, because it is pedagogically valuable. teachers would, of course, need to be able to get along with each other. A teacher: The religion teachers would like to keep the room they have had for the Sunday services. It should be used only for that. Dr. Steiner: I agree. What is important in these Sunday services is the attitude among those present. We can best achieve that by maintaining that arrangement. A teacher: Should Miss R. and Mr. W. hold the services? Dr. Steiner: They should both celebrate the sacraments. That is an obvious condition for the independent religious instruction. I would like to say something more. Experience has shown that the Independent Religious Instruction consists not only in what we teach during religion class, not only what we teach through feeling, but that a certain relationship needs to develop between the religion teacher and the student. You can develop that through the celebration of a sacrament. If someone else does the service, then, for the student who receives the sacrament from someone else, a large part of the intangibles necessary for teaching religion are missing between the students and the religion teacher. The reverse is also true. If someone gives the sacrament without teaching religion, that person falls into a difficult position that can hardly be justified. It is easier to justify teaching religion without leading a service than it is to justify leading a service without teaching religion. Through the service, we bring religious instruction out of empty theory. It is based upon a relationship between the religion teacher and the students. As I have said in connection with the sacrament, you should decide. A teacher: I did not understand that. Dr. Steiner: Now that we have completed things, in selecting a teacher for religion my first question is if he or she can lead the Sunday service. You might have the wrong impression. If the question is which one of you here do I think is appropriate, then I could reply, “Only those who I think are appropriate to give the service.” Many people could teach religion, but the giving of the sacraments can hardly be done by anyone other than the two whom I mentioned. You should not be angry that I am speaking quite straightforwardly in this connection, but each of you should know what I think of your capabilities, at least for now. That may change, though. The children need to become mature enough. This nonsense with a special confirmation class needs to stop. They should attend the Youth Service when they have reached a certain level of maturity, but that maturity cannot be taught. They will simply reach it, and for that reason, we should not have any special confirmation class. Only the person giving religious instruction should hold the Youth Service. A teacher asks about the decorations in the service room. Dr. Steiner: I would like to think about that. I think it would be nice to have a harmonium. We want to be careful about how we develop the service. There is not much to say about the text except that the Gospels are still missing. There is still much we can do in connection with music and also paintings. In contrast, though, there is something else we need to consider, namely, the participation of the faculty. There are two sides to the question. There is the very real question of whether things are moving too rapidly here. The services permeated by a religious renewal have the possibility of becoming something quite great. On the other hand, I hear in town among those who are working on this religious renewal that a religious community of a hundred members consists only of anthroposophists who are forming a sect. You see, there is a danger connected with all this. It is already present. I also hear that, “Those members who have not yet joined are being pressured.” The religious renewal was intended for those outside the Society. You need to be clear that such things have two sides, and that the primary thing is that our anthroposophical friends, both inside the school and outside, need to see that their mission is to straighten out people who are falling into an erroneous path. Those things connected with the most noble intent also have the greatest dangers. This is something that must be taken seriously. Before this religious renewal has withstood the test whether it is true and proper, we can certainly not say that we should respect someone who does not attend less than someone who does. It would be best if we create a service for the children that has a great deal of warmth and heart, if we did everything possible to create an attitude that is serious without being oppressive, but on the other hand, to keep it as simple as possible. A teacher: We have thought about some questions we would like to ask you. The question arose in connection with teaching foreign language about the musical/language and the sculptural/ painting streams. They were often mentioned in the course. Dr. Steiner: There are also a number of references to that in that short cycle of four lectures on pedagogy that I gave in September of 1920. You will forgive me if I mention that, but I believe it contains everything you need to come to more concrete actions. Concerning teaching modern languages—if you use the same methods, the effects upon the child will compensate each other, since the child’s head dies through French to the same extent as the child’s metabolism is enlivened through English. The difficulty arises, and this is something that just occurred to me, when you remove English for some of the children. Socially, that is unnatural. It should not happen, but there is nothing more we can do. We cannot have both English and the ancient languages. But, particularly during the present stages of their development, these two languages compensate one another unbelievably well. Take, for example, Mr. B’s French class today. He developed something extremely important for the more quiet listeners. The French language is in a process of eliminating all the “S’s”. It would not be proper to say Aisne (An). You can hear the “s”. But, during the Battle of the Marne, it was referred to only as “An”. In English, many suffixes are moving toward removing an “s.” When you use the same methods, these are completely compensating, particularly during the ages of nine and ten. Otherwise, it is best to do as little French grammar as possible. In contrast, it is good you emphasize the grammatical aspect of English around the age of eleven or twelve. I will discuss that in more detail later, but for now I wanted only to make a preliminary mention of it in order to hear from you how things are going. A question is asked about the stages of language teaching. Dr. Steiner: There are stages. It would be interesting to look at this question in connection with other things. I intend to write an essay about Deinhardt’s book about the basic elements of aesthetic principles in instruction. Of course, these things are overemphasized by Deinhardt as well as Schiller, but it is easy to discuss them. It would be good to mention the publisher at the same time. Perhaps one of the faculty members could write a critique of the book in relation to Schiller. You are not familiar with the book? It is difficult to read. Steffen was asked to write an introduction to this book, but he found it terribly boring. That is only because of his long sentences. An Austrian can understand having such long sentences in a book. Sometimes you have to stand on your head in order to understand such sentences, but Steffen does not like that. A teacher: We assumed such things would result in a textbook. Dr. Steiner: That would be a good idea. A teacher asks about how to ask questions using the Socratic method. Dr. Steiner: There is something about that in my lecture cycles. A teacher asks about having English as an elective in the upper grades. Dr. Steiner: That would be possible. A teacher asks a question about mathematics. Dr. Steiner: I would be happy to explain that if you would try to use such things in a non-pedantic way. You should remember that such rules are always flexible, so they must never become pedantic. Particularly concerning spatial questions, it is always bad when things become too rigid. Dr. Steiner: You need to understand the small bones within the ear, the hammer, stirrup, the oval window, the anvil, as small limbs, as arms or legs that touch the eardrum. A sense of touch enters the understanding of tone. The spiral, which is filled with liquid, is a metamorphosed intestine of the ear. A feeling for tone lives in it. What you carry within you as an understanding of language is active within the eustachian tubes that support the will to understand. Tone is primarily held in the three semicircular canals. They act as a memory for tone. Each sense is actually an entire human being. I often say such things as a paradigm in order to animate people like Baumann and Schwebsch to get to work and write a book about all their experiences. They said such things this morning. You only need to be more specific and things will seem plausible to them. Dr. Steiner is asked to open the new school building after Christmas.  Dr. Steiner: That is difficult, since not all the classes will be moving in. Quite a number will remain in the temporary buildings, so if we make this a particular celebration, those children staying in the temporary buildings will feel they are not as good as those moving into the new building. We need to consider the effects of a special ceremony upon those children remaining in the temporary buildings. It would be a different question if we were to open a new hall, such as a gymnasium. However, if we were to do this, it would fill the whole building with an inner disturbance. I want to characterize Leisegang as a philosopher, a caricature of a philosopher. He is just a windbag. What he is as a philosopher is complete nonsense. You can do this in a pedantic way: What are the characteristics of a philosopher? A philosopher needs a firm foundation under his feet, but all his assumptions are incorrect. You could actually prove that he, in fact, has no real foundation. If you proceed that way in philosophy, that is what happens. I do not know of any profession where such a person would belong. He certainly could not make jokes in the newspaper because he doesn’t have enough of a sense of humor. |
| The Case for Anthroposophy: Introduction
Owen Barfield |
|---|
| We perhaps take them for granted now; but the men of the seventeenth century—the members of the Royal Society for instance had a prophetic inkling of what the new liberty promised. You have only to read some of their pronouncements. |
| The Foreword to Von Seelenrätseln does in fact describe it as a Rechtfertigung—vindication—of anthroposophical methodology, but my choice of a title for these extracts came from the impression I had myself retained of its essential content after reading the whole and translating a good deal of it. |
| It is not only psychologically (for the reason already given) but also technologically that the scientific revolution was a necessary precondition of anthroposophical cognition. And this has a bearing on an objection of a very different order that is sometimes brought against it. |
| The Case for Anthroposophy: Introduction
Owen Barfield |
|---|
by Owen Barfield The prolonged historical event now usually referred to as “the scientific revolution” was characterised by the appearance of a new attitude to the element of sense perception in the total human experience. At first as an instinct, then as a waxing habit, and finally as a matter of deliberate choice, it came to be accepted that this element is, for the purposes of knowledge, the only reliable one; and further that it is possible, and indeed necessary, to isolate, in a way that had not hitherto been thought possible, this one element from all the others that go to make up man’s actual experience of the world. The word “matter” came to signify, in effect, that which the senses can, or could, perceive without help from the mind, or from any other source not itself perceptible by the senses. Whereas hitherto the perceptible and the imperceptible had been felt as happily intermixed with one another, and had been explored on that footing, the philosopher Descartes finally formulated the insulation of matter from mind as a philosophical principle, and the methodology of natural science is erected on that principle. It was by the rigorous exclusion from its field, under the name of “occult qualities”, of every element, whether spiritual or mental or called by any other name, which can only be conceived as non-material, and therefore non-measurable, that natural knowledge acquired a precision unknown before the revolution—because inherently impossible in terms of the old fusion; and, armed with that precision (entitling it to the name of “science”), went on to achieve its formidable technological victories. It is the elimination of occult qualities from the purview of science that constitutes the difference between astrology and astronomy, between alchemy and chemistry, and in general the difference between Aristotelian man and his environment in the past and modern man and his environment in the present. When two mutually dependent human relatives are separated, so that, for the first time, one of them can “go it alone”, there may be drawbacks, but it is the advantages that are often most immediately evident. By freeing itself from the taint of “occult qualities”, that is, by meticulously disentangling itself from all reference, explicit or implicit, to non-material factors, the material world, as a field of knowledge, gained inestimable advantages. We perhaps take them for granted now; but the men of the seventeenth century—the members of the Royal Society for instance had a prophetic inkling of what the new liberty promised. You have only to read some of their pronouncements. For them it was an emotional as well as an intellectual experience. “Bliss was it in that dawn to be alive ...” But when two people separate, so that one of them can go it alone, it follows as a natural consequence that the other can also go it alone. It might have been expected, then, that, by meticulously disentangling itself from all reference, explicit or implicit, to material factors, the immaterial, as a field of knowledge, would also gain inestimable advantages. That is what did not happen. But it will be well to state at once that it is nevertheless precisely this correlative epistemological principle that is the basis of Rudolf Steiner’s anthroposophy. It belongs to the post-Aristotelian age for the same reason that natural science does; but in the opposite way. Thus, the parallel terms, “spiritual science” and “occult science”, which he also used, do not betoken a fond belief that the methodology of technological1 science can be applied to the immaterial. The methodology of technological science is, rightly, based on the exclusion of all occult qualities from its thinking. The methodology of spiritual science is based on an equally rigorous exclusion of all “physical qualities” from its thinking. That is one of the things I hope this book will help to make clear. What did happen was well expressed by Samuel Taylor Coleridge, when he pointed out in his Aids to Reflection that Descartes, having discovered a technical principle, which “as a fiction of science, it would be difficult to overvalue”, erroneously propounded that principle as a truth of fact. (The principle in question was the necessity of abstracting from corporeal substance all its positive properties, “in order to submit the various phaenomena of moving bodies to geometrical construction”.) And of course the same point has since been made by A. N. Whitehead and others. But Coleridge could also point prophetically, in another place,2 to
The necessity for such a revolution, he said, arises from the fact that, for self-conscious man, although to experience a world of corporeal substance as existing quite apart from his thinking self is “a law of his nature,” it is not ‘;a conclusion of his judgment”. That this is indeed the case hardly needs arguing today, since it has become the discovery of technological science itself. Whether we go to neurology or to physics, or elsewhere, we are confronted with the demonstrable conclusion that the actual, macroscopic world of nature—as distinct from the microscopic, submicroscopic and inferred world of physical science—is (as, for instance, the biologist, Professor Marjorie Grene, puts it in her book The Knower and the Known) “mediated by concepts as well as presented through the senses”. What is remarkable is the rapidity with which the presence of this Trojan Horse in the citadel of its methodology was detected by technological science itself, as it was progressively realised that everything in nature that constitutes her “qualities” must be located on the res cogitans, and not the res extensa, side of the Cartesian guillotine. But this is as much as to say that those qualities are, in the technological sense, “occult”; and it could be argued without much difficulty that any science which proposes to enquire into them must also be “occult”—unless it is content to do so by extrapolating into the psyche a theoretical apparatus applicable, by definition, only to subject-matter that has first been sedulously dehydrated of all psyche. Yet this last is the approach which the methodology of natural science, as we have it, renders inevitable. If you have first affirmed that the material world is in fact independent of the psychic, and then determined to concentrate attention exclusively on the former, it does not make all that difference whether or no you go to the behaviouristic lengths of explicitly denying the existence of psyche. Either it does not exist or, if it does exist, it is occult and must be left severely alone. In any case you have withdrawn attention from it for so long that it might as well not be there, as far as you are concerned. For the purpose of cognition, it will gradually (as the author puts it on page 77) has “petered out”. Moreover this continues to be the case even after the failure of science to eliminate psyche from the knowable world has become evident. The demonstrative arguments of a Coleridge, a Whitehead, a Michael Polanyi are perforce acknowledged; but the acknowledgment remains an intellectual, not an emotional experience. The Trojan Horse certainly does seem to be there, and in rather a conspicuous way; but the necessary traffic-diversions can be arranged, and it is much less embarrassing to leave it standing in the market-place than to get involved. There is however one experience inseparable from the progress of natural science, which is apt to be an emotional as well as an intellectual one. And that is the fact that the exclusion of the psychic, as such, from matter of science entails recognition of the limits of science. This is, of course, the opposite experience from the one that enthralled the scientists of the seventeenth century. They rejoiced in a conviction that all the boundaries had gone and the prospects opened up to human knowledge had become limitless. Whereas, more and more as the nineteenth century progressed, it was the opposite that was stressed. “Ignorabimus.” We shall never know. There are limits beyond which, in the very nature of things, the mind can never pass. One of the things heavily stressed by Steiner (in Section I and again more specifically in Section III) is the significance, from the point of view of anthroposophy, of precisely this experience, and not so much in itself as for what it may lead to. The more monstrous and menacing the Horse is felt to be, towering there and casting its shadow over the centre of the town, the more ready we may be to begin asking ourselves whether there may not perhaps be something alive inside it. This experience can be an emotional, and indeed a volitional one, because it involves a frustrating, if suppressed, conflict between the scientific impulse, which is a will to know and a refusal to acknowledge boundaries except for the purpose of overthrowing them—and the scientific tradition, followed for the last three hundred years, which has ended in itself erecting boundaries that claim to be no less absolute than the old theological ones it did overthrow. In developing his contention that the shock of contact with these self-imposed limits of knowledge may itself be the necessary first step towards breaching them, the author refers in particular to two German writers, F. T. Vischer and Gideon Spicker. It would be a mistake to conclude from this, or from the nineteenth century idiom of the quotations, that the theme is out of date. The boundaries are still there and are still felt. The substance is the same, whether it is Gideon Spicker pointing out that every one, without exception, starts from an unproven and unprovable premise, namely the necessity of thinking. No investigation ever gets behind this necessity, however deep it may dig. It has to be simply and groundlessly accepted ... or Bertrand Russell, in Human Knowledge: Its Scope and Limits, conceding that the foundation, on which the whole structure of empirical science is erected, is itself demonstrably non-empirical: If an individual is to know anything beyond his own experiences up to the present moment, his stock of uninferred knowledge must consist not only of matters of fact, but also of general laws, or at least a law, allowing him to make inferences from matters of fact ... The only alternative to this hypothesis is complete scepticism as to all the inferences of science and common sense, including those which I have called animal inference. The abiding question is, how we choose to react to the boundaries. We may, with Russell and the empiricists, having once conscientiously “shown awareness” of them, proceed henceforth to ignore them and hope, so to speak, that they will go away; or, with the linguistic philosophers, we may flatly decline to look at them; or we may wrap ourselves in the vatic “silence” of a Heidegger or a Wittgenstein or a Norman O. Brown to be broken only by paradox and aphorism, or fall in behind the growing number of distinguished enthusiasts for metaphor, symbol and myth; or, with the scientific positivists, we may resign ourselves to the conviction that there is really no difference between knowledge and technology; we may even perhaps attempt some new definition of knowledge along the lines of the groping relativism, or personalism, of Karl Popper or of Michael Polanyi. But how far all of these are from the vision that was engendered by the scientific impulse in its first appearance among men! Steiner, as will be seen, advocates a different response, and one which, it seems to me, is more in accord with the fateful impulse itself, however it may differ from the methodology and the tradition which that impulse has so far begotten. At intervals through the ensuing pages the reader will encounter a passing reference to, and sometimes a quotation from, the German philosopher and psychologist, Franz Brentano. Here too he may be inclined to form a hasty judgment that the book is unduly “dated” by them. But here too it is the substance that matters, and that is far from being out of date. What that substance is, it is hoped, may be sufficiently gathered from the book itself. Brentano is however so little known to English readers that I have thought it best to omit from the translation that part of it which amounts to an exegesis of his psychology. There remain two points to which I wish to draw attention here. In a short section entitled “Direction of the Psychic from the Extra-psychic in Brentano” (also omitted) the author briefly capitulates the former’s refutation of a certain influential and still widely accepted psychological fallacy: namely, that the degree of conviction with which we treat a proposition as “true” (and thus, the existential component in any existential judgment) depends on the degree of intensity—the “passion”3—with which we feel it. This, says Brentano, is based on an impermissible analogy (“size”) between the psyche itself on the one hand and the world of space on the other. If conviction really depended on intensity of feeling, doctors would be advising their patients against studying mathematics, or even learning arithmetic, for fear of a nervous breakdown. What it in fact depends on, adds Steiner, is an inner intuition of the psyche neither similar nor analogous, but corresponding in its objectivity, to the psyche’s outer experience of causality in the physical world. And this experience is considered elsewhere in the book, for instance in Sections VII and VIII. The other point concerns Brentano’s relation to the present day. It is not always the philosopher whose name is best known and whose works are still read, whose influence is most abiding. Brentano was the teacher of Edmund Husserl, who acknowledged that teaching as the determining influence in his intellectual and vocational life; and without the Phenomenology of Husserl, with its stress on the “intentionality” or “intentional relation” in the act of perceiving, there is some doubt whether Existentialism would ever have been born. Thus, while from a superficial point of view the relation to Brentano, which certainly pervades the book as a whole, may be felt as a dating one, for anyone at all acquainted in detail with the history of western thought it can have the consequence of bringing it almost modishly up to date. Steiner’s Von Seelenrätseln (of which what follows is a partial translation) is not a systematic presentation of the philosophical basis of anthroposophy. For that the reader must go to his The Philosophy of Freedom, or Goethe’s Theory of Knowledge, or Truth and Science;4 and perhaps especially the last. The Foreword to Von Seelenrätseln does in fact describe it as a Rechtfertigung—vindication—of anthroposophical methodology, but my choice of a title for these extracts came from the impression I had myself retained of its essential content after reading the whole and translating a good deal of it. Steiner’s Von Seelenrätseln was published in 1917, the year of Brentano’s death; and its longest section (here omitted) amounts, as its title, Franz Brentano (Ein Nachruf), suggests, to an obituary essay. Steiner had always, he says in a Foreword, been both an admirer and an assiduous reader of Brentano and had long been intending to write about him. The main body of the essay is thus a patient and detailed exposition, supported by quotations, of Brentano’s psychology, in which the word “judgment” is used to name that intentional relation between the psyche and the extra-psychic, or physical world, which enables it either to reject a representation as subjective or to accept it as objective. This “judgment” is an exclusively psychic activity, and must be sharply distinguished as such from both representations and feelings. As the essay proceeds, Steiner makes it clear that he sees Brentano’s emphasis on intentionality as a first step in the direction of that psychological elimination of “physical qualities”, to which I have already referred. And he suggests that the only reason why Brentano himself could not take the logically indicated second step (which must have carried him in the direction of anthroposophy) was that at the very outset of his philosophical career, following Emanuel Kant, he had irrevocably nailed his colours to the back of the Cartesian guillotine, by accepting the axiom that concepts without sensory content are “empty”. Is this why today, although we have a philosophical and an ethical existentialism, and now even an existential psychology, we have as yet no existential epistemology? This essay is immediately preceded by a lengthy response in detail to a chapter in a then recently published book by Max Dessoir, and that in its turn by the introductory essay entitled Anthropology and Anthroposophy, which also forms the opening section of the book now presented to English readers. The arguments against including Max Dessoir über Anthroposophie seemed to me to be the same, only a good deal stronger than those against including the Brentano obituary. Steiner felt bound to go into Dessoir’s chapter in some detail, because it echoed irresponsibly a number of flagrant misunderstandings, or misrepresentations, of anthroposophy that were current in Germany at the time. Briefly, Dessoir’s arguments are all based on the assumption that anthroposophy ignores the principles of natural science and must collapse as soon as it is confronted with them; whereas Steiner’s real argument is, as he himself formulates it in the Foreword, that “either the grounds for there being such a thing as anthroposophy are valid, or else no truth-value can be assigned to the insights of natural science itself”. What he disputed was not facts, but hypotheses which have come to be treated as facts. I have omitted the Foreword; but the argument, so formulated, is sufficiently apparent from the rest of the book. The remainder of Von Seelenrätseln consists of eight Commentary Notes (Skizzenhafte Erweiterungen) of varying lengths, each referring specifically to a different point in the text, but each bearing a title and all of them quite capable, it seems to me, of standing on their own. Seven of them appear here as Sections II to VIII, and I have already borrowed from the eighth (Diremption of the Psychic from the Extra-psychic in Brentano) for the purposes of this Introduction. We are left with a book rather less than half the length of the original and requiring, if only for that reason, a different title; but still with a book which I have thought it important to make available, as best I can, in the English tongue; and that not only for the general reasons I have already suggested, but also for a particular one with which I will conclude. One of the Commentary Notes (Section VII) stands on rather a different footing, is perhaps even in a different category, from the others. At a certain point in the Brentano obituary Steiner quotes from a previous book of his own a passage in which he compares the relation between the unconscious and the conscious psyche to that between a man himself and his reflection in a looking glass. In which case the notion that the actual life of the soul consists of the way it expresses itself through the body, would be as fantastic as that of a man, regarding himself in a mirror, who should suppose that the form he sees there has been produced by the mirror. Whereas of course the mirror is the condition, not the cause, of what he sees. In the same way, the ordinary waking experience of the psyche certainly is conditioned by its bodily apparatus; but “it is not the soul itself that is dependent on the bodily instruments, but only the ordinary consciousness of the soul”. Now Section VII is, in form, a Note on this sentence; and it is somewhat odd that Steiner should have chosen a “Note” for the purpose to which he applied it. For he made it the occasion of his first mention (after thirty years of silent reflection and study) of the principle of psychosomatic tri-unity. Moreover it is still the locus classicus for a full statement of that same “threefold” principle, which, as every serious student of it knows, lies at the very foundation of anthroposophy, while at the same time it runs like a twisted Ariadne’s thread through nearly every matter selected for scrutiny. Even those readers, therefore, who are already too well convinced to feel that any “case” for anthroposophy is needed so far as they are concerned, will probably be glad to have it available in book form and in the English language. It has once before been translated—in 1925 by the late George Adams—but his version was only printed in a privately circulated periodical and has been out of print for more than forty years. It hardly needs adding that this Note in particular will repay particularly careful study. But there is one aspect of it, and of the doctrine it propounds, to which I feel impelled to direct attention before I withdraw and leave the book to speak for itself. If Section I is the statement, Section VII strikes me as a particularly good illustration, of the true relation between Steiner’s anthroposophy and that natural science which the scientific revolution has in fact brought about. Although he criticises, and rejects, a certain conclusion which has been drawn from the evidence afforded by neurological experiments, Steiner does not attack the physiology developed since Harvey’s day; still less does he ignore it; he enlists it. It is not only psychologically (for the reason already given) but also technologically that the scientific revolution was a necessary precondition of anthroposophical cognition. And this has a bearing on an objection of a very different order that is sometimes brought against it. I was myself once asked: What is there in Steiner that you do not also find in Jacob Boehme, if you know how to look for it? The content of Section VII (here called “Principles of Psychosomatic Physiology”) could never have come to light in the context of an Aristotelian physiology, a physiology of “animal spirits”, for example, and of four “elements” that were psychic as well as physical and four “humours” that were physical as well as psychic, no-one quite saw how. If your need is to know, not only with the warm wisdom of instinctive intelligence, but also with effective precision, you must first suffer the guillotine. Only after you have disentangled two strands of a single thread and laid them carefully side by side can you twist them together by your own act. The mind must have learnt to distinguish soma absolutely from psyche before it can be in a position to trace their interaction with the requisite finesse; and this applies not only to the human organism, but also to nature as a whole. It is the case that there is to be found in anthroposophy that immemorial understanding of tri-unity in man, in nature and in God, and of God and nature and man, which had long permeated the philosophy and religion of the East, before it continued to survive (often subterraneously) in the West in the doctrines of Platonism, Neo-Platonism, Hermetism, etc.; true that you will find it in Augustine, in pseudo-Dionysius, in Cusanus, in Bruno, in William Blake and a cloud of other witnesses, of whom Boehme is perhaps the outstanding representative. It would be surprising if it were not so. What differentiates anthroposophy from its “traditional” predecessors, both methodologically and in its content, is precisely its “post-revolutionary” status. It is, if you are that way minded, the perennial philosophy; but, if so, it is that philosophy risen again, and in a form determined by its having risen again, from the psychological and spiritual eclipse of the scientific revolution. To resume for a moment the metaphor I adopted at the outset of these remarks, it is because the two blood-relations were wise enough to separate for a spell as “family”, that they are able to come together again in the new and more specifically human relationship of independence, fellowship and love. Just how badly is it needed, a genuinely psychosomatic physiology? That is a question the reflective reader will answer for himself. For my own part, to select only one from a number of reasons that come to mind, I doubt whether any less deep-seated remedy will ultimately avail against a certain creeping-sickness now hardly less apparent from the Times Literary Supplement than in the Charing Cross Road; I mean the increasingly simian preoccupation of captive human fancy with the secretions and the excretions of its own physical body. A few final words about the translation. I have varied slightly the order in which the Sections are arranged and in most cases have substituted my own titles for those in the original. The German word Seele feels to me to be much more at home in technical as well as non-technical contexts than the English soul; and this is still more so with the adjective seelisch, for which we have no equivalent except soul—(adjectival). It is not however somewhat aggressively technical, as psyche is. I have compromised by using psyche and psychic generally but by no means universally. Habits of speech alter fairly quickly in some areas of discourse. Coleridge apologised for psychological as an “insolens verbum”. The same might possibly have been said of psyche in 1917, but hardly, I think, today and still less tomorrow. The mental or intelligential reference of Geist—operating towards exclusion, even from the sub-conscious imagination, of “physical qualities”—is more emphatic than that of spirit; and once again this is even truer of Geistig and spiritual. I doubt if much can be done about this; but I have sought to help a little by rather infrequently Englishing Geistig and Geist—(adjectival) as noetic. The distinctively English mind and mental sometimes appear to a translator of German as a sort of planets in the night sky of vocabulary and I have here and there adopted them both in seelisch and in Geistig contexts. And then of course there were those two thorns in the flesh of all who are rash enough to attempt translating philosophical or psychological German—Vorstellung and vorstellen. This is a problem that would bear discussing at some length. But it must suffice to say that I have mainly used representation and represent (after considering and rejecting presentation and present) occasionally substituting, where the context seemed to demand it, idea and ideation. The very meaning feels to me to lurk somewhere between the English terms—which is a good reason for using them both. Other usages are based on similar considerations and reflection. As to any habitual reader of Steiner who may suspect that I have taken too many liberties, I can only assure him that, as far as I know, I have at least had no other motive than a keen desire to do the fullest possible justice to thought-laden sentences written by an Austrian in 1917, but being read (as I hope) by an Anglo-Saxon in and after 1970.
|
| 108. The Answers to Questions About the World and Life Provided by Anthroposophy: Life between Two Reincarnations
02 Dec 1908, Wroclaw Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
| I would like to start by describing the life of a person between death and a new birth, but in order to understand what happens in this interim period, we must first consider the nature of the human being. For those who have been involved in anthroposophical studies for some time, the information in the introduction should not be new. But we must nevertheless consider these things very carefully from the outset in order to prepare ourselves for a complete understanding of the subsequent descriptions. For anthroposophical spiritual science, the essence of man is not merely that essence of a material nature, as it appears to the external senses, which we can touch with our hands and which is bound to the physical world by physical laws. |
| It is not so long ago that every child learns to read and write by the age of six, as is the case in our society today. In ancient times, there were highly educated people who were at the head of the state and could neither read nor write. |
| 108. The Answers to Questions About the World and Life Provided by Anthroposophy: Life between Two Reincarnations
02 Dec 1908, Wroclaw Rudolf Steiner |
|---|
Yesterday, we were able to discuss with a somewhat larger group the paths that lead to the higher worlds. Today, we may be permitted to say a few words about the higher worlds themselves. In particular, we want to pick out one of the most important chapters from the realm of the supersensible worlds and take a look at the processes that take place in a person between death and a new rebirth. This is one of the most important chapters in the realm of higher life because it concerns the most fundamental facts and processes of human development. And since the physical existence of man is connected and interwoven with significant processes in those worlds, one must penetrate into these secrets if one wants to understand the human being at all. I would like to start by describing the life of a person between death and a new birth, but in order to understand what happens in this interim period, we must first consider the nature of the human being. For those who have been involved in anthroposophical studies for some time, the information in the introduction should not be new. But we must nevertheless consider these things very carefully from the outset in order to prepare ourselves for a complete understanding of the subsequent descriptions. For anthroposophical spiritual science, the essence of man is not merely that essence of a material nature, as it appears to the external senses, which we can touch with our hands and which is bound to the physical world by physical laws. Spiritual science shows that this physical body of man is only part of his entire being, and that man has this physical body in common with the mineral world. We can see for ourselves outside in nature, everything that appears to be dead, mineral nature, consists of the same materials from which the human body is built. The same physical processes occur in stone and in the human body, but there is a big difference between the processes of ordinary, inanimate physical bodies and the nature of man. An external physical body, like a stone, has a form, and it retains its form until an external process, such as smashing or some other force, destroys the form. The human physical body, on the other hand, or that of any other living being, is destroyed in death by the inherent laws of physical and chemical substances, and the human body is a corpse in this case. Spiritual science now shows us that in the state between birth and death, that is, during our physical lifetime, a second part of the human being is present as a constant fighter against the disintegration of the physical body. We call it the etheric body or life body. It is present in all of us. If this second link were not present in the human being, the body would only follow the physical forces in every moment; it would disintegrate. The fighter against this disintegration is the etheric body or life body. Only at death does this life body separate from the physical body. Man has this life body in common with every other living being; the animal has it, and the plant also has such a continuous fighter. In them too, there must be such a continuous fighter against decay. If the physical body has been described as a first link of living beings, and the life body as a second, then man has a third link in addition to these. We are able to see this with our intellect alone, with logic. Let us assume that a person is standing before us. Is there nothing more in this space that he occupies, in this hand that he uses, than what has been mentioned so far? Oh, there is something more in it than just bones and muscles, than all kinds of chemical components that we can see with our eyes and feel with our hands. And each one of us also knows very well that there is something more to it. This something more is the sum of his suffering and his joy; everyone knows this something, for it is everything that takes place in sensations and feelings, from morning to evening, throughout one's entire life. There is an invisible carrier of these sensations, and we refer to it as the astral body or the human being's body of sensation. This astral body, which is not perceptible to the physical eye of man, is considerably larger than the physical body. To the clairvoyant consciousness, it is recognizable as a cloud of light in which the physical body is embedded. This third link of his being man has in common with the animal, because the animal also has an astral body. But then there is still a fourth link in the human being, the crown of the earthly kingdom, the crown of human nature. We can see this fourth link when we trace an intimate movement of the human soul. There is one thing in man that can never approach him from the outside. It is this one name, the simple name 'I'. Only from the deepest depths of the soul can this name, this designation 'I', resound. Never can another human being say 'I' to a fellow human being. Man can only speak this to himself; it can only come from within him, from his own deepest inner being, and here something completely different, something divine, begins to resound through the name “I”. All great religions also felt that there is something sacred in the I. This is also clearly recognizable in the Old Testament. There the name 'I' is equivalent to the name of God. Only the priest was allowed to pronounce the name of God on particularly solemn occasions, at particularly solemn services, and when he reverently uttered the name 'Yahweh' in the temple, the name 'Yahweh' meant nothing other than 'I' or 'I am'. It was meant to signify that the God within man expresses himself. And only that being can utter these words in the soul to its soul in whose nature the divine essence reveals itself. The revelation of God in man is a fourth link in the human being. But we should not think that we are now God ourselves. It is a spark from the ocean of divinity that flashes in man. Just as a drop from the ocean is not the ocean itself, but only a drop from it, so the human ego is not God, but a drop from the divine substance: God begins to speak in the human soul. Only the priest was allowed to pronounce the holy name, Yahweh, on particularly solemn occasions. To make this divine being resound in the soul of man, so that man can say, “I am,” is the crowning of creation. This I-bearer, the fourth link in human nature, makes man the first among the beings that are visible in earthly creation. That is why the ancient mysteries everywhere spoke of the holy tetrad, the first link of which is the visible physical body, the second link the etheric body or life body, the third link the astral body or sentient body, and the fourth link the I. These are the four links that we want to look at first. And human life, human consciousness, depends on the way in which they are connected with each other. Only in day consciousness, in waking, do the four aspects of human nature interpenetrate. Then we have the physical body permeated by the etheric body, only finer and somewhat larger, rising above the physical body. Then we have the astral body, the carrier of our feelings, permeating the etheric body and, like a large shiny oval, surrounding the physical body, which is connected to the etheric body. And then we have the ego body. However, the four aspects of human nature only permeate each other when we are awake. When a person sleeps, the astral body with the ego carrier emerges, while the physical body, connected to the etheric body, remains in bed. In the morning, or when the person wakes up, the former two of the four members descend again and reconnect with the other two. What does the astral body do at night in the ordinary person? It is not inactive. To the clairvoyant's eye it appears as a spiral cloud, and currents emanate from it, connecting it to the physical body lying there. When we fall asleep tired in the evening, what is the cause of this tiredness? The fact that the astral body uses the physical body during the day when we are awake and thus wears it out appears as tiredness. But during the whole of the night, while we are asleep, the astral body is at work dispelling the fatigue. That is why we feel refreshed after a good night's sleep, and it shows how important it is for a person to have a truly healthy sleep. It properly restores what has been worn out by waking life. The astral body also repairs other damage during sleep, such as diseases of the physical and etheric bodies. You will not only have observed this in yourself and in other people from your own life experience, but you will also have learned that every sensible doctor says that in certain cases sleep is an indispensable remedy for recovery. That is the significance of the alternating state between sleeping and waking. Now we will move on to consider an even more important alternating state, that between life and death. As we have seen, as soon as sleep sets in, the astral body with the vehicle of the ego leaves the physical body connected with the etheric body. In ordinary life, this separation of the etheric body from the physical body hardly ever occurs, except in certain exceptional cases, which will be mentioned later. It is only at death that the physical body and ether body normally separate for the first time. Now, at death, not only does the astral body leave the four-part human being with the ego, as in sleep, but the three parts, ether body, astral body and ego, leave the physical body, and we have on the one hand the physical body, which remains behind as a corpse, is immediately attacked by physical and chemical forces and falls prey to destruction; on the other hand, we have a connection between the etheric body, astral body and I-bearer. The question now arises as to how anyone can possibly know how these conditions develop at death. Well, if you followed yesterday's public lecture, you will understand that those people who are able to see into higher spheres are also able to report on the conditions after death. And means are available and ways are offered for every human being to acquire such abilities, which is why there is also the possibility of knowing what a person experiences when he passes through the gate of death. If any facts are reported that cannot be immediately verified by anyone, then only those who really know can decide on their correctness. But if the reproach were made to the one who knows by those who know not, that he too could not know anything, then the reproach of arrogance would lie entirely with those who know not and yet claim that one can know nothing. Thus only the one who knows can decide what can be known. When a person has passed through death, he first has a feeling that he is growing into a world in which he becomes bigger and bigger and that he is no longer outside of all entities as in this physical world, not facing all other things, but, as it were, within them, as if he were crawling into all things. At the moment immediately following death you feel not a here and there, but an everywhere; it is as if you yourself were slipping into all things. Then there is a total recollection of your entire past life, which stands before you with all its details like a large tableau. This recollection cannot be compared with any recollection, however good, of your previous life, as you know it in earthly life, but this memory tableau suddenly stands before you in all its grandeur. What is the reason for this? It is because the etheric body is in fact the carrier of memory. As long as the etheric body was still enclosed in the physical body during earthly existence, it had to function through the physical body and was bound to physical laws. There it is not free; there it forgets, for there all memory steps aside that does not directly belong to the very next thing that the person is experiencing. But in death, as explained earlier, the etheric body, the carrier of memory, becomes free. It no longer needs to function through the physical, and so memories suddenly arise in an unbound way. In exceptional cases, this separation of the physical and etheric bodies can also occur during life. For example, in cases of mortal danger, when drowning, when falling, that is, in such cases where the consciousness receives a great shock through the horror. People who have been subjected to such a shock sometimes report that for a few moments their whole life stood before them like a tableau, so that the vanished experiences from the earliest period of their lives suddenly emerged from oblivion with full clarity. Such stories are not based on deception, but on truth; they are facts. At that moment of the flash of the memory tableau, something very special happens to the person; only, with such a shock, consciousness must not be lost. At that moment of the crash or other horror that caused the shock, something occurs that the clairvoyant can see. Not always, but sometimes, the part of the etheric body that fills the head region emerges from the head, either completely or in part, and even if this only happens for a moment, it still frees the memory, because at such a moment the etheric body is freed from the physical matter that hinders uninhibited memory. We can also observe a partial emergence of the etheric body on other occasions. If you press or bump any part of your body, a peculiar tingling sensation may occur, and we tend to describe this feeling by saying that the limb has fallen asleep. Children who want to describe what kind of feeling they have when this happens have often been heard to say: “I feel like seltzer water in my hand.” What does that mean? The actual cause is that the corresponding part of the life body has been removed from this limb for a while. The clairvoyant person can then perceive the elevated part of the etheric body near the physical body, like a copy of it. For example, when a person falls, the corresponding part of the etheric body is pushed out of the head by the falling movement. At death, this tableau of memories occurs immediately and with full intensity because the entire physical body is abandoned. The duration of this tableau of memories after death is also known. It is three to four days. It is not easy to give the reasons for this. This period of time is different for each person and roughly corresponds to the ability of the person concerned to stay awake without falling asleep for as long as they could have done so during their lifetime. After that, something else happens. What happens then is that a kind of second corpse is released. The human being now also leaves the etheric body behind; but he retains a certain essence of it, and that is what the person takes with him and retains for all eternity. Now, after discarding the etheric body, the time of the Kamaloka begins for the person, the Kamaloka state. If you want to understand what kind of state this is, you have to bear in mind that after leaving the physical and etheric bodies behind, the human being still has the astral body and the ego of his four limbs, and the question now arises for us as to what the astral body, with which the ego now lives into the time of the Kamaloka, is all about. The astral body is the carrier of pleasure and pain, of enjoyment and desire, so these do not cease when the physical body is discarded; only the possibility of satisfying desires ceases, since the instrument for satisfying desires, the physical body, is no longer available. Everything that the person was as a sentient being in the physical body does not cease to be. The person retains all of this in their astral body. Let us think of an ordinary desire, and for the sake of simplicity, let us choose one of a rather banal nature, for example, the desire for a tasty dish. This desire is not based in the physical body, but in the astral body. Therefore, this desire is not discarded with the physical body; it remains. The physical body was only the instrument with which this desire could be satisfied. If you have a knife to cut with, that is the instrument, and you do not lose the ability to cut when you put the knife away. So at death only the tool for enjoyment is laid down, and therefore man is first in a state in which all his various desires are represented, which now must be laid down or rather must be learned to be laid down. The time when this happens is the Kamaloka time. It is a time of testing, and it is very good and important for the further development of man. Imagine you were suffering from thirst and you were in a region where there was no water, and of course no beer or wine, no drink of any kind at all. You would suffer from a burning thirst that cannot be quenched. In a similar way, a person experiences a certain feeling of thirst when he no longer possesses the instrument with which he was the only one able to satisfy his desires. Kamaloka is a period of weaning for the person, since he must give up his desires in order to live in the spiritual world. This Kamaloka period lasts for a longer or shorter time for each person, depending on how well he has mastered the habit of giving up his desires. It depends on how the person has already acquired the habit of regulating his desires in life, and how he has learned to enjoy and to renounce in life. But there are pleasures and desires of a lower and a higher kind. We call those pleasures and desires, for the satisfaction of which the physical body is not the actual instrument, higher pleasures and desires, and these are not among those that a person has to get rid of after death. Only as long as a person still has something that draws him towards the physical existence - lower pleasures - does he remain in the astral life of the Kamaloka period. When nothing draws him back down after this period of disaccustoming, then he has become capable of living in the spiritual world, and then a third corpse emerges from the human being. The human being's stay in this Kamalokai period lasts approximately as long as a third of one's lifetime. It depends on how old the person was when they died, that is, how long they had lived in the physical body. However, this time of transition is not always terrible or unpleasant. In any case, the human being becomes more independent of physical desires through it, and the more he has already made himself independent in life and acquired interests in the contemplation of spiritual things, the easier this time of the Kamaloka will be for him. It makes him freer, so that the human being becomes grateful for this time of the Kamaloka. The feeling of deprivation in physical life becomes bliss in the time of the Kamaloka. Thus opposite feelings arise, for everything one has learned in life one is glad to do without in the time of the kamaloka period. When, as already mentioned, the third corpse emerges from the human being, then everything that the person cannot use in the spiritual world floats away with this astral body. These astral corpses are visible to the clairvoyant and take twenty, thirty, even forty years to dissolve. Since such astral corpses are continually present, they occasionally pass through the bodies of the living, through our own bodies, especially during the night, when our astral bodies are separated from the physical bodies during sleep. Just as an extract, a certain essence, remains for all eternity for the actual human being after the ethereal corpse has left, so too does a certain essence remain for him for all eternity after the astral corpse has left, as the fruit of the last embodiment. And now the time of Devachan begins for the person, the entry into the spiritual world, into the home of the gods and all spiritual beings. When a person enters this world, he experiences a feeling that can be compared to the liberation of a plant that grew in a narrow crevice and suddenly grows up into the light. For when man enters this heavenly world, he experiences complete spiritual freedom and from then on enjoys absolute bliss. What, in fact, is the time of Devachan? You can get an idea of it if you consider that man is preparing here for a new life, for a new reincarnation. In the physical world, in this lower world, man has experienced and learned so much, and he has taken these experiences with him. He has absorbed them like a fruit of life, which he can now freely process within himself. He now forms an archetype for a new life during the devachan period. This happens during a long, long time. It is a working on one's own being, and every working, every producing is connected with bliss. You can get an idea of the fact that every producing, every working is connected with bliss by observing a hen brooding an egg. Why does she do that? Because it feels like doing it. In the same way, it is a pleasure for a human being to weave the fruits of the past life into the plan for a new life in Devachan. In the chain of reincarnations, the human being has indeed already gone through many lives, but at the end of a life he is never the same as he was at the beginning of that life. In this life, forced into the physical body, he must behave quite passively. But now that it is free, freed from the physical body, from the etheric body and from the astral body, it weaves an image into its eternal essence, and this weaving in is perceived as bliss, as a feeling that cannot be compared to anything that it can ever experience in the physical world as bliss. His life is bliss in the spiritual world. But do not think that the physical life has no significance in this spiritual world. When bonds of love and friendship have been formed from soul to soul in life, only the physical part is lost with death, but the spiritual bond remains and forms lasting, indestructible bridges from soul to soul, which condense into effects in the archetypes. These are then able to be lived out in the physical in the following re-embodiments. It is the same in the relationship that exists between mother and child. A mother's love for her child is the answer to the prenatal love of the child for the mother, who, because of the affinity of her soul with the child, felt drawn to her as a result of her longing for re-embodiment. What then takes place in the life, in the jointly experienced embodiment between mother and child, forms new, soul ties that remain. And everything that bound soul to soul is already woven into the spiritual life that you find when you enter the spiritual world after death. The life between death and a new birth is such that what was done in the previous physical life has an effect. Yes, even the favorite pastimes that a person was devoted to in life have an effect. But after death, the human being becomes freer and freer, because he becomes a preparer for the future, for his own future. Does a person do anything else in the hereafter? Oh, he is very active in the hereafter. Someone might ask why a person is reborn and why he comes back to this earth at all if he can also be active in the hereafter. Well, this happens because re-embodiments never occur in such a way that a person is unnecessarily reborn in the course of them. He can always learn new things, and conditions on earth have always changed so that he enters completely different circumstances to gain experience for his further development. The face of the earth, the regions, the animal kingdom, the plant cover, all this is constantly changing in a relatively short time. Think back a hundred years. What a difference compared to today! It is not so long ago that every child learns to read and write by the age of six, as is the case in our society today. In ancient times, there were highly educated people who were at the head of the state and could neither read nor write. Where are the forests and animal species that populated the land five hundred years ago, which is now criss-crossed by railways? What were the localities like where our big cities are today, what were they like a thousand years ago? Only then is man reborn, only then does he enter into a new rebirth when conditions have changed so much that man can learn something new. Follow the centuries as the face of the earth is changed, torn down and built up by the intellectual powers of men. But there is also much that changes that cannot be worked on by the external intellectual powers of people. The plant cover and the animal world change before our eyes; they disappear and other species take their place. Such changes are brought about from the other world. A person walking across a meadow can see how a bridge is built over the stream, but he cannot see how the plant cover is built up. The dead do that. They are working to reshape and rework the face of the earth in order to create a different setting for themselves for a new reincarnation. After man has been busy with the preparations for the new reincarnation in this way for a long, long time, the moment approaches when it is to take place. What happens now? What does man do when he enters into his new incarnation? At that time man finds himself in his Devachan, and there he feels that he must first attach a new astral body to himself. Then, as it were, the astral substance rushes towards him from all sides, and depending on his character, it crystallizes around him, so to speak. You have to imagine it like iron filings being drawn to a magnet and grouping themselves around it. In the same way, the astral substance groups itself around the re-embodied ego. But then it is still necessary to choose suitable parents, and so the person is led to this or that pair of parents, but not merely in obedience to his own attraction. For in this process, exalted beings intervene and take action, who, in keeping with the present state of human development, have taken on the work of karmically ordering these relationships in a correct and just manner. If, therefore, parents and children occasionally appear to be out of harmony, there need be nothing wrong or unjust in that. Sometimes it is good for man to be brought into the most complicated conditions and to have to adjust himself to the strangest circumstances, in order to learn thereby. The succession of these repeated re-embodiments is not, however, an endless one. There is a beginning and there is an end. Once, in the distant past, man did not descend to incarnations. He did not yet know birth and death. He led a kind of angelic existence, not interrupted by such drastic changes in his condition as are present today in the form of birth and death. But just as surely as man will come to a time when he has gained sufficient experience in the lower worlds to have acquired a sufficiently mature, enlightened state of consciousness to be able to work in the exalted upper worlds without being forced to descend again into the lower worlds. After hearing the conditions presented here about repeated lives on earth, some people believe they should be afraid that the feeling of parental love could be affected by a mother learning that the child is not entirely of her flesh, because there is something about this child that is not of her, something foreign. But the bonds that span parents and children are by no means subject to chance and lawlessness. They are not new bonds. They already existed in previous lives and once existed in kinship and friendly connections. These bonds of love unite them permanently even in the higher worlds in eternal reality, and all people will one day be embraced in eternal love, even if they no longer descend into the cycle of re-embodiments. |

