| 32. Collected Essays on Literature 1884-1902: Another Ghost from the People
04 Sep 1897, |
|---|
| "Freedom is the alarm clock of passion and the moving force of execution, it is the cauldron of all freedom and exuberance. - It is the dream of the imprisoned and the terror of the prison guards. - Freedom is the highest bliss for corner-cutters and drifters and the political glue rod for social robins and bloodthirsty finches." |
| 32. Collected Essays on Literature 1884-1902: Another Ghost from the People
04 Sep 1897, |
|---|
Franz Wörther Karl Weiß-Schrattenthal, who succeeded in discovering Johanna Ambrosius three years ago, has just brought another "poet and thinker from the people" into the public eye. This time the discovered person is a Bavarian shoemaker, Franz Wörther. Anyone who had a sincere interest in the poetry of Ambrosius should also feel the same for this shoemaker. I have occasionally formed my opinion about the causes of such an interest. At the time, the poet and literary historian Karl Busse lashed out like a bull at those who had warm words for the East Prussian poet. I believe the reason for his behavior is that Busse was unable to find the right point of view from which the Lober of Ambrosius judged. Busse took a naïve standpoint and allowed the poems as such to have an immediate effect on him. The Lober did not do this. They looked at these creations as one looks at happy memories from childhood alongside the experiences of the day. Whoever is involved in the spiritual life of the present can only take such an interest in the poetry of the simple woman. No one who naively enjoys Dehmel's or Hartleben's poems can be captivated by Ambrosius with the same immediacy. But just as the serious man likes to remember his childhood, the modern educated or over-educated also enjoys the natural tones of the folk poet. We enjoy the memories of childhood, even if they tell of incomprehensible and stupid things. We do not question their reasonableness. In the same way, we do not ask about the aesthetic form in which we encounter such true natural sensations as those of Ambrosius. For the same reason, poets such as Rosegger, for example, have a far more significant effect on the educated than on the people. The people live in the feelings that such poets portray to them from morning to night; the educated have outgrown them; but they like to put themselves in their place, because the memory of them is sacred to them. When the thirteen-year-old Franz Wörther lost his father in 1843, he was alone in the world, without a friend or patron. He could now not think of becoming a master builder, as his father had wanted; with his idealism in mind, he had to learn shoemaking. After his apprenticeship, he traveled through northern and central Germany. He then spent five years as a soldier. After completing his service, he returned to the shoemaking trade. Wörther went through struggles with his soul. Sometimes the thinker and poet wanted to despair when the shoemaker had to provide bread for himself and his seven children. But the "man of the people" accepted his fate with true philosophical composure. He said to himself: "I regard the poetic gift I have been given as a gift from heaven for the happiness I have been robbed of. The dark defiance of former times no longer took hold of me; I dallied, as it were, serenely and calmly through the cliffs of life on the muses' rosebands." In his own way, this nature poet drew strength and courage to live from his own soul. And even if his poetry is often just a stammer, he stammers sounds that come from the chest of a whole man. Wörther does not speak in the perfect forms of the artist; what he speaks is as appealing and captivating as the products of nature. The fact that he seeks forms of art that he has not mastered is disturbing, indeed often tempts him to express a true sentiment untruthfully: but the genuine original source can always be discovered. But the poems are not the most important part of the little booklet that Schrattenthal has published. The wisdom sayings are of far greater interest. A true nature Nietzsche comes to us in Wörther. It is true that the natural thinker did not go as far as to revaluate the concepts of value he inherited; nor did he harbor any anti-Christian sentiments, but remained "pious" to this day. But he coined the ancestral concepts anew for himself; he gave them an individual form. A man who wrote the following thoughts on "freedom" deserves our greatest attention. "Freedom is the alarm clock of passion and the moving force of execution, it is the cauldron of all freedom and exuberance. - It is the dream of the imprisoned and the terror of the prison guards. - Freedom is the highest bliss for corner-cutters and drifters and the political glue rod for social robins and bloodthirsty finches." Wörther gives a clear, understandable verdict in a transparent, simple form on the concept of "equality": "Equality is the longing of the ugly and the horror of the beautiful. It is the colorful, iridescent soap bubble of all social democratic phrases and the necessary embellishment of agitation speeches. - Equality is the dissolution of civilization and the return of humanity to its original state of the Stone Age and the pile dwellings with the uniform fashion of Adam and Eve. It is therefore the beginning of the end of all tailoring. - Equality is the tablecloth for the Cinderellas of destiny." A subtle sentiment is reflected in the sentence: "Envy even puts dirt in the hands of the child who secretly wants to throw at his playmate the colorful rag that his parents hang around his shoulders in monkey-like love." And the saying: "A heart without gratitude is like a faded rose bush that holds only thorns for the wanderer" reveals that a noble disposition can also thrive on the cobbler's chair. The pride of an independent personality built on its own strength and dignity is also characteristic of our shoemaker. He finds that "the cowardly sycophancy of the rich man is called pride of status, his avarice is called economic calculation, while the profligacy of a man's lower mind is called worldly noblesse, and the lack of character of a rich man is called miserable sycophancy diplomatic statesmanship". Franz Wörther currently lives in his birthplace of Kleinheubach am Main. He provided for his seven sons with his shoemaking skills. He was a valiant craftsman. Schrattenthal has shown that he was even more through the commendable publication of his intellectual products. Those who can only enjoy the book aesthetically will soon put it down; those who have a sense for the contemplation of a self-contained personality, perfect in its own way, will read it through from beginning to end. The coarse naturalness will refresh such a connoisseur, and the clumsiness in the artistic will not bother him much. |
| 24. The Renewal of the Social Organism: The Way to Save the German Nation
Translated by Ethel Bowen-Wedgwood, Ruth Marriot, Frederick Amrine |
|---|
| What kind of solution can b e found? Yes, they were dreamers if their descendants dream away their ideas; but they were radiant spirits of reality if these descendants receive their ideas as a force for living, awakened will and purpose. |
| 24. The Renewal of the Social Organism: The Way to Save the German Nation
Translated by Ethel Bowen-Wedgwood, Ruth Marriot, Frederick Amrine |
|---|
[ 1 ] In the year 1858, Hermann Grimm wrote an essay entitled “Schiller and Goethe.” It begins with these words: “The true history of Germany is the history of the spiritual movements among her people. Only when enthusiasm for some great thought has inspired the nation and set its frozen forces flowing, do deeds of great and shining fame occur.” And further on we read: “... the names of the German emperors and kings are not milestones of the nation's progress.” [ 2 ] Only a revival of the attitude underlying such words can shed light upon the troubled time that has come upon the German people. That something else from this attitude may yet awaken amid the commotion and labor of present times is the one hope to be cherished by he who holds it necessary above all for the German people to turn for help to the saving power of thoughts. Those who say today that one must first wait to see what shall come of the general situation and what relations with the people of the West and East shall result from new world conditions, have no concept of the age's necessities. This view has led to everything said in these pages about the idea of the threefold social order. I believe that in the previous essays I have sufficiently answered the constant objection that our first thought must be the outcome of our relations with foreign nations before we can turn our attention to social ideas, like that of the threefold system. This objection rests on a fallacy that may prove bitterly fatal to the German people. Germany has come out of the world catastrophe in such a way that she must first create a basis for future relations with the nations around her. Her economic life (if its development were detached from the political life of laws and from the cultural field) would take on a form that could give it a place in the whole system of world economy. As I have tried to show in these essays, it would be in the interest of other nations to give an economic life of this kind its place in the system of world economy. An independent cultural life can be regarded by no other nation as a ground for hostility; a political-legal life among the German people based on the equality of all adults could not be viewed as a hostile element by non-Germans without their deriding themselves. [ 3 ] However, an idea like the threefold order must come before the world with the driving force of a definite will in public affairs. The moment this idea is observed on the way toward becoming fact, it can become such a revelation of the innermost German being as will give the rest of the world something firm with which to reckon. Facing modern circumstances, facing the lack of faith in the practical efficacy of living ideas, one might well ask what has become of the German spirit. In ideas such as those written by Hermann Grimm sixty years ago, the voice of the greatest spirits of their own history speaks to the German people. In such ideas, these great spirits intended to utter the deepest will and purpose of their people. Shall the descendants of these spirits be deaf to them? [ 4 ] These descendants are in a situation where truly it is not enough merely to remember the ideas of their forefathers, but where they must carry forward these ideas in a new form suited to modern times. Would the German deny his own being through lack of faith in ideas, and thus lose his very self? Surely the best part of the German spirit lies in this faith in the potency of ideas. And a revelation of the German spirit, once displayed in its genuine truth, would be one with which the world must reckon. [ 5 ] A large enough number of Germans who share the heritage of faith in the intellectual world, and bring to it all the forces of their souls, must be the saving of their people. No negotiations with the world abroad will be of any good to the German people if carried on with indications of disbelief in ideas and their practical utility, for in all such negotiations the very core of the German spirit is absent. [ 6 ] All objections stemming from the view that now is not the time to indulge in ideas should be silenced. There can be no question of any time that will bear in it the seeds of any real possibility of life for the German people, until the power of ideas has been recognized by a sufficiently large number of people. Not a faith that trims its ideas according to outer events, but a faith in ideas—that shall be the force that moves the German nation. What results may be confidently awaited in the same faith; to thrust it aside and to wait idly in a round of false activity while destiny pursues its course—this, for every German, is a sin against his own being, a sin against the spirit of this world hour, a sin against the demand of true self-awareness. [ 7 ] Is not the influence of this sin plain enough to see? Are not the grievous effects of this sin already with us? Do not distress and want proclaim the sin in language comprehensible enough? Have the German people lost the power to recognize the sin they have committed against their own true spirit? These are questions that may well tear at the souls of all who study the public life of the German people. The pain should rightly lead to an awakening. Were the great spirits of the German past, with their faith in ideas, mere dreamers? Such questions find answers only in real life. What kind of solution can b e found? Yes, they were dreamers if their descendants dream away their ideas; but they were radiant spirits of reality if these descendants receive their ideas as a force for living, awakened will and purpose. |
| 36. Collected Essays from “Das Goetheanum” 1921–1925: Anthroposophy and Idealism
29 Apr 1923, |
|---|
| But such a person would be like someone who awakens from a dream but does not feel the awakening as a jolt of life, but instead sees both experiences, dreaming and being awake, as equivalent. |
| 36. Collected Essays from “Das Goetheanum” 1921–1925: Anthroposophy and Idealism
29 Apr 1923, |
|---|
A better understanding of anthroposophy would be gained than is the case today from some quarters if one were to delve into the nature of the intellectual struggles that took place in the second half of the nineteenth century. This was the time when certain thinkers believed that the victory of scientific research over philosophical endeavor, as it had been active in the previous epoch, seemed decisive. They pointed to Hegel, who, in the opinion of these thinkers, had wanted to develop the whole world out of the idea, but who had completely lost the world of reality in his thought constructions; while the sovereign natural science started from this reality and only engaged with ideas to the extent that observation of the sensory world allowed. This way of thinking seemed to be confirmed in every respect by the positive results of natural science. One has only to read books such as Moriz Carriere's “Moral World Order,” published in 1877, and one will become acquainted with a spiritual warrior who wanted to defend the right of idealism against “sovereign natural science.” There were many such spiritual fighters in those days. It may be said that the prevailing school of thought has stepped over them, in the knowledge that their cause is lost. Gradually, no more attention has been paid to them. Through their scientific idealism they wanted to save for humanity the knowledge of the spiritual world. They realized that “sovereign natural science” must endanger this knowledge. They contrasted what could be observed with the world of ideas living in human self-awareness and believed that this was a testimony to the fact that spirit rules in the world. However, they were unable to convince their opponents that the world of ideas speaks of a different reality than the one on which natural science is based. Anthroposophy, looking back at these spiritual warriors, feels differently than the thinkers standing on the ground of “sovereign natural science”. It sees in them personalities who came as far as the door of the spiritual world, but who did not have the strength to open it. Scientific idealism is right; but only as far as someone who sets out to enter a region, but only has the will to reach the border of the region, but not to cross that border. The ideas to which Carriere and his like pointed are like the corpse of a living being, which in its form points to the living, but no longer contains it. The ideas of scientific idealism also point to the life of the spirit, but they do not contain it. Scientific idealism aspired to the ideas; anthroposophy aspires to the spiritual life in the ideas. Behind the thinking power that rises to the ideas, it finds a spiritual formative power that is inherent in the ideas like life in the organism. Behind thinking in the human soul lies imagination. Those who can only experience reality in relation to the sense world must see imagination as just another form of fantasy. In our imagination, we create a world of images to which we do not ascribe any reality in relation to our sensory existence. We shape this world for our own enjoyment, for our inner pleasure. We do not care where we got the gift of creating this world. We let it spring forth from our inner being without reflecting on its origin. In anthroposophy, we can learn something about this origin. What often prevails in man as a frequently exhilarating imagination is the child of the power that works in the child as it grows, which is active in the human being at all when it forms the dead materials into the human form. In man the world has left something of this power of growth, of formative power, something that it does not use up in fashioning the human being. Man takes possession of this remnant of the power that shapes his own being and develops it as imagination. One of the spiritual warriors referred to here also stood at the threshold of this knowledge. Frohschammer, a contemporary of Carrieres, has written a number of books in which he makes imagination the creator of the world, as Hegel made the idea or Schopenhauer the will. But we cannot stop with fantasy any more than we can with ideas. For in fantasy there is a remainder of the power that creates the world and gives form to the human being. We must penetrate behind fantasy with the soul. This happens in imaginative knowledge. This does not merely continue the activity of imagination; it first stops in it, clearly perceiving why, in contrast to the sense world, it can only acknowledge unreality, but then turns around and, moving backwards, reaches the origin of imagination and thinking. She thus enters into spiritual reality, which reveals itself to her through inspiration and intuition (spiritual perception) as she advances. She stands in this spiritual reality as sensory perception stands in physical reality. Imagination can only be confused with fantasy by those who do not feel the jolt of life between the consciousness that depends on the senses and the consciousness that lives in the spirit. But such a person would be like someone who awakens from a dream but does not feel the awakening as a jolt of life, but instead sees both experiences, dreaming and being awake, as equivalent. The abstract thinker fears that imagination will continue to be fantasized; the artistic person feels slightly uncomfortable that the imaginative activity, in which he wants to develop freely, undisturbed by reality, should accept another activity, of which it is a child, but which reigns in the realm of true reality. He imagines that this casts a shadow over the free child of the human soul. But that is not the case. Rather, the experience of spiritual reality only makes the heart beat faster in the realization that the spirit sends an offspring into the world of the senses through art, which only appears unreal in the world of the senses because it has its origin “in another world”. Anthroposophy wants to open the gate where noble spiritual fighters stood in the second half of the nineteenth century, without the strength to unlock this gate. The power of thought showed them the way to the ideas; but this power of thought froze in the ideas; Anthroposophy has the task of melting the frozen power. |
| 36. Collected Essays from “Das Goetheanum” 1921–1925: The False and the True Threefold Order of the Social Organism
13 Nov 1921, |
|---|
| Even in the most practical questions of life, it dreams of goals that must falter in the face of reality. Only a keen observation of this reality can lead to recovery. |
| 36. Collected Essays from “Das Goetheanum” 1921–1925: The False and the True Threefold Order of the Social Organism
13 Nov 1921, |
|---|
The confusion in the economic conditions of Central and Eastern Europe is beginning to cause a kind of political nightmare for the leading circles of Western countries. There is a fear of being drawn into the general decline. Those who can look this fear in the eye without prejudice can see the perplexity in the conduct of public affairs. This lack of orientation is rooted in the lack of will to look beneath the surface of public life. People shy away from doing so. Because they sense that such a look would reveal things that cannot be dealt with by the means to which one has become accustomed. So people organize congresses and conferences: for the time being, it is taken for granted that they only think of these familiar means. But these means will inevitably fail in every case, because they do not address the forces that prevail in the depths of the life of nations. And it is in these depths that the questions that trouble the world are now taking shape. We should act on the realization that something in these depths is crying out for a change in our outlook on life and our way of life. In its view of world events, humanity has been torn out of real life. Even in the most practical questions of life, it dreams of goals that must falter in the face of reality. Only a keen observation of this reality can lead to recovery. All political and economic life is ultimately rooted in the spiritual. How people think is how they act. But healthy forces can only flow into action if the spiritual life has healthy nourishment. This nourishment is lost when the spirit denies itself. When it expresses not itself but spiritlessness in its revelations. Humanity has been thrown into this state in the most recent times. People have become accustomed to expressing not the spirit but only the spiritless, the materiality of life, through the spirit. But those who seek the truth in this way will ultimately lose it altogether. For the truth wants to be shaped out of the spirit even when it draws the material processes of life into its realm. A search for truth that cannot draw its juices from the spirit itself will, out of inner necessity, end up with the phrase. And the phrase is today the hallmark of public life. The parties coin the phrases. They agitate with the phrases; they find credence with the phrases. Phrases lack the lifeblood of the spirit. They will therefore never be able to permeate the reality of life. But they numb. They cast a spell over people's souls. They believe that through them they can master public life. However, recovery will not come until a sufficiently large number of people have recognized the infertility of phrases in their lives. Until then, we will not even be able to see the roots of the current widespread diseases. We will see reality sailing in the confusion of foreign currencies; but we will speak of “improving conditions” in party slogans. And when the slogan becomes the mistress of intellectual life, it also does not allow the truth to prevail in political and legal life. The behavior of men towards one another cannot take on the form of law. For the law must take root in the feelings. But phraseology withers the feelings. Law becomes convention. In the legal and political sphere, convention is the companion of phraseology, which lives out itself on the spiritual plane. Convention can eke out its existence in dead laws and administrative measures; real life needs the law rooted in the soul in the social sphere, just as the spiritual life needs the spirit, and under the power of phraseology it withers away. In economic life, routine develops under the influence of phraseology and convention instead of real practice. And this routine actually dominates the economic side of existence today. Economic life does not unfold in harmony with the other needs of the human way of life. It has gradually become an element of existence to which man devotes himself because he simply has to live, but which he does not include in the whole of his life's development. When the spirit and the law shape the mind in their truth, then in the economic field arises the genuine practice of life. But when the management of the purely material-technical in economic life prevails, then the bloodless, heartless routine arises. Like an automatic mechanism, the processes of economic life roll under the power of routine. They draw human life itself into their cycle. Today's humanity groans under the power of routine in economic life. It deserts the genuine sense of justice; it creates indifference to the spiritual and an inclination to get carried away by empty phrases. For in life, the cause not only produces the effect, but the effect also has an effect on the causal agent. Phrase and convention push towards routine; routine allows phrase to flourish, and the warm-hearted human coexistence in a fertilizing sense of right degenerates into heartless, life-paralyzing convention. A tripartite division of the social organism has arisen under the force of modern life, which expresses itself in phrase, convention and routine. The “threefold social organism” seeks to overcome this threefold division. It is criticized for wanting to divide what is social unity. It really wants the opposite. It wants it because it believes it has the knowledge that under that striving for unity, which is held against it, the threefold division of social life into phrase, convention and routine is forming. This tripartite division can only be remedied by the healthy interaction of the three elements of the social organism. The unreality of the phrase must be recognized through the impulses of a free spiritual life, the coldness of convention through the recovery of the sense of right, and the barrenness of routine through the mechanization of existence. Existence is only viable through truth in the spirit, justice in the coexistence of people, and genuine practice in economic activity. Just as the whole organism of the individual suffers when a limb is deprived of its very own conditions of life, so the social organism cannot flourish when the spiritual life wastes away in empty phrases, the legal life dies in convention, and the economic life mechanizes in routine. Even if this is expressed in the famous old Roman parable, humanity suffers particularly today from the fact that its leaders sin against it. This parable has also become a cliché. |
| 36. Collected Essays from “Das Goetheanum” 1921–1925: Further West-East Aphorisms
18 Jun 1922, |
|---|
| If, at the end of the Westerner's concern for proof, the Easterner finds his unproven truth dreams in a true awakening, then the Westerner will have to greet him in the work for human progress as a colleague who can achieve what he himself cannot. |
| 36. Collected Essays from “Das Goetheanum” 1921–1925: Further West-East Aphorisms
18 Jun 1922, |
|---|
The ancient Oriental felt that he was part of a spiritually ordained social order. The commandments of the spiritual power, which his leaders brought to his attention, gave him ideas about how he had to integrate himself into this order. These leaders had these ideas from their vision into the supersensible world. The follower sensed in them the guidelines for his spiritual, legal and economic life, which had been conveyed to him from the spiritual world. The views on man's relationship to the spiritual, on the behavior of man towards man, and also on the management of economic affairs, came to him from the same source of the spirit-willed commandments. In experience, spiritual life, the legal order, and economic management were a unity. The further culture spread to the West, the more the legal relationships between people and the management of economic affairs became separated from the spiritual life in the consciousness of people. The spiritual life became more independent. The other elements of the social order still remained as a unity. As civilization advanced further to the West, these too became separated. Alongside the legal-state order, which for a time also regulated all economic activity, an independent economic way of thinking developed. The Westerner still lives in the process of this latter separation. And at the same time, the task arises for him to shape the three separate elements of social life – intellectual life, legal and state behavior, and economic management – into a higher unity. If he succeeds in doing so, the Easterner will look sympathetically at his creation, for he will rediscover what he once lost, the unity of human experience. Among the partial currents, whose interaction and mutual struggle constitute human history, is the conquest of labor by human consciousness. In the ancient Orient, man worked in accordance with the spirit-willed order imposed on him. In this sense, he found himself as a master or a worker. With the westward march of cultural life, the relationship between human beings entered human consciousness. Interwoven into this was the work that one person does for another. The value of labor found its way into legal concepts. A large part of ancient Roman history depicts this growing together of the concepts of law and labor. As culture advanced further westward, economic life took on ever more complicated forms. It absorbed labor, but the legal form which it had previously taken did not meet the demands of the new forms. Disharmony between labor and legal conceptions arose. To restore harmony between the two is the great social problem of the West. How labor can find its form in the legal system without being torn out of its essence by the economic administration, that is the content of the problem. If the West, through insight and social calm, sets out on the path of solution, the East will meet it with understanding. If in the West the problem gives rise to a way of thinking that lives out in social upheaval, the East will not be able to gain the trust of the West in the further development of humanity. Unity of spiritual life, legal system and economic management in the sense of an order willed by the spirit can only exist as long as agriculture predominates in the economy, and trade and industry are integrated as subordinate to land management. Therefore, the spiritually inspired social thinking of the ancient Orient essentially supports the economic management of agriculture. With the spread of civilization to the West, trade first emerges as an independent economic activity. It demands the provisions of the law. It must be possible to trade with every human being. Only the abstract legal norm can meet this need. As civilization progresses further west, trade in industry becomes an independent element in the provision of economic services. One can only produce goods fruitfully if one lives in a way that corresponds to human abilities and needs with the people with whom one has to work in production. The development of the industrial spirit requires associative links shaped by economic life, in which people know that their needs are met, as far as natural conditions allow. Finding the right associative life is the task of the West. If it proves equal to this task, the East will say: our life once flowed in brotherhood; it has faded over time; the progress of humanity has taken it from us. The West will make it flourish again through associative economic life. It will restore the vanished trust in true humanity. In the old East, when man composed poetry, he felt that the powers of the spirit were speaking through him. In Greece, the poet allowed the muse to speak to his fellow men through him. This consciousness was the heritage of the ancient Orient. With the westward course of spiritual life, poetry became more and more the revelation of man. In the ancient Orient, the spiritual powers sang through people to people. The word of the world resounded from the gods down to men. — In the West it has become the word of man. It must find the way up to the spiritual powers. Man must learn to write poetry in such a way that the spirit may listen to him. The West must shape a language that is appropriate to the spirit. Then the East will say: the word of the gods, which once flowed out to us from heaven to earth, finds its way back from human hearts to the spiritual worlds. In the rising human word, we see and understand the world word, whose descent our consciousness once experienced. The Eastern man has no sense of “proof”. He experiences the content of his truths by looking at them and thus knows them. And what one knows, one does not “prove”. — The Western man demands “proof” everywhere. He struggles to the content of his truths through the outer reflection of thought and thus interprets them. But what one interprets, one must “prove.” If the Westerner frees the life of truth from his proofs, then the Easterner will understand him. If, at the end of the Westerner's concern for proof, the Easterner finds his unproven truth dreams in a true awakening, then the Westerner will have to greet him in the work for human progress as a colleague who can achieve what he himself cannot. |
| 91. Man, Nature and the Cosmos: Forms of Consciousness
12 Aug 1905, Haubinda |
|---|
| The consciousness of deep trance, dreamless sleep consciousness, dream sleep consciousness, waking consciousness, psychic consciousness, super-psychic consciousness, spiritual consciousness. |
| 91. Man, Nature and the Cosmos: Forms of Consciousness
12 Aug 1905, Haubinda |
|---|
In addition to the seven known forms of consciousness, there are five more, twelve levels in total. The consciousness of deep trance, dreamless sleep consciousness, dream sleep consciousness, waking consciousness, psychic consciousness, super-psychic consciousness, spiritual consciousness. Spiritual consciousness on the volcano is so high that the person becomes a kind of creator. But what about the higher beings that have begun to develop even higher abilities than merely knowing, doing and creating everything? With spiritual consciousness, the person would be a magician, he could create beings. But there is one thing he still cannot do: emanate from his own being, give off substance. That is the ability of the five higher levels of consciousness: the ability not only to shine, to radiate light, but to radiate matter, to give off one's own substance. We can distinguish between emanating consciousness, perceiving consciousness and active consciousness, that is, consciousness that creates forms. When we create forms, substance is already there; we merely give it form. When we perceive, form is already there; we emanate images. When we have emanating consciousness, we let the substance itself flow out. The actual emanating consciousness is the stages twelve, eleven, ten and nine of consciousness; the stages of perceiving consciousness are eight, seven, six, five, and of forming consciousness four, three, two, one. Before something is formed or perceived, something must first be there, and therefore the emanating consciousness first has the task of radiating the material for such a world, of spinning the material out of itself, so to speak. This is called the 'first emanation': the emanating consciousness emits the substance. The substance should not be underestimated; it arises from the sacrifice of a higher consciousness. Where does the substance come from? It comes from where the future substance will come from, it comes from consciousness. The second thing that happens is that the forming consciousness intervenes; that is the 'second emanation'. And when this forming consciousness has created forms, the perceiving consciousness can take them up – the 'third radiation'. The first emanation that emanates the material is also called the third logos; the forming one that builds the plastic figures is called the second logos; and the perceiving consciousness is called the first logos. Christian esotericism calls the world of the third logos, in which the gods sacrifice their consciousness, radiate: the heavenly world; the world of the second logos: the underworld; and the world of the first logos: the human world. Let us apply these general concepts to our own humanity. On Saturn, we have the emanation of a matter; on the Moon, the emanation of a spirit. The spirits of will emanate matter out of their consciousness. The human body is formed out of this matter. The primal forces – Asuras – first embody themselves in it; they become human, so to speak. [Christian Science also calls the spirits of the personality primal forces.] On the sun, it is the spirits, the Sons of Fire, the Agnishvattas, who become men. On the moon, the spirits of the twilight, the Lunar Pitris, become men. On the earth, men become real men. On Jupiter, lower beings become men – these are the evil ones. Man rises higher, becomes an angel in a certain sense; on Venus he becomes an archangel and on Vulcan a primal power. We now have to fall back on radiating matter on the part of the spirits of will. From this matter the physical body is formed on Saturn, transformed on the Sun, on the Moon and on the Earth, and now it begins to crumble, to peel off from the human being - when he becomes an angel, an angel of light. We have an analogy in the coral colony; it is rooted in the water, more and more lime is deposited on it, and more and more little animals form on it, which die; the coral grows as a result. In this way our planet will deposit more and more coal. Nothing is without matter; when one loses itself, a new one, albeit thinner, must take its place. People move into the angelic stage, lose physical matter, but maintain the etheric body. Etheric matter forms the body up to the volcano, where it loses itself, as does physical matter here. The other beings, who were already higher, will naturally continue to ascend. The spirits of twilight – Lunar Pitris – are on Earth one step higher than humans, and accordingly, they progress upwards. This level of entities will not only be endowed with spiritual consciousness on Vulcan, but also on Venus. On the level before that, on Jupiter, the Agnishvattas – archangels – have spiritual consciousness. And still one level earlier, on Earth, the elemental forces – Asuras – have their spiritual consciousness, so that in the normal course on Earth, those spirits of personality who had reached their humanity on Saturn attain their spiritual consciousness. They are endowed with free will, so they can stray here. Therefore, here on Earth, the battle takes place between the elemental forces that turn away and those who follow their ascent. This battle between the elemental forces of light and those of darkness is described in the Bhagavad Gita and the Book of Enoch. It takes place at the moment of human incarnation. Two elemental forces are born, one group under the leadership of the descending one, another group under the leadership of the ascending one; the latter is called Christ by Christian esotericism. [Do you remember the image?] The plant represents the inverted human being. In the plant, the head is directed downwards; in the human being, it is directed upwards. The incarnation is an inversion. As a lower being, the human being was directed head downwards; later, he turned upwards. When we remember Hephaestus, it is an image of the crumbling away of the parts that are directed downwards. Hephaistos is wounded by the evil leader. The good primal power — Christ — shines forth from the earth from humanity in the forefront with a consciousness that will only be granted to man himself on Vulcan. Christ is the first to reveal himself from the new matter emanating from earthly existence. The first to manifest in the new matter independently of the old matter is Christ. This manifestation is called: the birth out of the virgin matter [or out of the Virgin]; out of the second Logos, the beginning of the Gospel of John. Thus, the appearance of Christ on earth is the center of the whole evolution. It is a cosmic event that has significance for the whole evolution. |
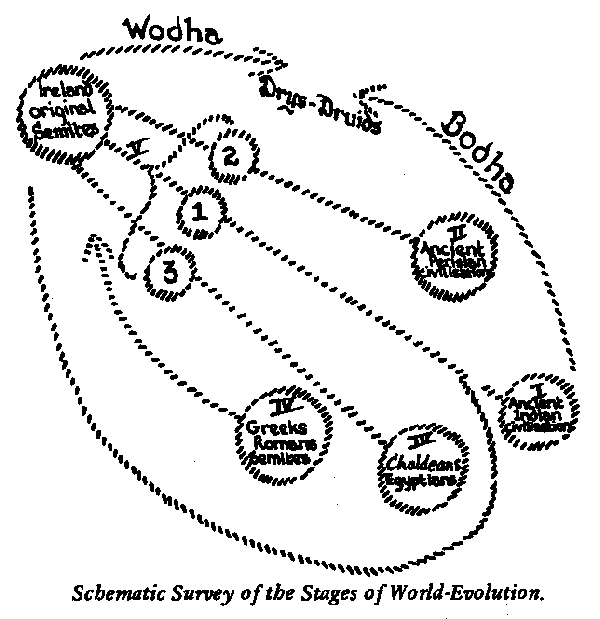
| Foundations of Esotericism: Schematic Survey of the Stages of World Evolution
Translated by Vera Compton-Burnett, Judith Compton-Burnett |
|---|
| Seven Stages of Consciousness (Planetary Evolutions) Trance Consciousness, Universal Consciousness (Old Saturn) Deep Sleep Consciousness, Dreamless Consciousness (Old Sun) Dream Consciousness, Picture Consciousness (Old Moon) Waking Consciousness, Awareness of Objects (Earth) Psychic or Conscious Picture Consciousness (Future Jupiter) Super-Psychic or Conscious Sleep-Consciousness (Future Venus) Spiritual or Conscious Universal Consciousness (Vulcan) Each of these develops through Seven Conditions of Life (Rounds, Kingdoms) First Elementary Kingdom Second Elementary Kingdom Third Elementary Kingdom Mineral Kingdom Plant Kingdom Animal Kingdom Human Kingdom Each of these pass through Seven Conditions of Form (Globes) Arupa Rupa Astral Physical Plastic-Astral Intellectual Archetypal or Primal-Pictorial Every Condition of Form again goes through 7 x 7 stages of development; for instance our present Fourth Condition of Form (of the Mineral Kingdom, within the Fourth Planet, the Earth) goes through the so-called 7 Root-Races (ages or Main Periods of Time) and again through the Cultural Epochs of our present Fifth Root-Race (Post-Atlantean Age). |
| Foundations of Esotericism: Schematic Survey of the Stages of World Evolution
Translated by Vera Compton-Burnett, Judith Compton-Burnett |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 90a. Self-Knowledge and God-Knowledge I: Further Development of our Planet
10 Jul 1904, Berlin |
|---|
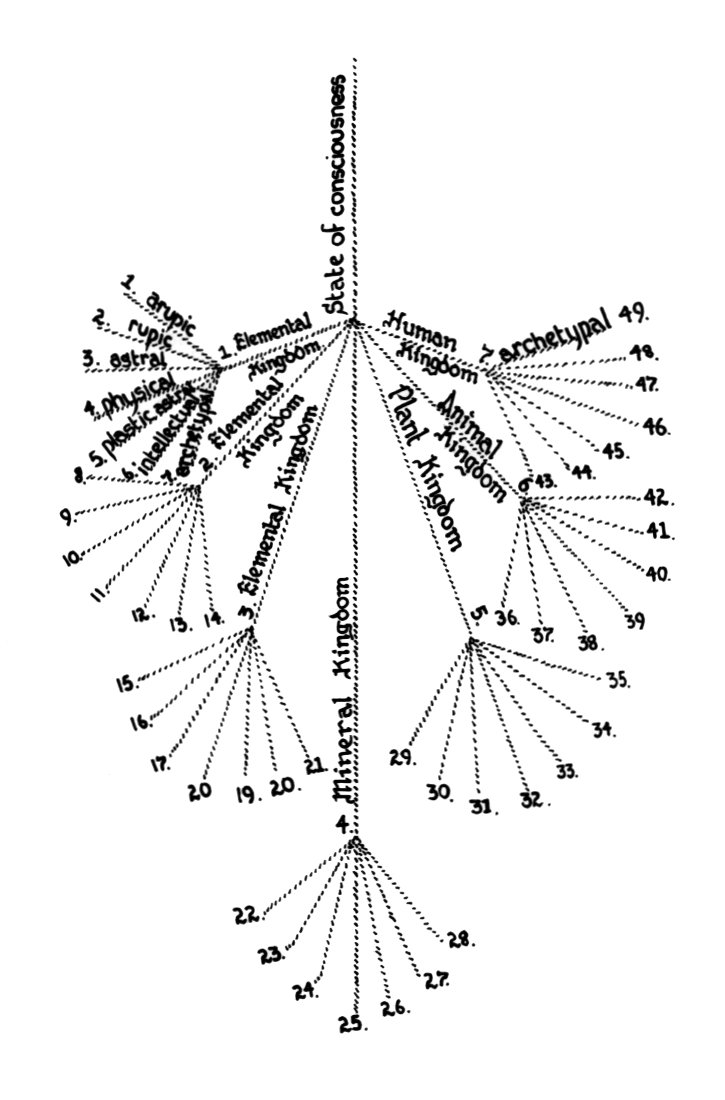
| Trance consciousness 2. Deep sleep consciousness 3. Dream consciousness 4. Wakefulness consciousness] 5. Soul consciousness 6. Oversoul consciousness 7. |
| 90a. Self-Knowledge and God-Knowledge I: Further Development of our Planet
10 Jul 1904, Berlin |
|---|
We are dealing with a progressive development of our planet. The purpose of our Earth is to develop this consciousness within us. Each planet goes through metamorphoses of seven successive levels of consciousness: [1. Trance consciousness We have now established the [seven] metamorphoses of the father principle. Each of these seven metamorphoses of the father principle now undergoes seven principles in itself. Seven times seven. Now we come to the son principle: 1. Elemental kingdom Each of these 49 metamorphoses undergoes seven transformations, and the transformations through the spirit principle. Each realm undergoes the seven powers once. For example, plant consciousness undergoes the seven powers once through the seven realms and seven times seven – each realm seven times the powers. su>run The father metamorphoses seven times in seven levels of consciousness. All – plant – animal – human [gap in the transcript] Puruscha: The Father metamorphoses seven times in seven stages of consciousness: All-consciousness - plant consciousness - animal consciousness - human consciousness - soul consciousness - oversoul consciousness - spirit consciousness. Pakriti: The son metamorphoses seven times at each of these levels: first elemental realm, second elemental realm, third elemental realm, mineral realm, plant realm, animal realm, human realm. Mahat: The mind metamorphoses seven times in each realm: Divine Spirit, Fire Spirit, Warmth Spirit, Light Spirit, Power Spirit, Creative Spirit, Blissful Spirit. [IMAGE REMOVED FROM PREVIEW] The way the realms are arranged in the individual levels of consciousness, however, makes us think as we describe them. On the first planetary chain, the forces of light rule the first elemental realm in the fourth round. That is a fixed point. On the second chain or level of consciousness, the forces of light mainly rule the second elemental realm in the fourth round. On the third chain or level of consciousness, the forces of light rule the third elemental realm, and on the fourth, our level of consciousness, the forces of light rule the mineral realm. This is important because the rulers are not always the same. During each round, all seven forces are experienced, but not in the same way. On the moon, the mineral kingdom was ruled by the forces of warmth, -— previously by the forces of fire, on the first / gap in the transcript] by the forces of life. When Mars completed its fourth stage, its mineral state, its angel of orbital period was the divine spirit. Consciousness was an all-consciousness. When the beings arrived in the mineral kingdom, they were ruled by divine spirits. On the first globe (arupa), the power spirit rules. Because this goes in a circle, Mars concludes with the highest development of light. Now he has developed light to the highest degree; the second planet begins. And what he has conquered in the previous one, he carries over. Now he shines and is called esoterically: the sun. Now he has during his the creator spirit, the blessed spirit, the divine spirit. Now the sun reveals itself during its mineral state as fire, the plants are cooked. - Now it continues: Fire and hands over the power to the moon, and the power becomes that which permeates the moon, therefore it organizes [gap in the transcript] the moon period begins with creative spirit, develops arbitrariness, man arises as pleasure and pain. Arupa stage – blissful mind Warmth is revealed on the moon while it is physical. The earth begins with Arupa stage – Divine spirit We are ruled by the light spirit, which is why the sun shines for us. Now it depends on when a certain stage of Pitri is reached. Imagine you remain behind, a certain constellation of the stars comes, in which violence has a different relationship to the realm; the spirit to the son in another relationship, and that is decisive, as we are in our state of development. That is esoteric astrology. He must know at which level the Pitri stands and what the relationship between father and son is. This is also the danger of the higher development of man: he comes out and into other cosmic influences. - He practices black magic by being carried away and coming into another sphere of influence. - Look at the diagram: Each time we have seven kingdoms that go through certain stages of development. These are the son principle; hence 343 states, but only after every 49 states - so that every time a person has gone through 49 states, they have a particular turning point in their development. Something special is revealed to them. They enter a new series of 49. The Son reveals Himself. The human being becomes more inward-looking. The kingdom principle is evoked through the Son, and so the Son, Christ, reveals Himself. So Christ appears each time. Our Christ is the one. And when the experience of Christ is fully realized within a person, they have undergone the 172nd metamorphosis. After the 343rd metamorphosis, they have returned to the Father. This is why Christ can say: “No one comes to the Father except through me.” There are Our Christ was the twenty-fifth; in every kingdom the Son reveals Himself once. 49 times in a planetary development. The Father reveals Himself in the constellation. On our Earth it is the fourth, on the planetary chain the twenty-fifth. 7 x 49 = 343. The Son reveals Himself every 49th time. 49 |
| 14. Four Mystery Plays: The Soul's Awakening: Scene 4
Translated by Harry Collison |
|---|
| Romanus: I were a dreamer if I acted thus. I spin no dreams about mankind's whole life With eyes fast closed. I ne'er had use for thoughts That show themselves and forthwith fade away. |
| ‘The magical web That forms their own life.’ Johannes: ‘And clairvoyant dreams Make clear unto souls The magical web That forms their own life.’ (While Johannes is speaking these lines his Double approaches him. |
| 14. Four Mystery Plays: The Soul's Awakening: Scene 4
Translated by Harry Collison |
|---|
(The Manager and Romanus, pausing in their walk, speak as follows.) Manager: Romanus: Manager: Romanus: Manager: Romanus: Manager: Romanus: Manager: Romanus: Manager: Romanus: Manager: (Exeunt Manager and Romanus. Johannes comes from another direction, deep in thought, and sits down on a boulder. Johannes is at first alone; afterwards appear his Double, the Spirit of Johannes' youth, and finally the Guardian of the Threshold, and Ahriman.) Johannes: (A voice from the distance, that of Johannes' Double.) ‘The magical web Johannes: (While Johannes is speaking these lines his Double approaches him. Johannes does not recognise him, but thinks ‘the Other Philia’ is coming towards him.) O spirit-counsellor, thou com'st once more; The Double: Johannes: The Double: Johannes: The Double: Johannes: The Double: Johannes: The Double: (The Spirit of Johannes' youth appears.) The Spirit of Johannes' youth: (The Spirit of Johannes' youth disappears: only now does Johannes recognise the Double.) Johannes: The Double: (The Guardian of the Threshold appears and stands beside the Double.) The Guardian: Johannes: Ahriman: Johannes: The Double: Johannes: The Double: Johannes: (The Guardian disappears: in his place appear Benedictus and Maria.) Maria: Benedictus: (The Double, Benedictus, and Maria disappear.) Johannes: (Exit, right.) (Enter Strader, Benedictus, and Maria, left.) Strader: Benedictus: Strader: Benedictus: Strader: Benedictus: Strader: (Benedictus and Maria retire a little way; Strader remains alone; the soul of Theodora appears.) Theodora's Soul: (Disappears. Exit Strader. Benedictus and Maria come to the front of stage.) Maria: Benedictus: Maria: Benedictus: Maria: Benedictus: Maria: Benedictus: Maria: Benedictus: Maria: |
| 51. Philosophy, History and Literature: Truth and Science
07 May 1902, Berlin |
|---|
| If nature has provided and developed everything for us except the final point, then what the human spirit dreams and creates does not belong to reality. For this point of view, which appears grotesquely in today's science, even in Haeckel's “Welträtsel” (World Riddle), man is nothing more than a mere speck of dust in the cosmos, differing from the worm only quantitatively. |
| The truth, which wants to fertilize, will always be a search, will always have to “falsify” the image of the fact fanatics; but it stands infinitely above this, in that it develops something intuitive, spiritual in man, adding something new to nature, which would not be without the human spirit. Thus, what man cherishes in his dreams, what he creates in his mind, acquires more than the significance of mere luxury; in life, it becomes a cosmic truth, something that man has newly generated. |
| 51. Philosophy, History and Literature: Truth and Science
07 May 1902, Berlin |
|---|
An introductory lecture by Rudolf Steiner: “Before which forum can a decision be made regarding ‘a unified worldview?’ — An attempt at an answer to the question of ‘Truth and Science’ ”; followed by discussion. Dr. Rudolf Steiner, as speaker: I was once inspired to pose our question “Before which forum must a unified worldview be decided?” by the earlier discussions of our association, which, after all, wants to cultivate a monistic worldview, and also by my personal involvement in the dispute over Haeckel's “Welträtsel” (World Riddle). Here in the group, the questions were often considered: What is the essence of a unified worldview, what is its value, do we actually have the right to speak of a specifically monistic one? It was emphasized once that according to the present standpoint of science we have no right to speak of unity in material respects, and on another occasion Dr. Penzig explained that in the striving after a unified world picture embracing the whole of nature and the spiritual world one could not but round off the objective picture given by the individual sciences, thus forcing the facts. Even then I noticed that the greatest advances often originated from such supposed falsifications. The Copernican system, for example, was a “falsification” of the facts available for its time, just as the Lamarck-Darwin theory of evolution is nothing more. Just as Tycho de Brahe provided the only possible world view for his time, so it is easy for the fact fanatic, who does not want to go beyond the objectively given facts with his thinking, to prove the “falsifications” that Lamarck-Haeckel's theory of evolution contains according to the current state of science. Nevertheless, I believe that, like Copernicus, Haeckel will be proved right. At the time, I strongly supported the much-debated “Welträtsel” because I admired the consistency and extreme boldness with which a mind creates and “falsifies” a world view from a one-sided point of view. Although my basic philosophical views are only opposed to his in what he fights against in them and agree with him in what he presents positively. At the same time, however, I was described as one of Haeckel's main opponents, an experience that seems symptomatic to me of our time, in that the author's world of ideas takes on a completely different image in someone else's mind. We use our terms, based on their usual position in intellectual life, to put forward ideas that mean something other than what we want to express. In the course of these arguments about Haeckel and in the discussions within the Bund, a question has been brought to life for me that I have often asked myself: What is the relationship between truth and science? Does science contain truth? Does it contain any elements that could lead to the construction of a unified world view? Do we have the right to construct a unified world view or any world view at all on the basis of science? This question, which has occupied people for centuries, has been closer to being solved in the past than in modern times, and has been obstructed in way of solution by the so-called theory of knowledge has blocked itself, one must realize before which forum anything at all can be established in relation to truth and science, in relation to the truth content of science. Nowadays, after all the developments of the 19th century, we have the idea of truth as something that must correspond to objective reality. We find ourselves in an intensive fanaticism of facts that does not allow us to go beyond mere registration. If truth is only a conceptual repetition of what exists outside of us, then, according to the perception of those who today strive for a worldview, this is also nothing more than a counter-image of facts existing outside of us, of the reality already finished in the world outside of us. If it were possible to take a photograph of the world from some corner in the most favorable perspective possible, the ideal of a worldview would be achieved. But to construct such a world view would actually be superfluous, a mere luxury of the human mind, if, like science, it were to be nothing more than a mere repetition, a kind of photographic counter-image of what is going on in the world, what is available in a completed form. The fact that the individual still forms an individual counter-image alongside science would be completely superfluous, infinitely unimportant for the whole world context. If nature has provided and developed everything for us except the final point, then what the human spirit dreams and creates does not belong to reality. For this point of view, which appears grotesquely in today's science, even in Haeckel's “Welträtsel” (World Riddle), man is nothing more than a mere speck of dust in the cosmos, differing from the worm only quantitatively. If he forms a picture of the world, he lives a life of luxury, doing something that adds not the slightest thing to the evolution of the world. Rather, he is required never to contribute anything of his own that is not found in the rest of nature, but only to register, compare, and logically combine. We ask: Is this procedure of merely confronting objective nature logically, never adding anything beyond the current state of affairs, consistent with the course of nature's entities; is there perhaps nothing in the direction of nature's development that compels us to add anything to reality? Nature gives us the answer itself. In particular, it should give it to the evolution theorist. Allow me to explain this to you in a concise way, assuming that nature is at the stage of its development that there were only monkeys and no humans. The monkeys would have investigated the phenomena of the world, they would have found what lies beneath them, and monkeys too. If they had taken the empirical standpoint, they would have been satisfied with the realization that the world ends with monkeys. Perhaps they would have founded a monkey ethic based on general monkey perception, so that nothing new would have been added to the world here and they would have remained at their standpoint. But from our standpoint of knowledge, we know that in the principle of development there was indeed something that led beyond the ape genus, that, because it was a productive principle, because it led beyond what was present as a completed reality, , led to the development of man, something that was not limited to the actual, which, as a real imagination, as it were, real intuition in nature, leads it beyond its individual stages and lifts it beyond the immediate present. Man, too, as a product of evolution, as a being in nature, is there to live for evolution, not merely to look back and form a picture of evolution and regard himself as the end of the series. A Weltanschhauung that seeks to summarize the content of all his thinking and doing will therefore not only be theoretical and contemplative, but also practical and postulating. Man should therefore not only repeat nature in some way, but see if there are not forces within him that lead beyond the immediately given. He should make the development spiritually, ideally alive in himself, should seek the forces that drive the species forward, that bring about progress, not merely examine his mental powers to see if they correspond to reality. The question “Can we penetrate to the thing in itself, see into the essence of the world?” is a disaster, an obstacle for man. But when he places himself in the process of evolution, intervening in nature to advance it a step further, he comes to a sense of his exalted task, of his position within the world. There are in fact rudiments for the formation of this superscientific standpoint, which fully recognizes science but rises above what science offers it as the lawfulness of logical thought. Maeterlinck, for example, has advanced similar views in one of his more recent books, in which he describes the marriage of the bees. One wonders: can we speak of truth in the sense of scientific truth, of agreement with the given reality, which is always in the material small print, if it is to be the content of a world view, or does it, as a world view , does it lead beyond the purely objective truth in a similar way to the poetic truth according to the view of those who understand it in the Goethean sense, as the poetic truth leads beyond the immediate naturalistic truth? Such approaches can be found in many forms today, to the delight of those who see truth in living life, and to the horror of fact fanatics like Tycho de Brahe or Haeckel's opponents. But it does not belong in their forum. The truth, which wants to fertilize, will always be a search, will always have to “falsify” the image of the fact fanatics; but it stands infinitely above this, in that it develops something intuitive, spiritual in man, adding something new to nature, which would not be without the human spirit. Thus, what man cherishes in his dreams, what he creates in his mind, acquires more than the significance of mere luxury; in life, it becomes a cosmic truth, something that man has newly generated. Thus, on the foundation of science, he rises to productive work that flows freely from his soul as original intuition. At the highest level of development, he has a task that no other being in the world has; he adds something that would not exist forever without him. These views may be abhorrent to the pure scientist, but I believe it is a correct insight that man has the right to be productive in his world view, a feeling that was different times, when we had not yet been blinded by a fanatical belief in facts and by epistemology, times that were convinced from the outset of the cosmic character of this addition. Let me conclude with the words of Angelus Silesius, which express the realization of the unique significance of the human spirit in the world: Without me, God could not create a single little worm; if I became nothing, it would have to break into nothingness.
Dr. Steiner: “I must confess that the attacks have not touched on what I have said today at all. I did not speak of a contradiction between humanity and nature. I was speaking rather from the standpoint of the most consistent point of view in the theory of evolution, that I regard all stages of nature, from the lowest to the highest stirrings of the spirit, as unified, and only appearing in different forms. But an amoeba is not a human being, and it is not a matter of blurring all distinctions. But if I say that in nature everything is only force, resistance, motion, then it is too reminiscent of the sentence: All cats are gray at night. It is not possible to get to the bottom of the world in the twinkling of an eye. Only when I have distinguished things can I look for a unifying, connecting principle. In the sense of the connecting principle of development, I have spoken of the task of man as one within nature, given by the facts of development. I fully agree that we must adhere to reality if we want to be productive, and that we must correct our imagination in line with it. I only pointed out that efforts to present a world view that is only a copy of reality, as Büchner wants, have not yet met these requirements, and that, for example, this too is forced to do violence to the facts. It is not the intention that is important here, but the result. One behaves as if one wanted to give a picture of reality, but cannot. My principle is therefore not a theoretical, but a practical going beyond reality in the sense in which I see it in the principle of development, where creatures go beyond their own kind. This aspect of the problem has not been touched upon in the discussion. I did not use the word falsification in the sense of the imperfection of a presentation that will only be clarified later, but rather meant that researchers are always forced into deliberately false representation for the sake of the system when they seek comprehensive unity, and therefore asked whether what we are entitled to call reality in the highest sense at all coincides with what the naturalist thinks of as reality. When Haeckel illustrates three stages of embryonic development with the same stereotype, he is forced to falsify in order to be able to provide evidence according to the scientific method. I mean that such forgers are nevertheless right, as Haeckel is in relation to his opponents who cling to the purely factual nature of the scientific method, because they intuitively see beyond the individual facts, not in a fanciful way. But when Dr. Stern rejects the possibility of a world picture, of an overall view in principle, and in doing so draws on the diversity of philosophical systems to support his view, it is a fable convenue based on incomplete ideas of the individual systems. The most significant attempts at truth that have been made, from Vedanta philosophy through Greek to German, are approximations to the truth in varying degrees. The forum before which the legitimacy of one or the other view is decided can only be the forum of the human being, his sovereign personality, as I agree with Dr. Schäfer. This sentence seems to me to be a truly real one, which has been formed not out of theoretical fantasies but out of the experience of men who have worked practically. But just as it is true that the personality is the ultimate forum, so it is certainly true that then the personality must always feel the responsibility of this position and the duty to constantly develop, to educate the depths of the personality. The child cannot be a forum in the same way as someone who is at the height of knowledge. The question therefore arises: Where in us humans lies the potential for development, the productive element? What in us corresponds to that which nature drives forward, which allowed apes to leave their species and become human? If I regard man as a product of evolution, then I can indeed see him as the highest possible forum. But I also have the obligation to constantly call the highest human in me into existence and have no right in any moment of my life to recognize myself as the final and absolute forum, but I can, as I am in development, give myself up to the expectation that in every moment of my existence a higher point of knowledge than I now have can arise. The further development of the personality must be based on science, but it must also go beyond it, as art and poetry do. Just as art and poetry cannot be reduced to blind phantasms, so, when people control their personality by means of the principle of development, however far they go beyond objective nature, agreement will arise in the most diverse people, as the agreement of philosophical systems of all times shows. The solution to the question “To what extent does science contain truth? Can it alone lead to truth?” lies in this sovereign meaning of human personality. The world, especially for science, is in many respects dualistically constructed. Evolution is only possible because nature has prepared the future in it in a twofold way. Nature presents itself to man as an apparent, seemingly irreconcilable contradiction that cannot be resolved by science, as force, matter, and so on. This is where the significance of human personality comes in. Only the life activity of man can be unifying, monistic. It consists in dissolving these apparent contradictions into a higher, productively generated view of life, in the life of development, in the uniting of contradictions, in living action. Therefore, the question of the validity of the world view is to be decided before the forum of life, not before the forum of knowledge. |